INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES:-
- Write you name and index number in the spaces provided above.
- Answer all the questions in the spaces provided.
- Mathematical tables and electronic calculators may be used form calculations.
- All working MUST be clearly shown where necessary.
|
Question |
Maximum score |
Candidate’s score |
|
1-28 |
80 |
|

QUESTIONS
- The table below gives some properties of gases M and N
GASES
Density
Effect of HCl(aq)
Effect of KOH(aq)
M
Lighter than air
Reacts to form a salt
dissolves without reacting
N
Heavier than air
Not affected
Not affected
- Describe how one would obtain a sample of gas N from a mixture of gases M and N (2mks)
- Name two neutral oxides (1mk)
- Iron roofing sheets are coated with zinc as sacrificial metal;
- What is meant by the term ‘sacrificial’? (1mk)
- Give the name given to the process by which iron sheets are coated with zinc. (1mk)
- Zinc is higher than iron in reactivity series yet it does not corrode as fast as iron.
Explain (1mk)
- The set-up below was used to investigate the properties of hydrogen gas.
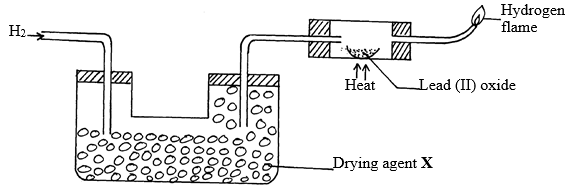
- Write an equation for the reaction that takes place in the combustion tube. (1mk)
- Suggest a possible drying agent X. (1 mk)
- Which property of Hydrogen is under investigation in the set up above? (1mk)
- The table below shows pH values of solutions A to E
Which solution;Solution
E
B
D
A
C
pH
3
14
7
6
9
- Contains the largest concentration of hydroxyl ions? (1mk)
- Contains the largest concentration of hydrogen ions (1mk)
- Is likely not to react with solution A? (1mk)
- Potassium is isotopic and has a relative atomic mass (R.A.M) of 39.5, work out the percentage abundance of each isotope. The three isotopes are, 39K, 40K and 38K (0.01%) (3mks)
- An ion of element Q can be represented as
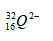
- Draw the structure of the ion (2mks)
- How does the ionic radius of Q compare with its atomic radius? Explain. (1mk)
- The electronic configuration for elements represented by letters A, B, C and D are
A 2.8.6
B 2.8.2
C 2.8.1
D 2.8.8- Select the element which forms;
- A double charged cation (1mk)
- A soluble carbonate (1mk)
- Which element has the shortest atomic radius (1mk)
- Select the element which forms;
- When concentrated sodium chloride was electrolysed for a long time. Two gases were
Obtained at the anode;- Name the two gases (1mk)
- Explain why the gases were obtained. (2mks)
- Using dots (.) and crosses (X) to represent electrons, draw diagrams to show bonding in;
- C2H4 (C=12 H=1) (1mk)
- Hydroxonium ion H3O+ (H=1 O=8) (1 mk)
- A student reacted Silver Nitrate and Barium Chloride solutions to prepare two salts.
- Write an ionic equation for the reaction that took place. (1mk)
- Describe how a sample of Lead (II) Chloride and Silver Chloride can be differentiated in the laboratory (2 mks)
- A monomer has the following structure. (1mk)
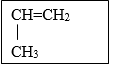
- Draw the structure of its polymer that contains four monomers. (1 mk)
- A sample of the polymer formed from the monomer has a molecular mass of 4116. Determine the number of monomers that formed the polymer (C = 12, H = 1) (2mks)
- Use the diagram below to answer the questions below:
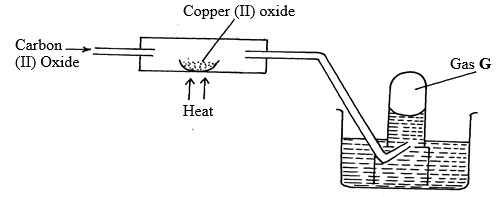
- Identify gas G (1mk)
- Write an equation for the reaction taking place in the combustion tube. (1mk)
- Carbon (IV) oxide is said to be a “silent killer”. Explain why? (1mk)
- 400cm3 of Nitrogen gas diffuses through a porous plug in 70seconds. How long would it 200cm3 of Carbon (IV) oxide to diffuse through the same porous pot? (C=12, O=16, N=14) (3mks)
- 20.0cm3 of NaOH solution containing 8.0gdm-3 were required for complete neutralization of 0.118g of a dibasic acid. Calculate the Relative Molecular Mass (R.M.M) of the acid.
