- Meaning of Communication
- Importance of Communication (Purposes)
- Communication Process
- Lines of Communication
- Essentials of Effective Communication
- Forms and Means of Communication
- Barriers to Effective Communication
- Services that Facilitate Communication
- Current Trends and Emerging Issues in Communication

Meaning of Communication
- Communication is the transfer or conveyance of messages or information from one person to another.
- Communication is the process of sending and receiving meaningful messages, information and ideas between two or more people located at different points in space.
Note: The space between the sender (s) and the receiver (s) maybe as narrow as when people are talking to each other or as wide as between the North Pole and the South Pole. - Effective communication is vital/important for business in that it serves the following purposes.

Importance of Communication (Purposes)
- To give and obtain information
- For an organization to run smoothly there should be proper flow of information within the business and also between the firm and outsiders e.g. the manager may inform members of staff about a planned meeting. Similarly the business may receive a letter of inquiry from a customer - To clarify issues and points
- Through proper communication the organization is able to clarify confusing issues from within and without the firm for example in cases where there are many managers. It would be necessary to clarify the responsibilities of each manager. - To enhance public relations
- Good/efficient communication enables the business to create a more positive image and a favorable reputation of itself to outsiders and overcome prejudices and negative attitudes that people may have against the business. - To start and influence Action
- Proper communication enables the business to get new ideas make plans and ensure that they are implemented in the desired way. - Improving customer service; Good communication helps in reducing errors providing customers with desired feedback and assisting in handling inquiries more efficiently
- Giving instructions; Through proper communication management is able to get work done by issuing instructions (procedures and orders)e.g. a supplier may be instructed when and where to deliver the goods ordered.
- To give Reassurance; Information is needed to reassure people that their performance is good e.g. an employee may feel better is he/she is served with a “will done”memo or a “customer of the year” award.
- Confirming arrangements; Through communication arrangements are confirmed for example confirmation of meetings conferences or details of transactions
- Co-ordinating departments of the firm; Charges in one department are communicated to other departments that have a direct bearing to those changes e.g. when sales increase the sales department informs the production department so as to increase production proportionality
- Modifying behavior of persons within or outside the organization;
- Through effective communication persons are trained and counseled and as a result their behavior knowledge and attitudes change

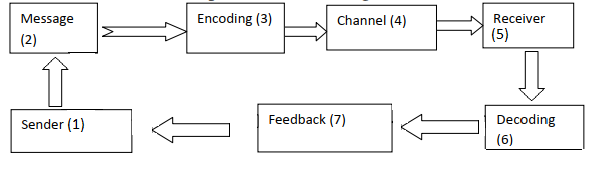
Communication Process
- Communication is a process that involves interchange of information and ideas between two or more people.
- Communication therefore is a circular process i.e communication may lead to some reaction which in turn may generate further communications or feedback.
- This flow can be illustrated as below:

Sender –this is the person who writes, speaks or sends signs (symbols or signals) and is the source of the information.
Receiver - this is the person to whom the information or the message is sent.
Message – this is the information that is transmitted from the sender to the receiver. It may be spoken, written or in the form of symbols.
Feed back – this is the response to the sender’s message. A message is said to have been understood if the receiver provides the desired feedback.

Lines of Communication
- Communication can be classified according to
- The levels of the communicating parties
- According to the nature of the message.
According to Levels
- This can either be:
- Vertical
- Horizontal
- Diagonal
Vertical Communication
- This is where messages are passed between a senior and her/his juniors in the same organizations
- Vertical communication can be divided into two parts
- Downward communication
- Upward communication
- Downward communication-This is a communication process which starts from the top manager to her/his juniors. This can be informed of:
- Training juniors
- Evaluating performance
- Delegating duties
- Solving the problems facing workers
- Inspiring and motivating the juniors(giving rewards)
- Upward communication-This is a communication process that starts from the juniors to the seniors and maybe in the form of:
- Submitting reports
- Giving suggestion
- Submitting complaints a grievances
- Making inquiries
Horizontal Communication (Lateral Communication)
- This is communication between people of the same level (rank) in the same organization e.g. departmental heads in an organization may communicate to achieve the following:
- Co-ordination and harmonization of different activities.
- To create teamwork within the department.
- To exchange ideas in order to develop human resources.
- To reduce goal blindness among different departments.
- To create a sense of belonging among department heads thus acting as a motivating factor.
- One of the major characteristics of this type of communication is that there are less inhibitions. The people involved are more open and free with each other than in the case of people with different ranks.
Diagonal Communication
- This is communication between people of different levels in different departments or different organizations e.g. an accounts clerk may communicate with a sales manager of the same organization or of different organizations. Diagonal communication enhances team work.
