GEOGRAPHY
Paper 1
Instructions to the candidates
- This paper consists of two sections; A and B
- Answer all the questions in section A in the spaces provided after each question.
- In section B, answer question 6 and any other two questions.
- Candidates should answer the questions in English.

Questions
SECTION A (25 Marks)
Answer all the questions in this section in the spaces provided below each question
-
- Differentiate between rotation and revolution of the earth. (2 marks)
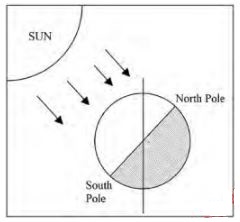
- The diagram below shows an effect of the rotation of the earth. Use it to answer the questions that follow.
- Identify the effect. (1 mark) .
- Other than the effect shown in the diagram, give two other effects of the rotation of the earth. (2 marks)
-
- Give three life cycles of a volcano. (3 marks) .
- State three characteristics of a composite cone . (3 marks)
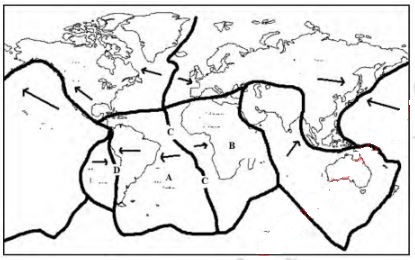
- The diagram below shows major plate boundaries of the world. Use it to answer the questions that follow.
- Identify the plates marked A and B. (2 marks) A: B:
- Name the boundaries labeled C and D. (2 marks) C: D:
-
- Give three conditions that favour the growth of coral polyps. (3 marks) .
- State two importance of emerged coasts. (2 marks)
-
- Define a local climate. (2 marks)
- State three characteristics of equatorial climate. (3 marks)
SECTION B (75 Marks)
Answer question 6 and any other two questions in this section
- Study the map of Kijabe (Sheet 134/3 and Scale 1: 50,000) provided and answer the questions that follow.
-
- Give two scales used in the map of Kijabe. (2 marks)
- Name three physical features found in grid square 2699 (3 marks)
-
- Measure the distance of the dry weather road in the north-western edge of the mapped area.. Give your answer in kilometres (2 marks)
- Give the approximate position of Kijabe Station in terms of latitudes and longitudes. (2 marks) .
-
- State two evidences that show the area covered by the map receives high rainfall (2 marks) .
- Give two social functions of the mapped area. (2 marks) . .
- Measure the bearing of the trigonometrical station SKP 209 (in grid square 3793) from the point (10 00’ South, 360 45’ East) (2 marks)
-
- Draw a frame measuring 14 cm by 10 cm to represent the area bound by Eastings 30 to 37 and Northings 90 to 95 (2 marks)
- On the frame, mark and label:
- Thicket vegetation (1 mark)
- All weather road bound surface (C 68) (1 mark)
- Citing evidence from the map, explain three factors that influence coffee farming in the area covered by the Kijabe map. (6 marks)
-
-
-
- Name two areas in East Africa with glaciers (2 marks)
- Give two processes of glacial movements (2 marks)
- Explain how the following factors influence glacial erosion
- Presence of debris (2 marks)
- Nature of underlying rocks (2 marks)
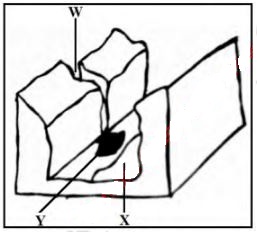
- The diagram below shows features resulting from glacial erosion in highland areas. Use it to answer the questions that follow.
- Name the parts labeled W and Y. (2 marks) (ii) Describe how the feature marked X forms. (4 marks)
- Explain three ways in which glaciation influences agriculture. (6 marks)
- Members of your class plan to conduct a field study on glaciated lowland area.
