CHEMISTRY
PAPER 2
(THEORY)
INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
- Write your name and index number in the spaces provided above
- Sign and write the date of examination in the spaces provided.
- KNEC Mathematical tables and silent electronic calculator may be used.
- All the working must be shown clearly where necessary
- Candidates should answer questions in English.
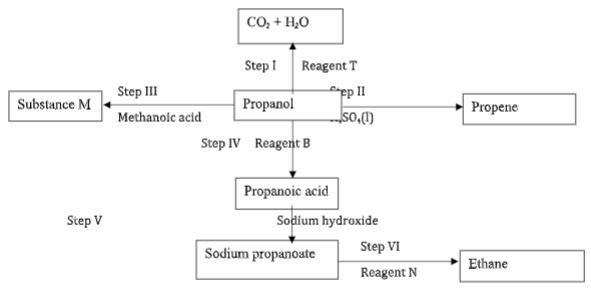
- The flow diagram below shows some reactions starting with propanol. Study it and use it to answer the questions that follow.
- Name the process in step; (3 marks)
I
III
IV - Write an equation for the reaction in step (2 marks)
I
V - Give the name and structural formula of substance M (2 marks)
Name
Structural formula - Name the reagent; (2 marks)
B
N - State the condition necessary for reaction in step II (1 mark)
- The diagram below shows the structure of a detergent.
- Identify the detergent (1 mark)
- A sample of water was found to contain magnesium ions. Explain why the detergent above is a suitable reagent to be used in the water. (1 mark)
- Name the process in step; (3 marks)
-
- The table below shows properties of four substances. Study it and use it to answer the questions that follow.
Substance Melting point
(0C)Electrical conductivity Solid Molten A -33 Poor Poor B 801 Poor Good C 1083 Good Good D 1417 Poor Poor - Identify the structure in the following: (2 marks)
A
C - Explain the conductivity in substance B (2 marks)
- Give a reason why substance D has a h-igh melting point. (1 mark)
- Identify the structure in the following: (2 marks)
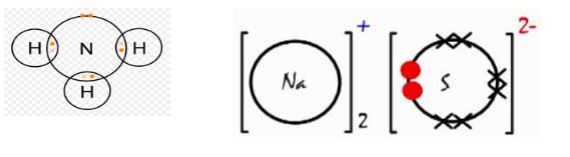
- Draw dot and cross diagram showing bonding in the following; (2 marks)
- Ammonia gas (N=7, H=1)
- Sodium sulphide ( Na=11, S=16)
- Explain the following; (3 marks)
- Magnesium and sulphur are in the same period of the periodic table. However, magnesium oxide is a solid while sulphur (IV) oxide is a gas at room temperature (Mg = 12, S=16, O=8)
- Ethanol is molecular but it dissolves in water
- Solid copper metal is a better electrical conductor than molten copper
- The table below shows properties of four substances. Study it and use it to answer the questions that follow.
-
- The diagram below shows the set-up used to test a property of carbon in the laboratory. Study it and use it to answer the questions that follow.
- State the role of potassium hydroxide solution (1 mark)
- Write an equation for the reaction in the combustion tube (1 mark)
- State the property of carbon being investigated. (1 mark)
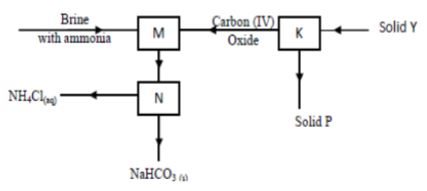
- Sodium carbonate is prepared industrially using Solvay process. The flow diagram below shows some of the reactions in the process. Study it and use it to answer the questions that follow.
- Identify; (2 marks)
Solid Y …………………………………………………………………………
Solid P …………………………………………………………………………. - Write an equation for the reaction taking place in chamber M (1 mark)
- Name the process taking place in chamber N. (1 mark)
- State two uses of sodium carbonate (2 marks)
- Identify; (2 marks)
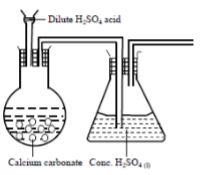
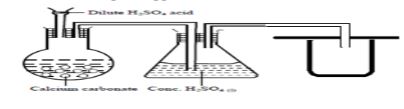
- The set-up below was used to prepare carbon (IV) oxide gas in the laboratory. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
- Identify the mistake in the set-up and suggest a possible correction. (2 marks)
- Complete the diagram showing how the gas can be collected (1 mark)
- The diagram below shows the set-up used to test a property of carbon in the laboratory. Study it and use it to answer the questions that follow.