According to Nature of Message
- This can either be;
- Formal communication
- Informal communication
Formal Communication
- This is the passing of messages or information using the approved and recognized way in an organization such as official meetings, memos and letters. This means that messages are passed to the right people following the right channels and in the right form.
- Formal communication is also known as official communication as it is the passing of information meant for office purposes.
- Formal systems of communication are consciously and deliberately established.
Informal Communication
- This is communication without following either the right channels or in the right form i.e. takes place when information is passed unofficially. It is usually used when passing information between friends and relatives hence it lacks the formality.
- Informal communication may also take the form of gossips and rumormongering.
- Informal communication usually suppliments formal communication as is based on social relations within the organization.
Note: Both formal and informal communication is necessary for effective communication in an organization.

Essentials of Effective Communication
- For communication to be effective it must be originated produced transmitted received understood and acted upon.
- The following are the main essentials to effective communications.
- The sender/communicator
- This is the person from whom the message originates. He/she encodes the message i.e. puts the message in the communicative form. - Message
- This is the information to be sent. It is the subject matter of communication and may contain words, symbols, pictures or some other forms which will make the receiver understand the message - Encoding; This is the process of expressing ones ideas in form of words, symbols, gestures and signs to convey a message
- Medium/channel; This refers to the means used in communicating. This could be in the form of letters, telephones and emails among others.
- The receiver; This is the person for whom the message is intended. The receiver decodes the message for proper understanding.
- Decoding; This is the process of interpreting or translating the encoded message to derive the meaning from the message
- Feed-back; This refers to the reaction of the receiver of the message. This maybe a reply /response which the receiver sends back to the sender.
- The above can be represented in a diagram as shown below;

Forms and Means of Communication
- Forms; These are channels or ways of passing on messages. The four main forms are:
- Oral communication
- Written communication
- Audio –visual communication
- Visual communication
- Means; This is the device used to pass on information e.g. messages, letters, telephones e.t.c
Oral Communication
- This is where information is conveyed by talking (word of mouth)
- It is also known as verbal communication
Means of Oral Communication
- Face-to-face conversation
- This involves two or more people talking to each other. The parties are usually near each other as much as possible to ensure effective communication.
- It is suitable where subject matter of discussion require convincing persuasion and immediate feed-back.
- It may be used during meetings, interviews, seminars, private discussions, classrooms e.t.c
- It is the most common means of oral communication
Advantages of face-to-face communication- Provides for immediate feedback
- Has personal appeal
- Body language can be easily expressed
- One can persuade or convince another
- It is the simplest communication to use
- It is direct i.e. does not pass through intermediaries
- Convenient for confidential messages
Disadvantages of face-to-face communication
- No record for future reference
- Can be time consuming
- Messages can be distracted
- Not suitable when people are far apart
- Unsuitable for the dumb and deaf
- Telephone
- This form of communication is commonly used in offices and homes. It is useful in sending messages quickly over short and long distances.
- It is however not suitable for sending;- Confidential messages
- Long and detailed reports, charts and graphs
- Messages that would require reference or evidence
- In Kenya telephone services are mainly provided by Telkom Kenya Limited.
- The subscriber is required to purchase the telephone equipment from the post office or other authorized dealers before installation.
- Installation is done on application by the subscriber (applicant).He/she pays the installation fee in addition; the subscriber is sent a monthly bill with the charges for all the calls made during the month.
- The charges for calls depend on the time spent time of the day of the week and distance of the recipient from the caller e.g. it is cheaper to call at night than during the day. It is also cheap to make calls during public holidays and weekends than on weekdays.
- There are also mobile phones which have no physical line connection to exchange and may be fixed to a vehicle or carried in pockets. In Kenya these services are provided by safaricom, Airtel, Telkom and Faiba mobile communications.
Advantages of Telephones- Relatively fast
- Has personal appeal
- Provides for immediate feedback
- One can persuade or convince another
- Suitable for long distance communication
Disadvantages of Telephone- Can be expensive especially over long distances
- No record for future reference
- Lacks confidentiality
- Not convenient for dumb and deaf
- Can be time consuming
Reasons why mobile phones have become popular
- They are portable and can be conveniently carried around.
- It is not very expensive especially when making local calls.
- Relatively cheap to acquire.
- Some mobile phones can record conversations / calls thereby acting as evidence.
- Can be used to send short text messages (sms)
- Can be used anywhere since they are portable.