(Na=23, O=16, H=1) (3mks) - The diagram below shows the combustion of ethane gas. Study it and answer the questions that follow:
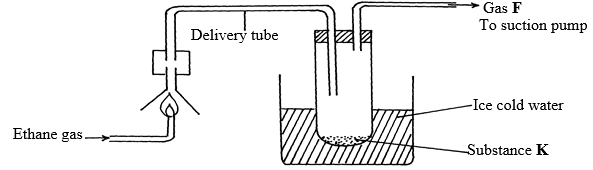
- Identify substance K (1mk)
- Write an equation for the complete combustion of ethane gas. (1mk)
- The pH of substance K is found to be less than 7. Explain this observation (1mk)
- The structure of hydrogen sulphide can be represented as shown below:
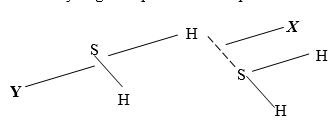
- Name the bond type represented by letters X and Y (2mks)
X…………………………………….
Y…………………………….………. - Give a chemical test for hydrogen sulphide gas (1mk)
- Name the bond type represented by letters X and Y (2mks)
- In the Haber process, the industrial manufacture of ammonia is given by the following equation;
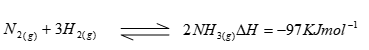
- What is source of the Hydrogen that is used in the process (1 mk)
- Name the catalyst used in the above reaction (1mk)
- What is the effect of increasing temperature on yield of ammonia? Explain (1mk)
- The curves below were obtained when equal volumes of 1.5M HCl were reacted with 2.0g of marble chips (CaCO3). In one of the reactions, the acid was warmed before adding the marble chips.
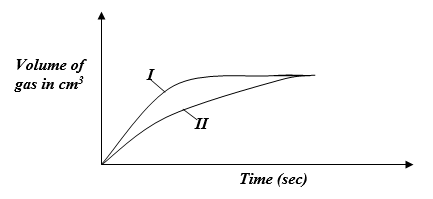
- Write the equation for the reaction (1mk)
- Identify the curve representing the reaction where the acid was warmed. (1mk)
- The volume of the gas produced in the two experiments is the same. Explain. (1mk)
- Chlorine gas was bubbled into a solution of hydrogen sulphide as shown below:
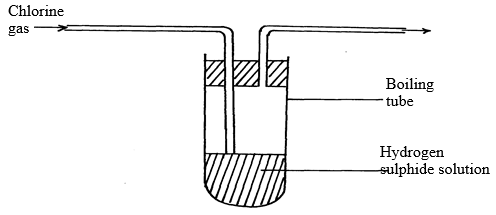
- Explain the observation made in boiling tube. (2mks)
- What precautions should be taken in the experiment (1mk)
- Given the bond energies:
H-Cl 431kJ/mol
H-H 435kJ/mol
Cl-Cl 243kJ/mol
Calculate the molar enthalpy change for the formation of hydrogen chloride as per the equation below
H2 (g) + Cl2 (g) → 2HCl (g) (3 mks) - Study the physical properties of Magnesium and Beryllium. Use it to answer the questions that follow:
Element
Be
Mg
Mp oC
1280
650
Bp oC
2450
1110
Atomic number
4
12
Atomic radius (nm)
0.086
0136
- Explain why Beryllium has a higher m.p than Magnesium (2mks)
- Write the electron arrangement of Magnesium in the following compound; Mg3(PO4)2 (1mk)
- Study the diagram below and answer the questions that follow:
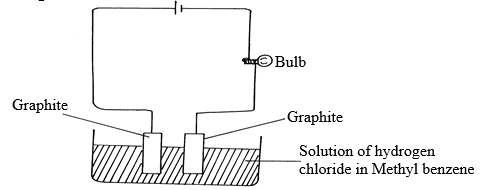
- What observation was made during the experiment? Explain? (1½mks)
- What observation would be made if the solution of hydrogen in methylbenzene was replaced with solution of hydrogen chloride in water? Explain (1½mks)
- Describe how you would prepare Copper (II) Chloride, staring with copper metal. (3mks)
- 0.28g of iron burns in air to form Iron (II) oxide. Calculate the mass of Iron (II) oxide formed (O=16, Fe=56) (2mks)
-
- Define the term solubility (1 mk )
- The following were the results obtained in an experiment to determine the solubility of potassium nitrate at room temperature.
