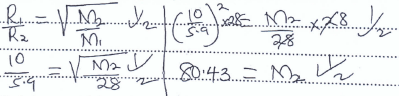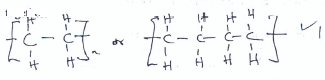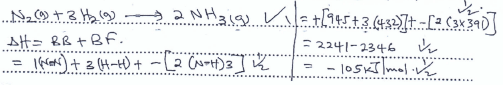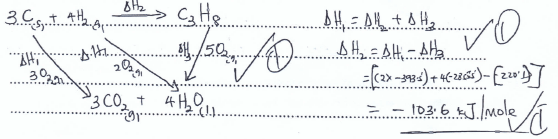-
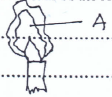
- The flame below is obtained when the air hole of the Bunsen burner is fully closed. State and explain the colour of the region marked A. (1 mk)
-
- Give a reason for the following safety rule in the laboratory
Use a separate dropper for each of the stock solutions in reagent bottles. (1/2 mk) - Using diagrams differentiate between a volumetric flask and retort flask. (2 mks)
- Give a reason for the following safety rule in the laboratory
- The flame below is obtained when the air hole of the Bunsen burner is fully closed. State and explain the colour of the region marked A. (1 mk)
- Element W whose RAM is 79.99 has two isotopes W-79 and W-81. Determine the percentage relative abundance of the least abundant isotope. (3 mks)
- Describe how to obtain elianto cooking oil from corn grains. (2 mks)
- In an attempt to prepare nitrogen gas in the laboratory, a student mixed 7g of sodium nitrite and 5.5g of solid X, added some water to the mixture heated, then collected the gas in a test tube.
- Identify solid X. (1 mk)
-
- A burning splint was inserted into a test tube containing the gas collected. State the observation made. (1 mk)
- State one use of nitrogen gas. (1/2 mk)
-
- Define an acid according to Lewis. (1 mk)
- Identify the acid in the reaciton below. (1 mk)
NH3(aq) + AlCl3(aq) -> H3N:AlCl3(aq)
- Fatuma measured the pH of some commonly used substances and recorded them in the table below.
Substance ph value A
B
C
D
E2.0
5.0
7.0
8.0
13.0- Which of the pH values represents a weak base? (1 mk)
- What would be the colour of litmus solution in substance E? (1 mk)
- What is the advantage of the universal indicator over the other acid-base indicators. (1 mk)
- Elements Q, R, S and T not their actual chemical symbols have atomic numbers 3, 7, 11 and 12 respectively.
- Write the formula of: (2 mks)
- The ion of R ..............
- The compound formed when S burns in excess oxygen gas
- How do the ionization energies of Q and S compare (1 mk)
- Write the formula of: (2 mks)
-
- State the Graham's law of diffusion of gases. (1 mk)
- Nitrogen gas diffuses through a porous plug at a rate of 10cm3/min and a gas P diffuses through the same plug at a rate of 5.9 cm3/min.
What is the molar mass of gas P. (N = 14) (2 mks)
- Study the structure below and answer questions that follow.
- Name the above structure. (1 mk)
- Identify the bonds marked: (1 mk)
X__
- A hydrated copper salt has a formula CuSO4.XH2O. 50g of a sample was heated until all the water evaporated. Its new mass was 32g. Find the value of X in the formula (Cu = 64, S = 32, O = 16, H = 1) (3 mks)
- Chloride gas was bubbled through cold dilute sodium hydroxide solution, to the resulting solution coloured flower petals were dipped in.
- Write the chemical equation of reaction between the gas and the hydroxide. (1 mk)
- Explain what happens to the flower petals at the end of the experiment. (1 mk)
- Hydrogen Chloride gas was bubbled through water and the resulting solution reacted with a 2cm long magnesium ribbon.
- State and explain the observations made. (11/2 mks)
- Explain what happens if methyl benzene is used in the above experiment in place of water. (11/2 mks)
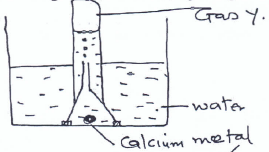
- A student obtained gas Y in the laboratory using the set up below.
-
- Name gas Y (1 mk)
- Give one industrial source of gas Y. (1 mk)
-
- Dry gas Y was passed over heated lead (ii) oxide in a combusion tube. Write the equation for this reaction. (1 mk)
- State and explain the observations that could be made if potassium oxide was used in place of lead (II) oxide in reaction b(i) above. (1 mk)
-
- Burning magnesium metal continues to burn in a gas jar of carbon (iv) oxide gas.