- The list below shows reduction potentials of element M, N, P and Q
Eθ volts M2+(aq) + 2e → M(s)
N2+(aq) + 2e → N(s)
P+(aq) + 2e → P(s)
Q2+(aq) + 2e → Q(s)-0.76
-2.37
+0.80
-0.14- Identify the element that is strongest reducing agent (1 mark)
- Which elements would form an electrochemical cell with the highest e.m.f. (1 mark)
- The half cells of M and P were combined to form an electrochemical cell.
- Draw the electrochemical cell formed (3 marks)
- Calculate the e. m. f of the cell formed (1 mark)
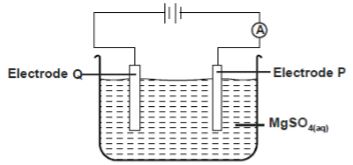
- The set-up below was used during the electrolysis of a solution of Magnesium sulphate using inert electrodes.
- State the observation made in electrode Q. Explain (2 marks)
Write an equation for the reaction in electrode P (1mark) - A current of 0.5 Amperes was passed through the cell for 16 minutes and 5 seconds. Calculate the volume of product at the anode at RTP (1M= 24l ,I F=96500C)(3 marks)
- State the observation made in electrode Q. Explain (2 marks)
- Give one application of electrolysis (1 mark)
-
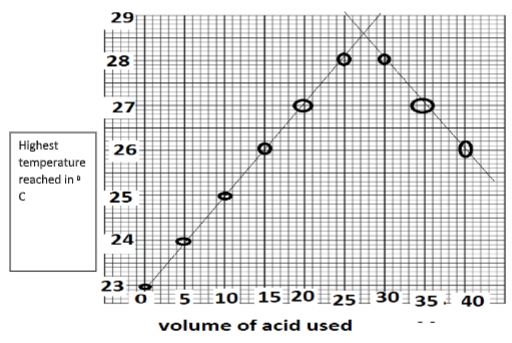
- Define molar heat of neutralization (1mark)
- The table below shows temperature reached when equal volumes of an alkaline solution of 1.5M concentration was reacted with 0.95M sulphuric (VI) acid.
Plot a graph of temperature against volume of acid used (3mks)
Total volume of Sulphuric VI acid added 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 Volume of alkaline solution 30 30 30 30 30 30 30 30 30 Highest temperature reached 23 24 25 26 27 28 28 27 26 - From the graph determine
- the volume of sulphuric VI acid needed to completely neutralize 30cm3 of the alkali solution ( 1mk)
- the temperature change (1mk)
- Calculate the heat change for the above reaction density of solution 1g/cm3, Specific Heat Capacity 4.2g/J/K (2mks)
- Calculate the molar heat of neutralization for the reaction (2mks)
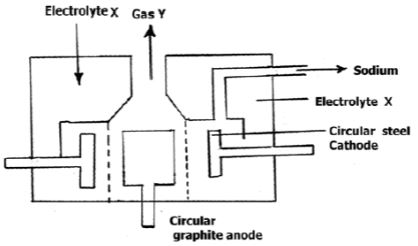
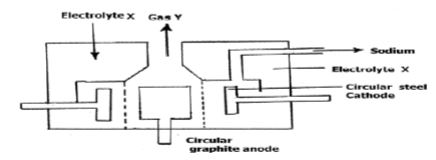
- The diagram below shows the set-up used to extract sodium metal.