- State two reasons why they would likely use observation as a method of data collection. (2 marks)
- Name three features of glacial deposition they are likely to observe during the study. (3 marks)
-
-
-
- Other than lakes, seas and rivers, give two other sources of underground water. (2 marks)
- Name two ways in which underground water may reach the surface of the earth. (2 marks)
- State four importance of underground water (4 marks)
-
- Give three conditions necessary for development of karst scenery (3 marks)
- State three reasons for few settlements in karst landscape (3 marks)
-
- Draw a well labeled diagram of a limestone cave. (2 marks)
- On the diagram, mark and name the following features:
- Stalagmite (1 mark)
- Limestone rock (1 mark)
- Describe the formation of the following features:
- Limestone Cavern (3 marks)
- Uvalas (4 marks)
-
-
-
- Define the term faulting (2 marks)
- Name four main parts of a fault (4 marks)
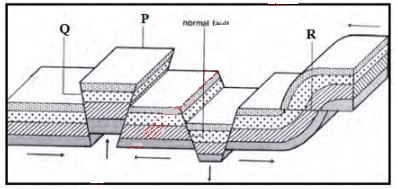
- The figures below show some types of faults. Use them to answer the questions that follow
- Name two examples in East Africa of the feature labeled P. (2 marks)
- Identify the fault types marked Q and R (2 marks)
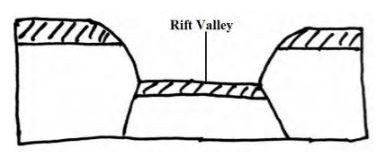
- With the aid of clearly labeled diagrams, describe the formation of a Rift Valley through the compressional forces. (7 marks)
- Members of your class plan to conduct a field study on the section of the Gregory Rift Valley.
- Give two ways in which they would prepare for the study. (2 marks)
- State three characteristics of the Great Rift Valley they are likely to observe during the study. (3 marks)
- State three ways in which faulting may affect drainage. (3 marks)
-
-
-
- Differentiate between a lake and a river (2 marks)
- Name two sources of rivers in Kenya. (2 marks)
- State three reasons why some lakes may contain saline water (3 marks)
-
- Describe the formation of an oasis. (5 marks)
- Give three examples of lakes formed due to faulting in Kenya. (3 marks)
- Describe the following drainage systems
- Superimposed (3 marks)
- Concordant (1 mark)
- Explain three economic significance of rivers. (6 marks)
-

Marking Scheme
-
- Rotation is the spinning of the earth around an axis while revolution of the earth is the movement of the earth around the sun
-
- Day and night
-
- Time difference of 1 hour between meridians that are 15° apart
- Rise and fall of ocean tides
- Deflections of winds and ocean currents
-
-
- - Pacific
- - African
-
- C- constructive
- Destructive
-
-
-
- Active
- Dormant
- Extinct
-
- It has a depression/crater/caldera at the top
- Has subsidiary cones/conelets
- Has alternating layers of lava and pyroclastic materials
- It is steep sided
- It has a side vent
- It has a conical shape
- It consists of a vertical vent
-
-
-
- Temperature of 25°C to 29°C and should never fall below 20°C for proper growth
- The polyps must be submerged in the ocean
- Water must be clear and salty
- The waters must be shallow
- Absence of moving wave and tidal load
-
- Provides land for settlement
- Exposition of features for tourist attraction
-
-
-
- These are climates that are experienced in the immediate surroundings of some phenomena on the earth's surface
-
- Temperatures are high throughout the year 24°C - 27°C
- Small annual range of temeprature 3°C - 5°C
- Moderate diurnal range of temeparture 8°C
- Thick cloud cover
- High rainfall throughout the year/ mean annual rainfall exceeds 1500mm
- Rainfall is mainly convectional
- Rainfall regime is double
- High relative humidity throughout the year
- Atmospheric pressure is relatively low even at sea level
-
-
-
-
- Ratio/ representative fraction scale
- Linear scale
-
- Kijabe hill
- Steep slopes
- Scrub vegetation
-
-
-
- 8.5km ± 0.1km
-
- 0° 55' south, 36° 35' East
-
-
-
- Presence of coffee plantation
- Presence of many permanent rivers
- Presence of a forest on the eatern parts of the map
-
- Education - presence of many schools
- Healthcare provision- dispensary in grid square 3790, Kijabe hospital in grid square 3295
- Religion- a church grid square 3890
-
-
-
- Thicket vegetation
- All weather road bound surface (C68)
- 308° ± 1°
-
- Highlands/ areas of high relief evidenced by forests to the eastern parts of the map, ideal for coffee growing
- High rainfall evidenced by forests, many permanent river that ensure enough water supply during the growing
- Shelter of young coffee trees from dirtect sunlight evidenced by the forests
- Undulating/gently rolling topography evidenced by widely spaced contours to ensure the soils are well drained.