- Radio calls
- This involves transmitting information by use of radio waves i.e. without connecting wires between the sender and the receiver
- The device used is called a radio telephone. It is commonly used in remote areas where normal telephone services are lacking or where telephone services are available but cannot be conveniently used e.g. policemen on patrol in different parts of a town
- Radio transmission is a one way communication system i.e. only one person can speak at a time. It is therefore necessary for the speaker to say’over’ to signal the recipient that the communication is through so that the recipient can start talking. To end the conversation, the speaker says ‘over and out’
- The radio calls are commonly used by the police, game rangers, researchers, foresters, ship owners and hotels situated in remote areas. They are also used for sending urgent messages such as calling for an ambulance and fire brigade
Note; Radio calls are not confidential since they use sound frequencies that can be tapped by any radio equipment that is tuned to that frequency
Advantages of Radio calls- Relatively fast
- Has immediate feedback
- Has personal appeal
- Provide room for one to persuade and convince another
- Suitable for remote areas
- Convenient for long distances
Disadvantages of Radio calls
- No record for future reference
- Lacks confidentiality
- Messages are sent one way at a tim
- Can be expensive
- Cannot be used by dumb and deaf
- Can be time consuming.
- Paging
- This is a means of communication used to locate staff or employers who are scattered in an organization or who are outside and need to be located urgently
- When within the organization portable receivers, lighted signals, bells, loudspeakers etc are used
- When outside the organization employees are contacted using portable receivers (pocket-size) used to send messages through sms (short message services)
- The paying system can only be used within a certain radius. When using a portable receiver, the caller will contact the subscriber by calling the post office which will then activate the pager.
- The subscriber is then informed to contact the originator of the message.
- Paging is mostly used in emerging cases - Radio
- Usually messages intended for a wide audience can be transmitted through a radio more quickly and economically than by using other forms of communication.;`
- Radio is used for different reasons apart from advertising e.g for formal notices, and venue for activities
Advantages of Oral/Verbal Communication
- Very effective method of communication since the recipient can be persuaded/convinced
- It is relatively faster method of communication
- The sender can get immediate feedback
- It indicates some sence of regard hence more appealing.
Disadvantages of Oral/Verbal communication
- Has no records for future reference
- Is an expensive method especially if the two parties are far apart
- Is not good for confidential messages
- It is not suitable for confidential messages
- It may be time wasting especially where one needs to be convinced
Written Communication
- This involves transmission of messages through writing. It is the most formal way of communication because the information is in recorded form and can be used for reference
Means of Written Communication
- Letters
- Letters are the most commonly used means of communication.
- There are two categories of letters;- Formal letters
- Informal letters
- Formal letters; These include business letters and official letters.
- Business letters are written to pass messages and information from businessmen to customers and vice versa e.g. letters of inquiry and acknowledgement notes.
- It can also be used between employees and employers in an organization e.g. a complimentary note.
- Official letters are letters between people in authority and others that touch on the activities of the organization e.g. an application letter for an advertised vacancy in an organization.
- Formal letters have a salutation clause which usually starts with “Dear Madam “or “Dear Sir”. It also bears the addresses of both the sender and the recipient, a subject heading and a complimentary clause ending with “Yours faithfully”.
Informal Letters; These are letters between friends and relatives
- They are also known as Personal letters - Telegrams
- This is a means of communication provided by the post office. The sender obtains the telegram form from the post office and fills the message on it in capital letters and hand it over to the post office employees at the counter.
- Alternatively the sender may use a telephone to read the message to the post office. The post office then transmits the message to the recipient post office.
- The charges of a telegram are based on the number of words used, the more the words used the higher the charges. However there is a standing charge.
- Telegrams are used for sending urgent messages.
Note; Due to changing technology telegrams have lost popularity. Short messages can now be sent by cell phones (mobile phones) using the short messages services (sms) - Telex
- This is a means of communication used to send short or detailed messages quickly by use of a teleprinter. The service is provided by the post office on application.
- A message is sent by use of two teleprinters one on the senders end and another on the recipients end. When sending information through a teleprinter which is a form of electric typewriter producing different electric signals, its keys are pressed and automatically the message is printed at the recipient’s machine.
- Telex saves time for both the sender and recipient as the messages are brief precise and received immediately. However, it’s an expensive means of communication - Facsimile (Fax)
- This involves transmission of information through a fax machine. Both the sender and the receiver must have a fax machine. These machines are connected using telephone lines
- Fax is used to transmit printed messages such as letters, maps, diagrams and photographs. To send the information, one dials a fax number of the required destination and then the document is fed into the sender’s machine. The receiving machine reproduces the document immediately. It is used for long distance photocopying service. - Memorandum (Memo)
- This is printed information for internal messages within an orgaanisation. It is normally used to pass information between departments or offices in an organization.
- Memoranda have no salutation or complimentary clause. They are suitable for informing the officers within an organization of matters related to the firm.
