Definition
- The product market is the interaction of buyers and sellers to transact business pertaining to a particular commodity.

Types and Features of a Product Market.
Perfect Competition
- A perfect competition is very rare and it has the following characteristics
- Large number of buyers and sellers
- Buyers and sellers are so many that the separate actions of each person of them has no effect on the market. This implies that no single buyer or seller can influence the price of the commodity. - Homogeneity (uniformity) of the product.
- Commodities from different producers are identical in all aspects such that one cannot distinguish them hence there would be no advantage or disadvantage of buying from a particular producer. - Perfect knowledge of the market
- Each buyer and seller has perfect knowledge about the market and therefore no one would affect business at any price other than the equilibrium price. - Freedom of entry or exit
- The buyers and sellers have the freedom to enter and leave the market at will. - Uniformity of buyers and sellers
- All buyers and sellers are identical so there is no benefit of selling to a particular buyer or buying from a particular seller. - No government interference
- The price prevailing in the market is determined strictly by the interplay of demand and supply and there should not be any form of government intervention. - No excess supply or demand
- The sellers are able to sell all that they supply into the market and the buyers are able to buy all what they require hence there are no excess supply and demand. - No transport costs
- In a perfect competition market, it is assumed that the buyers and sellers are located in one area hence there is no need for transportation.
Monopoly
- This is a market situation where there are many buyers but only one seller called a monopolist
Characteristics
- Only one supply
- There is only one supplier for the entire market hence the firm is the industry. - No close substitute
- The commodity supplied does not have close substitutes which may bring competition. - Difficulty to enter
- It is difficulty for other firms to enter into the market - Fixed prices
- Prices are fixed by the supplier - Possibility of price discrimination
- Price discrimination may be possible. This is charging different prices for the same commodity in different markets.
Conditions necessary for price discrimination- Consumers are in different markets making it difficult for one to go to another market.
- The cost of maintaining the separate market is not very high.
- The production of the commodity is in the hands of monopolist hence they are able to control production.
Basis of Market Separation
- Geographical
- Goods may be sold differently in different market. The price charged in local market may be cheaper than foreign market. - Income
- Consumers may be charged differently according to their income level - Time
- A firm may sell the same commodity at a high price during the peak period and lower the price during the off peak period.
Sources of Monopoly Power
- Control of an important input in production.
- A firm may draw its monopoly from having control of an important factor of production such as raw material. - Ownership of production rights
- Monopoly can be created if a firm has the right to production or ownership of a commodity such as patents rights, copyrights and royalties belonging only to the firm. - Internal economies of scale
- The existence of internal economies of scale that enables a firm to reduce its production costs to the level that other firms cannot. This will force these firms out of business leaving creating a monopoly - Size of the market
- The size of a market may be best served by one person or a firm. Addition of more than one firm may lead to all of them incurring losses. - Addition costs by other firms
- If other firms have to incur additional cost to enter into the market then their products may be less attractive due to increased price. This make the local firm to be monopolist. - Where a group of firms combines to act as one
- Some firms may combine/amalgamate or work together for the purpose of controlling the market of their product. They therefore create monopoly. - Restrictive practices
- A firm may include price limit where a firm sells its product at a very low price to drive away competitors, then raising the price after putting the other firms out of business creating monopoly. - Financial factors
- If huge capital is required to enter into the market, it may make it very difficult for other firms to enter into the market making the existing firm to operate as a monopoly.
Monopolistic Competition
- A market structure that combines the aspects of perfect competition and those of a monopoly.
Characteristics
- Many buyers and sellers
- Many buyers and sellers acting independently - Variation in quality
- The products vary in quality or are a close substitutes of each other. - No barriers to entry or exit exists.
- New firms wishing to supply the same commodity are free to do so and existing firms wishing to leave are also free. - Perfect knowledge of the market
- There is perfect knowledge of the market for both sellers and buyers.
Oligopoly
- A market structure with few firms
Types
- Duopoly
- Where the industry is made up of two firms. - Perfect /pure oligopoly
- Where the products are identical - Imperfect/differentiated oligopoly
- Where the markets have products which are close substitutes or are the same but made to appear different.
Characteristics
- There are few firms in the market.
- Interdependence among the firms.
- Has few large sellers and many buyers.
- The firms are interdependent among themselves especially in their output and pricing.
- Non-price competition, firms are in a position to influence the prices. However, they try to avoid price competition for the fear of price war.
- There is barriers to entry of firms due to reasons such as; requirement of large capital, Ownership of production rights, control over crucial raw materials, Restrictive practices etc
- High cost of selling through methods of advertisement due to severe competition.
- Products produced are either homogeneous or differentiated.
- Uncertain demand curve due to the inter-dependence among the firms. Hence the shifting of the demand curve is not definite.
- There is price rigidity i.e. once a price has been arrived at in an oligopolistic market, it tends to remain stable. This feature explains why a firm in oligopolistic market faces two sets of demand curves resulting to a Kinked Demand Curve
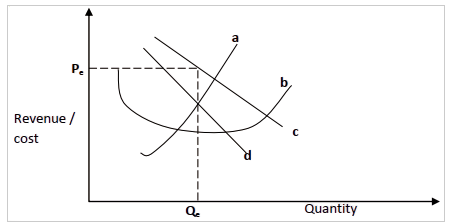
The Kinked Demand Curve
- Once a price has been arrived at in an oligopolistic market it tends to remain stable. It follows that a firm in oligopolistic market faces two sets of demand curves. One curve, for prices above the determined one. Which is fairly gentle. The other curve, for prices below the determined one which is fairly steep. This is illustrated below.
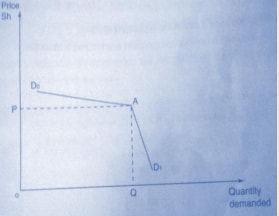
- It can be noted from the above diagram that:
- The price that is generally charged in the industry is P. This is the point at which the price is rigid.
- The demand curve (kinked) is D0AD1 .
- At prices above P the curve is fairly gradual and as such, an increase in price will lead to a big loss in quantities demanded as consumers will shift to suppliers who have not raised their prices.
- At prices below P the curve is fairly steep. A reduction in price will therefore create little additional sales as other firms are likely to reduce their prices to the same level or even lower.

Past KCSE Questions on the Topic
Paper 1
- State four reasons why the government should control activities on monopoly
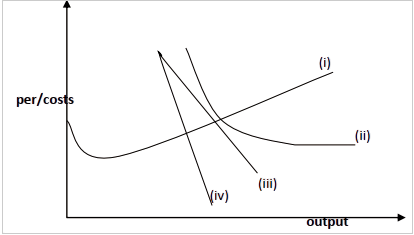
- The following diagram shows how price and output is determined under monopolistic competition.
Name the curves: - The diagram below represents the short-run equilibrium of a firm in monopolistic competition.
Label the curves and show the best output and price on the graph -
State four circumstances under which the phenomenon exhibited above can be experienced in a market structure - State four sources of Monopoly power
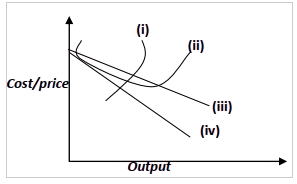
- The diagram below relate to a market structure
- Name the market structure represented in the diagram shown above
- Name the curves marked
- Give four reasons why market research is important to a trader
Download Product Markets - Business Studies Form 3 Notes.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students