Instructions to candidates
- Write your Name and Index Number in the spaces provided above,
- Sign and Write the Admission number in the spaces provided above;
- This paper consists of two Sections; A and B.
- Answer all the questions in Section A.
- Answer question6 and any other two questions from Section B.
- Answers must be written in the spaces provided at the end of question 10.
- This paper consists of 4 printed pages,
- Candidates should check the question paper to ascertain that all the pages are printed as indicated and that no questions are missing.
- Candidates should answer the questions in English.
SECTION A (25 MARKS)
ANSWER ALL THE QUESTIONS IN THIS SECTION
-
- Define the term energy crisis (2mks)
- State three limitations of using solar energy (3mks)
-
- Give two problems facing river transport in African. (2 marks)
- The diagram below shows the Great Lakes and the St. Lawrence sea way.
Use it to answer the questions below.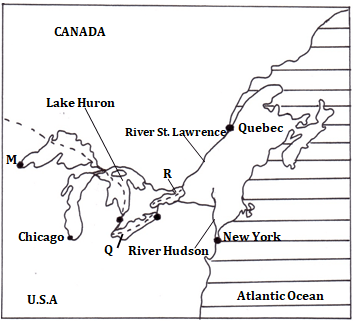
Name the lakes M, Q and R. (3mks)
-
- Apart from tropical hardwood forests name two other types of natural forests (2mks)
- State three problems experienced in exploitation of tropical hardwood forests (3mks)
-
- Give three physical factors that favour coffee growing in Kenya highlands (3mks)
- State two problems facing coffee farming in Kenya (2mks)
-
- Give three types of fish (3mks)
- List two traditional methods of fishing (2mks)
SECTION B
Answer question 6 and any other two questions from this section
- The table below shows crops production in Kenya for a period of five years in 1000 kilograms. Use it to answer question (a)
CROP/YEAR 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 Coffee 1000 900 800 700 800 Tea 700 700 600 680 600 Cotton 500 400 300 600 350 Pyrethrum 300 200 300 440 450 -
- Using a scale of 1 cm represent 200 kilograms present the above data using a compound bar graph. (9 marks)
- List two advantages of using a compound bar graph to represent statistical data. (2mks)
-
- Other than Ghana, name other two countries West Africa where cocoa is grown (2mks)
- State three physical conditions that favor the growth of cocoa in Ghana. (3mks)
- Describe how cocoa is processed in Ghana (6mks)
- Give three importance of cocoa production to the economy of Ghana.(3mks)
-
- Study the photograph shown below and use it to answer the following questions.

-
- Identify the type of the photograph shown above. (1mks)
- Identify two characteristic of the photograph shown above. (2mks)
- Give three parts of a photograph. (3mks)
- Name the type of mining method shown above. (1mks)
- Explain how the method named above (b) is carried out. (6mks)
- Explain four negative effects of the above method of mining on the environment. (8mks)
- Draw a sketch diagram to represent the photograph shown above. (4mks)
-
-
-
- Define the term land rehabilitation (2 marks)
- Apart from irrigation, name three other methods of land reclamation in Kenya. (3 marks)
- Explain three problems facing irrigation farming in Kenya. (6 marks)
- Describe the stages of polderization in the Netherlands (5 marks)
- You intend to carry out a field study on irrigation farming in Mwea Tebere irrigation scheme
- Identify the two types of hypothesis you would develop for the study (2mks)
- Name five crops grown in the scheme that you are likely to identify (5mks)
- Give two reasons why you need to sample the area of study (2mks)
-
-
-
- Define the term industrial inertia (2mks)
- Give three causes of industrial inertia (3mks)
- Name three agricultural non-food processing industries in Kenya (3mks)
-
- What is cottage industry (2mks)
- List four ways in which Jua Kali industries is important to the Kenyan economy (4mks)
-
- State three problems facing cottage industry in India (3mks)
- Explain four factors that led to the development of iron and steel industry in the Ruhr region of Germany (8mks)
-
-
-
- What is environmental management (2mks)
- Give four reasons why it is necessary for Kenya to conserve her environment (4mks)
- Explain four measures that can be taken to combat pollution (8mks)
-
- Name five types of wastes found in urban areas (5mks)
- Explain three ways in which wastes in urban centres can be managed(6mks)
-

MARKING SCHEME
-
- Define the term energy crisis (2mks)
Is a situation where the demand for oil is higher than the amount being supplied leading to high oil prices. - state three limitations of using solar energy (3mks)
- Solar energy is unable to run heavy machinery
- Batteries used for storing solar energy are cumbersome and are to be replaced oftenly.