- A memo is pinned on the notice board of an organization if it is meant for everybody otherwise passed to the relevant staff. - Notice
- This is a written communication used to inform a group or the public about past current or future events. It is usually brief and to the point. It can be placed on walls, in public places, on trees, in newspapers or on notice boards. - Reports
- These are statements/within records of findings recommendations and conclusion of an investigation/research. A report is usually sent to someone who has asked for it for a specific purpose. - Circulars
- These are many copies of a single letter addressed to very many people when the message intended for each is the same. - Agenda
- This is an outline of the items to be discussed in a meeting. It is usually contained in a notice to a meeting sent in advance to all the participants of the meeting. The notice of the meeting contains;- The date of the meeting
- The venue of the meeting
- Time of the meeting
- Items to be discussed
- Minutes
- These are records of the proceedings of a meeting. Keeping minutes of certain meetings is a legal requirements e.g. companies
- Keeping minutes for other meetings are for management purposes to ensure that decisions made at the meetings are implemented
Advantages of Written Communication
- It can be retained for future reference
- Some like letters are relatively cheap(can produce many copies)
- It is suitable for confidential messages
- Allows for inclusion of fine details
- It is not prone to distortion of messages
- Can be used as evidence
- Can be addressed to many people.
Disadvantages of Written Communication
- It lacks personal appeal
- It takes time to prepare and reach the recipient
- Suitable for the literate only
- Immediate feedback may not be possible
- Does not offer room for persuasion and convincing
- It may be expensive because it involves a lot of paperwork and time.
- Not suitable if the sender and the receiver do not share a common language.
Visual Communication
- This is the process of passing information by use of diagrams, drawings pictures, signs, and gestures e.t.c
Means of Visual Communication
- Photographs
- A photograph is an image (visual representation of an object as it appeared at the time when the photograph was taken
- Photographs are self-explanatory and may not be accompanied by any narration or explanation. The recipient is able to get the message at a glance. - Signs
- Refer to marks, symbols, drawings or gestures whose purpose is to inform the public about such things as directions, distances, dangers and ideas.
Examples; road signs, traffic lights and danger signs on electricity poles
- This means of communication can only be effective if the meaning of the sign used is understood. - Graphs; These are used to show and illustrate statistical information
- Charts; These are diagrams which show or illustrate the flow of an idea e.g. an organization chart illustrates the whole organization structure indicating the chain of command
Advantages of Visual Communication
- It can be used to pass confidential information
- The information may be obtained at once
Disadvantages of Visual Communication
- Can only be used by people who can see
- The information may be wrongly interpreted
- It may be an expensive method of communication
- Cannot be used for long distances
Audio-Visual Communication
- This is a form of communication in which messages are sent through sounds and signs.
- This form of communication ensures that the receiver gets the message instantly.
- It is suitable where both the sender and the receiver know the meaning of specific sounds and signs.
Means of Audio-Visual Communication
- Television (TV): This is a device that transmits information inform of a series of images on a screen accompanied by sound. It is a very effective method of communication since it combines the advantages of image and sound
- A television can be a very suitable means of sending urgent messages especially when it gives live coverage of events. - Siren: This is a device used to produce a loud shrill sound accompanied by a flashing light. It is commonly used by the police, ambulances, and the fire brigade and security firms to alert the public of the danger involved e.g. the ambulance siren conveys the message that somebody is seriously sick and therefore other motorists should give way.
Advantages of Audio-Visual Communication
- It reaches many people
- It is more appealing than other means of communication
- Reinforces verbal communication
- May have a lasting effect on the receiver
- Suitable where receivers are illiterate.
Disadvantages of Audio-Visual Communication
- It is suitable to those people who can interpret the messages correctly
- It is not suitable for confidential messages
- Preparation may take long.
Audio Communication
- This is when the message is transmitted through sounds. Examples include
- A whistle; This is a device which is blown to produce a sharp shrill sound to alert or warn the public or employees in an institution. It is normally used by security guards when there is danger. In some organization, a whistle is used to announce change in shifts
- Horn; This is also an instrument that is used to produce sound which passes different information depending on the way it is blown.
- Other methods of audio communication include drums, alarms, and bells among others
Advantages of Audio Communication
- Is a faster method of communication
- It can reach several people at once
- The message is received instantly
Disadvantages of Audio Communication
- The message may be interpreted wrongly
- It can only be used within a certain radius at a time
- It distracts people’s attention

Factors to Consider when Choosing Means of Communication
- Speed: Speed is an important factor when the message is urgent. In such a case telex, fax, telephone, telegram or e-mail would be the most suitable means of communication. Otherwise ordinary mail would be used
- Cost: The cost incurred in using a means of communication vary from one means to another e.g. it is cheaper to send messages by ordinary mail than by telegram or telex
- Confidentiality: Some messages are quite confidential and are intended for certain person only. Where confidential messages are involved, appropriate means should be used e.g. registered mail or internal memo enclosed in an envelope
- Distance: The geographical gap between the sender and recipient is very important in determining the means of communication to be used. Some means are suitable for long distances while others are not. Paging and sirens are suitable for short distances. For long distances, fax letters, telephone, e-mail may be appropriate
- Evidence: Some means of communication do not provide record of the message communicated while others do. All means of written communication provide evidence of messages communicated.
