INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
- Write your name and index in the spaces provided.
- This paper consists of three sections A, B and C.
- Answer all the questions in sections A and B and one question in section C.
- Answers should be written in the spaces provided.
For Examiner’s Use Only
|
Section |
Question |
Candidates Score |
|
A |
1 |
|
|
B |
2 |
|
|
3 |
||
|
4 |
||
|
5 |
||
|
6 |
||
|
C |
||
|
Total Score |
||
Questions
SECTION A: (20 Marks)
Answer all questions in this section in the spaces provided below.
-
- What are the “elements” of Art and Design (1 mark)
- How is colour used to model forms (2 marks)
- Study the figures below
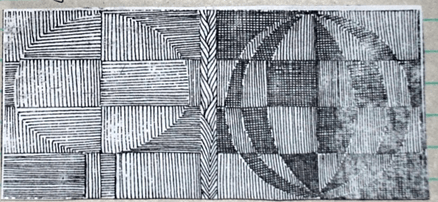
Identify the use of lines in the figures above (1 mark) - Explain how tessera distinguishes mosaic from collage (1 mark)
- Which method of fabric decoration is common to tie and dye and Batik? Describe it. (2 marks)
- Give the other name used to refer to plain weave. (1 mark)
- Define the term “slip” as used in pottery (1 mark)
- State two functions of slip in pottery work (2 marks)
- State and describe the quality of clay that makes it an ideal modeling material. (2mks)
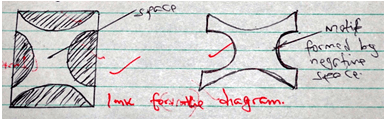
- Using illustrations, describe the use of negative space in pattern making. (2 marks)
- Explain any two methods of print making process. (2 marks)
- Define “Illustrations” in graphic design. (1 mark)
- What is an “armature” in sculpture making (1 mark)
- Distinguish between caricature and cartoon (1 mark)
SECTION B: (25 Marks)
Answer ALL questions in this section in the spaces provided below.
- The illustrations below show beadwork technique in ornament making.

- Identify the beadwork technique. (1 mark)
- By use of diagrams outline the two steps prior to the two shown by the illustration above. (2 marks)
- Describe the steps shown by the illustrations above. (2 marks)
- In the space below, draw a landscape and in it show atmospheric perspective. (5 marks)
-
- What is a colour scheme? (1 mark)
- Explain the following colour schemes (4 marks)
- Monochromatic colour scheme
- Analogous colour scheme
- Complementary colour scheme
- Triad colour scheme
-
- Identify and explain the two aspects of balance in sculpture (4 marks)
- How is movement expressed in a sculpture? (1 mark)
-
- Using illustrations depict the following shading techniques in drawing: (3 marks)
- Hatching
- Cross-hatching
- Smudging
- List the four major categories of drawing. (2 marks)
- Using illustrations depict the following shading techniques in drawing: (3 marks)
SECTION C: (15 Marks)
Answer any ONE question in this section. Write your answer in the space after Question 9
-
- Describe a “squeegee” (1 mark)
- What is the work of a squeeze in art and design activities? (1 mark)
- Outline the procedure of blocking out stencil using shellac or glue in developing a stenciled screen. (12 marks)
- State the main factor considered when choosing the medium of blocking the screen. (1 mark)
-
- State the three purposes that the rigid heddle loom serve. (3 marks)
- Apart from rigid heddle loom, name two other types of loom (2 marks)
- Using diagrams, describe the process of weaving on the rigid heddle loom. (10 marks)
-
- State and describe the stages of graphic design process. (10 marks)
- Give two characteristics of Roman letters (4 marks)
- What is layout in graphic design? (1 mark)

