- Introduction
- The Internet
- Brief History and Development of the Internet
- Importance of the Internet
- Advantages of Internet
- Disadvantages of Internet
- Telecommuting
- Internet Connectivity
- Internet Services
- Accessing Internet Services
- Electronic Mail (E-Mail)
- Use of Internet to Access Information on Emerging Issues
- Positive Effects of the Internet
- Negative Effects of Internet
- KCSE Revision Questions

Introduction
- Computers can be connected together using data transmission media like cables, to communicate with one another.
- Communication in this case will be in the form of exchange of data and information. Such interconnection of computers to achieve message transfer is called networking. This is because the computers are linked to form a net.
- In most cases computer networks are unique to an organization. For example the computers in your computer laboratory may be networked. Such a network is local in nature hence it is usually called a local area network (LAN).

The Internet
- It is a large no. of connected computers (or a large set of computer networks) linked together that communicate with each other, over telephone lines.
- It is a worldwide computer network connecting thousands of computer networks, through a mixture of private & public data using the telephone lines.
- It is a worldwide (global or an international) network of computers that provide a variety of resources and data to the people that use it.
- Internet refers to a global inter-connection of computers and computer networks to facilitate global information transfer. It is an interconnection of computers throughout the world, using ordinary telecommunication lines and modems.
- The Internet uses VSATS (Very Small Aperture Telecommunication Systems) such as Telephone lines, Satellite.
- The other names for the Internet are:
- The Net.
- Information Superhighway.
- Cyber space. - Internet is a facility that links the Internet users to the actual Internet documents. Therefore, it is a system that links together many kinds of information all over the world. This technology allows computers equipped with telecommunication links to exchange information freely, and as such, the Internet has enhanced what is being referred to as a global village.
- Internet enables companies, organizations, individuals, schools and governments to share information across the world.
- A computer on the Internet can be located anywhere in the world. The Internet enables the computer to communicate with any other computer

Brief History and Development of the Internet
- The Internet was started by the U.S Department of Defence in 1969 as a network of 4 computers called ARPANET. Its aim was to connect a set of computers operated by several Universities and Scientists doing military research so as to enable them share research data.
- The original network grew as more computers were added to it. By 1974, 62 computers were already attached.
- In 1983, the Internet split into 2 parts; one dedicated exclusively (solely/only) to military installations (called Milnet), and the other dedicated to university research (called the Internet), with around 1,000 host computers.
- In 1985, the Canadian government developed the BITNET to link all the Canadian Universities, and also provided connections into the U.S Internet.
- In 1986, the U.S National Service Foundation created NSFNET to connect leading U.S universities. By the end of 1987, there were 10,000 host computers on the Internet and 1,000 on BITNET.
- In 1987, the National Science Foundation leased (acquired/rent) high-speed circuits to build a new high-speed backbone for NSFNET. In 1988, it connected 13 regional internal networks containing 170 LAN’s and 56,000 host computers.
- The Canadian Research Council followed in 1989, replacing BITNET with a high-speed network called CA*net that used the Internet protocols. By the end of 1989, there were almost 200,000 host computers on the combined U.S and Canadian Internet.
- Similar initiatives (plans/projects) were undertaken by other countries in the world, such that by the early 1990s, most of the individual country networks were linked together into one worldwide network of networks.
- Each of these individual country networks was different (i.e., each had its own name, access rules, and fees structure), but all the networks used the same standard as the U.S Internet network. So, users could easily exchange messages with each other.
- By 1990s, the differences among the networks in each of the countries had disappeared, and the U.S name; Internet began to be used to mean the entire worldwide system of networks that used the Internet TCP/IP protocols.
- A Protocol - a set of rules and standards that computers use to communicate with each other over a Network.

Importance of the Internet
- It is a research tool in new developments of products, competitors, market news and customer opinions and feedback.
- It enables advertisement and marketing of goods and services via web pages on a 24-hour basis.
- It is a source of entertainment through games, songs, movies, online TV channels etc.
- Supports communication especially by use of Electronic mail (e-mail). In addition, you can have live, interactive conversations with people around the world.
- It stores data by use of cloud computing.

