CHEMISTRY
PAPER TWO
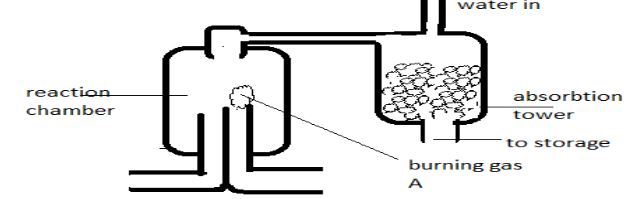
- The above diagram shows a set up that can be used for industrial manufacture of hydrochloric acid. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
- Identify Burning gas A (1mk)
- Write a balanced equation for the reaction that takes place in the reaction chamber (1mk)
- Identify two reagents that are used in the laboratory manufacture of hydrochloric acid (1mk)
- Hydrochloric acid was added to iron powder in a test-tube and shaken thoroughly to mix to 1cm3 of the resulting solution, six drops of aqueous solution of ammonia were added. State and explain the observation made on adding ammonia solution (2mks)
- Concentrated hydrochloric acid is 35% pure with a density of 1.18g/cm3.Calculate its concentration in moles per litre. H=1, Cl= 35.5 (3mks)
- write one industrial use of hydrochloric acid (1mk)
- explain the observation made when a moist blue flower is placed in a gas jar containing chlorine gas (2mks)
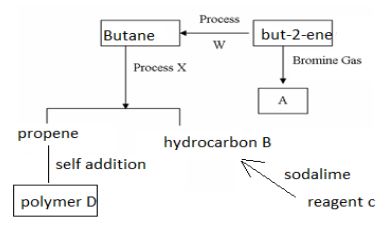
- Study the flow chart below then answer the questions that follow.
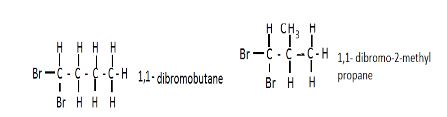
- Draw and name two isomers of substance A (4mks)
- Name (3mks)
- process W ________________________________
- process X ________________________________
- reagent C __________________________________
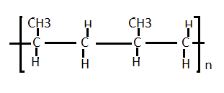
- Draw two repeated units of polymer D (2mks)
- Ethyne is a hydrocarbon belonging to the alkyne homologous family . Identify
- two reagents used to prepare ethyne in the laboratory (1mk)
- Name the third member of this family (1mk)
- Explain the observation made when ethyne is burned in air (2mks)
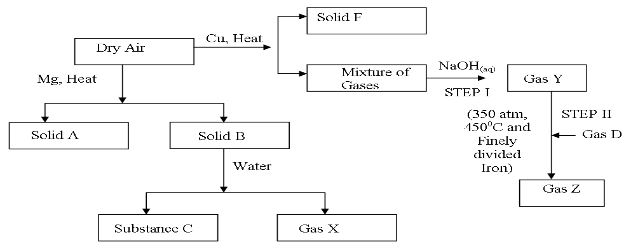
- Study the diagram below that shows some reactions of dry air, then answer the questions that follow.
- Identify; (2mks)
- Solid A ________________________________
- Solid B ________________________________
- Gas D ________________________________
- Gas Z ________________________________
- Why is the amount of solid B obtained much less than solid A? (2mks)
- Write a balanced equation for the reaction between solid B and water (1mk)
- Which gas is absorbed by sodium hydroxide in step I (1mk)
- Gas Y obtained in step I is impure, Name one impurity it contains (1mk)
- What name is given to the process that occur in step II (1mk)
- 300 liters of ammonia are catalytically oxidized to form nitrogen II oxide which is further oxidized to nitric acid.
