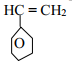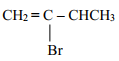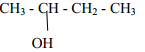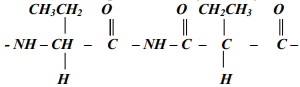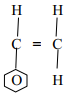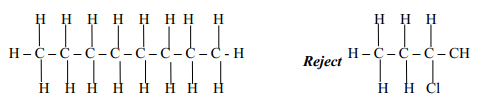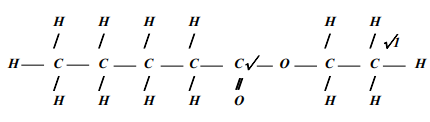Questions
- A student mixed equal volumes of Ethanol and butanoic acid. He added a few drops of concentrated Sulphuric (VI) acid and warmed the mixture
- Name and write the formula of the main products
Name………………………………….
Formula…………………………………….. - Which homologous series does the product named in (i) above belong?
- Name and write the formula of the main products
- The structure of the monomer phenyl ethene is given below:-
- Give the structure of the polymer formed when four of the monomers are added together
- Give the name of the polymer formed in (a) above
- Explain the environmental effects of burning plastics in air as a disposal method
- Write chemical equation to represent the effect of heat on ammonium carbonate
- Sodium octadecanoate has a chemical formula CH3(CH2)6COO-Na+, which is used as soap.
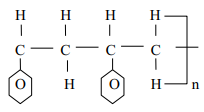
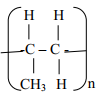
Explain why a lot of soap is needed when washing with hard water - A natural polymer is made up of the monomer:
- Write the structural formula of the repeat unit of the polymer
- When 5.0 x 10-5 moles of the polymer were hydrolysed, 0.515g of the monomer were obtained.
Determine the number of the monomer molecules in this polymer.
(C = 12; H = 1; N = 14; O =16)
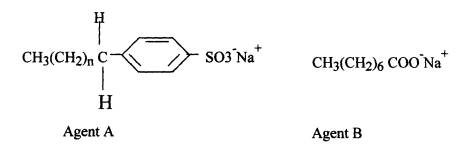
- The formula below represents active ingredients of two cleansing agents A and B
Which one of the cleansing agents would be suitable to be used in water containing magnesium hydrogen carbonate? Explain - Study the polymer below and use it to answer the questions that follow:
- Give the name of the monomer and draw its structures
- Identify the type of polymerization that takes place
- State one advantage of synthetic polymers
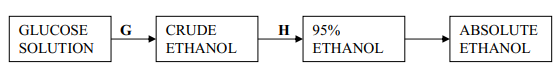
- Ethanol and Pentane are miscible liquids. Explain how water can be used to separate a mixture of ethanol and pentane
-
- What is absolute ethanol?
- State two conditions required for process G to take place efficiently
-
- The table below shows the volume of oxygen obtained per unit time when hydrogen peroxide was decomposed in the presence of manganese (IV) Oxide. Use it to answer the questions that follow:-
Time in seconds Volume of Oxygen evolved
(cm3)0
30
60
90
120
150
180
210
240
270
3000
10
19
27
34
38
43
45
45
45
45- Plot a graph of volume of oxygen gas against time
- Determine the rate of reaction at time 156 seconds
- From the graph, find the time taken for 18cm3 of oxygen to be produced
- Write a chemical equation to show how hydrogen peroxide decomposes in the presence of manganese (IV) Oxide
- The diagram below shows how a Le’clanche (Dry cell) appears:-
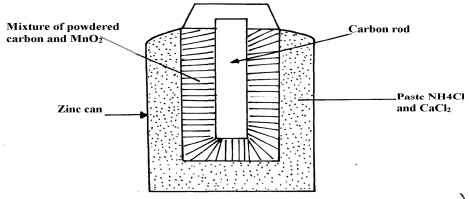
- What is the function of MnO2 in the cell above?