Advantages of Internet
- Internet is a Wide Area Network (WAN) and has the following advantages:
- Enables sharing of expensive peripherals like laser printers, modems and servers etc.
- Enables sharing of all kinds of information on every topic, held an one computer across a number of users. iii) It enables applications/programs to be shared across a network by use of NetWare.
- Used to facilitate "group working".
- Facilitates telecommuting. For example, the office at home where users can conveniently work from any part of the geographical stations and link to their offices remotely.
- Facilitates communication between users and terminals such as video conferencing and email. vii) Eliminates duplication of tasks (redundancy).
- Reduces costs and delays in processing and transmitting data.
Some of the unique characteristics of Internet making it popular include:
- The internet technology makes responses to be instantaneous.
- Geographical spread of internet enabled devices is currently very wide meaning a large population can use it. iii) It is easy creating a network with people or organisations with similar concerns.
- It can create confidentiality to some degree especially when the user intends to be anonymous or shy.
- Because of non-physical content during communication, is less vulnerable to attack during transmission of signals in comparison to manual ways of communicating.

Disadvantages of Internet
- The cost of hardware, software and cabling is high.
- The Internet is not owned by an individual or organisation hence difficult to control.
- Security is a major concern over the Internet. For example, malware, predators and cyber bullying if adequate procedures are not adopted.
- Not all information on the internet is correct. Anyone can post anything, and much with it is garbage.
- Same people are addicted to the internet and thus cause problems with their interactions of friends and loved ones.
- Spread of pornography, terrorism and other vices can get in the hands of young children too easily.
- A lot of time is lost and wasted an the internet.

Telecommuting
- The office at home where users can conveniently work from any part of the geographical stations and link to their offices remotely. This is called telecommuting. It is also called teleworking.
Advantages of Home Based Work (Telecommuting)
- Saves travel costs by the workers. No need to physically converge to an office.
- No necessity to live within traveling distance to the office as you can have access remotely.
- Flexible hours ofwark and not necessarily between Bam to Spm.
- Saving for the institutions in terms of renting expensive city-centre offices and learning areas or premises.
Disadvantages of Home Based Work
- Loss of social contact between the clients.
- Need for quiet workroom at home. This can be difficult in a small flat or noisy estates.
- The difficulty of office' accommodation is compounded when two or three members of a family all work at home.
- Loss of visible status for senior staff in terms of a 'plush' office and other staff to command.
- The cost of hardware, software and cabling is out of reach to so many people. The network communication cost is out of reach too (expensive bandwidths).
- So many homes are not supplied witn electricity making it impossible to use battery backups.

Internet Connectivity
Requirements before can connect to the Internet include:
- Data Terminal Equipment (CITE) such as a computer or internet enabled device such as smartphanes, Personal Digital Assistants (PDEs). Remember not all DTEs can send or receive data signals via internet.
- Transmission medium: this is the physical or wireless path which acts as a channel or link through which messages travel from sender to receiver such as twisted pair, satellite.
- MODEM - a Data Communication Equipment (DCE) which converts digital signal from a transmitting computer to analogue and from analogue to digital signals on the receiving computer. A modem is used in case where a computer is used.
- Internet Software - often installed with your operating system or can be downloaded from the Internet such as Web browser, internet protocols, and email software. Web browsers usually allow the user to navigate (surf) the web pages such as Netscape Navigator, Chrome, Microsofs Internet Explorer, Mosaic, Opera, and Mozilla_
- An Internet Service Provider (ISP) is a company that connects your home or office computer to the Internet at a fee. Examples are Zuku, Safaricom, Airtel, Telkom, Faiba, Access Kenya.