-
-
-
-
- Mt. Kenya
- Mt. Elgon
- Mt. Kilimanjaro
-
- Plastic flowage
- Basal slip
- Extrussion flow
-
-
-
- The more the debris embedded in the glacier the more effective is abrasion process
-
- Well jointed/ faulted rocks are easily eroded by plucking since the joints allow water to enter the rock. Less resistant rocks are eroded faster by abrasion compared to more resistant rocks.
-
-
-
- W- Hanging valley
Y- alluvial fan
- W- Hanging valley
-
- They start occurring when a pre-existing river valley is filled with ice/glacier
- As glacier moves downstream, tributary glaciers increase the amount of ice in the main valley
- Glacier erodes the main valley by plucking and abrasion
- Interlocking spurs in the main valley trimmed into truncated spurs
- Continued glacial erosion depens, widens and straightens the main valley floor forming a U-shaped or glacial trough.
-
-
- Areas uner glaciation may experience permafrost condition that are less ideal for plant growth.
- Some glacial features eg outwash plains, tills and old glacial beds may contain fertile soils that favour growth of crops and pasture for livestock
- Some outwash plains may contain infertile sandy soils that hindert agricultural practices.
- Glaciation may lead to rugged landscape that discourages agricultural activities.
-
-
- It gives first hand/ real time information
- It saves time during the field study
- It is cheap/ less expensive
- Data collected by observation is reliable.
-
- Erratics
- Boulder trains
- Kames
- Eskers
- Drumlins
- Terminal moraines
- Outwash plains
-
-
-
-
-
- Magmatic/ plutonic
- Water from snow melt
- Rain water
-
- As springs
- Capillary action
- Wells drilled in to the water table
-
-
- Springs are sources of many rivers that provides water for domestic, industrial and irrigation.
- Wells, boreholes, oases also provide water for domestic and industrial uses
- A line of springs at the foot of an escarpment can attract escarpment
- Valuable minerals salts may be deposited at the mouth of hot springs and mined to earn revenue, create employment opportunities.
- In areas under volcanic influence, underground water is heated to form geysers and hot springs that are sources of geothermal energy and tourists attractions- earn foreign exchange.
-
-
- Soluble rocks at the surface and below
- Rock well jointed
- Resistant rocks
- Hot and humid climate
- Water table deep below the surface.
- The areas are rocky/ have a rugged surface that discourages settlement and agriculture
- They have thin soils that are less ideal for growth of crops
- There is inadequate water supply/ lack adequate water supply.
-
-
-
- Stalagmite
- Limestock rock
-
-
- Carbonation and solution process along the joints of limestone rock leads to formation of a tunnel
- Continued solution enlarges the tunnel to form a cave
- The process of cave formation may continue, widening and deepening the existing cave to form cavern
-
- River or rain water disappear into the ground through joints in the rock
- The water widens and deepens the joints through solution leading to the development of a vertical hole/ shaft called a sink or swallow hole.