- Write the equation of a reaction that occurs at the cathode
- Calculate the mass of Zinc that is consumed when a current of 0.1 amperes flows through the above cell for 30minutes (1F =96500c Zn =65)
- The table below shows the volume of oxygen obtained per unit time when hydrogen peroxide was decomposed in the presence of manganese (IV) Oxide. Use it to answer the questions that follow:-
-
- Give the IUPAC names of the following compounds:
- CH3COOCH2CH3
-
- The structure below shows some reactions starting with ethanol. Study it and answer the questions that follow:
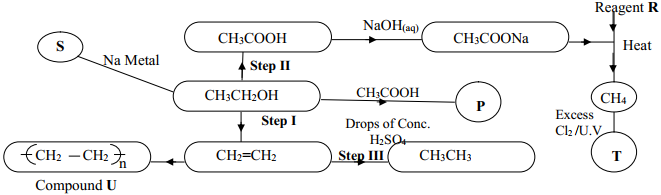
- Write the formula of the organic compounds P and S
- Name the type of reaction, the reagent(s) and condition for the reactions in the following steps :-
- Step I
- Step II
- Step III
- Name reagent R ……………………………………………………………
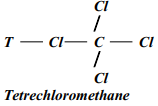
- Draw the structural formula of T and give its name
-
- Name compound U………………………………………………………..
- If the relative molecular mass of U is 42000, determine the value of n (C=12, H=1)
- State why C2H4 burns with a more smoky flame than C2H6
- Give the IUPAC names of the following compounds:
-
- State two factors that affect the properties of a polymer
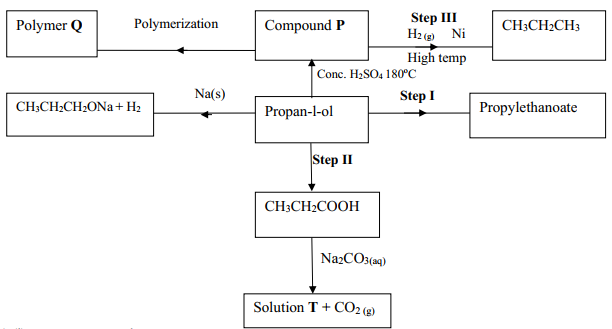
- Name the compound with the formula below :
CH3CH2CH2ONa - Study the scheme below and use it to answer the questions that follow:-
- Name the following compounds:-
- Product T …………………………
- K ………
- State one common physical property of substance G
- State the type of reaction that occurred in step J
- Give one use of substance K
- Write an equation for the combustion of compound P
- Explain how compounds CH3CH2COOH and CH3CH2CH2OH can be distinguished chemically
- If a polymer K has relative molecular mass of 12,600, calculate the value of n (H=1 C =12)
- Name the following compounds:-
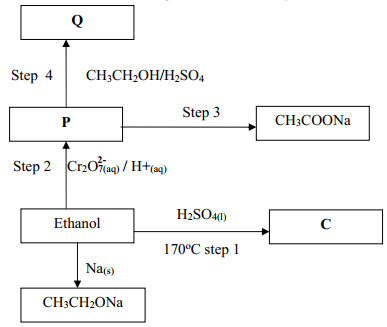
- Study the scheme given below and answer the questions that follow:-
-
- Name compound P ……………………………………………………………………
- Write an equation for the reaction between CH3CH2COOH and Na2CO3
- State one use of polymer Q
- Name one oxidising agent that can be used in step II …………………………………..
- A sample of polymer Q is found to have a molecular mass of 4200. Determine the number of monomers in the polymer (H = 1, C = 12)
- Name the type of reaction in step I …………………………………………………………..
- State one industrial application of step III
- State how burning can be used to distinguish between propane and propyne. Explain your answer
- 1000cm3 of ethene (C2H4) burnt in oxygen to produce Carbon (II) Oxide and water vapour.