Internet Services
- Communication - One can exchange information through e-mails, video-conferencing, chat n]oms and newsgroups.
- E-commerce - Buying and selling of goads and services over the internet. Currently, you can access cyber shops for online purchasing and pay for the sewices through electronic funds transfer (EFT), cheque and credit cards among others.
- Advertisement and marketing - Through creating a web site it enables a business to be visible worldwide at a cheaper cast. This can also boost sales internationally, those who create websites are known as web designers, webmaster, web programmers or web developers.
- Research and browsing - Researchers and scholars use Internet to access digital (virtual) libraries far the latest information and archives.
- Entertainment - Users can watch online TVs, vid eas and play games.
- Education and E-learning - Academic materials for all levels of education are readily available on the Internet. The Internet has opened the door for those who would like
to do distance education programs and home schooling. Learning through interaction with special programs on the computer is called electronic learning (e- learning). - Discussion group - Is a collection of users who join together to discuss some topic such as cookery, politics, education, recreational and scientific research.
- Telnet - Logging into a remote computer and work on it as your local computer. Remember telecommuting
- File transfer -Data in the form of files can be transferred across the Internet from one site to another using the File Transfer Protocol (FTP).
- Software downloads -Users can download program from remote computers to their computers such as antivirus software update.
- Search engines Or search services - Software that helps in locating information in the Web for any information that you want to find, especially when you do not know where to find it. Examples of search engines include Google, Bing, Yahoo, Ask. com, AOL.com, Baidu.
Information on the Internet is made available through the following items
- Website: A collection of web pages stored as a file in a special type of a computer called web server. Every website is accessed using a unique address known as Uniform Resource Locator (URL) such as https://wwwknec.ac_ke.
- Web portal - A web site that provides an excellent starting point for exploring the net. They let users to type a word or phrase to quickly search for information an the web. They also allow users to browse or search by categories. Examples of web portals, excite. cam, ananzi.co.za, netscape.com, msn.com, yahoo.com
- Blog - A regularly updated website or web page, typically run by an individual or small group and is written in an informal or conversational style.
- Multimedia - A term used in computing concerned with controlled integration of text, graphics, drawings, still pictures, videos, animation, audio, and any other media where every type of information can be represented, stared, transmitted and processed digitally.
Common protocols used in Internetworking
- Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) - Governs how data is transferred from one DTE to another on the nternet_
- Internet Protocol (IP) -Determines the unique addressing of communication devices an the internet.
- Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) - A language that web clients and servers use to communicate with each other in order to send and receive data signals or messages.

Accessing Internet Services
Log In/Sign In
- To access a website, type the full address of the website in the address bar then press the Enter key on the keyboard. If the Internet connection is working properly, the browser will start connecting to the requested web site or URL. Notice that the status bar will be reading something like "connecting to site www.yahoo.com "
- Some web sites allow free access to all their pages by all visitors. However, others require people to be members hence a new visitor has to register (sign up) by filling some on-line forms. The registration process gives the visitor a user name and password that can be used to sign in or log on the website for each successive visit. This is very common for e-mail account providers like at www.mail.yahoo.com.
- Websites that give users a chance to log in are better especially if the services offered need some degree of privacy and customizing for individual customers e.g. it would be a gross mistake to have everybody accessing the other's e-mail account.
Web Browsing/Surfing
- To navigate or move around the web pages you require a web browser. A web browser is a program that lets the user surf through information an the internet. Information on the Web is structured into pages with each having a specific address that is used to locate and access information on that page called URL.
- Users navigate the pages by use of hyperlinks.
- Hyperlinks are clickable texts or objects which connect users to different pages of the web document. If they are made up of text only, they are referred to as hypertext. Others made up of non-texts are referred to as hyperobjects.
- During browsing a user can upload or download data and files.
- Upload when you send data or information from your computer terminal to another computer on the net.
- Download when you receive and store information from another computer on the Internet. Lifting information from another Internet computer.
- Home page is the first page that appears each time start your web browser or open a web site.