- Write a balanced equation of reaction for this experiment. (1 mk)
- Explain how the mixture of the products formed above can be separated. (2 mks)
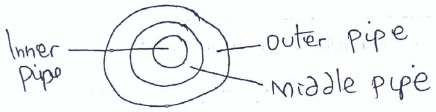
- The diagram below represents a cross-section of the extraction of Sulphur by the Frasch process. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
-
- Name the substance that passes through the outer pipe. (1 mk)
- The middle pipe is centrally placed between the inner and outer pipe. Give a reason for this placement. (1 mk)
- Give
- another source of Sulphur apart from the naturally occuring deposits. (1 mk)
- One use of Sulphur. (1 mk)
-
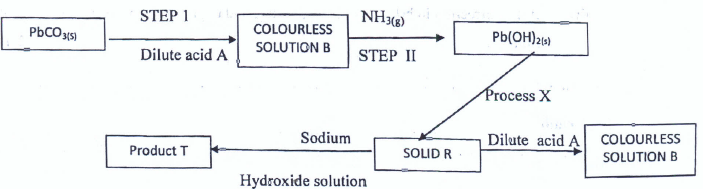
- Study the flow chart below and answer questions that follow.
- Identify (11/2 mks)
- The colourless solution B__
- Process X _______
- Solid R ____________
- Write the equation of reaction for the formation of product T. (1 mk)
- Identify (11/2 mks)
- Electronegativity in halogens decreases down the group. Explain. (2 mks)
- The set up below was used to investigate on the effect of an electric current on lead (II) iodide.
- When the switch was connected to complete the circuit the bulb did not light. Explain. (1 mk)
-
- What mistake was done on the above set up? (1/2 mk)
- If the correction in b(i) above is made, state and explain the observation made on the cathode. (2 mks)
-
- Using Bromine water and the other apparatus found in the laboratory, describe how C2H6(g) can be differentiated from C2H4(g) (2 mks)
- Write the formula of the product formed when two molecules of C2H4(g) are added together. (1 mk)
-
- Define the term molar heat of fusion. (1 mk)
- Calculate the heating value of fuel x given that 0.84kJ of heat is produced by 0.0087 moles of fuel X. (Molar mass of X = 46)(2 mks)
- When concentrated Sulphuric (vi) acid is reacted with common salt, an acidic gas G is formed.
- What property of concentrated sulphuric (vi) acid is being investigated in this experiment. (1 mk)
- Write the correct chemical equation:
- For the above reaction. (1 mk)
- When gas G is reacted with ammonia gas. (1 mk)
- An organic compound B has a formula CH3CH2COOH.
- To which homologous series does this compound belong? (1 mk)
- Write the correct name and formula of the organic product formed when compound B reacts with:
- Sodium carbonate. (1 mk)
- Ethanol. (1 mk)
- Use the bond energy values below to answer questions that follow.
N-N 945 kJmol-1
H-H 432 kJmol-1
N-H 391 kJmol-1- Calculate the enthalpy change for the formation of Ammonia gas given. (3 mks)
- Your laboratory technician forgot a salt labelled sodium carbonate in an open petri dish in the laboratory after an experiment. A day later, he found out that the transparent crystalling salt had formed a white powder which your chemistry teacher identified as sodium carbonate monohydrate.
- Name the process that describes the behaviour of the salt above. (1 mk)
- Write the correct balanced equation illustrating the above behavior of the salt. (1 mk)
- The diagram below represents one of the allotropes of carbon.
- What are allotropes? (1 mk)
-
- Identify the allotrope above. (1 mk)
- State and explain one use of the allotrope above. (1 mk)
- Calculate the relative molecular mass of 0.8g of gas Q that occupies 560 cm3 at STP. (Molar gas volume at STP = 22.4 litre) (2 mks)
- Rusting is one of the chemical reactions that is relatively slow. State one importance of this process. (1 mk)
- 25cm3 of 0.12M sodium hydroxide was completely neutralized by 30cm3 of dibasic acid solution containing 6.3g per litre of solution. Calculate the molarity of the acid. (3 mks)
- Propane is a common fuel used in the school laboratory. With the aid of an energy cycle diagram, calculate the standard enthalpy of formation of propane.