- Quality solar panels are quite expensive to manufacture.
- Installation of solar panels require technical skills which are undeveloped in most people.
- Solar energy depends on weather patterns which makes its use unreliable.
- Define the term energy crisis (2mks)
-
- Give two problems facing river transport in Africa. (2 marks)
- Inadequate capital to develop waterways, ports and for the purchase of vessels.
- Fluctuation of water levels which makes sailing difficult as a result of rivers passing through dry areas.
- Presence of rapids and waterfalls which hinders the vessels’ movement.
- Siltation of rivers which makes their channels shallow hence hindering movement of vessels.
- Presence of floating vegetation or swamps which makes it difficult for vessels to sail due to narrowing of the river channel.
- Most rivers pass through unproductive zones hence its uneconomical to develop river transport.
- Rivers flow across political boundaries which may require negotiation in order for the countries involved to use them for transport.
- Some rivers meander through their flood plains which increase the distance.
- Some rivers originate/pass through areas that experience long periods of drought leading to changes in the river regime.
- The diagram below shows the Great Lakes and the St. Lawrence sea way. Use it to answer the questions below.
Name the lakes P, Q and R.
M -Lake Superior
Q -Lake Erie
R -Lake Ontario
- Give two problems facing river transport in Africa. (2 marks)
-
- Apart from tropical hardwood forests name two other types of natural forests (2mks)
- Temperate hardwood forests
- Coniferous forests /temperate softwoods
- Montane forests
- Mangrove forests
- State three problems experienced in exploitation of tropical hardwood forests (3mks)
- Presence of tree climbers
- Attack by wild animals
- Trees are found in mixed stands
- Dense/thick forests making penetration into the forest hard.
- The roads are muddy making transport difficult/ impassable roads.
- The trees take long to mature.
- Apart from tropical hardwood forests name two other types of natural forests (2mks)
-
- Give three physical factors that favour coffee growing in Kenya highlands (3mks)
- Deep well drained volcanic soils.
- High rainfall throughout the year.
- Well distributed rainfall throughout the year.
- Gentle sloping landscape.
- Warm climates
- State two problems facing coffee farming in Kenya (2mks)
- Attack by pests eg lady bird, aphids and diseases eg CBD, Leaf rust hence low yields
- Fluctuation of coffee prices in the world market reducing the profit margins.
- Delayed payments hence demoralizing the farmers.
- Low payments hence discouraging farmers.
- Mismanagement of coffee cooperatives.
- Give three physical factors that favour coffee growing in Kenya highlands (3mks)
-
- Give three types of fish (3mks)
- Salt water fish
- Fresh water fish
- Anadromous fish
- List two traditional methods of fishing (2mks)
- Basket
- Spear and arrow method
- Barriers
- Herbs
- Lamp and net
- Hook and line method
- Use of gill nets
- Give three types of fish (3mks)
SECTION B
-
-
-
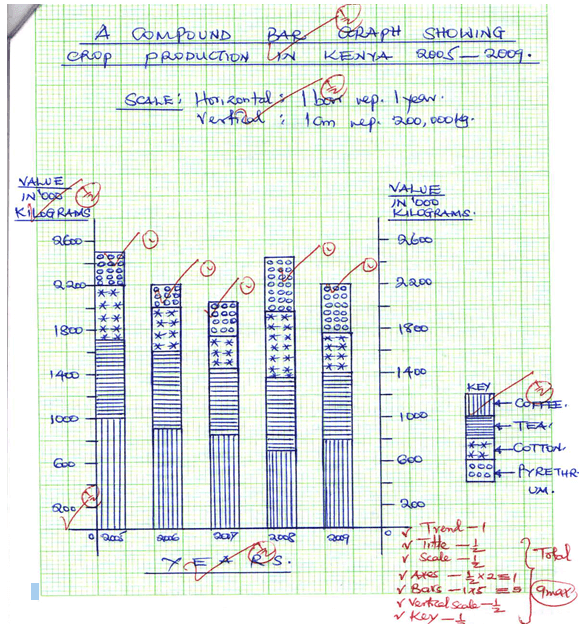
- Advantages of using a compound bar graph to represent statistical data. (2 marks)
- Facilitates comparison of data
- A number of variables can be represented in one bar
- Changes /trend is easy to trace
- Good visual impression (any 2×1=2 marks)
-
-
- Other than Ghana, name two countries in West Africa where cocoa is grown. (2 Marks)
- Nigeria
- Cote -de -voire
- Cameroon (Any 2×1=2 marks)
- Physical conditions that favor the growth of cocoa in Ghana. (3 mks)
- High/ well distributed rainfall, exceeding 1200mm p.a.