Electronic Mail (E-Mail)
Definition of Terms
- Postal mail: This is the conventional regular postal sewice delivery of letters and paper messages to the recipient's local past office whose implication means, it is very slow i.e. Snail Mail.
- Facsimile (Fax): Is a telephone transmission of scanned and printed material (text or image) usually to a telephone number associated with a printer. The receiving Fax machine reconverts the coded image and prints a paper copy ofthe document. It is reliable, secure, faster and easy to use.
- Electronic mail (E-mail): Refers to the sending and receiving of electronic letters and documents on the Internet as apposed to postal mail.
Advantages of Emails Over the Traditional Paper Mail or 'Snail Mail'
- It is very fast.
- It is low cost, almostfree.
- It is convenient to access from any internet enabled device anywhere anytime.
- Easy to send one mail to many recipients by use of carbon copies.
- Can be saved far future retrieval.
- Easy to send and reply. It does not require a lat of training to browse.
- Can easily be forwarded to another recipient.
- Document created using other application can easily be attached to the mail.
- Reliable if all email etiquette and netiquette is observed.
Disadvantages of Emails
- Security of message may not be guaranteed due to tapping while on transit.
- Lack of infrastructure.
- The cost of calling is still very high.
- Requires some ICT literacy to use and enjoy.
- Unsolicited emails (spams) clog the computer memory while others are malware.
Email Requirements
Any user accessing an email must have the following items:
- A computer or an internet enabled device to send or receive the e-mail messages.
- An e-mail program allows users to send, receive and manage e-mail messages.
- Popular email programs include, Gmail, Hotmail. cam, Yahoo.com, Microsoft outlook express, qualcomm eduro pro. - A unique e-mail address of the sender and the recipient. An email address directs a message to the recipient.
- An Internet Service Provider (ISP) - Company who will deliver your message to the receiver.
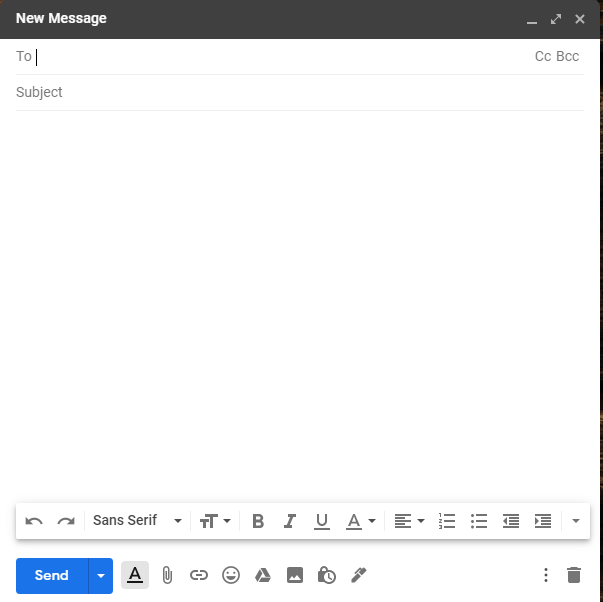
Parts of an E-mail Compose Window
The figure below illustrates a Gmail email software display window when the compose button is clicked.
- To: - The email address ofthe receiver.
- Cc: - Contains the e-mail addresses of each recipient, when want to send copies of the message to multiple users at the same time.
- Bcc: - Blind Carbon Copy (acc) is used when sending the message to multiple recipients however their names are hidden from other recipients of the message.
- Subject: - An appropriate title of the email message.
- Attachments: - One can add documents, pictures, sound, videos, programs among others to message.
- Email body: The large rectangular box where the sender types in the message to be sent before clicking the send command button.
Note: A message that returns to the sender because it cannot reach destination is referred to as a bounced message.
E-mail Addresses
- It defines location of an individual mailbox on the internet.
- Parts of an e-mail address consists of two parts separated by the © (at) symbol The left part contains the user name. For example, the name of the person's account. This can be real or nickname.
- The right part (second part) is known as the domain name. It is the location ofthe person's account on the Internet. Full stops (E) separates the various parts of the domain name such as This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it..
Organisation or Country Domains
The last few characters in an email address usually indicate the domain type or the region or both.
|
Top level |
Domain |
Country |
Region code |
|
com |
commercial |
au |
Australia |
|
edu |
education |
ca |
Canada |
| gov |
government |
it |
Italy |
| mil |
military |
jp |
Japan |
|
net |
network |
ke |
Kenya |
|
org |
organisation (Often non-profit) |
ug |
Uganda |
Examples of current domain levels include:
- ac.ke - academic institution in Kenya
- co.ke - commercial entity located in Kenya
- go.ke government entity located in Kenya
Example Introduction - Website for Kenya National Exam Council
E-mail Features
- Inbox - contains received mails
- Outbox - It contains sent mail or waiting sending/ delivery_
- Attachments - You can attach document'picture,' sound/video/pragram to your message_When attaching a file keep the size of your attachment small. Attachment is an example of uploading.
- Downloading - Enables attached messages to be downloaded before they can be accessed.
- Forwarding a message - After reading a message, you can add comments and then send the message to a friend or colleague. This is called forwarding.
- Printing a message - Enables printing a message to produce a hard/paper copy
- Telephone messages
- Because of integration between mobile telephony and the Internet technology, it is possible to send e-mail to a mobile handset and a mobile message to e-mail account. This
mobile computing is made possible by a special Internet access protocol called wireless access protocol (WAP) and wireless markup language (WML). - Contact management
- Most mail programs allow the user to develop an address book which holds 'contact information like e-mail addresses of different people along with other necessary information.
- The e-mail software usually provides a simple way of accessing these contacts when required

