Questions
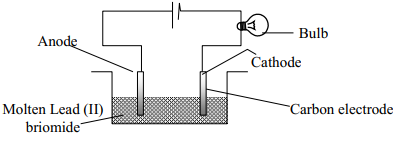
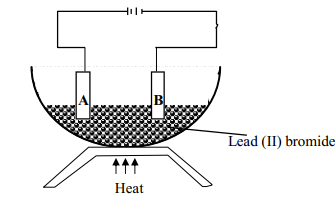
- The set-up was used to electrolyse Lead (II) bromide. Study it and answer the questions that follow;
- Write an ionic equation for the reaction that occurred at the cathode
- State and explain what happened at the anode
- When an electric current was passed through two molten substances E and F in separate voltammeters. The observations recorded below were made:-
Substance Observation Type of structure E Conducts electric current and a gas is formed at one of the electrodes F Conducts an electric current and is not decomposed
Complete the table above -
- Differentiate the following terms :-
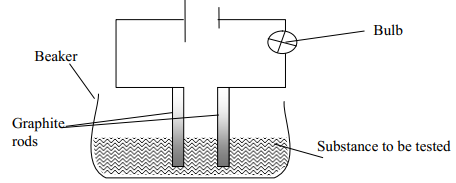
Electrolyte and non-electrolyte - The diagram below is a set-up used to investigate the conductivity of electric current by some aqueous solution. Study it and answer the questions that follow;
- State the observation made on the bulb when each of the following solution were put onto the beaker
- Sugar solution
- Salt solution
- Classify the substances in (i) above as either electrolyte or non-electrolyte
- State the observation made on the bulb when each of the following solution were put onto the beaker
- If in the above set-up of apparatus, the substance to be tested is Lead II Bromide, what modification should be included in the set-up?
- Write an Ionic equation at the electrodes and state the observation:-
- Differentiate the following terms :-
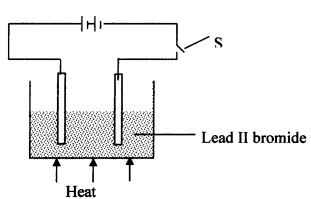
- The diagram below shows the set up used to investigate the effect of an electric current on molten lead (II) bromide
- Explain what happens to the lead II bromide during electrolysis
- Why is it important to carry out the experiment in a fume chamber?
-
- Define the following terms:
- Crystallization
- Salting out as used in soap making
- Starting with barium carbonate solid, dilute sulphuric acid and dilute nitric acid, describe how you would prepare dry barium sulphate solid
- Study the scheme below and answer the questions which follow:
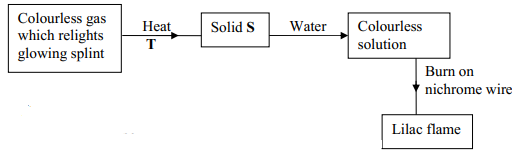
- Identify ;
- The cation present in solid S
- The anion in solid S
- Write an equation to show how solid S is heated in process T
- Identify ;
- Copper II chloride solution dissolves in excess ammonia solution to form a deep blue solution. Give the ion responsible for the deep blue solution
- A solution of hydrogen chloride is an electrolyte but a solution of hydrogen chloride in methylbenzene in a non-electrolyte. Explain
- Define the following terms:
-
- State Faraday’s first law of electrolysis
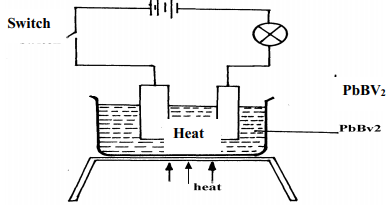
- The diagram below shows a set-up used for the electrolysis of molten Lead bromide:-
State the observations that would be made at the anode and cathode as the electrolysis progressed
-
-
- Describe how you would prepare pure crystals of lead II nitrate in the laboratory from lead II oxide
- Write an equation for the reaction that takes place in (a)(i) above
-
- State what happens when lead II nitrate is strongly heated
- Write an equation for the reaction in b(i) above
-
- State what is observed when ammonia solution is gradually added to a solution of lead II nitrate until the alkali is in excess
- Write an ionic equation for the reaction that takes place in (i) above
-
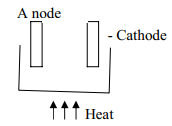
- The diagram show an experiment for investigating electrical conduction in lead (II) fluoride.
Study it and answer the questions that follow: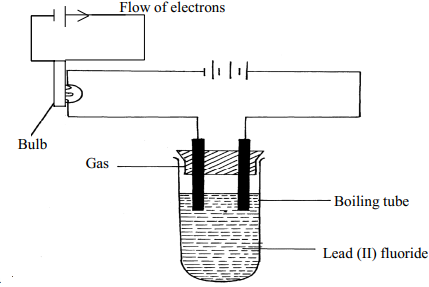
- On the diagram
- Label the anode and the cathode
- Show the direction of movement of electrons
- Complete the diagram by indicating the condition that is missing but must be present for electrical conduction to take place.
- Why is it necessary to leave a gap between the cork and the boiling tube?
- State the observations that are expected at the electrodes during electrical conduction and at the experiment
- Write equations for the reactions that take place at the electrodes
- Why should this experiment be carried out in a fume chamber?
- On the diagram
- The table below shows the electrical conductivity of substance A, B and C
Substance Solid state Molten state Aqueous solution A Conducts Conducts Not soluble B Doesn’t conduct Conducts Conducts C Doesn’t conduct Doesn’t conduct Not soluble - Which one of the substance is likely to be plastic?