- write a balanced equation for the catalytic oxidation of ammonia (1mk)
- which catalyst is used in this process (1mk)
- determine the volume of the products in the above reaction (2mk)
- Identify; (2mks)
-
- Define the term allotrope (1mk)
- Identify the two allotropes of sulphur (1mk)
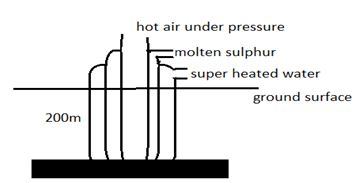
- In the extraction of sulphur three concentric pipes are sank into the ground 200 m away from the surface. Use a well labeled diagram to describe the above process (3mks)
- The table below shows some reactions of concentrated sulphuric VI acid. Study it and answer the questions that follow (2mks)
Reaction of sulphuric acid Observation Property of sulphuric acid being investigated Reaction with blue
copper sulphate crystalsMoist hydrogen gas is
bubbled in and collected
in a syringe - 50 ml of dilute Sulphuric VI acid was placed in 3 separate beakers and the following substances were added as shown in the table below
Using relevant equationsBeaker A B C Magnesium powder Lead carbonate powder Copper oxide - Explain the observation in beaker B and beaker C (3mks)
- Magnesium powder in beaker A was replaced with silver powder. Explain the difference in the two reactions (3mks)
- A student was given water containing suspected to be hard
- What is hard water? (1mk)
- The sample was divided into three portions and the following tests were carried out and the following observations were made
Sample Test Observations 1 10 ml of soap solution was added drop wise till excess 2ml lather formed 2 A sample is boiled White precipitate 2 Boiled sample 10ml of soap is added 10 ml lather formed - Identify the type of hardness in the above sample. Explain (2mks)
- Write an equation for the formation of the white precipitate (1mk)
- Ammonia solution was added drop wise till excess in the third sample. A white precipitate was observed. Identify the cation present in the water. (1mk)
- Write one advantage and one disadvantage of hard water (2mks)
- Advantage
- Disadvantage
- Salt B has a solubility of 20g/100g of water at 40oC. A solution containing 6g of salt B in 10ml of water is cooled to 40oC. Calculate the amount of salt that crystalized out (2mks)
A student was provided with Calcium carbonate, sodium hydrogen carbonate , zinc sulphate , ammonium nitrate and Aluminium chloride
Which salts- are Insoluble in water (1mk)
- forms a white precipitate which dissolves to form a colourless solution when dissolved in excess sodium hydroxide solution (1mk)
- write 2 ionic equation for the reaction between zinc sulphate and excess ammonia solution (2mks)
- Use the table below to answer the following questions. Letters represent the most stable ion of elements in the periodic table
Ions P+ Q-1 R-1 W2+ Y3+ Z+ Ionic
radius0.086 0.056 0.044 0.073 0.064 0.097 - Explain the trend in the ionic radius of P+ and W2+ and Y3+ given that they are in the same period (3mks)
- Element Q and R are in the same group.
- Identify the family name of the group to which they belong (1mk)
- Which element is more electronegative? Explain (2mks)
- Given that ion P+ has electronic configuration 2, write the electronic configuration of ion Z+ (1mk)
- Write the formulae of the element formed when Y reacts with oxygen (1mk)
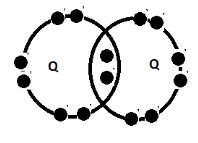
- Using dot and cross diagrams show the bonding
- between P and chlorine (1mk)
- Two atoms of Q (1mk)
-
- Define the term heat of solution (1mk)
- In an experiment to determine the heat of solution 4.8g of ammonium nitrate were added to 100ml of water at 20oC. The temperature dropped to 9oC.
- Calculate the heat change in the above experiment given that C= 4.2 J/g/C (2mks)
- determine the molar heat of solution for the above reaction N=14, O=16 H=1 (2mks)
- determine the lattice energy of ammonium nitrate given that
Hydration energy is -12kJ/mol (2mks)
- Ethanol has a heating value of 14.5kJ/g while methane has a heating value of 10kJ/g. Which of the two fuels has a higher molar heat of combustion C=12, H= 1, O=16 (2mks)
MARKING SCHEME
- The above diagram shows a set up that can be used for industrial manufacture of hydrochloric acid. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
- Identify Burning gas A (1mk)
- hydrogen
- Write a balanced equation for the reaction that takes place in the reaction chamber (1mk)
- H2 (g) + Cl2(g) → 2HCl(g)
- Identify two reagents that are used in the laboratory manufacture of hydrochloric acid
- Conc H2SO4 and NaCl
penalize fully for any wrong (1mk)
- Conc H2SO4 and NaCl
- Hydrochloric acid was added to iron powder in a test-tube and shaken thoroughly to mix to 1cm3 of the resulting solution, six drops of aqueous solution of ammonia were added. State and explain the observation made on adding ammonia solution (2mks)
- Green precipitate insoluble in excess (1) .
- Hydrochloric acid reacts with iron to form iron II chloride (1) .
- Concentrated hydrochloric acid is 35% pure with a density of 1.18g/cm3.Calculate its concentration in moles per litre. H=1, Cl= 35.5 (3mks)
- 1.18g x 1000cm 3 = 1180g per liter
1180/ 35% = 413g/l
molarity = 413/36.5
= 11.31M
- 1.18g x 1000cm 3 = 1180g per liter
- write one industrial use of hydrochloric acid (1mk)
- Etching of glass,
- explain the observation made when a moist blue flower is placed in a gas jar containing chlorine gas (2mks)
- blue flower will be bleached (1) chlorine gas forms chloric I acid and HCl when mixed with water. HOCl is reduced to HCl while the dye in the flower is oxidized to a colorless compound
- Identify Burning gas A (1mk)
- Study the flow chart below then answer the questions that follow.