Calculate the minimum volume of air needed for the complete combustion of ethene
(Air contains 20% by volume of oxygen)
-
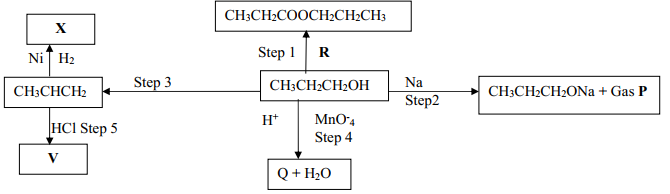
- Study the schematic diagram below and answer the questions that follow:-
- Identify the following:
Substance Q ..............................................................................................................
Substance R...............................................................................................................
Gas P.......................................................................................................................... - Name:
Step 1.................................................................................................
Step 4................................................................................................. - Draw the structural formula of the major product of step 5
- State the condition and reagent in step 3
- Identify the following:
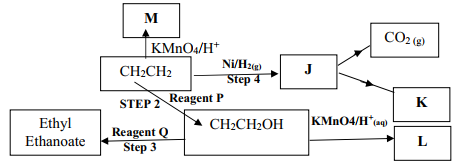
- Study the flow chart below and answer the questions that follow
- Name the following organic compounds:
M……………………………………………………………..……..
L………………………………………………………………….. - Name the process in step:
Step 2 ………………………………………………………….….
Step 4 ………………………………………………………….… - Identify the reagent P and Q
- Write an equation for the reaction between CH3CH2CH2OH and sodium
- Name the following organic compounds:
- Give the names of the following compounds:
- CH3CH2CH2CH2OH ……………………………………………………………………
- CH3CH2COOH …………………………………………………………………
- CH3C – O – CH2CH3 ……………………………………………………………………
- Study the scheme given below and answer the questions that follow;
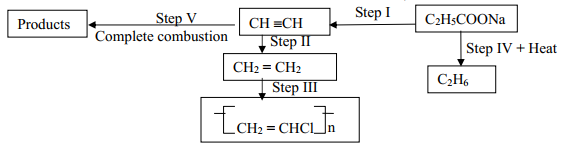
- Name the reagents used in:
Step I: ………………………………………………………………………
Step II ……………………………………………………………………
Step III ……………………………………………………………………… - Write an equation to show products formed for the complete combustion of CH = CH
- Explain one disadvantage of continued use of items made form the compound formed in step III
- Name the reagents used in:
- A hydrated salt has the following composition by mass. Iron 20.2%, oxygen 23.0%, sulphur 11.5%, water 45.3%
- Determine the formula of the hydrated salt (Fe=56, S=32, O=16, H=11)
- 6.95g of the hydrated salt in c(i) above were dissolved in distilled water and the total volume made to 250cm3 of solution. Calculate the concentration of the resulting salt solution in moles per litre. (Given that the molecula mass of the salt is 278)
- Give the IUPAC name for each of the following organic compounds;
-
-
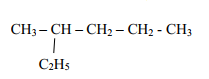
- CH3COOCH2CH2CH3
-
- The structure below represents a cleansing agent.
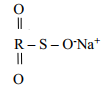
- State the type of cleansing agent represented above
- State one advantage and one disadvantage of using the above cleansing agent.
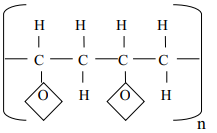
- The structure below shows part of polymer .Use it to answer the questions that follow.
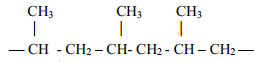
- Derive the structure of the monomer
- Name the type of polymerization represented above
- The flow chart below represents a series of reactions starting with ethanoic acid:-
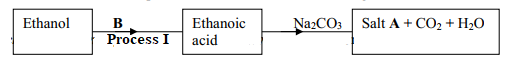
- Identify substances A and B
- Name the process I
-
- Write an equation showing how ammonium nitrate may be prepared starting with ammonia gas
- Calculate the maximum mass of ammonium nitrate that can be prepared using 5.3kg of ammonia (H=1, N=14, O=16)
-
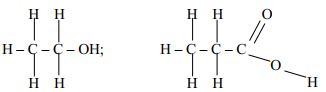
- What is meant by the term, esterification?