- Identify; (2 marks)
- Electrolyte X
- Gas Y
- During extraction of sodium using the down's process, calcium chloride is added to the ore. Give a reason for the addition of calcium chloride. (1 mark)
- State two uses of sodium (2 marks)
- Give a reason why sodium is extracted using electrolysis (1 mark)
- Why is the anode made of graphite and not steel? (1 mark)
- On the diagram, label the steel diaphragm. (1 mark)
- State the role of the steel diaphragm (1 mark)
- State and explain two observations made when sodium metal is placed in a trough of cold water. (3 marks)
- Identify; (2 marks)
-
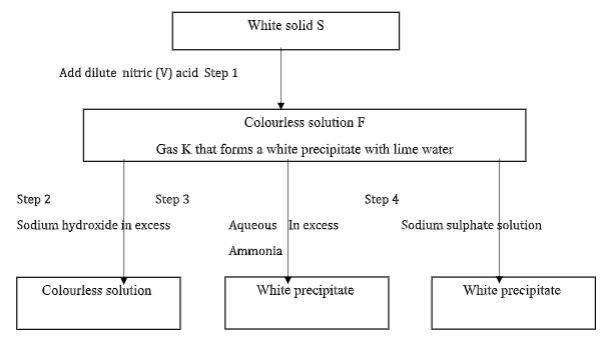
- The figure below shows some properties and reactions starting with solid S. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
- Identify; (2 marks)
Solid S
Gas K - Write an equation for the reaction in step 1 (1 mark)
- State the property of solution F that makes the reaction in step 2 possible. (1mark)
- Write an ionic equation for the reaction in step 2 (1 mark)
- Identify; (2 marks)
- Starting with Zinc oxide, describe how a dray sample of zinc carbonate can be prepared in the laboratory (3 marks)
- Name the process taking place when the following reactions take place (3 marks)
- Calcium chloride placed on a watch glass overnight forms a solution
- Sodium hydroxide reacts with sulphuric (VI) acid to form a colourless solution
- Silver nitrate and potassium chloride react to form a white solid
- The figure below shows some properties and reactions starting with solid S. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
MARKING SCHEME
-
- Name the process in step; (3 marks)
I – Combustion (1 mark)
III – Esterification (1 mark)
IV – oxidation (1 mark) - Write an equation for the reaction in step (2 marks)
I – 2CH 3 CH 2 CH 2 OH (l) + 9O 2 (g) → 6CO 2 (g) + 8H 2 O(g) (1 mark)
V - CH 3 CH 2 COOH (l) + NaOH (aq) → CH 3 CH 2 COONa (aq) + H 2 O(g) (1 mark)
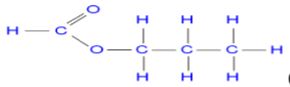
allow fractions and ignore state symbols - Name propylmethanoate (1 mark) (2 marks)
Structural formula
(1 mark) - B - Acidified potassium manganate(VII) or Acidified potassium dichromate (VI) accept the respective formulaes (1 mark)
N – Soda lime(1 mark) - 170 – 180 0 C/ reject high temperature of temparatures out of range ((1 mark)
-
- Soapless (1 mark)
- Magnesium ions make water hard. The detergent forms lather easily with hard water and doesn’t form scum (1 mark)
- Name the process in step; (3 marks)
-
-
A …Molecular/ simple molecular (1 mark)
C …Giant metallic/ metallic (1 mark)- In solid state the ions are in fixed (1 mark)state hence a non-conductor. In molten state the ions dissociate and become mobile(1 mark) hence it conducts eletricity
- It has covalent bonds/ giant covalent structure which are strong throughout the structure hence a lot of energy is required to break them(1 mark)
-
-
(1 mark) ii. (1 mark)
-
- Explain
- Magnesium oxide has strong ionic bonds hence ions are held strongly. Sulphur (IV) oxide has molecules held together by weak van der waals forces(1 mark)
- Ethanol is molecular but it dissolves in water
Ethanol has hydrogen bonds which make it polar and soluble in water(1 mark) - In molten state the electrons have increased kinetic energy which make them move randomly reducing their conductivity. (1 mark)
-
-
-
- To absorb unreacted carbon (IV) oxide (1 mark)
- CO2(g) + C(s) → 2CO(g) (1 mark)
- Reducing property (1 mark)
-
- Solid Y ……Limestone or Calcium carbonate (1 mark)
Solid P ……Calcium oxide (1 mark) - NaCl (aq) + NH3(g) + H2O(l) + CO2(g)→ NaHCO3(s) + NH4Cl(aq) (1 mark)
- Filtration (1 mark)
-
- It is used in the manufacture of detergents, soaps, paper.
- Also used in the manufacture of water glass (sodium silicate), borax, sodium phosphate, and many other sodium compounds.