- Draw and name two isomers of substance A (4mks)
- Name (3mks)
- process W
- hydrogenation
- process X
- cracking
- Reagent C
- sodium ethanoate
- process W
- Draw two repeated units of polymer D (2mks)
- Ethyne is a hydrocarbon belonging to the alkyne homologous family . Identify
- two reagents used to prepare ethyne in the laboratory (1mk)
- Calcium carbide and water
- Name the third member of this family (1mk)
- butyne
- two reagents used to prepare ethyne in the laboratory (1mk)
- Explain the observation made when ethyne is burned in air (2mks)
- Burns with a yellow sooty flame(1) because it has a high carbon to hydrogen ratio(1)
- Draw and name two isomers of substance A (4mks)
- Study the diagram below that shows some reactions of dry air, then answer the questions that follow.
- Identify; (2mks)
- Solid A Magnesium oxide
- Solid B Magnesium nitride
- Gas D hydrogen
- Gas Z ammonia
- Why is the amount of solid B obtained much less than solid A? (2mks)
- nitrogen is a stable gas and has three n-n triple bond that requires more energy to break
- Write a balanced equation for the reaction between solid B and water (1mk)
- Mg3N2 (s) + 6H2O(l) → 3Mg(OH)2(aq) + 2 NH3(g)
- Which gas is absorbed by sodium hydroxide in step I (1mk)
- Carbon (IV) oxide
- Gas Y obtained in step I is impure, Name one impurity it contains (1mk)
- argon, neon, helium dust particles penalize noble gases
- What name is given to the process that occur in step II (1mk)
- haber process
- 300 liters of ammonia are catalytically oxidized to form nitrogen II oxide which is further oxidized to nitric acid.
- write a balanced equation for the catalytic oxidation of ammonia (1mk)
- 4NH3(g) + 5O2(g) → 4NO(g) + 6H2O(g)
- which catalyst is used in this process (1mk)
- platinum
- determine the volume of the products in the above reaction (2mk)
- molar ratio 4:4(1)
- volume of NO = 300 liters, (½) volume of H2O =6/4 X300 = 450L(½)
- write a balanced equation for the catalytic oxidation of ammonia (1mk)
- Identify; (2mks)
-
- Define the term allotrope (1mk)
- Atoms of the same element existing in different forms in the same physical state
- Identify the two allotropes of sulphur (1mk)
- monoclinic (½) and Rhombic (½)
- In the extraction of sulphur three concentric pipes are sank into the ground 200 m away from the surface. Use a well labeled diagram to describe the above process (3mks)
- The table below shows some reactions of concentrated sulphuric VI acid. Study it and answer the questions that follow (2mks)
Reaction of sulphuric acid Observation Property of sulphuric acid being investigated Reaction with blue
copper sulphate crystals
Blue crystals form a white powderDehydrating Moist hydrogen gas is
bubbled in and collected
in a syringeHydrogen gas is collected dry Drying agent/ hygroscopic - 50 ml of dilute Sulphuric VI acid was placed in 3 separate beakers and the following substances were added as shown in the table below
Using relevant equations- Explain the observation in beaker B and beaker C (3mks)
- B reaction starts and then stops due to formation of a leadsulphate coating on the lead carbonate that stops further reaction (1)
- C blank copper oxide dissolves to form a blue solution of copper sulphate (1)
- H2SO4(aq) + CuO(s) → CuSO4(aq) + H2O(aq)(1)
- Magnesium powder in beaker A was replaced with silver powder. Explain the difference in the two reactions (3mks)
- Effervesce(½) as hydrogen gas(½) is produced when sulphuric VI acid reacts with Magnesium. Magnesium is above Hydrogen(½) in the reactivity series. No effervescence(½) when sulphuric VI acid reacts with silver
- H2SO4 (aq) + Mg (s) → MgSO4 (aq) + H2(g)
- Explain the observation in beaker B and beaker C (3mks)
- Define the term allotrope (1mk)
- A student was given water containing suspected to be hard
- What is hard water? (1mk)
- Water that does not lather easily with soap
- The sample was divided into three portions and the following tests were carried out and the following observations were made
- Identify the type of hardness in the above sample. Explain (2mks)
- Temporary hardness(1) is removed by boiling/ permanent harness is not removed by boiling (1)