- Draw the structural formulae of two compounds that may be reacted to form ethylpropanoate
-
- Draw the structure of pentanoic acid
- Draw the structure and give the name of the organic compound formed when ethanol reacts with pentanoic acid in presence of concentrated sulphuric acid
- The scheme below shows some reactions starting with ethanol. Study it and answer the questions that follow:-
- Name and draw the structure of substance Q
- Give the names of the reactions that take place in steps 2 and 4
- What reagent is necessary for reaction that takes place in step 3
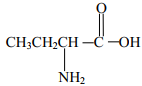
- Substances A and B are represented by the formulae ROH and RCOOH respectively.
They belong to two different homologous series of organic compounds. If both A and B react with potassium metal:- Name the common product produced by both
- State the observation made when each of the samples A and B are reacted with sodium hydrogen carbonate
- A
- B
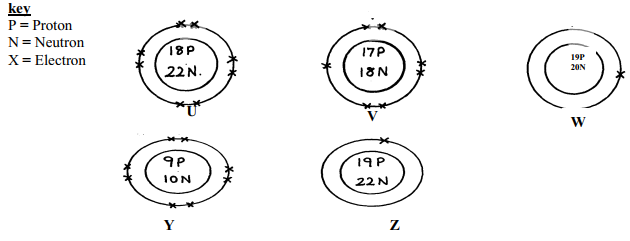
- Below are structures of particles. Use it to answer questions that follow. In each case only electrons in the outermost energy level are shown
Identify the particle which is an anion - Plastics and rubber are extensively used to cover electrical wires.
- What term is used to describe plastic and rubbers used in this way?
- Explain why plastics and rubbers are used this way
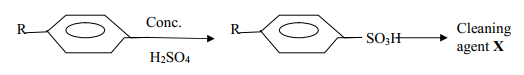
- The scheme below represents the manufacture of a cleaning agent X
- Draw the structure of X and state the type of cleaning agent to which X belong
- State one disadvantage of using X as a cleaning agent
- Y grams of a radioactive isotope take 120 days to decay to 3.5grams. The half-life period of the isotope is 20 days
- Find the initial mass of the isotope
- Give one application of radioactivity in agriculture
- The structure below represents a polymer. Study and answer the questions that follow:-
- Name the polymer above..................................................................................
- Determine the value of n if giant molecule had relative molecular mass of 4956
- RCOO-Na+ and RCH2OSO3-Na+ are two types of cleansing agents;
- Name the class of cleansing agents to which each belongs
- Which one of these agents in (i) above would be more suitable when washing with water from the Indian ocean. Explain
- Both sulphur (IV) oxide and chlorine are used bleaching agents. Explain the difference in their bleaching properties
- The formula given below represents a portion of a polymer
- Give the name of the polymer
- Draw the structure of the monomer used to manufacture the polymer
Answers
-
- Ethylbutanoate
- CH3CH2CH2
- Esters
-
-
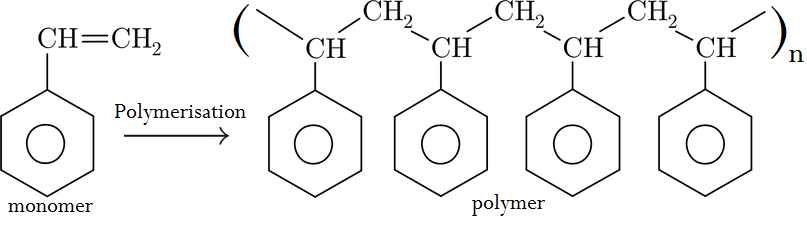
- Polypheny/ ethane
-
- Plastics may contain chlorine or fluorine compounds apart from hydrogen and carbon when burnt, fluorine and chlorine compounds are released into the air destroying Ozone layer
- (NH4)2CO3(s) → 2NH3(g) + CO2(g) + H2O(l)
- The first amount of soap precipitates Ca2+(aq) and Mg2+(aq) ions and soften water.
Then additional soap dissolves oil from the fabric. -
-
- .00005mol. P = 0.515 g of monomer.