- The swallow hole is widened through continued solution until the rock blocks between the hollows are completely dissolved to form a doline
- Continued solution dissolve the rock blocks between dolines leading to their collapse or merger to form uvalas
-
-
-
-
-
- Breaking / cracking/ fracturing of crustal rock due to tectonic forces
-
- Upthrow
- Downthrow
- Fault scarp
- Throw
- Heave
- Hade
-
-
-
- Pare
- Usambara
- Ruwenzori
- Matthews Range
- Ndoto hills
- Nyiru Hills
-
- Q- thrust
R- reversed
- Q- thrust
-
-
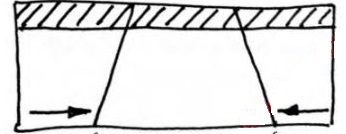
- When sections of crustal rocks are subjected to forces of compression, lines of weakness occur and leads to development of adjacent reversed faults
- Continued compression pushes the outer blocks towards each other and as a result, they thrust/ rise over/ above the central block to form the rift valley floor
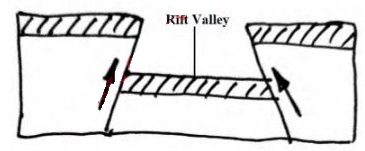
- The steep fault scarp on either side of the outer blocks are further worn out by denudation to form gentle slopes
- When sections of crustal rocks are subjected to forces of compression, lines of weakness occur and leads to development of adjacent reversed faults
-
-
- Seeking permission from school adminitration and local administration
- Conducting a reconnaissance
- Indentification of data collection techniques/ equipment
- Heights of the fault scarps vary
- Major fault scarps here include Elgeyo, Mau, Laikipia, Nyandarua and Nguruman
- Step faulting is common within this.
- The width of the rift valley varies
- The height of the valley floor also varies
- Volcanic activity on the floor of this rift
- Unequal subsidence has created shallow basins, some occupied by lakes
-
-
- Faulting along a river may make the river change/ reverse its direction of flow.
- It may lead to a back tilted drainage system
- It may make a river to completely disappear
- It may make the river to flow along the fault line/ fault guided drainage pattern
- faulting may lead to formation of depressions in which water may collect to form lakes
- Step faulting along a river course may lead to dvelopment of waterfalls.
-
-
-
- A lake is a water body that occupies a depression/ hollow/basin on earth's surface where as a river is a body of water flowing in a valley( along a natural channel) from an upland area towards the lowland.
-
- Forests e.g Mau
- Mountains eg, Mt. Kenya, Mt. Elgon
- Springs
-
- Absence/lack of out-flowing rivers/ outlets to drain out excess salts
- Some lakes lack enough fresh water rivers that drain into them.
- Some rivers empty into the lakes or are fed by underground water that may contain high concentration of salt.
- Some lakes are located in arid areas with very high rate of evaporation which leads to increased concentration and accumulation of dissolved mineral slats in the lake.
- The bed of the lkae may comprise of soluble rock with mineral salts which dissolve in the lake water.
- Surface run-off and rivers may dissolve a lot of salt from the rocks on which they flow.
-
-
- Physical weathering and abrasion in arid areas result in large scale production of unconsoloidated materials of dust and sand particles.
- The loose materials are then scooped/ removed by wind through deflation to form a shallow depression/basin.
- Continued abrasion and deflation in the depression over time widens and deepens the depression to form a deflation hollow.
- Wind eddies may remove unconsolidated materials from the deflation hollow through deflation.
- If the surface of the deflation hollow is lowered until it reaches the water bearing rocks/aquifier/ water table, water oozes out of the ground and collects in the deflation hollow to form an oasis.
-
- Turkana
- Bogoria
- Baringo
- Nakuru
- Naivasha
- Elementaita
- magadi
-
-
- Superimposed
- If a river flows over the rocks it is down cutting. These rocks are removed through erosion.
- The river begins to flow over a new set of rocks of a different structure that are older.
- The river maintains its original direction of flow without being influenced by the newly exposed rock structure.
-
- The river flows according to the rock structure and slope by following less resistant rocks.
- Superimposed
-
- Rivers provide water used for domestic, industrial and irrigation purposes.
- Some rivers especially uin their older stage form natural waterways that can be used for transport.
- Drowned or submerged river mouths form rias/ fjords that are deep and well sheltered thus facilitate development of ports
- Some rivers are rich fishing around hence source of food.
- Gravel and sand harvested from river banks are used for building and construction purposes.
- Some river deposits contain alluvial soils with valuable mineral that can be mined for sale.
- Features formed by rivers (waterfalls, gorges, meanders) are tourist attraction hence earning foreign revenue.
- Some rivers provide sites for development of hydroelectric power stations and projects.
- River deposit fertile alluvia; soil good for cultivation.
-
Download Geography Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Maranda Mocks 2022 Exams.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students