BIOLOGY
PAPER 2: THEORY
INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
- This paper consists of two sections; A and B.
- Answer ALL the questions in section A in the spaces provided.
- In section B answer question 6 (compulsory) and either question 7 or 8
SECTION A (40 Marks)
- An analysis was done on the contents of faeces of a cow. The results are as shown in the table below.
Content Percentage Carbohydrates
Proteins
Fiber
Fats12
0.8
14
1- Name the other component that makes up the faeces of a cow and give its percentage. (1 mark)
- Name the substance that contributes the fiber in the faeces. (1 mark)
- Cow faeces are normally used as fertilizer that increases nitrates in the soil.
- State the component in the faeces that yield nitrates. (1 mark)
- Describe how the component named in (c)(i) above is converted into nitrates (4 marks)
- Explain why the manure would be better if the cows urine was added to the faeces. (2 marks)
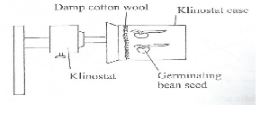
- In an experiment to investigate a plant response, the set up in the diagram below was used.
- Name the type of response that was being investigated. (1 mark)
- If the Klinostat was not rotating.
- State the observation that was made on the seedlings after three days. (2 marks)
- Explain the observations in (b) (i) above. (3 marks)
- If the experiment was repeated with the Klinostat rotating;
- State the observation that was made on the seedling after three days. (1 mark)
- Give a reason for the observation made on the seedling. (1 mark)
-
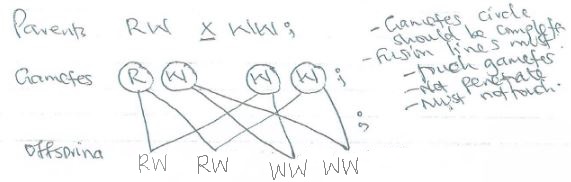
- In an experiment, plants with red flowers were crossed with plants having white flowers. All the F 1 plants had pink flowers. Using R to represent the gene for red flowers and W to represent the gene for white flowers, work out the genotypic ratio and phenotypic ratio of the offspring if the F 1 plants were crossed with white flowered plants. (5 marks)
- Give two reasons why Drosophila melanogaster is a suitable organism for genetic studies. (2 marks)
- What is genetic engineering? (1 mark)
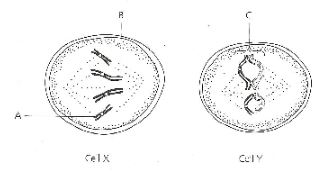
- The diagram below shows two cells, X and Y from the same organism. Study the diagrams and answer the questions that follow.
- Name the parts labelled A, B and C . (3 marks)
-
- Which cell is diving by meiosis? (1 mark)
- Give two reasons for your answer in (b) (i) above (2 marks)
- The diagram below represents a flower.
- On the diagram, name two structures where meiosis occurs (2 marks)
- How is the flower adapted to prevent self-pollination? (2 marks)
-
- State the meaning of the term adaptive radiation. (1 mark)
- Explain how continental drift is an evidence for organic evolution (3 marks)
- State two disadvantages of natural selection to organisms (2 marks)
SECTION B (40 Marks)
Answer question 6 (Compulsory) and either question 7 or 8 in the spaces provided after question 8.
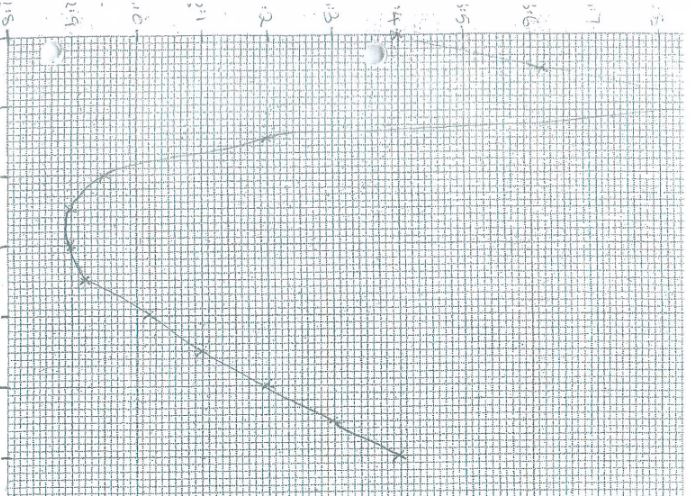
- In an experiment carried out in a tropical country, carbon (IV) oxide concentration was measured
around a plant in an open air at two hour intervals for a period of 24 hours. The results are as in the table
below.
Time Percentage of carbon (IV) oxide
concentration ( x10-2 )3a.m
5a.m
7a.m
9a.m
11a.m
1p.m
3p.m
5p.m
7p.m
9p.m
11p.m
1a.m
3a.m3.40
3.62
3.90
3.20
2.95
2.90
2.90
2.92
3.02
3.10
3.20
3.30
3.40- Using the data, plot a graph of carbon (IV) oxide concentration against time in the grid provided (6 Marks)
- Calculate the rate of change in carbon (IV) oxide concentration between 4a.m and 7a.m (3 marks)
- Account for the shape of the graph between the following times:
- 7a.m to 11a.m . (2 marks)
- 12 noon to 4p.m . (2 marks)
- 5p.m to 5a.m. (3 marks)
- The experiment was repeated on another day and the results were different.
