INSTRUCTIONS TO THE CANDIDATES:
- Answer all the questions.
- All working must be clearly shown where necessary.
- Mathematical tables and electronic calculators can be used.
- Use the table below to answer the questions that follow. (The letters do not represent the actual symbols of the elements).
Element Atomic Number Melting point ° A
B
C
D
E11
13
14
17
1997.8
660
1410
− 101
63.7- Write the electronic arrangement for the ions formed by element B and D. [2mks]
- Select an element which is:
- A non-conductor of electricity [1mk]
- The most reactive non-metal [1mk]
- To which period of the periodic table does element E belong? [1mk]
- Element E losses its outermost electron more readily than A. Explain. [1mk]
- Use dots (.) and crosses (x) to represent the valence electrons and show the bonding in the compound formed between element C and D. [1mk]
- Explain why the melting point of element B is higher than that of element A [1mk]
- Write an equation for the reaction that takes place between element A and water. [1mk]
-
- The set-up below was used to collect gas F, produced by the reaction between water and calcium metal.
- Name gas F [1mk]
- At the end of the experiment the solution in the beaker was found to be a weak base. Explain why the solution is a weak base. [1mk]
- Give one laboratory use of the solution formed in the beaker. [1mk]
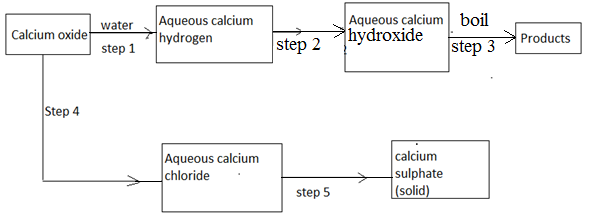
- The scheme below shows some reaction starting with calcium oxide. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
- Name the reagent used in step 2 and 4 [1mk]
- Write an equation for the reaction in step 3 [1mk]
- Describe how a solid sample of anhydrous calcium sulphate is obtained in step 5 [3mks]
- The set-up below was used to collect gas F, produced by the reaction between water and calcium metal.
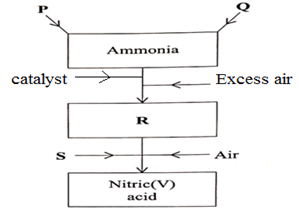
- The figure below is a flow chart showing the process that occurs in the manufacture of nitric (V) acid.
- Name substance P, Q, R and S. (4 mks)
- To obtain substance R, ammonia is heated at 9000C in the presence of air and a catalyst.
The product is then cooled in the heat exchanger and mixed with more air.- Name the catalyst for the reaction (1mk)
- Write the equation for the reaction described (1mk)
- When ammonia is reacted with nitric (V) acid, it produces a nitrogenous fertilizer.
- Calculate the percentage of nitrogen in the fertilizer obtained. (N=14,H=1,O=16) (2mks)
- State one problem associated with the use of nitrogenous fertilizers. (1mk)
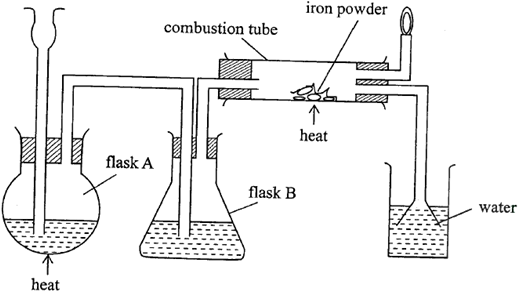
- The diagram in Figure below was used to prepare hydrogen chloride gas which was then passed over heated iron powder.
- Give a pair of reagents that will produce hydrogen chloride gas in flask A. (2mks)
- Name the substance in flask B. (1mk)
- State the observation made in the combustion tube after the reaction is complete. (1mk)
- Write an equation for the reaction in the combustion tube. (1mk)
- Describe a chemical test for hydrogen chloride gas. (1mk)
- Identify the gas that burns at the jet and explain why the gas is burned. (1mk)
- Give reasons why excess hydrogen chloride gas is dissolved using the funnel arrangement. (1mk)
-
- Define the following:
- Empirical formula. (1mk)
- Molecular formula. (1mk)
- A major textile dye manufacturer developed a new yellow dye. The dye has a percent composition of 75.95% Carbon, 17.72% Nitrogen, and 6.33% Hydrogen by mass. Determine;
- The empirical formula of the dye. (C=12, H=1, N=14) (3mks)
- The molecular formula of the dye, if it has a molar mass of about 237 g/mol. (C=12, H=1, N=14) (2mks)
- Define the following:
-
-
- Define the term fuel [1mk]
- Determine the heating value of ethanol [2mks]
(C = 12, H = 1, O = 16)
(ΔHc(C2H5OH) = -1368KJ/mol)
- The diagram below represents a set-up that was used to determine the enthalpy of combustion of ethanol.