Mass of evaporating dish = 20.66 g
Mass of evaporating dish+ saturated solution = 44.16 g
Mass of residue on the evaporating dish = 6.1 g
Calculate the solubility of potassium nitrate from the above result. (2 mks)
- Given that the Eᶿ of Cu(s) /Cu2+(aq) is +0.34V and that of Zn(s)/ Zn2+ (aq) is -0.76 V, draw a labeled diagram of zinc and copper electrochemical cell. (3 mks)
- Aluminium is obtained from its ore, with formula Al2O3.2H2O. The ore is first heated and refined to obtain pure aluminium oxide (Al2O3). The oxide is then electrolysed to get Aluminium and Oxygen gas using carbon electrodes
- Write the equation that takes place at the anode (1mk)
- What would be the importance of heating the ore before electrolysed (1 mk)
- Explain why Aluminium is used for making cooking pans yet it is a reactive metal (1 mk)
- State two advantages of hard water ( 1 mk)

MARKING SCHEME
-
-
- Pass mixture through HCl (absorbs M) √1mk
- Collect E by downward delivery /upward displacement of air√1mk
-
- water/√ ½ mk
- Carbon (II) Oxide√ ½ mk
-
-
- Zinc is oxidized in place of iron and therefore iron is prevented from rusting √1mk
- Galvanization √1mk
- Zinc reacts with air to form a non-porous √ ½mk oxide layer which hinders further corrosion/reaction of zinc. √ ½mk
-
- PbO(s) + H2(g) →Pb(s) + H2O(g) √ 1 mk (-balanced - State symbols ) not balanced -0mk
-Incorrect state symbols – ½ mk - Anhydrous calcium chloride//
Calcium chloride√ 1 mk - Hydrogen as reducing agent√1mk
- Hydrogen acts as a reducing agent √ ½ mk
- PbO(s) + H2(g) →Pb(s) + H2O(g) √ 1 mk (-balanced - State symbols ) not balanced -0mk
-
- B √ 1 mk
- E√ 1 mk
- D/C √ 1 mk
- % abundance of 38K = 0.01
%abundance or 39K and 40K = (100 – 0.01)
= 99.99%
Let % abundance of 39K be x √ ½ mk
% abundance of 40K = 99.99-x √ ½ mk
39x + 40 (99.99 –x) + 38.001 = 39.5 √ 1 mk
100
-x+3999.6 + 0.38 = 3950
-x = 3950 – 3999.98
-x=-49.98% √ ½ mk
x=49.98%
38K = 0.01%
39K=49.98% √ ½ mk
40K=50.01% T. mks =3mks\ -
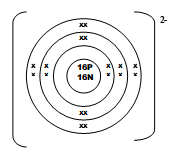
Correct nucleus comp. √ 1 mk
Correct energy levels √ 1 mk
Electrons with correct charge
Charge is missing/incorrect 0mk- Ionic radius is greater than the atomic radius√ ½mk due to reduction in nuclear attraction// repulsive effect as a result of extra electrons√ ½mk
-
-
- B√ 1 mk
- C√ 1 mk
- D√ 1 mk
-
-
- Oxygen √ ½ mk reject formula
Chlorine √ ½ mk - Initially chloride ions are highly concentrated √ 1 mk after a while OH- ions concentration
Increase due to chloride ion discharge previously √ 1 mk
- Oxygen √ ½ mk reject formula
-
- C2H4 √ 1 mks
–Carbon electron pairs for C = C should be similar
-Deny full marks incase of C = C electron pairs being different √ 1 mks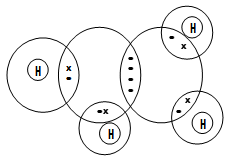
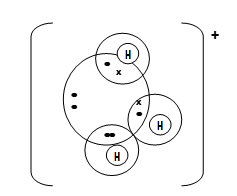
–charge √ 1 mk
-missing charge penalize fully
-Oxygen hydrogen bond must have similar electrons
- C2H4 √ 1 mks
-
- Ag+(aq) + Cl-(aq) →AgCl(s) √ 1 mk
Not balanced -0mk
Miss state symbols – ½ mk
- Ag+(aq) + Cl-(aq) →AgCl(s) √ 1 mk
-
- Monomer mass =( 3*12+6*1) = 42√ 1 mk
Number of units = 4116/42
= 98 monomers√ 1 mk
-
- Carbon(IV) oxide √ ½ mk (Deny carbon dioxide – 0mk)
- CO (g) +CuO(s) → CO2 (g) +Cu(s) √ 1 mk
- Its colourless
Oduorless √ ½ mk
- Time for 200cm3 of Nitrogen to diffuse = 200*70/400
= 35seconds √1 mk