- Name two environmental factors that were likely to have affected the results (2 marks)
- State how each of the factor named in (d) (i) above could have affected the results (2 marks)
-
- Describe how excretion occurs in plants. (4 marks)
- Explain how the osmotic pressure in the human blood is maintained at normal level (16 marks)
-
- Describe how reproduction occurs in yeast (5 marks)
- Describe secondary thickening in flowering plants (15 marks)
MARKING SCHEME
-
- Water
- Cellulose
-
- Proteins
-
- Proteins are converted to ammonia
- By saprophytes/ bacteria and fungi
- ammonia is converted to nitrites by nitrifying bacteria Acc: Nitrococcus & nitrosomes
- Nitrites are converted to nitrates by nitrifying bacteria/ nitrobacter
- Urine contains more proteins/ nitrogenous compounds which yield more nitrates.
-
- Geotropism; Rej wrong spelling +ve, -ve geotropism
-
- The shoot tip/ plumule curved upwards root tip/ radicle curved downwards
Acc bending rej growing - Auxins migrated downwards/ to the lower side; caused more growth on the lower side than on the lower side than upper side in roots
- The shoot tip/ plumule curved upwards root tip/ radicle curved downwards
-
- The seedling will continue growing horizontally; rej laterally
- There was even distribution of auxins to the tip
-
-
genotype ratio ; rej 2:2
RW:WW
phenotype ratio
1 pink flowered: 1 white flowered -
- Produces large number of offspring
- Has many observable contrasting characteristsics
- short life cycle
- offspring can be crossed with parents
-
-
-
- Chromatid; Acc chromosome rej plural
- Spindle fibres
- Homologous chromosomes Acc, Bivalent
-
- Cell Y
-
- Homologous chromosomes have paired
- Chiasmata have been formed
-
- Anther
Ovary
(should be labelled on diagram
rej - plural, wrong spelling) -
- Large petals to attract insects
- Stigma located above the anthers
- Anther
-
-
- A situation where organisms have homologous structures with a common embronic origin which are modified to perform different functions
- Continents existed as one large land mass (Acc; pangea)
The current continents drifted leading to isolation/ separation of organisms; organisms in each continent evolved along different lines -
- Assists to eliminate disadvantages characteristics/ perpetuate advantageous characteristics
- Assists to eliminate disadvantages characteristics/ perpetuate advantageous characteristics
-
-
- Carbon (IV) oxide concentration at 4:am = 3.5 x 10-2%
Acc 3.48 - 3.52
rate of change
(3.9 - 3.5) x 10-2
3
= 1.33 x 10-2 / hour
Acc 0.0013%/hr
rej; without units -
- Rapid decrease in CO2 concentration due to utilisation of CO2 in photosynthesis due to increase in light intensity.
- CO2 conc remains almost constant; photosynthesis rate is equal to respiration rate;
- Increase in CO2 conc; rate of photosynthesis drops due to decrease in light intensity respiration produces CO2 which accumulates;
-
-
- Wind/ air currents
- Light intesity
- Temperature
- Soil water
-
- Wind blows CO2 avoiding its accumulation around the plant
- Light intensity affects rate of photosynthesis hence rate of CO2 assumption
- Temperature affects rate of photosynthesis hence CO2 around the plant
- Water affects rate of photosynthesis hence accumulation of CO2 around the plant
-
-
-
-
- CO2/O2 / Water vapour diffuse through the stomata/ lenticels
- Some toxics wastes are converted to non-toxic substances and deposited in certain tissues of the plant/ stored in ageing structures
- Resins/ tanins are exuded through the bark of the stem/ lost during leaf fall
-
- When osmotic pressure is high
- When the op(osmotic pressure) of blood rises increases beyond the normal range/ level the (osmoreceptors in) hypothalamus; detects and stimulates the pituitary gland.
- To secrete more ADH/ wasopressin which makes the kidney tubules more permeable to water and more water reabsorbed into the blood stream reducing the op to the normal level
- When there is too much sodium ions in the blood adrenal cortex responds by secreting less alodsterone which causes less Na+ to be reabsorbed from the kidney tubules in to blood of lowering the OP to normal level
- When OP is low
- When op is low ( the osmoreceptors) the hypothalamus defect and the pituitary gland is less stimulated
- And secrets less ADh/ vasopressin which makes the kidney tubules less permeable to water ; less water is re-absorebed into the blood stream.
- When there is too little Na+ ions in the blood, adrenal cortex responds by secreting more adosterone.
- When osmotic pressure is high
-
-
-
- Reproduces asexually by budding;
- (under favourable conditions) a small area of the cell wall of the parent cell softens and forms a projection of bud
- The nucleus divides by mitosis into two
- One of the daughter nucleus moves into the new bud
- The bud increases in size and forms new organelles then detaches from the parent cell.
-
- Secondary thickening is facilitated by meristematic cells known as cambium located between phloem and xylem in vascular bundles of plants
- (vascular cambium divides radially to form a ring of cambium tissue) With the xylem inside the ring and the phloem outside the ring.
- Cells of cambium ring divide to form secondary xylem on the inside.
- Interfascicular cambium/ cambium between vascular bundles divides to form secondary parenchyma which becomes medullary rays
- Much more xylem is formed than the phloem, thus pushing the phloem outwards.
- Cork cambium is a layer of meristematic cells beneath the epidermis
- Division of cork cambium cells forms secondary cortex on the inside and cork cells on the outside
- The walls of the cork cells become coated with suberin and die( they increase in number and become the bark of the stem)
- The bark prevents water loss, inecftion from fungi and damage by insects.
- In some areas, the cork cells form a loose mass known as lenticels for gaseous exchange.
- Rate of secondary growth in stems varies with seasonal changes resulting in annual rings.
-
Download Biology Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Kapsabet Pre Mock Exams 2021/2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students