The following results were obtained:
Volume of water = 500cm3
Initial temperature of water = 25oC
Final temperature of water = 38oC
Mass of ethanol + lamp before heating = 120.5g
Mass of ethanol + lamp after heating = 119.5g- Calculate the heat evolved
(Specific heat capacity = 4.2jg-k-, density of water = 1g/cm3) [2mks] - Determine the molar heat of combustion of ethanol (C = 12, H = 1, O = 16) [3mks]
- Write the thermochemical equation for the reaction. [1mk]
- The theoretical value for the molar enthalpy of combustion of ethanol is -1368kJ/mol
Why is the value calculated from the experimental results different from this? [1mk] - Define the term molar heat of combustion [1mk]
- Calculate the heat evolved
-
-
-
- Give the systematic name of the following compound. [1mk]
CH3CH2COOCH3 - Draw the structure of 2-methyl but -1, 3-diene [1mk]
- Give the systematic name of the following compound. [1mk]
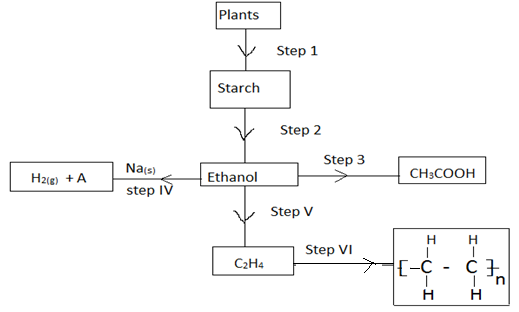
- The scheme below shows the reactions of organic compounds, study it and answer the questions that follow.
- Name the process in step 1 [1mk]
- State the condition for the process in step 2 [1mk]
- Write the equation for the process in step 4 [1mk]
- Name the process taking place in step 3 [1mk]
- Name the organic compound A the product of step (IV) [1mk]
- Given that the relative formula mass of the product of step (VI) is 56000. Determine the value of n. (C=12, H=1) [2mks]
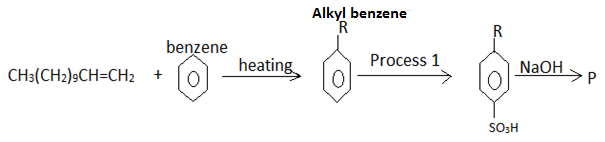
- The flow chart below is a summary of the process involved during preparation of a detergent.
- Name the reagent in process 1 [1mk]
- Draw the structure of P; Give its name [2mks]
- State one advantage of detergent P
over COO-Na+ [1mk]
-
-
- Define the term solubility [1mk]
- Experiments were done to determine the solubility of two salts X and Y in water at different temperatures. The following results were obtained:
Temperature (°C) Solubility in g/100g of water X Y 0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
8014.0
17.5
21.0
25.0
28.5
33.0
40.0
47.0
55.025.0
27.0
30.0
32.5
35.0
37.5
40.0
42.5
45.0- On the same axis plot the solubility corves for salts X and Y [5mks]
- Determine the solubility of salt Y at 45oC [1mk]
- At what temperature is the solubilities of the two salts equal [1mk]
- 80g of a saturated solution of salt X was cooled from 75°C to 15°C, determine the mass of salt X that crystallized out [3mks]
- A mixture containing 20g of X and 40g of Y in 100g of water at 80°C was cooled to 30°C. Identify the salt that crystallized out. Calculate the mass of the salt that crystallized. [3mks]
MARKING SCHEME
-
- B – 2.8 √
D – 2.8.8√ (2mks) -
- D √ (1mk)
- D√ (1mk)
- Period 4√ (1mk)
- E – has a bigger/greater/larger atomic radius√ hence loses its outermost electrons easily. √ (1mk)
-
√(1mk)
- B has more delocalized electrons√1/2 than A hence has stronger metallic bond. √1/2 (1mk)
OR B has smaller atomic radius√1/2 hence stronger metallic bond√1/2 - 2A(s) + H2O(l)
2AOH(aq) + H2(g) (1mk) √
(Accept if actual symbols used, award 0 if not balanced, penalize half mark for wrong state symbol)
- B – 2.8 √
-
-
