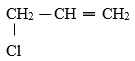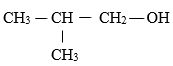INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
- Answer all the questions in the spaces provided.
- Mathematical tables and silent electronic calculators many be used.
- All working must be clearly shown where necessary.
FOR EXAMINER’SUSE ONLY
|
QUESTION |
MAXIMUM SCORE |
CANDIDATE’S SCORE |
|
1 |
10 |
|
|
2 |
14 |
|
|
3 |
12 |
|
|
4 |
12 |
|
|
5 |
11 |
|
|
6 |
11 |
|
|
7 |
10 |
|
|
Total score |
80 |
|

QUESTIONS
-
- The set up below was used to collect gas F, produced by the reaction between water and calcium metal.
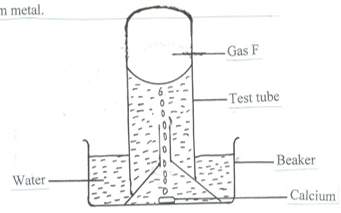
- Name gas F ( 1 mark )
- At the end of the experiment, the solution in the beaker was found to be a weak base. Explain. ( 2 marks )
- Give one laboratory use of the solution formed in the beaker. ( 1 mark)
- The scheme below shows some reactions starting with calcium oxide. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
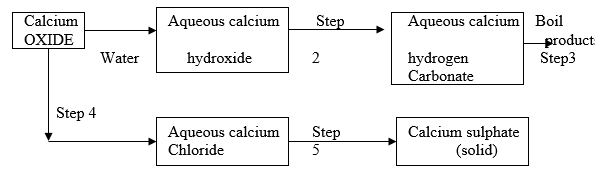
- Name the reagents used in steps 2 and 4.
Step 2 ________________ ( 1 mark)
Step 4 ________________ ( 1 mark) - Write an equation for the reaction in step 3. ( 1 mark)
- Describe how a pure solid sample of anhydrous calcium sulphate is obtained in step 5. (3 marks )
- Name the reagents used in steps 2 and 4.
- The set up below was used to collect gas F, produced by the reaction between water and calcium metal.
- The diagram below shows part of the periodic table. The letters used in it do not represent the actual symbols of the elements. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
A
-------------------
B
--------------------
C
D
E
-------------------
-------------------
- Compare the:
- Reactivity of elements A and B. ( 2 marks )
- Atomic radii of elements C and D. ( 2 marks )
- What name is given to the elements in the same group as element E. ( 1 mark)
- Write down the formula of the compound formed when D reacts with excess oxygen. (1 mark)
- An element F is found just above element D in the periodic table. Write down the electronic configuration of element F. (1 mark)
- A sample of the chloride of C was dissolved in distilled water. Both red and blue litmus papers were dipped into this solution. State and explain what was observed.(2 marks )
- 2g of element B react with 0.6 dm3 of oxygen at r.t.p. From these results, calculate the relative atomic mass of B. (Molar gas volume = 24.0dm3 at r.t.p ) ( 3 marks)
- Helium is used in filling weather study balloon. Name another gas which is used for this purpose and explain which of the two is better suited for use for this purpose. (2 marks )
- Compare the:
-
- Give the systematic names of the compounds with the structures below. ( 2 marks )
- Describe a chemical test that can be used to distinguish between ethanol and ethanoic acid. (2 marks )
- Study the scheme below and answer the questions that follow.
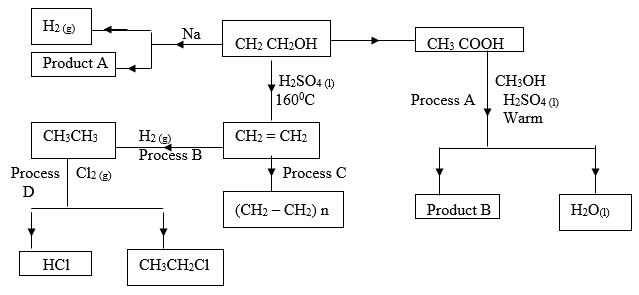
- Name product A ___________________________________ (1 mark)
- State the industrial application of process B. ( 1 mark)
- Write down the equation for the reaction that takes place in process A. (1 mark)
- Explain why high pressure is necessary when carrying out process C. ( 1 mark)
- Give the condition necessary for process D to take place. (1 mark)
- When a hydrocarbon is burnt in excess oxygen 3.3g of carbon (IV) oxide and 1.8g of Water are produced. Find the empirical formula of the hydrocarbon. (3 marks)
- Give the systematic names of the compounds with the structures below. ( 2 marks )
- Use the standard electrode potentials for the elements RST and U given below to answer the questions that follow. The letters do not represent the actual symbols of the elements.