- Reliability: This is the assurance (certainty) that the message will reach the intended person at the right time in the right form. Face-to-face communication is more reliable than other forms of communication because one can ask for clearly and get answers immediately. For some written information, courier service may be preferred
- Accuracy: This refers to the exactness of the message communicated as intended by the sender. Written messages are generally more accurate than other means of communication.
- Desired impression: The impression created upon the recipient of a message is very important e.g. a telegram or speed post mail will carry some sence of urgency, registered mail will create an impression of confidentiality while use of colourful and attractive letterheads would convey a good image of the business.
- Availability: One may want to telephone, for example, but the services are not there so the person would be forced to use alternative means e.g. letters or radio call.

Barriers to Effective Communication
- Communication is said to be complete only when the recipient gets the message the way the sender intends it to be. When information is not received the way it was intended then it has been distorted. Distortion of a message is brought about by some communication barriers which may exists in the path of the message between the sender and the recipient.
- Some of these barriers are:
- Language used: the language used by the sender should be known (understood) by the recipient so that communication can take place
- Poor Listening: the effectiveness of communication will depend on the willingness of the recipient to listen keenly .listening require careful attention and concentration. It may however be the task of the sender of the message to attempt to gain the attention of the listener. Through his/her choice of words and expression among others.
- Negative Attitude: Attitude refers to the feelings of the communicating parties towards each other. It is important that there exists a mutual feeling of trust and respect between the parties concerned in order to avoid bias. If there is mistrust and prejudice then there may be deliberate or unintentional misunderstanding of the message involved.
- Poor Timing: poor timing leads to breakdown in communication, therefore for effective communication to take place the message must be sent and received at an appropriate time, eg a message sent when one is in a hurry may not be properly received or delivered
- Wrong medium: the medium used to communicate must be appropriate for the message being conveyed otherwise there may breakdown in communication e.g. one may not convey a confidential message over the telephone effectively
- Prejudgment: our understanding of the message is often conditional by our earlier experiences and knowledge this may make one individual draw premature conclusion e.g. a student who always fail in a subject and this time round has improve may be failed by the teacher because he has always failed in the past .
- Ambiguities: it occurs when the sender express in a manner which leads to wrong interpretation. When the receiver interprets the message differently it automatically leads to communication breakdown.
- Emotional responses: emotional responses such as those resulting from hunger or excitement may lead to distortion of message.
- Unclear System within the organization: if the channels of passing information in an organization are not clear then the message will not get to the right people for whom the messages intended
- Noise: it refers to any disturbing sounds which interfere with concentration or listening ability of the recipient of the message the presence of noise may make it impossible for any message to be received in the right way.
- Unfamiliar Non-verbal signals: lack of understanding of non-verbal sign may be a barrier to effective communication.

Services that Facilitate Communication
Services that facilitate communication include:
- Mailing services
- Telephone services
- Broadcasting services
Mailing Services
- This refers to handling of letters and parcels. They are offered by organizations such as postal corporation of Kenya (P.C.K) securicorl courier and Document handling Limited (D.H.L)
- Some of the services offered by the postal corporation include:
- Speed post: This is service offered by the post office to send correspondence and parcels to a destination in the shortest time possible. The post office uses the quickest means of transport available to deliver the mail.
- The sender pays the normal postage fee plus a fee for special service. An example of such a service is Expedited Mail Service (EMS) speed post - Ordinary Mail
- These include surface mail and airmail.
Surface Mail: These include letters and parcels delivered by road, rail, water and hand.
AirMail: This consists of letters and light parcels delivered by air. - Express Mail;
- An express mail is/must be presented at the post office counter by the sender and the envelope clearly addressed and a label with the word “express” affixed. Normal postage plus an extra fee (commission) is charged
- The mail is delivered to the receivers nearest post office from where the post office makeS arrangements to deliver the mail to the receiver within the shortest time possible.
NOTE: For speed post special arrangements to deliver the mail start at the sender’s post office whereas express mail, the arrangements start at the addressers post office. - Poste Restante;This is a service offered by the post office to travelers who may wish to receive correspondence right away from their post office box. The addressee has to inform those who may wish to correspond with him/her of the nearest post office he is likely to use at a particular time
- Under this arrangement when addressing the letter, the words poste Restante must be written on the envelope clearly. The addressee must identify himself/herself when collecting the correspondence from the post office.