- Write an equation for the formation of the white precipitate (1mk)
- Mg (HCO3)2 (aq) → MgCO3 (s) + H2O (l) + CO2(g) (1)
- Ammonia solution was added drop wise till excess in the third sample. A white precipitate was observed. Identify the cation present in the water. (1mk)
- Mg2+ ions are present
- Identify the type of hardness in the above sample. Explain (2mks)
- Write one advantage and one disadvantage of hard water (2mks)
- Advantage
- Good for bones and teeth because it contains useful Ca and Mg minerals /useful in brewing industry
- Disadvantage
- Forms scum when used for washing in soap
- Advantage
- Salt B has a solubility of 20g/100g of water at 40ºC. A solution containing 6g of salt B in 10ml of water is cooled to 40ºC. Calculate the amount of salt that crystalized out (2mks)
- 6g in 1oml of water = 60g/100g of water (1)
60-20 = 40g of salt B (1)
- 6g in 1oml of water = 60g/100g of water (1)
- A student was provided with Calcium carbonate, sodium hydrogen carbonate , zinc sulphate , ammonium nitrate and Aluminium chloride
Which salts- are Insoluble in water Calcium carbonate, (1mk)
- PENLIZE FULLY FOR CONTRADICTION
- forms a white precipitate which dissolves to form a colorless solution when dissolved in excess sodium hydroxide solution (1mk)
- Aluminium chloride,( ½ )zinc sulphate ,( ½) PENALIZE FULLY FOR CONTRADICTION
- write 2 ionic equations for the reaction between zinc sulphate and excess ammonia solution (2mks
- Zn +2 (aq) +2OH- (aq) Zn(OH)2 (s)
Zn(OH)2 (s) + 4NH3(aq) [Zn(NH3)4] +2 (aq) + 2OH-(aq) (1mk)
- What is hard water? (1mk)
- Use the table below to answer the following questions. Letters represent the most stable ion of elements in the periodic table
- Explain the trend in the ionic radius of P+ and W2+ and Y3+given that they are in the same period (2mks)
- Y3+ has the smallest ionic radius ,( ½) while P+ has the largest ,( ½) ecause ionic radius decreases across the period ,( ½) due to the high increase in the positive nuclear charge ,( ½)
- Element Q and R are in the same group.
- Identify the family name of the group to which they belong (1mk)
- halogens
- Which element is more electronegative? Explain (2mks)
- R(1) because it is above Q in the group/ has a smaller atomic radius than Q,( ½) R has higher ability to attract electrons ,( ½)
- Identify the family name of the group to which they belong (1mk)
- Given that ion P+ has electronic configuration 2, write the electronic configuration of element Z
- Z 2:8:1 (1mk)
- Write the formulae of the element formed when Y reacts with oxygen (1mk)
- Y2O3
- Using dot and cross diagrams show the bonding
- between P and chlorine (1mk)
- Two atoms of Q (1mk)
- between P and chlorine (1mk)
- Explain the trend in the ionic radius of P+ and W2+ and Y3+given that they are in the same period (2mks)
-
- Define the term heat of solution (1mk)
- Enthalpy change when one mole of a substance is dissolved in water to give an infinitely dilute solution
- In an experiment to determine the heat of solution 4.8g of ammonium nitrate were added to 100ml of water at 20ºC. The temperature dropped to 9ºC.
- Calculate the heat change in the above experiment given that C= 4.2 J/g/C (2mks)
- h= mct
100g x 4.2 x(20-9) = 4620J
(½) (½) (1)
- h= mct
- determine the molar heat of solution for the above reaction N=14, O=16 H=1 (2mks)
- NH4NO3 molar mass = 80g (1) 4.8g = 4620
80g= 77,000(½)
+77kJ/Mol (½)
- NH4NO3 molar mass = 80g (1) 4.8g = 4620
- determine the lattice energy of ammonium nitrate given that
Hydration energy is -12kJ/mol (2mks)- heat of solution = hydration energy + lattice energy(1)
77 = -12kJ +89kJ (1)
- heat of solution = hydration energy + lattice energy(1)
- Calculate the heat change in the above experiment given that C= 4.2 J/g/C (2mks)
- Ethanol has a heating value of 4.5kJ/g while methane has a heating value of 10kJ/g. Which of the two fuels has a higher molar heat of combustion C=12, H= 1, O=16 (2mks)
- C2H5OH = 46g. CH4 = 16g
4.5kJ= 1g 10kJ = 1g
207kJ/Mol 160kJ/Mol
- C2H5OH = 46g. CH4 = 16g
- Define the term heat of solution (1mk)
Download Chemistry Paper 2 Questions and Answers - MECS Cluster Joint Pre Mock Exams 2021/2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students