- High temperatures /between 240c-300c
- High relative humidity throughout the year
- Deep ,fertile well drained soils
- Low altitude/below 700m a.s.l. 3×1=3 marks)
- Other than Ghana, name two countries in West Africa where cocoa is grown. (2 Marks)
- How cocoa is processed in Ghana (6 mks)
- Beans are fermented for 5-6 days and dried
- The fermented beans are washed / cleaned
- The beans are roasted
- The roasted beans are then crushed to extract cocoa butter
- Cocoa is blended and mixed with sugar (1 mark×6= 6 marks)
- Importance of cocoa production to the economy of Ghana. (3 mks)
- Has contributed to development of industries which use cocoa as raw materials
- Earn the country foreign exchange since most of it exported
- Provide employment opportunities to people working in the cocoa farms and distributing it.
- Has contributed to development of infrastructure in the country
- Has attracted foreign investments into the country (Any 4×1=4 marks)
-
-
-
- Identify the type of the photograph shown above. (1mks)
Ground oblique photograph - Identify two characteristic of the photograph shown above. (2mks)
Taken from the ground with camera focused on general scenery - Give three parts of a photograph. (3mks)
- Foreground
- Middle ground
- Background
- Identify the type of the photograph shown above. (1mks)
- Name the type of mining method shown above. (1mks)
Panning method - Explain how the method named above (b) is carried out. (6mks)
- The method involves digging out the sand/gravel which contains mineral particles
- The particles are mixed with water from the river in a shallow pan.
- The mixture is then whirled.
- The lighter particles of sand/gravel are pushed on the sides of the pan.
- The heavier mineral particles remain at the bottom of the pan.
- The minerals are easily removal by hand as the waited mineral.
- Explain four negative effects of the above method of mining on the environment. (8mks)
- Leaves the land with depression which are dangerous to animals and people.
- Make land unsuitable for agriculture.
- Breeding grounds for mosquitoes. that cause diseases such as Malaria
- Makes the land susceptible to landslides etc any 3x2=6mks
- Draw a sketch diagram to represent the photograph shown above. (4mks)
- The rectangle should be of the same size as the photograph—1mk
- Insert the features in their exact positions-1mk
- Label the important features people and the deposits-1mk
- Give the sketch a suitable title-1mk
-
-
-
- Define the term land rehabilitation (2 marks)
This is the process of restoring land that was once productive back to its productive state. - Apart from irrigation, name three other methods of land reclamation in Kenya. (3 marks)
Draining of swamps
Control of pests
Introduction of drought resistant crops
Afforestation.
Reforestation
Use of manures and fertilizers.
- Define the term land rehabilitation (2 marks)
- Explain three problems facing irrigation farming in Kenya (6marks)
- Disease incidences such as bilharzia and malaria transmitted by vectors in stagnant waters.
- Payment of low prices to the farmers which kills morale of the farmers.
- High cost of production making the farmers to sell their produce at high costs
- Mismanagement of irrigation bodies leading to losses, lack of credit and low prices.
- Shortage of labour during planting, weeding and harvesting giving the farmers the burden of hiring labour at high cost.
- pest infestation which lowers production eg Quelea birds.
- low water levels in the rivers during dry season
- water weeds which compete with crops for nutrients
- siltation in the canals reduces the amount of water
- Describe the stages of polderlization in the Netherlands (5 marks)
- Protective dykes/sea walls are constructed enclosing the part of the sea to be reclaimed.
- Rings canals are constructed.
- Pumping stations are installed to pump out sea water from the area enclosed by the dyke.
- Water is pumped out of the area enclosed by the dyke
- Drainage ditches and more pumping stations are made on the land being reclaimed.
- Drainage pipes are laid below the soil.
- The area is divided into rectangular portions using. Inner dykes and ring canal.
- The drained land is flushed with fresh water to remove salt from the soil.