- Hydrogen gas (1mk) (strictly the name)
- Ca (OH)2 slightly soluble in water, √ only few OH- are produced√½ in solution. (1mk)
- It is used for testing presence of CO2. √ (1mk)
Prepare ammonia √ (any one)
-
-
- Step 2 - carbon (IV) oxide√½ (½mk)
- Step 4 – Dilute HCL√1/2 (½ mk)
- Ca (HCO3)2(aq)
CaCO3(s) + CO2(g) + H2O(l) (1mk)
-
- Add an aqueous solution of sulphuric (VI) acid/Na2SO4/K2SO4 (1mk)
- Filter to obtain CaSO4 √
- Wash with distilled water√ and dry between filter papers√
-
-
-
-
- P Hydrogen/nitrogen 1mk
- Q Nitrogen /hydrogen 1mk
- R Nitrogen (IV) oxide 1mk
- S Water 1mk
-
- Platinum – rhodium 1mk
- 4NH3(g) + 5O2(g)
4NO(g) + 6H2O(g) √
2NO(g) + O2(g)2NO2(g) √
-
- NH4NO3√½ (REM = 80) √½
28/80 x 100 √½ = 35% √½ -
- Lowers soil Ph
- Increase soil acidity
- Causes euthrophication
- Pollution of water
(any one)
- NH4NO3√½ (REM = 80) √½
-
-
-
- solid sodium chloride/rock salt
- Concentrated Sulphur (VI) acid
- Concentrated Sulphur (VI) acid(penalize formula)
- Grey iron powder turns to green iron (II) chloride (acc. Green solid formed)
- HCl(g) + Fe(s)
FeCl2(s) + H2(g) 1mk
- When in contact with ammonia gas, dense white fumes of ammonium chloride are formed (1mk)
- hydrogen gas √½
- Mixture of hydrogen and air burns explosively√½
- to prevent sucking back in increasing surface area for dissolution
-
-
-
- formula showing the simplest whole ratio in which atoms combine to form compound
- Formula showing the actual number of each kind of atoms present in molecule of the compound
-
-

- n(79)=237√½
237 = 3 √½
79
C15H15√1
-
-
-
-
- A substance that burns in air to produce useful energy (1mk)
- CH3CH2OH
RFM = 46√½
= 1368 (√½) =29.74 kJ/g (√1mk)
46
-
- ΔH = MCDJ
= 500 x 4.2 x 13 (1mk)
= 27,3005
= 27.3Kj 1mk
(penalize half mark for wrong units) - Mass of ethanol
120.5-119.5=1g (√ 1mk)
1g – 27.3kJ
46g – 46 x 27.3 ( √ 1mk)
1
= 1255 .8Jk
= -1255.8kJ/mol (1mk)(penalize half mark for missing –ve sign Penalize fully for wrong units) - CH3CH2OH(g) + 3O2(g)
2CO2g + 3H2OΔH = -1255.8 kJj/mol (√ 1mk)
- heat loss to the surrounding (1mk)
- Error in measurements of volume and temperature (experiment errors)
- Heat change that occur when one mole of a substance burns completely in oxygen. (√ 1mk)
- ΔH = MCDJ
-
-
-
- Methylpropanoate (√ 1mk)
-
-
- Photosynthesis (√ 1mk)
- yeast (√ 1mk)
- 2CH3CH2OH + 2Na
2CH3CH2ONa + H2 (√ 1mk)
- Oxidation (√ 1mk)
- sodium ethoxide (√ 1mk)
- ? - (C2H4) = 56000
28n = 56000√
?n = 2000√ (2mks)
-
- concentrated sulphuric acid (√ 1mk)
-
(√ 1mk)
- Sodium alkylbenzene sulphanoate (√ 1mk)
- Does not form scum with hard water (√ 1mk)
-
-
- The maximum mass of a solute that can dissolve in 100g of solvent (water) at a particular temperature to form saturated solution. (√ 1mk)
-
- 36.5g/100g of water ± 1 (1mk)(Read from correct curve)
- 60°C ± 1 (1mk)
- 51.5 x 80 – 28.5 x 80 = 9.452g (√ 1mk)
151.5 (√1mk) 128.5 (√ 1mk) - Solubility of g/100g of water at
Crystal of y (√ 1mk)Salt 30°C 80°C X 25 55 Y 32.5 45
40 − 32.5 = 7.5g (√ 1mk)
Download Chemistry Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Eagle II Joint 2021 Mock Exams.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students