= 1.0 mole of poly mer = 1 × 0.515 = 10300 g
0.0005
RFM ( C4H9NO2)n = 48 + 9 + 32 = 103
= (C4H9NO2) = 10300
103n = 10300
∴ n = 100 molecules
-
- Agent A – magnesium salt formed is soluble hence doesn’t form scum
-
- Styrene/Phenylethene
- Addition polymerization
- – can be made into different shapes easily
- are cheaper
- are not corroded by acids, alkalis or air
- are stronger and long lasting
- are water-proof
(any 1 correct)
- Styrene/Phenylethene
- – Add water to the mixture and shake where ethanol dissolves in water while pentane is immiscible.
- Transfer the mixture in a separating funnel and allow it to settle when pentane floats on top of water-ethanol mixture.
- Turn on the tap to collect water-ethanol mixture while pentane remains in the separating funnel.
- Separate ethanol from water by fractional distillation based on the differences in boiling points. -
- Is 100% ethanol/is pure ethanol without water in it
- 30oC and yeast
-
-
- R = Δv
Δ t
= 43 – 40.5
180 -150
= 25
30
= 0.0833cm3/s - 57seconds
- 2H2O2(l) → 2H2O(l) + O2(g)
-
- To oxidize H2 produced to water
- Z
- Q = 1t
= 0.1 x 30 x 60
= 180C
96500c = 1F
180c = ?
180 x 1
96500
= 0.001865F
Zn(s) → Zn2+(aq) + 2e-
2F = 65g
0.001865F = 0.001865 x 65
2
= 0.0606g of Zn was consumed
-
-
-
- Ethylethanoate.
- 2 – bromobut – 1 – ene
-
- P – CH3COOCH2 CH3
S – CH3CHONa -
- Step I -Type – dehydration.
Reagent – Concentrated sulphur acid. - Step II- Type – Oxidation
Reagent – acidified potassium magnate VII/ Potassium dichromate (VI) - Step III- Type – Hydrogenation
Reagent – Hydrogen
- Step I -Type – dehydration.
- R – Soda lime
-
- U – Polythene/Polyethene
- 28n = 42000
n = 42000 = 1500
28
- P – CH3COOCH2 CH3
- – It is unsaturated.
-
-
- - The length of the chain
- Intermolecular forces
- Cross linking of the molecules (Any two correct = 2 marks) - Sodium propoxide
-
-
- – T is ethane
- – K is polypropene
- has a sweet smell
- Neutralization
- - Used to make ropes √ 1 mark
- Used to make crates of bottles
- Used as surface for all weather football and hockey pitches (Any correct use) - CH3CH2CH3 + SO2 → 3CO2 + 4H2O
(N.B ignore state symbols) - React a small sample of each of the two substances with sodium carbonate separately. Bubbles// efferrescence are observed with CH3CH2COOH and no reaction with CH3CH2CH2OH
- RMM of monomer = 42 √ ½
42n = 12600
N = 12600 = 300√ ½
42
-
- - The length of the chain
-
-
- Propene √1
- 2CH3CH2COOH + Na2CO3√½ → 2CH3CH2COONa + CO2 + H2O
- Making packing materials √1
- KMnO4√½ /K2CrO7
-
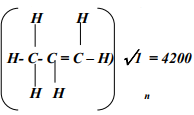
42n√ = 4200
n = 4200∕42
= 100 √ - Esterification √1
- Conversion of oils to fats. √1
- Propane burns with a clear falme√1 while propyne burns with a sooty flame √1because propyne has a higher √1 C : H ration than propane.