- Soils are treated with chemicals to remove salinity
- Pumping water from the polders is a continuous process to prevent water from accumulating in the reclaimed land.
- You intend to carry out a field study on irrigation farming in MweaTebere irrigation scheme
- Identify the two types of hypothesis you would develop for the study (2mks)
- Null hypothesis
- Alternative hypothesis
- Name five crops grown in the scheme that you are likely to identify (5mks)
- Maize
- Rice
- Beans
- Tomatoes
- Vegetables
- Identify the two types of hypothesis you would develop for the study (2mks)
- Give two reasons why you need to sample the area of study (2mks)
- To save on time spent during fieldwork.
- To minimize biasness during the study.
- To reduce cost of the study.
-
-
-
- Define the term industrial inertia (2mks)
It is the tendency 0f an industry to remain in a particular area even when the locational factors no longer exist - Give three causes of industrial inertia (3mks)
- availability of experienced workers
- availability of well developed transport and communication system already in place
- It is expensive to move to a new site
- Industrial independence.
- Define the term industrial inertia (2mks)
- Name three agricultural non-food processing industries in Kenya (3mks)
- leather industry
- sisal industry
- pyrethrum industry
- textile industry
- timber industry
- tobacco industry
-
- What is cottage industry (2mks)
is an industry located in villages and people’s homes using locally available raw materials, simple tools and skills to produce valuable items. - List four ways in which Jua Kali industries is important to the Kenyan economy (4mks)
- creates employment opportunities
- Source of income to many Kenyan raising their standards of living.
- Saves on foreign exchange earned
- Earns the country foreign exchange through exports.
- Produce cheaper goods.
- What is cottage industry (2mks)
-
- State three problems facing cottage industry in India (3mks)
- Inadequate funds among people in rural areas
- Stiff competition for the market.
- High danger of exploitation from middlemen
- Production of similar goods
- Competition from manufactured goods.
- Explain four factors that led to the development of iron and steel industry in the Ruhr region of Germany (8mks)
- Availability of coal which is the main source of energy
- Availability of limestone and iron ore as raw materials
- Availability of energy
- Availability of adequate water from river Rhine
- Centrality of Germany in Europe/Accessibility of Germany
- Availability of capital
- Availability of ready market
- Availability of skilled labour
- State three problems facing cottage industry in India (3mks)
-
-
-
- What is environmental management (2mks)
- These are the measures /controls taken to ensure sustainable utilization of resources in a given environment.
- This is the planning and implementation of effective and proper utilization of the available resources in the environment.
- Give four reasons why it is necessary for Kenya to conserve her environment (4mks)
- To maintain source of food supply/ to maintain soil fertility..
- For modification of climate.
- For keeping air clean.
- To prevent desertification.
- Protect water catchment areas.
- For its aesthetic value.
- To sustain the sources of raw materials.
- For maintaining natural habitat for wild animals.
- What is environmental management (2mks)
- Explain four measures that can be taken to combat pollution (8mks)
- Control of soil erosion to reduce the amount of silt getting into rivers, wells, lakes and other water bodies.
- reating of sewage and industrial effluents before being released into the environment.
- Carrying out regular inspections of factories to ensure that toxic fumes are not released into the atmosphere.
- Use of unleaded fuel to promote a cleaner environment as well as to reduce pollution released by the cars.
- Establishing recycling plants to recycle the different categories of wastes and make them user friendly to the environment.
- Setting up proper garbage collection and management programmes.
-
- Name five types of wastes found in urban areas (5mks)
- Industrial wastes
- Biomedical/clinical wastes.
- Household wastes
- Agricultural wastes
- Commercial/business waste
- Construction wastes
- Sewage/sludge waste.
- E-waste/Electronic waste
- Explain three ways in which wastes in urban centres can be managed (6mks)
- By recycling wastes so as to produce useful products from the wastes.
- By asking companies /firms to treat wastes prior to disposing it off to the local surrounding.
- Discourage the use of plastic bags that are non-biodegradable and thus a serious pollutant to the land.
- Place many waste collection bins so as to reduce haphazard manner of disposal of waste.
- By creating awareness on the significance of sound waste management practices by the urban population.
- By ensuring that the county government do not allow accumulation of waste in the urban centres.
- Name five types of wastes found in urban areas (5mks)
-
Download Geography Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Samia Joint Mock Examination 2021/2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students