Molar mass of N2 = 48, CO2 = 28 √½ mk
TN2 = √(RMMN2/RMMCO2)
TCO2
35/x = √ (28/48) √1 mk
35/x = 0.977
X = 43.88 seconds√½ mk - H2X +2NaOH→ Na2X+H2O (balanced equation/ Mole ratio √½ mk )
moles of NaOH = 8g/l
40
= 0.2m
=0.2 × 20 moles of base √½ mk
100
= 0.004 moles
moles of acid = ½ × 0.004
= 0.002 moles moles of acid √½ mk
if 0.002 moles = 0.118g
1 mole (1 × 0.118)
0.002
= 59 -
- Water/H2O √ 1mk
- 2C2H6+7O2 → 4CO2(g)+6H2O(l) (balanced =√ 1 mk)
- Carbon(IV) oxide formed dissolves slightly in water to make it acidic √1 mk
- X-Van-der-waal √ 1 mk
Y-covalent √ 1 mk
Bubble through Lead(II) Nitrate/Lead Acetate which turn black √ 1mk -
- - Cracking of hydrocarbons
-Electrolysis (any =√ 1 mk) - Finely divided Iron √ 1 mk
- – Reduces the yield of Ammonia √ ½ mk
-Equilibrium shifts to the left since the reaction is exothermic √ ½ mk
- - Cracking of hydrocarbons
-
- 2HCl(aq) +CaCO3(s) → CaCl(aq) + CO2(aq) + CO2(g) + H2O
Incorrect formula -0mks - Curve 1
- The amount/concentration of the reagents used is the same/ equal √ 1 mk
- 2HCl(aq) +CaCO3(s) → CaCl(aq) + CO2(aq) + CO2(g) + H2O
-
- Yellow deposits will be seen √ 1 mk
Chlorine oxidizes hydrogen sulphide to sulphur √ 1 mk - Experiment should be done in open air/fume chamber any√ ½ mk
- Yellow deposits will be seen √ 1 mk
- Bond breaking energy = 435+ 243 = + 678 kJoules √ ½ mk
Bond formation energy = 2*431 = -862 kJoules √ ½ mk
Heat of reaction = +678-862 √ ½ mk
= -184 kJ √ ½ mk
Molar enthalpy of formation = -184/2 kJ √ ½ mk
= -72 kJoules/mol √ ½ mk Total = 3mks -
- Beryllium atomic radius is smaller than Magnesium√ 1mk hence stronger metallic bonds√ 1 mk
- 2.8 √ 1 mk
-
- Bulb doesn’t light /no observable change√ ½ mk HCl remains in molecular form /non-electrolyte √ 1mk
- -Bulb lights /effervescence observed at the electrode√ ½ mk
-It ionizes and therefore becomes an electrolyte√ ½ mk
- Roast/ heat√ ½ copper in air to form Copper (ii) oxide. React the copper (ii) oxide with a given amount of dilute hydrochloric√ ½ acid until effervescence stops/ in excess√ ½. Filter √ ½ to remove unreacted oxide. Evaporate√ ½ to saturation, leave to cool, dry√ ½ the crystals between filter papers √ 3 mks
- 2Fe(s) +O2(g) →2FeO(s) must be there√ ½ mk
Mole ratio √ ½ mk
Moles of Fe = moles of FeO = 0.28/56 = 0.005moles √ ½ mk
Mass of FeO=0.005x72=0.36g √ ½ mk -
- is the maximum amount of a solute that can saturate 100 grams of a solvent at a particular temperature √1 mk
- Mass of saturated solution = 44.16-20.66
= 23.5 g √ ½ mk
Mass of the solvent = 23.5 – 6-1
= 17.4 g √ ½ mk
Solubility = 6*100/17.4 √ ½ mk
= 35.96 g/ 100 g of water at room temperature √ ½ mk
- Zn (S)// Zn2+(aq) half cell√ ½ mk ------Cu/ Cu2+ half cell √ ½ mk
Salt bridge indicated √ 1 mk
Electrodes indicated and connected via connecting wires √ ½ mk
Workability of the cell √ ½ mk -
- 2O2-(l) → O2 (g) + 4e- √ 1 mk
- To free up the ions/ make the ions mobile √ 1 mk
- Forms aluminium oxide layer that prevents reaction with steam and water √ 1 mk
- Presence of mineral salts like calcium for strong bone formation√ 1 mk
–Beer brewing√ 1 mk
- Prevents internal corrosion of water pipe √ 1 mk (any 1)= 1mk
Download Chemistry P1 Questions and Answers - Nambale Mock Exams 2021/2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students