- There is no additional charge made apart from normal postage charges. This service can only be offered for three months in the same town - Registered Mail;
- This service is offered by the post office for sending articles of value for which security handling is required. A registration fee and a commission is paid. The commission depends on the weight of the article and the nature of registration. The sender is required to draw a horizontal and a vertical line across the faces of the envelope.
- A certificate of registration is given to the sender. In case of loss, the sender may be paid compensation on production of the certificate of registration.
- A green card is sent to the recipient. The card bears his name and the post office at which the mail was registered. The recipient will be required to identify himself before being allowed to posses the mail.
- Items that may be registered include jewels, certificate, land title deeds e.t.c. - Business Reply Service; This is a service offered by the post office to business firms on request. The firm pays some amount to the post office and an account is then opened from which posted charges are deducted.
- The service is useful/more common with firms which would like to encourage their customers to reply their letters. Customers are issued with reply card envelopes (or envelopes marked ‘postage paid’)
- They can send letters to the business by using these envelopes/the card. The customers then place the card/envelope in the post box and the firms post office branch will deduct postage charges from the lump sum amount.
- Speed post: This is service offered by the post office to send correspondence and parcels to a destination in the shortest time possible. The post office uses the quickest means of transport available to deliver the mail.
Courier Services
- These are services where a service provider receives transports and delivers parcels or important documents to destinations specified by customers in return for payment of fees or charges.
Examples; Fargo courier, G4S courier services e.t.c
Telephone Services
- Landline/fixed line services
- Cellular(mobile) phone services
Landline(Fixed)line Services
- Telkom Kenya, through the post office, provides telephone services which offer direct contact between people who are far apart. It makes conversation between people at any distance possible, as long as there are transmission facilities between them. Urgent matters can be discussed and consultations can take place so that instant decision or actions are taken.
- The telephone assists organizations to establish a fast and convenient machinery for its internal and external communication network.
Cellular(mobile)phone Services
- These are hand held telephones with digital links that use radio waves.
- They are sometimes called cell-phones since they use power stored in a dry cell
- In Kenya mobile phone services are provided by safaricom Ltd.(a subsidiary of Telkom Kenya)and Airtel communications Ltd(formally Kencel Communication Ltd)which is a joint venture between a French company and a Kenyan company and Orange mobile services . This sector therefore greatly benefits from foreign investment to improve services.
- The use of this service is popular. Apart from the provision of telecommunication service, cell phones have different attractive features or services such as short messages service (sms) whereby a caller can send a written message. Recent models of mobile phones enable the user to access the internet and send e-mail messages
Advantages
- They are portable
- Written messages can be transmitted easily and cheaply through the short message service(sms)
- Enables both local and international communication
- The cost of acquiring the equipment is relatively affordable
- Direct feedback is possible
- Has memory for storing written messages
- Has got e-mail capability
Disadvantages
- Some kinds of mobile phones are expensive to buy
- Maintenance expenses of a mobile phone are high. They are also susceptible to damage and repair can be very costly
- Users are greatly inconvenienced in case there is no network coverage
- A special facility where the callers identity is known(displayed on screen)can be abused where recipient does not wish to answer the call
- Mobile phones are a security problem. They are easy targets for thieves
- There is a danger of the radioactive rays or emissions negatively affecting the users health, if such emissions are not adequately controlled
Broadcasting Services
- Communication commission of Kenya is a regulatory body that receives applications and issues licences for radio and television broadcasting stations.
Radio Stations
- Radio broadcasting is a very important mode of giving news and information to people in the whole world.
- The liberalization of the communications sector in Kenya in 1999, Kenya has witnessed a mushrooming of F.m. Stations which are owned by private sector operators e.g. Kiss Radio, Easy fm,Classic fm,Family fm,Kameme e.t.c
- They have helped to spread news and information countrywide. Before liberalization, Kenya Broadcasting corperation (KBC) radio was operating as a state owned monopoly.
Television Stations
- Television broadcasting (telecasting) does not reach as wide an audience as radio broadcasting in Kenya. It however serves the same purpose of relaying news and information to Kenyans. Both radio and television stations are widely used for advertising purposes.
- The T.V subsector has been liberalized since 1999 and a number of privately owned stations have emerged e.g. Kenya Television Network (KTN), Nation Television, Family T.V etc. Prior to that time KBC television was in operation as a state owned monopoly.
- Other services that facilitate communication
- Telex
- Facsimile
- Paging

Current Trends and Emerging Issues in Communication
- With the advancement of information technology (I.T) there has been a lot of revolution in communication.