MARKING SCHEME
-
- Elements of Art and Design are the components of design arranged on a surface or worked on an object to produce work of art that is interesting. (1mk).
- By applying different shades and tints of colours onto a shape of a flat surface until it appears to have volume. (2 mks)
- Lines have been used to create shapes and patterns. (1mk)
- In Mosaic only one type of tesserae is used while in collage a variety is used. In mosaic tesserae are juxtapose while in collage it is superimposed. (1mk)
- Crumpling
- The fabric is either crumpled and tied or waxed and crumpled to create a crazed effect. (1mk)
- Tabby weaves (1mk)
- Slip is clay mixed with water to alight thin consistence porridge like (1mk)
- Slip is used for decorating pottery work.
- It is used in casting objects using plaster of Paris moulds.
- It is used for joining coils in the pottery technique of coil method. (Any two – 2mks)
- Plasticity.
- This is the quality of clay that enable it to be shaped and reshaped into any form before drying. ½ mk for giving quality ½ mk for describing
- Negative spaces are the spaces between motifs or designs used in pattern making. If the motifs are well arranged the spaces in between them making the pattern work interesting. 1mk for the text
- Relief method – Printing is made by raised surface.
Intaglio – Printing is made from sunken areas
Lithography (Planography) printing is made from a flat surface.
Serigraphy- Printing is done through a surface.
(Any two = 2mks) - These are visual images that form the pictorial part of design. The pictorial images can be made by drawing, painting, printing or pasting. (1mk)
- Armature is the skeleton that forms the base onto which plastic material is modeled. It strengthens and supports the sculpture. (1mk)
- caricature is a distorted image of a known character while cartoon is a drawing which expresses humour and which in most cases is accompanied with a caption. (1mk)
-
- Woven beadwork (1mk)
- Thread a row of beads on the sisal string. (1mk)
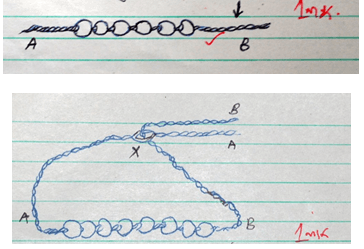
- Bring the ends of the string together. Untwist end A slightly to create an opening at point X through which end B posses. Hold ends A and B horizontally together so that they form three lengths of string with the main section of string B.
- In the illustration
- After end B is passed through the opening it is held firmly between fingers. (1mk)
- Beads are slid along A to pass point x and enter B, A, B/ push the beads past point x so that they enter. A and B and the main section of B. (1mk)
- Landscape. (1mk)
- The teacher judges appropriately. 1mk
- Atmospheric perspective is achieved by making colours in the background look feint and pale. Colours in the foreground look bold and neat. (3mks)
-
- Colour scheme is the total effect of the colours used in different surface make ups e.g the room, the body (clothing), the painting, the graphic work etc (1mk)
- Monochromatic colour scheme. It is also known as one colour plan. It is the use of one colour with shades and tints. (1mk)
- Analogous colour scheme – use of colours that are next to each other on the colour wheel.
- Complementary colour scheme use of colours that are directly opposite each other on the colour wheel. (1mk)
- Triad colour scheme use of colours that form egui distance triangle on the clour wheel – also known as equi distance harmonies. (1mk)
-
- Balance that makes the sculpture stable.
- Balance of attraction created by arrangement of planes contours texture and colour. (2mks).
- By visual stimulation to produce a feeling of actual movement e.g. human figure may be curved to show movement in space often made by human beings. (1mk)
- Balance that makes the sculpture stable.
-
-

- The four major categories of drawing are:
- Still life drawing
- Landscape
- Human figure/portraiture
- Portrait
-
-
- A squeegee is a long board which has a flat blade of hard rubber, fixed into a wooden handle. (1mk)
- The work of a squeegee is to force a thin film of pigment evenly through the stencil to the surface being printed. (1mk)
- The procedure of blocking out stencil using shellac or glue.
- Have a stretched screen
- Develop a design on paper and then transfer it onto the screen
- Mark the areas to be clocked out
- Use a brush to apply shellac or glue to the areas which should resist the penetration of the dye.
- After blocking out the required parts, allow it to dry up. Do not touch the screen while it is still wet
- Check for pinholes in the screen holding it against the light. Areas that have not been fully completed and areas with pin holes should be retouched with the same liquid used to make the stencil. The screen is left to dry up in readiness for use.
- The main factor considered when choosing the medium of blocking the screen is the type of colour or dye to be used.
-
- Three purposes that the rigid heddle loom serves
- It spaces out the warp
- It creates two sheds
- It is used to beat down the weft threads
- Other types of loom
- Paper loom
- serrated card loom
- Frame loom
- Dowel loom
- Inkle loom
- The procedure of weaving on the rigid heddle loom
- Raise the heddle and insert a flat stick through the opening. This is to spread out the warp threads evenly.
- Depress the heddle and insert another flat stick through the opening
- Raise the heddle and pass a weft thread through the opening shed from right leave out at the selvedge.
- Depress the heddle and pass the weft thread back from left through the shed. At the same time slip the end hanging out into this shed for a distance of about. 1.7cm pull the end to the surface of the weaving. All the subsequent ends must be inserted in this manner and when the weaving is complete they will be trimmed. This neatens the selvedge.
- Continue weaving until the whole length of the warp is woven.
- Carefully cut off the woven fabric and knot the treads at both ends so that the weft threads do not slip out. (6mks)
Diagram (4mks)
- Three purposes that the rigid heddle loom serves
-
- The stages of graphic design process.
- A problem ought to exist – The problem must be identified
- Collection of information – This can be recorded by way of sketches, note taking, photography etc.
- Analysis- The information gathered is carefully examined to determine if it can solve the problem
- Composition – Various gathered elements, are brought together to build up a possible solution
- Development – Testing and refining stage. Modification may be necessary.
- Evaluation – self criticism should be done at this stage to find out if the design is successful. (12mks)
- Characteristics of roman letters.
- They are written from left to right
- They are composed of geometrical lines or strokes
- They are not evenly spaced when composing words but the spaces are visually judged and letters arranged to achieve unity
- Spacing between words is equal to the width of letter O. (any two 2 mks)
- The stages of graphic design process.
Download Art and Design P1 Questions and Answers - Wisdom Pre-Mock Form 4 Exams 2021/2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students