Given
ΔHc (propane) = -2220.1KJ/mole
ΔHc (Hydrogen gas) = -285.8 KJ/mole
ΔHc (Graphite) = -393.5KJ/mole

Marking Scheme
-
- The flame below is obtained when the air hole of the Bunsen burner is fully closed. State and explain the colour of the region marked A. (1 mk)
-Bright yellow 1/2
-Due to hot unburnt tiny carbon particles 1/2 -
- Give a reason for the following safety rule in the laboratory
Use a separate dropper for each of the stock solutions in reagent bottles. (1/2 mk)
To avoid contamination - Using diagrams differentiate between a volumetric flask and retort flask. (2 mks)
- Give a reason for the following safety rule in the laboratory
- The flame below is obtained when the air hole of the Bunsen burner is fully closed. State and explain the colour of the region marked A. (1 mk)
- Element W whose RAM is 79.99 has two isotopes W-79 and W-81. Determine the percentage relative abundance of the least abundant isotope. (3 mks)
Let x be relative abundance of w-79
(100 - x) be relative abundance of W-81
79.99 = (79 x x)/100 + 81(100-x)/100 1/2
7999 = 79x + 8100 - 81x 1/2
101 = 2x
x = 50.5% 1/2
100 - x = 100 - 50.5 = 49.5% 1/2 - Describe how to obtain elianto cooking oil from corn grains. (2 mks)
Crush the nuts in a mortar using a pestle while adding propanone.1/2 Decant the resulting solution into an evaporating dish.1/2 Leave the solution in the sun for some time to evaporate 1/2 the propanone. - In an attempt to prepare nitrogen gas in the laboratory, a student mixed 7g of sodium nitrite and 5.5g of solid X, added some water to the mixture heated, then collected the gas in a test tube.
- Identify solid X. (1 mk)
Ammonium chloride 1 -
- A burning splint was inserted into a test tube containing the gas collected. State the observation made. (1 mk)
Extinguishes a burning splint. - State one use of nitrogen gas. (1/2 mk)
- Manufacture of ammonia
- as a refrigerant
- In light bulbs (each 1/2)
- A burning splint was inserted into a test tube containing the gas collected. State the observation made. (1 mk)
- Identify solid X. (1 mk)
-
- Define an acid according to Lewis. (1 mk)
- An acceptor of the unshared/lone pair of electrions. - Identify the acid in the reaciton below. (1 mk)
NH3(aq) + AlCl3(aq) -> H3N:AlCl3(aq)
AlCl3(aq)
- Define an acid according to Lewis. (1 mk)
- Fatuma measured the pH of some commonly used substances and recorded them in the table below.
Substance ph value A
B
C
D
E2.0
5.0
7.0
8.0
13.0- Which of the pH values represents a weak base? (1 mk)
8.0 - What would be the colour of litmus solution in substance E? (1 mk)
Blue - What is the advantage of the universal indicator over the other acid-base indicators. (1 mk)
- Which of the pH values represents a weak base? (1 mk)
- Elements Q, R, S and T not their actual chemical symbols have atomic numbers 3, 7, 11 and 12 respectively.
- Write the formula of: (2 mks)
- The ion of R
R3- - The compound formed when S burns in excess oxygen gas
S2O2
- The ion of R
- How do the ionization energies of Q and S compare (1 mk)
-Q has a hgher ionization energy than S
-Because outer electrons are closer to the nucleus hence held firmly
- Write the formula of: (2 mks)
-
- State the Graham's law of diffusion of gases. (1 mk)
- Under the same conditions of temperature and pressure, the rate of diffusion of a gas is inversely proportional to the square root of its density. - Nitrogen gas diffuses through a porous plug at a rate of 10cm3/min and a gas P diffuses through the same plug at a rate of 5.9 cm3/min.
What is the molar mass of gas P. (N = 14) (2 mks)
- State the Graham's law of diffusion of gases. (1 mk)
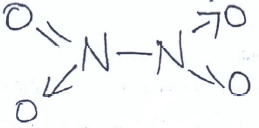
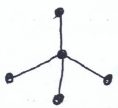
- Study the structure below and answer questions that follow.
- Name the above structure. (1 mk)
Dinitrogen tetraoxide/nitrogen (iv) oxide - Identify the bonds marked: (1 mk)
X - Double Covalent
Y - Covalent
- Name the above structure. (1 mk)
- A hydrated copper salt has a formula CuSO4.XH2O. 50g of a sample was heated until all the water evaporated. Its new mass was 32g. Find the value of X in the formula (Cu = 64, S = 32, O = 16, H = 1) (3 mks)
- Chloride gas was bubbled through cold dilute sodium hydroxide solution, to the resulting solution coloured flower petals were dipped in.