Eθ volts
R+ (aq) + 2e (s) -0.76
S2+ (aq) + 2e S (s) -0.44
T2 (g) + 2e 2T- (aq) + 0.54
U4+ (aq) + e 3+ (aq) +1.61- Which element is the strongest reducing agent? Explain. ( 1mark)
-
- Draw a labelled diagram of the electrochemical cell that would be formed when half cells of elements R and S are combined. On the diagram show the direction of flow of electrons. (3 marks)
- Calculate the e.m.f of the cell formed in b (i) above. ( 2 mark)
- In an experiment to electroplate iron with silver, a current of 0.5 amperes was passed through a solution of silver nitrate for one hour.
- Give two reasons why it is necessary to electroplate iron with silver. (2 marks)
- Calculate the mass of silver that can be deposited on iron (Ag = 108, I faraday = 96500C) (3 marks)
-
- Briefly explain how nitrogen gas is obtained industrially from air. (3 marks)
- Study the flow diagram below and answer the questions that follows.
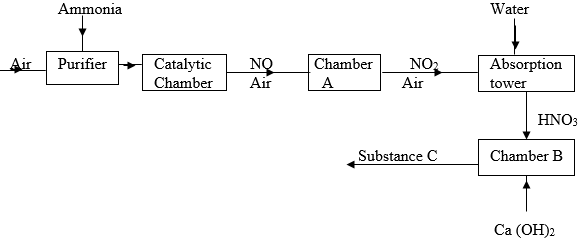
- Name the catalytic used in the catalytic chamber. (1 mark)
- Name the process that takes place in chamber A. ( 1 mark)
- Write down the overall equation of the reaction that takes place in the absorption tower.(1 mark)
- State one use of substance C. (1 mark)
- Write down the equation for the reaction that takes place when silver nitrate is heated. (1 mark)
- Urea (NH2 CONH2) is commonly applied to the soil as a fertilizer. Calculate the Percentage of nitrogen by mass in urea. (2 marks)
(N = 14, H = 1, C = 12, O = 16) - Name the process through which substance C is formed. (1 mark)
- Aluminium is extracted using the electrolytic cell represented by the diagram below.
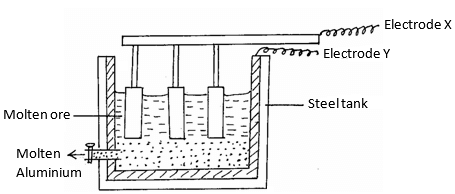
- Why is aluminium extracted by electrolytic method? (1mk)
- Name the electrodes labeled.
X (1mk)
Y (1mk) - The chief ore from which aluminium is extracted is bauxite.
- Name two main impurities present in bauxite. (2mks)
- Aluminium oxide is the main component in bauxite with a melting point of 201 but electrolysis of molten aluminium oxide is carried out at 800°C. Explain how this is achieved.(2mks)
- Write the equations for the reaction taking place at the anode. (1mk)
- One of the electrodes is replaced periodically. Which one and why? (2mks)
- Duralumin (an alloy of copper, aluminium and magnesium) is preferred to pure aluminium in the construction of aeroplane bodies. Give one property of duralumin that is considered.(1mk)
-
- In an experiment to study the rate of reaction a 10cm length of magnesium ribbon was reacted with 50cm3 of 1M hydrochloric acid. The table below gives the data that was collected.
Time(sec)
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
Volume of hydrogen (cm3)
0
60
90
105
112
116
118
120
120
120
- Plot a graph of volume of hydrogen against time. (3 marks )
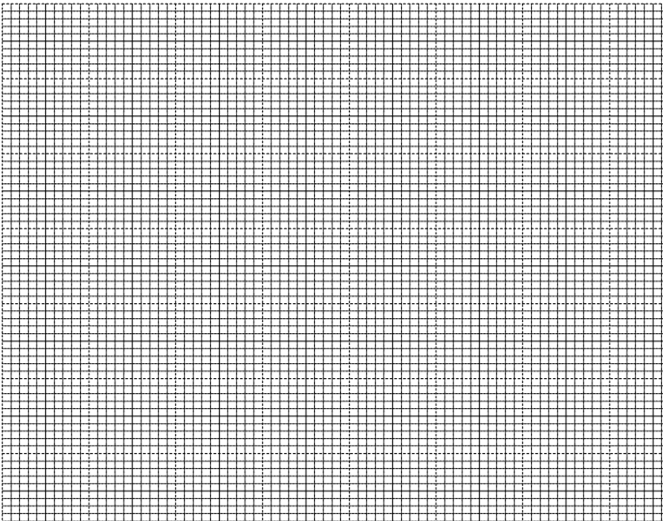
- From the graph find:
- the volume of hydrogen that had been produced when time was 35 seconds. (1 mark)
- The rate of reaction when time is 45 seconds. (2 marks)
- Sketch on the diagram the curve you would obtain if the reaction is repeated Using 0.5M HCl. Label this curve 0.5M HCl. (1 mark)
- Plot a graph of volume of hydrogen against time. (3 marks )
- Study the equilibrium equation below and answer the questions below it.