- Explain why the substance you have given in (a) above behaves in the way it does
- Which of the substances is likely to be sodium chloride? Explain
- Give the type of structure and bonding that is present in substance A
- Study the diagram below and use it to answer the questions that follow:-
- Identify electrodes A and B
- Name the product formed at the anode
- Write the electrode half equation of reaction at electrode A
- Explain the differences in electrical conductivity between melted sodium chloride and liquid mercury
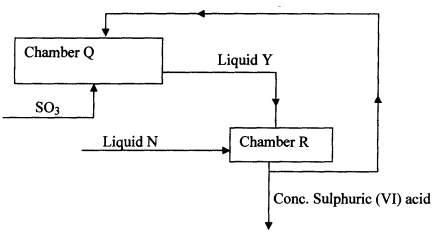
- Below is part of a flow diagram for the contact process:
- Name :
- Liquid Y ……………………………………………………….
- Liquid N………………………………………………………….
- Write the equation for the reaction taking place in;
- Chamber Q
- Chamber R
- Name :
- In an experiment to investigate the conductivity of substances, a student used the set-up shown below.
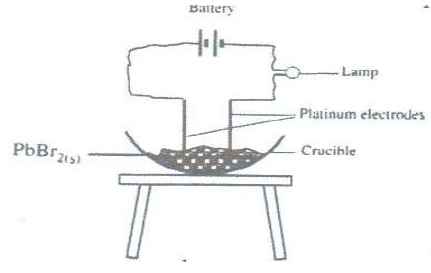
The student noted that the bulb did not light.- What had been omitted in the set up.
- Explain why the bulb lights when the omission is corrected
Answers
-
- Pb2+(l) + 2e- → Pb(s)
- - There is liberation of brown vapour
- The brown vapour is due to the formation of bromine molecule
- E – Giant ionic structure
F – Giant metallic structure -
- - Electrolytes are melts or acqueous solutions which allow electric current to pass through them and are decomposed by it while non-electrolyte are melts or acqueous solution which do not conduct electric current
- Electrolytes contain mobrite ions while non-electrolyte contains molecules. -
-
- bulb did not light when sugar solution was put into the beaker
- bulb light when slat solution was put into the beaker
- Non- electrolyte - I
Electrolyte - II
-
- heating
- Cathode
Pb2+(aq) + 2e- → Pb(s) grey deposit metal is observed
Anode
2Br-(aq) → Br2(g) + 2e- A brown yellow gas is evolved
- - Electrolytes are melts or acqueous solutions which allow electric current to pass through them and are decomposed by it while non-electrolyte are melts or acqueous solution which do not conduct electric current
-
- Decomposes to Pb2+ and ions which are later reduced to Pb and are oxidized to Br
- Br2(g) produced is poisonous
-
-
- Crystallization – The solidifying of a salt form a saturated solution on cooling.
- Addition of sodium chloride to soap-glycerol mixture in order to precipitate the soap.
- – to the nitric acid in a beaker, add barium carbonate solid as you stir until effervescence stops.
- Filter to obtain the filtrate
- Add dilute nitric acid to the filtrate and filter to obtain the residue
- Dry the residue under the sun or between filter papers. -
-
- K+
- NO3-
- 2KNO3(s) → 2KNO2(s) + O2(g)
-
- [Cu(NH3)4(OH2)2]2+.
- In water HCl ionizes into mobile into mobile ions which conduct because water is polar while methyl is non-polar hence HCl does not ionize hence does not conduct electricity
-
-
- Faraday first law of electrolysis.
- The mass of a substance dissolved on liberated in electrolysis is proportional to the quantity of electricity which passes through the electrolyte. - (anode) – Brown/fumes of a gas were evolved
(cathode) – grey beads.
- Faraday first law of electrolysis.
-
-
- - Place elilute nitric acid (HNO3) in a beaker and warm.
- Add lead II oxide until no more dissolves
- Filter the un reacted lead II oxide
- Heat to evapourae & leave to crystallize. - PbO (s)+ 2HNO3(aq) → Pb(NO3)2 (aq) + H2O (l)
- - Place elilute nitric acid (HNO3) in a beaker and warm.
-
- - Crystals crack and split because of the gas accumulating inside
- Brown gas of Nitrogen IV oxide.
- Solid resolute, lead II oxide which is orange when hot is yellow when cold. - 2 Pb(NO3)2(s) → 2PbO (s) + O2(g) + 4NO2(g)
- - Crystals crack and split because of the gas accumulating inside
-
- white precipitate which is insoluble in excess ammonia
- Pb2+(aq) + 2OH-(aq) → Pb(OH)2(s)
-
-
-
- To let the gas produce out, so that it does not explode due to pressure.
- At the anode a pale yellow gas is observed
Cathode – grey solid is formed. - Anode: 2F-(aq) → F2(g) +2e- Cathode: Pb2+(aq) + 2e- → Pb (s)
- the gas produced is poisonous.
-
-
- C
- Because it does not conduct electricity in solid state and not soluble.
- B because it does not conducts electricity in solid state but in molten or aqueous solution it conducts.
- Metallic bond.
-
- A is Anode √1
B is cathode. √1 - Bromine gas. √1
- 2Br-(l) - 2e- → Br2(g) √1
- A is Anode √1
- B and D or F2 and Ne
-
-
- olcum
- Water
-
- SO3 (g) + H2SO4(l) →H2S2O7(l)
- H2S2O7(l) + H2O(l) → 2H2SO4(l)
-
-
- Source of heat. ✓1
- The solid PbBr2 melts to form Pb2+✓½ and 2 Br-✓½ that conduct electric current in the circuit hence the bulb lights/Pb2+ and 2Br- carry the current. ✓1
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download Effect of an Electric Current on Substances Questions and Answers - Chemistry Form 2 Topical Revision.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students