- The following are some of the current trends and emerging issues in communication;
Telephone Bureaux(Bureaus)
- These are privately owned kiosks where telephone services are sold. The owner of the kiosk must get authority from the service provider in order to run the bureau. The individual wishing to use the services of the bureau makes payments to the owner of the service. Other services offered by the bureau include selling of scratch cards for mobile telephones and credit cards for landline telephone services.
Mobile Phones (Cell Phones)
- These are hand held telephones with digital links that use radio waves. They have become an important business and social tool. This is because most people and traders want some flexibility to be able to communicate whenever they are.
- Other reasons that have led to the popularity of cell phones include:
- Pre paid services which enable the owners to control communication costs.
- Most cellular phones now allow the owners to browse the internet, check and send mail. This allows business people to communicate research and even place orders.
- Cellular phones have short message services (sms) which enables the owners to send written messages.
E- mail (Electronic Mail)
- This is a service provided through the internet for sending messages.
- It is similar to sending a letter through the postal system only that it is done electronically.
- Messages can be sent to anyone on the network, anywhere in the world. For this to take place, computers have to be connected to each other to form a network.
- To communicate, one is required to have an email address e.g. raeform2@yahoo.com. Messages arrive at the e – mail address immediately they are sent.
- It is only the addressee of the message who can retrieve the message since a password is required to access the mailbox.
- E – mail can also be used to send documents and photographs like certificates by scanning and attaching.
- More and more businesses are using e- Mail to communicate with other businesses, their customers and suppliers.
Question: Outline the advantages of using e- mail as a means of communication.
Internet
- The internet links computers all over the world. Written and oral information is transmitted on the internet through the use of telephone wires, fibre- optic cables and wireless devices.
- The internet has changed the way people communicate in the following ways;
- Increased use of electronic mail (e-mail)
- Quick access to information from all over the world.
- Development of home offices and remote offices.
- Use of teleconferencing and video conferencing.
- Development of e-commerce.
Move Towards a Paperless Office
- The future office will rely largely on computers. Most of the communication will be done through computers. This may result in less use of paper, hence the use of the term “the paperless office”.
Decline in the Use of Postal Services
- Decline in the use of postal services is a result of the impact of the internet. Email has become a popular and preferred mode of communication since it is fast and cheap. However, ordinary mail/ use of postal services may not be completely phased out since the government, businesses and people do not regard an e-mail as a binding or formal communication.
Transformation of Language
- The language used to pass and receive messages has evolved through time.e.g the youth have adopted the use of “sheng” in exchanging messages. such language is largely understood by its youthful users. There is also the use of cell phones to send short text messages; which are highly abbreviated and may use slang whose meaning is only known to the users e.g ‘av a gr8 day’.
Communication Revision Questions
- Define the term communication
- Communication is the process by which information is passed from one person or place to another.
- Outline the role played by communication in any given organization
- It is used to give instructions on what should be done at work and during work.
- It enhances good relations among workers thereby promoting and enhancing their efficiency.
- Through communication most organizations have been able to improve their image, for example through advertising.
- It used to improve the relationship between the organization and the customer or clients.
- For co-ordinating purposes, communication is used to ensure all departments work in harmony.
- The feedback got from the clients or customers helps to improve an organization’s reliability and quality of goods and services offered.
- Communication is used as a tool for management.
- Good decisions are made as communication helps one understand all the necessary matters.
- Briefly explain the following levels of communication
- Vertical communication
- Involves the flow of information either downwards or upwards, for example, from a senior employee to a junior employee
- Horizontal communication
- Is also referred to as lateral communication which is passing of information between people of the same rank or status, for example from one departmental manager to another departmental manager
- Diagonal communication
- Is communication of different people in different levels of management or departments for example a receptionist communicating to a production manager.
- Vertical communication
- Distinguish between formal and informal communication
- Formal communication is official and documented and follows certain rules for example a worker writing an official letter to an organization’s seniors.
- Informal communication does not conform to any time, for example communicating to friends and relatives.
- State the essential elements in communication.
- The sender who is the source of the information being communicated
- The receiver(or recipient) of information
- The message being communicated
- The channel (or medium) through which the message is passed on
- Feedback which is the response or reaction of the recipient.
- Highlight the various types of verbal communication
- Face-to-face communication
- Telephone conversation
- Radio calls conversation.
- State the advantages and disadvantages of verbal communication
Advantages- A large number of people can receive the information at once for example when addressing in a meeting.
- There is immediate feedback
- Clarification can be made easily and immediately
- This is personal appeal
- It can be very convenient and persuasive
- It is fast since the intended information reaches the recipient immediately.