A2 (g) + B2 (g) ⇌ 2AB (g) ΔH = + 7 kJmpol-1- Explain the effect of changing pressure on the equilibrium above. (2 marks)
- What is the effect of raising the temperature of the equilibrium mixture? (1 mark)
- In an experiment to study the rate of reaction a 10cm length of magnesium ribbon was reacted with 50cm3 of 1M hydrochloric acid. The table below gives the data that was collected.

MARKING SCHEME
-
-
- Hydrogen gas / H2 √1
- Calcium hydroxide √1 formed is slightly √1 soluble in water // Only a few OH- ions are produced in solution.
-
- It is used for testing for presence of carbon (IV) oxide √1
- Used in preparation of ammonia.
- Used in preparation of calcium oxide.
Any one correct
-
- Step 2 – Excess carbon (IV) oxide √1 CO2
Step 4 – Dilute hydrochloric acid √1, HCl (aq)
Accept formula - Ca(HCO3)2 (aq) → CaCO3 (s) + CO2 (g) + H2O (l) √1
- Add an aqueous solution of sulphuric (VI) acid √ ½ / add aqueous sodium sulphate / potassium sulphate √ ½ ( soluble sulphate ) filter √ ½ to obtain calcium sulphate as residue. Rinse √1 the residue with distilled water to remove traces of the filtrate. Heat √ ½ the residue to dryness.
- Step 2 – Excess carbon (IV) oxide √1 CO2
-
-
-
- B is more √1 reactive than A. The valence electrons in B are further from the nucleus than those of A. They therefore experience less nuclear attraction √1 they are lost more readily.
- Atomic size of D is smaller √1 than that of C.
D has more nuclear charge than C hence stronger nuclear attraction √1 to the outermost energy level electrons.
- Halogens √1
- D2O5 √1 penalise fully for writing or including D2O3
- F : 2.5
- Red litmus paper remains red
- While blue litmus paper turned red √ 1 Both correct
Chloride of C hydrolyses in water to form an acidic solution (1mk)
- 2B(s) + O2 (g) → 2BO (s) equation √1
2g 0.6dm3
x 24dm3
x = 2 x 24
0.6
= 80 √ ½
R.A.M = 80/2 √ ½
= 40 √ ½ penalize ( ½ ) for including units for r.a.m- Helium is preferred to hydrogen √1 since it is inert unlike hydrogen which is
- Explosive when mixed with air.
-
-
-
- 3-chloroethene √1
- 2-methylpropan -1-ol √1
-
- To each of the two substances placed in separate test tubes add some sodium carbonate √1
- Effervescence occurs in one of them confirming it is ethanoic acid.