Use of Internet to Access Information on Emerging Issues
- The Internet is a storehouse for all types of information, presented in the form of text documents, pictures, sound and even video. Many emerging issues in the world today may not be properly documented in terms of hardcopy textbooks and journals but the Internet has a wide range of information concerning the issues.
- Emerging issues in this context refer to HIV/AIDS, drug abuse, environmental issues and moral issues

Positive Effects of the Internet
- Easy research: It is easier to do research and gather information an materials relevant to their research topics.
- Enhanced communication: Communication with family, friends and relatives is faster.
- Creation of jobs: There is a great possibilityta earn while working from home.
- Easy for doing business: Faster business transactions and cheaper products has been enhanced.
- Savings on travel cost: Through the use of the internet, it is passible far executives or business managers to do teleconferencing.

Negative Effects of Internet
- Lack of face to face communication: Many people find it easier to communicate through the Internet instead of the traditional direct way. This limits ane on one interactions.
- Cyber bullying: People use internet to bully or harass others, for example, an social media sites.
- Disrupted privacy: Because of free information people tend to exchange private data such as pictures, cell phone numbers, and ID numbers unknowingly. These data can easily land in the wrong hands or hacked. • Insecurity: It has made easier for criminal elements to access private data belonging to organisations and individuals in order to advance their malicious intents.
- Immorality and cultural erosion: A lot of pornographic materials are easily accessible to teenagers leading to premarital sex, early teen pregnancies, Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STD) and HIV and AIDS, drugs and substance abuse.
- Viruses: Malicious programs spread very fast through the internet which could lead to data loses.

KCSE Revision Questions
- Explain n,'da ways in which the use of Internet could make reporting of corruption easier. (4 marks) KCSE 2016 Paper 1
-
- What is meant by the term e-learning? (1 mark)
- A school intends to set-up an e-learning system. List three problems that are likely to be encountered. (3 marks) KCSE 2006 Paper 1
- A worker is unable to travel to the office but may still be able to do the office work through telecommuting. Explain the benefits that the employer will get by allowing the worker to do the office work through telecommuting. (4 marks) KCSE 2013 Paper 1
- Explain why telecommuting is NOT suitable for a doctor when carrying out an operation. (2 marks) KCSE 2010 Paper 1
- With the improvement in price and performance of computers and communication equipment, it wil be possible for people in various business organisations to work from home. Such working using a PC as a remote terminal is often described as teleworking. State three advantages and three disadvantages of working from home. (12 marks) KCSE 2004 Paper 1
-
- Write the acronym MODEM in full. (1 mark)
- Explain the purpose of a modem when connecting to the internet. (2 marks) KCSE 2015 Paper 1
- List six activities performed on the web. (3 marks) KCSE 2008 Paper 1
- An institution has ten stand-alone computers. State the necessary steps required to connect the computers to the internet. (4 marks) KCSE 2008 Paper 1
-
- What is a search engine? (1 mark)
- The internet can be used to source information about emerging issues that may not be available in print form. Give the advantages and two disadvantages of information obtained from the internet. (4 marks) KCSE 2006 Paper 1
- Protocols used in sending and receiving of emails. (1 mark) KCSE 2012 Paper 1
-
- What is an internet protocol (IP) address? (1 mark)
- Why is an IP address necessary? (1 mark) KCSE 2009 Paper 1
- Describe the term 'home page' as applied in the internet. (2 marks) KCSE 2008 Paper 1
- Define the following web related terms: KCSE 2007 Paper 1
- Web browser (1 mark)
- Hyperlink (1 mark)
- Hypertext document. (1 mark)
- Give two differences between post office mail and electronic mail (e - mail). (2 marks) KCSE 2003 Paper 1
- State two functions of e-mail software. (1 mark) KCSE 2012 Paper 1
-
- Differentiate between Bcc and cc in an email. (2 mark)
- Explain why a worker may use each of the following:
- email; (2 marks)
- fax; (2 marks) KCSE 2014 Paper 1
- What is the purpose of the following internet domains?
- .org (1 mark)
- .gov (1mark) KCSE 2009 Paper 1
- What is meant by each of the fallowing terms as used in the internet?
- Surf (1 mark)
- Uploading (1 mark) KCSE 2011 Paper 1
Download Internet and Email - Computer Studies Form 2 Notes.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students