- It is used in as a wetting agent in brick industry
- It is used as an abrasive and foaming agent in toothpaste
- It is used as a pH modifier
- It is used as water softener – Hard water which consists of magnesium and calcium ions are precipitated by carbonate.
- As a laboratory reagent to standardize acids and as an analytical reagent. any one (1 mark)
- Solid Y ……Limestone or Calcium carbonate (1 mark)
-
- Sulphuric(VI) acid forms an insoluble salt with calcium carbonate(1 mark)
Correction: use of nitric(V) acid or hydrochloric acid(1 mark) -
accept syringe 1 mark)
- Sulphuric(VI) acid forms an insoluble salt with calcium carbonate(1 mark)
-
- The list below shows reduction potentials of element M, N, P and Q
- N
- N and P
-
-
½ mark for correct anode, cathode salt bridge, voltmeter, and workability
(TOTAL 3 mark) - 0.80 – (– 2.37) = +3.17V(1 mark)
-
-
- Colourless bubbles as oxygen gas is formed (1 mark)
or 4OH-(l)= 2H2O(l) + O2(g) +4e-
electrode P 2H+(aq) + 2e → H2(g) (1 mark) - Q = It
Q = 965 x 0.5 = 482.5 C
2H + (aq) + 2e → H 2 (g)
1F = 96500 x 4 = 386000C → 1 mole / 24l
482.5 C → 0.03litres
- Colourless bubbles as oxygen gas is formed (1 mark)
- Extraction of reactive metals like Na, Ca, Al,
Purification of metals
Electroplating
galvanization of iron
Manufacture of pure chemicals like hydrogen, chlorine and sodium hydroxide
-
- heat change when one mole of water is formed by the reaction of H+ ions and OH- ions (1 mark)
- The table below shows temperature reached when equal volumes of an alkaline solution of 1.5M concentration was reacted with 0.95M sulphuric (VI) acid.
s=1
p=1
c=1 (1 mark each total 3mks) - From the graph determine
use correct graph reading = 27.7cm 3 (1 mark)
the temperature change use graph(23-28.5)
don’t penalize –ve sigh - Calculate the heat change for the above reaction density of solution 1g/cm3 , Specific HeatCapacity 4.2g/J/K (2mks)
Highest
(4.2 x (27.7+30) x(23-28.5)) = -1333.87J - Calculate the molar heat of neutralization for the reaction (2mks)
0.026315M = --1333.87J
1M = -50.65kJ/mol
-
- Identify; (2 marks)
- Electrolyte X – Molten sodium chloride
- Gas Y – Chlorine
- An impurity to reduce the melting point of the ore(1 mark)
- State two uses of sodium (2 marks)
- Sodium is used in the production of titanium, sodamide, sodium cyanide,
- sodium peroxide, and sodium hydride.
- Liquid sodium has been used as a coolant for nuclear reactors.
- Sodium vapor is used in streetlights and produces a brilliant yellow light.
- It is a very reactive metal which cannot be reduced by the reducing agents used
- Sodium reacts with steel
- On the diagram, label the steel diaphragm. (1 mark)
- Prevents sodium and chlorine from recombining
-
- Hissing sound as hydrogen gas is produced
- It darts on the surface as the reaction is exothermic
- It melts into a silvery ball as the reaction is exothermic
- Identify; (2 marks)
-
-
- Identify; (2 marks)
- Solid S – lead (II) carbonate
- Gas K – carbon (IV) oxide
- PbCO3(s) + 2HNO3(aq) → Pb(NO3)3(aq) + CO2(g) + H2O(l)
- Amphoteric
- Write an ionic equation for the reaction in step 2 (1 mark)
Pb2+(aq) + SO4(aq) → PbSO4(s)
- Identify; (2 marks)
- Add zinc oxide to warm nitric (V) acid until in excess. Filter to obtain zinc nitrate as filtrate. Add sodium carbonate solution into the filtrate. Filter to obtain zinc carbonate as residue. Wash residue with distilled water and dry between filter papers.
- Name the process taking place when the following reactions take place (3 marks)
- Deliquescence
- Neutralization
- Precipitation or double decomposition
-
Download Chemistry Paper 2 Questions and Answers - MECS Cluster Joint Mock Exams 2021/2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students