- C2H4(g) + 3O2(g) → 2CO2(g) + 2H2O(l) √1
1 Vol. 3 vol
1 Vol. = 1000 cm3 √½
Vol of O2 required = 3 x 1000 cm3 = 3000 cm3 √½
Vol of air required = 100 x 3000 cm3
20
= 15,000 cm3√½
-
-
-
- Q - CH3CH2COOH (accept name (propanoic acid)
R – CH3CH2COOH (Propanoic acid)
P- Hydrogen - Step I Esterification
Step 4 – Oxidation -
- Condition – 180 – 250oC
reagent – Conc. H2SO4
- Q - CH3CH2COOH (accept name (propanoic acid)
-
-
- M: Ethan – 1, 2- diol
L: Ethanoic acid - Step 2: Polymerisation
Step 4: Hydrogenation - Concentrated sulphuric acid
Ethanoic acid
- M: Ethan – 1, 2- diol
-
- Butan – 1 – ol// 1- Butanol// n-Butanol
- Propanoic acid
- Ethylethanoate
-
- Step I: Hydrogen
Step II: Hydrogen chloride gas// HCl
Step III: Sodium hydroxide/ NaOH/ Sodalime - 2C2H2(g) + 5O2(g) → 4CO2(g) + 2H2O(g)
- Environmental pollutant
It is not biodegradable/ Not decomposed by bacterial
- Step I: Hydrogen
-
- Fe S O H2O
20.2/56 11.5/32 23.0/16 45.3/18
0.36/0.36 0.36/0.36 1.44/0.36 2.52/0.36
1 1 4 7
Empirical formula: FeSO4.7H2O - 6.95g = 6.95/278 = 0.025
∴ 0.05 moles in 250cm3 = 0.025 x 1000/250 = 0.1
Concentration = 6.95/278 x 1000/250 = 0.1
- Fe S O H2O
-
- Butan – 2 – ol √ ½
- 4 – methylhex – 2- ene √
- Propyl ethnoate √
-
- Soap less detergent √
- Non- biodegradable resulting in pollution √
-
- Addition
-
- A – Sodium ethanoate
B – Acidified KMnO4 or K2Cr2O7 - Oxidation
- A – Sodium ethanoate
-
- NH3(g) + HNO3(aq) → NH4NO3(s)
- 17 kg ammonia = 80kg NH4NO3 (½)
∴5.3kg =?
80 x 5.3 = 24.94Kg (1½)
17
-
- A reaction between an ethanol and alkanoic acid to form ester;
-
-
-
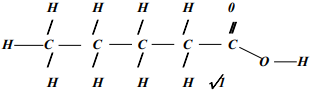
-
-
- Ethylpentanoate . √1
-
-
-
- ethylethanoate√ ½
CH3 - H2C- O-C-CH3 √ ½ - step 2: oxidation √ ½
step 4: esterification √ ½ - sodium hydroxide ,or NaoH√1
- ethylethanoate√ ½
-
- Hydrogen. √1
-
- A No effervescence takes place. √½
- B There is effervescence √½ and the gas produced turns lime water into white precipitate.√½
-
- Y √1
- Z and W √1 have same atomic number but different mass number. √1
-
- Insulators
- Are non-conductor since they lack delocalised electrons
-
- Soapless detergent
- Non-biodegradable
-
-
- No. of half –lifes (n) = 120 = 6
20
Y x (½)6 = 3.5
Y = 3.5 x 26
Y = 224g
(all steps for equation )
OR: - – To study the rate of absorption of fertilizer by plants using radioactive phosphorous
- Tracing chemical and physiological processes such as photosynthesis
- Sterilizing equipment (1ny one )
- No. of half –lifes (n) = 120 = 6
-
- Polypropene
- (H2C= CH – CH3)n = 4956
(12 x 3) + (6x1) = 36 + 6 = 42 (molecular mass of 1 unit)
no. of units = 42n = 495
42n = 4956
42n = 4956
42 42
n = 118
-
- RCOONa+ Soapy detergent
R CH2OSO3-Na+ soap less detergent - RCH2OSO3 -Na+ does not form scum. Its calcium and magnesium salts are soluble
- Chlorine bleaches by oxidation
SO2 bleaches by reduction
- RCOONa+ Soapy detergent
-
- Polyphenylethene
-
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download Organic Chemistry 2 Questions and Answers - Chemistry Form 4 Topical Revision.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students