- Write the chemical equation of reaction between the gas and the hydroxide. (1 mk)
2NaOH(aq)+ Cl2(g) -> NaCl(aq) + NaOCl(aq) + H2O(l) - Explain what happens to the flower petals at the end of the experiment. (1 mk)
Coloured flower petals bleached
NaOCl has bleaching properties -> adds nascent oxygen atom to the dye
- Write the chemical equation of reaction between the gas and the hydroxide. (1 mk)
- Hydrogen Chloride gas was bubbled through water and the resulting solution reacted with a 2cm long magnesium ribbon.
- State and explain the observations made. (11/2 mks)
-Effervescence of a colourless gas
HCL dissolves in water to give H+(aq) that are displaced by Mg to give H2(g) - Explain what happens if methyl benzene is used in the above experiment in place of water. (11/2 mks)
-No bubbles/No effervescence
-Methylbenzene is non-polar hence doesn't dissolve to H+(aq) remains as molecules.
- State and explain the observations made. (11/2 mks)
- A student obtained gas Y in the laboratory using the set up below.
-
- Name gas Y (1 mk)
Hydrogen - Give one industrial source of gas Y. (1 mk)
Coal mines/cracking of alkanes/elecrolysis of acidified water
- Name gas Y (1 mk)
-
- Dry gas Y was passed over heated lead (ii) oxide in a combusion tube. Write the equation for this reaction. (1 mk)
PbO(s) + H2(g) -heat-> Pb(s) + H2O(l) - State and explain the observations that could be made if potassium oxide was used in place of lead (II) oxide in reaction b(i) above. (1 mk)
-No observable change
-Potassium is more reactive than H2(g)
- Dry gas Y was passed over heated lead (ii) oxide in a combusion tube. Write the equation for this reaction. (1 mk)
-
- Burning magnesium metal continues to burn in a gas jar of carbon (iv) oxide gas.
- Write a balanced equation of reaction for this experiment. (1 mk)
2Mg(s) + CO2(g) -> 2MgO(s) + CO2(g) - Explain how the mixture of the products formed above can be separated. (2 mks)
-Add dilute HCL/HNO3/H2SO4
-Filter to obtain carbon as residue
-Wash residue with distilled water
-Crystallize the salt formed
- Write a balanced equation of reaction for this experiment. (1 mk)
- The diagram below represents a cross-section of the extraction of Sulphur by the Frasch process. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
-
- Name the substance that passes through the outer pipe. (1 mk)
-Super heated water - The middle pipe is centrally placed between the inner and outer pipe. Give a reason for this placement. (1 mk)
Avoids/Prevents Sulphur from solidifying since it is in between hot substances.
- Name the substance that passes through the outer pipe. (1 mk)
- Give
- another source of Sulphur apart from the naturally occuring deposits. (1 mk)
Metal sulphide / pyrites - One use of Sulphur. (1 mk)
-Vulcanisation
-fungicide
-Manufacture of H2SO4(l)
-Bleaching wood pulp
-Fireworks
- another source of Sulphur apart from the naturally occuring deposits. (1 mk)
-
- Study the flow chart below and answer questions that follow.
- Identify (11/2 mks)
- The colourless solution B - Lead (II) nitrate
- Process X - Heating/Thermal decomposition
- Solid R - Lead (II) Oxide
- Write the equation of reaction for the formation of product T. (1 mk)
PbO(s) + 2NaOH(aq) -> NaPbO(aq) + H2O(l)
- Identify (11/2 mks)
- Electronegativity in halogens decreases down the group. Explain. (2 mks)
As atomic radius increases down the group, the effective force to attract electrons in the outermost energy level also increases. - The set up below was used to investigate on the effect of an electric current on lead (II) iodide.
- When the switch was connected to complete the circuit the bulb did not light. Explain. (1 mk)
Lead (II) Iodide ions are in fixed positions hence unable to conduct. -
- What mistake was done on the above set up? (1/2 mk)
Source of heat ommited. - If the correction in b(i) above is made, state and explain the observation made on the cathode. (2 mks)
Observation: Grey deposits
Explanaiton: Lead gains 2electrons to form lead metal
- What mistake was done on the above set up? (1/2 mk)
- When the switch was connected to complete the circuit the bulb did not light. Explain. (1 mk)
-
- Using Bromine water and the other apparatus found in the laboratory, describe how C2H6(g) can be differentiated from C2H4(g) (2 mks)
Bubble each of the gases through bromine water in two separate test tubes.