- It is not easy to know if the message or information has been received particularly if the receivers are many
- It is prone to outside interference due to noise and other forms of disruptions
- In case of incorrect pronunciation of words, there could be distortion of the information
- There is no record for future reference.
- The method is not effective for recipients with learning problems.
- Can take a lot of time to pass intended information.
- Outline the various barriers to effective communication
- Noise may hinder effective communication
- The emotional state of both the sender and the recipient
- Use of the wrong channel to communicate
- Breakdown of a channel used to communicate
- Illiteracy of the recipient particularly for written communication.
- The attitude of the recipient towards the sender and the information being communicated
- Use of difficult vocabulary or words by the sender
- Lack of concentration on the part of the recipient may affect communication
- Poor timing by the sender.
- Highlight reasons that would make an organization use cell phones for communication within and outside the organization.
- One gets immediate feedback
- It is fast and can be used to send urgent messages
- There is personal appeal
- The sender has a great opportunity to convince and persuade the recipient.
- It is not very expensive particularly for making calls for a short duration of time
- It can be used even when both the sender and the recipient are far apart
- State the various types of written communication.
- Written
- Memorandum(memos)
- Reports
- Notices
- Telegrams
- Circulars
- Minutes
- State the reasons why an organization would use written communication instead of verbal communication.
- Written communication provides evidence which may not be there in verbal communication
- Written information can be stored for future reference unlike verbal which cannot be stored and depends on the recipients memory
- It is not prone to distortions and therefore more accurate than verbal communication
- Written communication can be in form of diagrams, illustration and maps which is not possible for verbal communication
- Some written communication such as letters would be cheaper and time saving than verbal communication, for example making long telephone calls.
- Written communication can be used for confidential messages, for example registered mails.
- State the disadvantages of written communication
- Written is not very persuasive or convincing
- There is no personal touch
- It can only be used by literate
- It can be slow where letters take time to reach the recipient
- It takes time to get a feedback from the recipient
- Messages cannot be enhanced by gestures, that is, body language or face expressions
- It can be expense to file all the written communication
- Outline the various means of visual communication
- Charts
- Photographs
- Gestures, which may include signs and symbols
- Slides
- State the advantages and disadvantages of audio-visual of communication
Advantages- Information is more attractive and appealing
- Can reach many people at once
- It can be used even for those who cannot read and write
- Immediate feedback is received from the way the recipient behave
- Can be entertaining
Disadvantages
- Can be misinterpreted, for example if the receiver does not understand the signs or gesture
- Not suitable for passing confidential information
- It is not possible for the recipient to give a feedback
- Gesture and signs are only suitable to those who can understand them
- The initial cost of preparing these forms of communication may be high for the sender
- It may take a lot of time to prepare these forms of communication
- Outline the various service that facilitate communication
- Registered mail, for sending valuable or confidential information.
- Speed post services offered by the post office to send letters parcels using the quickest means possible
- Poste restante, usually used by those without postal addresses
- Business reply service which enables customers and clients to reply to a business without having to pay for postage stamps
- Broadcasting services through various radio stations
- Print media such as the various newspapers, magazines and journals
- Internet services which connect one to the world wide website
- Telephone services
- State the various trends in communication
- Mobile or cell phone use
- Internet which uses inter linked computers to the world wide website
- Fax, which can be used to send written messages very fast
- Information and telephone bureaus where one can make local and international calls
- Move towards a paperless office.
- Transformation of language.
- Highlight the factors to be considered when choosing a means of communication.
- The cost because some are more expensive than others
- Availability of the means
- Reliability or assurance that the message will reach the recipient
- The distance between the sender and the recipient
- The literacy level of both the receiver and the recipient
- The confidential nature of the information being sent
- The urgency of the message
- If there is need for evidence or need for future reference
- The desired impact of the means upon the recipient
- Advice Mary Wakio why she should not use telex to communicate to her friends
- Her friends may be illiterate and may be unable to read the message received
- Her friends may not have a receiving machine and will be unable to get the information
- It can be expensive to use as the sender pays a subscription fee and rental fee while he and the recipient pays for the sent message
- It can be expensive to buy the teleprinters used in receiving and sending information
- Telex may only send written messages but cannot be used to send maps, diagrams and charts
- State circumstances when sign language can be the most appropriate form of communication
- When communicating to someone who has a hearing problem
- If one wishes to pass a secret or coded message
- If both the receiver and the sender are far apart but can see each other
- It can be used in case there is a language barrier
- In an environmental where there is a lot of noise or physical interference to other forms of communication, sign language may be used
- It can be appropriate where both the recipient and the sender understand the signs.
- Explain four factors that have led to the popularity of mobile phones as a means of communication.
Download Communication - Business Studies Form 2 Notes.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students