- No effervescence with ethanol √ ½
-
- Sodium ethoxide √1
- Hardening of oils to make fat / margarine √1
H2SO4 - CH3 COOH + CH3 OH → (l) CH3COOCH3 + H2O √1
Warm
Ignore / do not penalize for wrong states - To bring the reacting particles close to one another √1
- Sunlight / UV √1
- Mass of C = 12 x 3.3 = 0.9 g √ ½
44
Mass of H = 2 x 1.8 = 0.2 √ ½
18
C H
0.9 0.2
Moles 0.9 = 0.075 0.2 = 0.2 √ ½
12 1
Ratio of mole 1 22/3
Ratio of atoms 3 : 8 √ ½
E.F C3H8 √1
-
-
- R √ ½ , losses electrons √ ½ most readily, most electro - positive √ ½
-
-
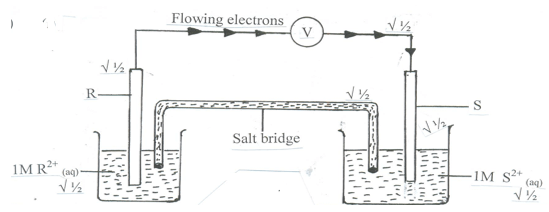
- Ecell = E reduced - E oxidsed
= -0.44 – (– 0.76 ) √ ½
= + 0.32v √ ½
-
-
- Improve its appearance √1
Prevent it from rusting √1 - Ag+ (aq) + e1 Ag (s) √1
Q = 1t 0.5 x 1 x 60 x 60 = 1800C √ ½
108g requires 1 faraday -1 √ ½
∴ 108g requires 96500C
? 1 800C
108g x 1800C
96500 √ ½
= 2.01 g √ ½
- Improve its appearance √1
-
-
- Pass the air through filters √ ½
- Pass the gas through NaOH (aq) √ ½
- Cool to -25ºC √ ½
- Compress and cool the air to -20º % and 200 atmosphere. Liquid air is obtained √ ½
- Fractionally distil the liquid air √ ½
- Nitrogen gas is obtained at -196ºC
NB: The steps should follow one another in that order. If one is wrong the rest after it do not core.
-
- Platinum √1 / Rhodium gauze catalyst
- Cooling √1
- 4NO2 (g) + 2H2O (l) + O2 (g) 4HNO3 (aq) √1
- Used as a fertilizer √1
- 2 AgNO3 (s) → 2Ag (s) + 2NO2 (g) + O2 (g)
- Molar mass = 60 √ ½
Mass of nitrogen = 28
% of nitrogen = 28/60 x 100 √ ½
= 46.66% √ ½ - Neutralisation √1
-
-
- Aluminium is very reactive metal hence extracted by electrolysis.
- X – Anode 1mk
V – Cathode 1mk -
- Iron (II) oxide 1mk
Silicon (IV) oxide 1mk - Cryolite is added. 1mk This lower the temperature from 2015ºC to 800ºC. 1mk
- Iron (II) oxide 1mk
- Anode 6O2- → 6Og + 12e OR 6O2-→ 3O2 + 12e 1mk
- The anode. The oxygen liberated at the anode reacts with carbon anode to form carbon (IV) oxide hence its corroded.
-
- Stronger than pure aluminium.
- Harder than pure aluminium.
- Has higher tensile strength than aluminium.
- Not easily corroded compared to aluminium.
- More durable. (Any 1mk)
-
-
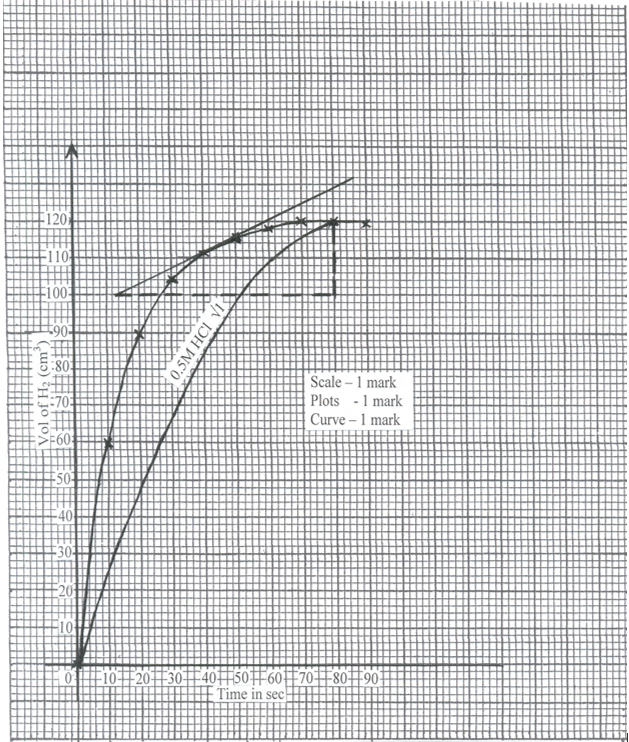
-
- 108cm3 ± 1cm3 √1
- Tangent must be drawn at t = 45 sec
Determination of gradient of the drawn tangent √1
Rate of change = 129 – 100 √ ½
80 – 12
= 29/68
= 0.4265cm3 / second √ ½
-
- No effect on equilibrium √ pressure change has no effect on reactions where there is no change in volume when change goes either way. √1
- Equilibrium shifts to the right more products are formed √1
-
Download Chemistry Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Kigumo Mocks 2021 Exams.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students