C2H4 decolourises the yellow bromine water white C2H6 does not. - Write the formula of the product formed when two molecules of C2H4(g) are added together. (1 mk)
- Using Bromine water and the other apparatus found in the laboratory, describe how C2H6(g) can be differentiated from C2H4(g) (2 mks)
-
- Define the term molar heat of fusion. (1 mk)
Amount of heat energy required to convert one mole of a solid substance to a liquid at its melting point. - Calculate the heating value of fuel x given that 0.84kJ of heat is produced by 0.0087 moles of fuel X. (Molar mass of X = 46)(2 mks)
- Define the term molar heat of fusion. (1 mk)
- When concentrated Sulphuric (vi) acid is reacted with common salt, an acidic gas G is formed.
- What property of concentrated sulphuric (vi) acid is being investigated in this experiment. (1 mk)
Conc. H2SO4 as a less volatile acid. - Write the correct chemical equation:
- For the above reaction. (1 mk)
NaCl(s) + H2SO4(l) -> NaHSO4(s) + HCl(g) - When gas G is reacted with ammonia gas. (1 mk)
NH3(g) + HCl(g) -> NH4Cl(s)
- For the above reaction. (1 mk)
- What property of concentrated sulphuric (vi) acid is being investigated in this experiment. (1 mk)
- An organic compound B has a formula CH3CH2COOH.
- To which homologous series does this compound belong? (1 mk)
Alkanoic acid - Write the correct name and formula of the organic product formed when compound B reacts with:
- Sodium carbonate. (1 mk)
CH3CH2COONa Sodium Propanoate - Ethanol. (1 mk)
CH3CH2COOCH2CH3 Ethyl ethanoate
- Sodium carbonate. (1 mk)
- To which homologous series does this compound belong? (1 mk)
- Use the bond energy values below to answer questions that follow.
N-N 945 kJmol-1
H-H 432 kJmol-1
N-H 391 kJmol-1- Calculate the enthalpy change for the formation of Ammonia gas given. (3 mks)
- Calculate the enthalpy change for the formation of Ammonia gas given. (3 mks)
- Your laboratory technician forgot a salt labelled sodium carbonate in an open petri dish in the laboratory after an experiment. A day later, he found out that the transparent crystalling salt had formed a white powder which your chemistry teacher identified as sodium carbonate monohydrate.
- Name the process that describes the behaviour of the salt above. (1 mk)
Efflorescence - Write the correct balanced equation illustrating the above behavior of the salt. (1 mk)
Na2CO3.10H2O -Heat-> Na2CO3.H2O(g) + 9H2O(l)
- Name the process that describes the behaviour of the salt above. (1 mk)
- The diagram below represents one of the allotropes of carbon.
- What are allotropes? (1 mk)
Forms of the same element in the same physical state. -
- Identify the allotrope above. (1 mk)
Diamond - State and explain one use of the allotrope above. (1 mk)
-Strong covalent bonds hence hard - used in drilling rocks, glass cutting/ball bearings
-Sparkling brilliance when cut and polished - jewellery
- Identify the allotrope above. (1 mk)
- What are allotropes? (1 mk)
- Calculate the relative molecular mass of 0.8g of gas Q that occupies 560 cm3 at STP. (Molar gas volume at STP = 22.4 litre) (2 mks)
- Rusting is one of the chemical reactions that is relatively slow. State one importance of this process. (1 mk)
-dispose off scrap metal
-adds iron nutrients to the soil. - 25cm3 of 0.12M sodium hydroxide was completely neutralized by 30cm3 of dibasic acid solution containing 6.3g per litre of solution. Calculate the molarity of the acid. (3 mks)
- Propane is a common fuel used in the school laboratory. With the aid of an energy cycle diagram, calculate the standard enthalpy of formation of propane.
Given
ΔHc (propane) = -2220.1KJ/mole
ΔHc (Hydrogen gas) = -285.8 KJ/mole
ΔHc (Graphite) = -393.5KJ/mole
Download Chemistry Paper 1 - 2020 MOKASA JOINT MOCKS EXAMINATION (QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS).
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students