Instructions to candidates
- Write your name, index number, school and stream in the spaces provided above.
- Sign and write the date of examination in the spaces provided above.
- Answer ALL the questions in the spaces provided in the question paper
- Marks are given for clear record of the observations actually made, their suitability, accuracy and the use made of them.
- Candidates are advised to record their observations as soon as they are made
- Silent non-programmable electronic calculators may be used.
SECTION A (25 MARKS)
Answer ALL the questions in this section in the spaces provided
- State one major difference between a primary cell and a secondary cell (1mk)
- A bar magnet was placed in Petri dish and made to float on water in a metallic dish placed in a strong magnetic field as shown below:- (1mk)
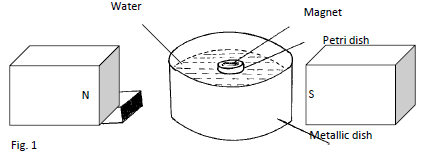
State the direction in which the small bar magnet in the Petri dish will rest. - A positively charged rod is brought near the cap of a lightly charged electroscope.
The leaf divergence first reduces and as the rod comes nearer, it diverges more.
State the charge on the electroscope (1mk) - Explain the behaviour of the leaf in Q3 above. (2mks)
- An object 10cm high is placed 30cm in front of a concave mirror. The image is 45cm in front of the mirror. Determine its magnification and size of the image. (3mks)
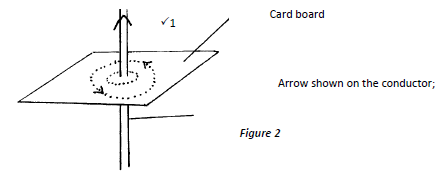
- Fig 2 below, shows magnetic field around a current carrying conductor.
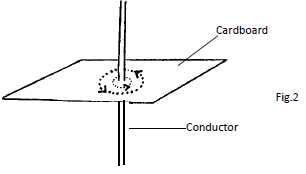
Indicate on the diagram the direction of the current (1mk) - Briefly explain how a p-type semiconductor is formed (2mks)
- Determine the effective capacitance of the following circuit. (2mks)
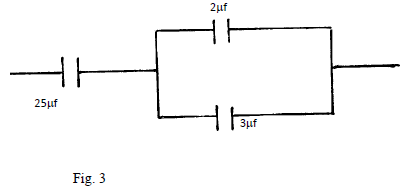
- A transformer of 480 turns in the primary coil is used to connect a 9.0 volt a.c. electric device to a 240V a.c mains supply. Determine the number of turns in the secondary coil. (2mks)
- State two uses of infrared radiation. (2mks)
- A house has a lighting circuit operated from a 240 Volts mains supply. Three bulbs rated 100W 240V, ten bulbs rated 40W 240V and eight bulbs rated 60W 240V are switched on at the same time. Determine the most suitable fuse for this circuit. (3mks)
- An object is placed 20cm in front of a concave lens of focal length 15cm. State two characteristics of the image formed. (2mks)
- A ray of light is incident on the surface of water at an angle as shown in figure 4 below.
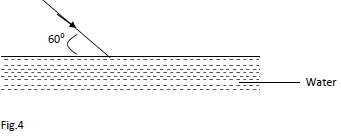
Determine the angle through which it emerges on the water surface. (Take refractive index of water = 4/3) (3mks)
SECTION B (55 MARKS)
Answer ALL questions in this section in the spaces provided.
-
- Fig 5 shows plane waves in a ripple tank. The water is deeper in section A & C than in section B.
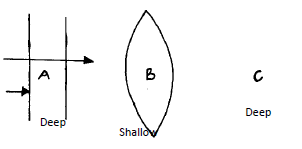
Draw the waves after passing section B. (2mks) - State two conditions necessary for production of interference. (2mks)
- A tube is closed at one end. It is in resonance with a tuning fork of frequency 256Hz sounded above the open end. Given that the velocity of sound in air is 334m/s determine the wavelength of the wave generated by the tuning fork (2mks)
- State two factors affecting the velocity of sound in air. (2mks)
- Fig 5 shows plane waves in a ripple tank. The water is deeper in section A & C than in section B.
-
-
- State what is meant by photoelectric effect. (1mk)
-
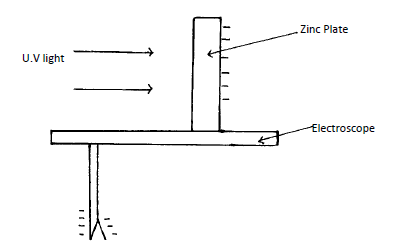
- You are provided with highly polished Zinc Plate, electroscope, source of ultra – Violet rays, and materials for charging the electroscope. Draw a set up of the apparatus to show how photoelectric effect may be demonstrated in a laboratory. (2mks)
- Explain how the set up can be used to determine the nature of photoemission taking place. (3mks)
-
- State two factors that affect photo- electric emission. (2mks)
- When a certain photoelectric surface is illuminated with light of different frequencies, the corresponding stopping potential was measured.
The graph below shows how frequency (f) varies with stopping potential, Vs.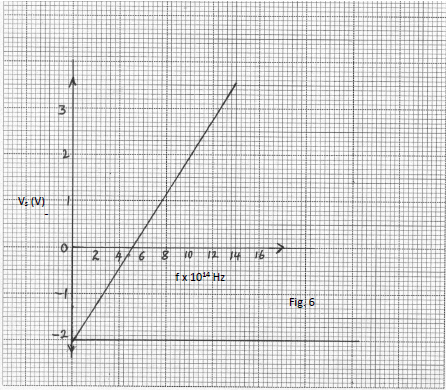
Given that eVs = hf - ø, determine the values of h and ø from the graph. (5mks)
(electronic charge = 1.6 x 10-19C)
-
- The current in a wire varied with voltage as shown in the following table.
Voltages(V) 1.05 1.40 1.80 2.20 2.60 Current (mA) 150 200 250 300 350 - Plot a graph of V against current. (5mks)
- From your graph, determine the resistance of the wire. (3mks)
- Plot a graph of V against current. (5mks)
-
- A radio active element has an initial count rate of 3200 counts per minute on a scaler.
The count rate falls to 200 counts per minute in 4 hours.- Determine the half – life of the element. (2mks)
- If the initial number of atoms in another sample of the same element is 4.0 x 1023, how many atoms will have decayed in 30hrs. (3mks)
- What are the values of m and n in the nuclear equation given below. (2mks)
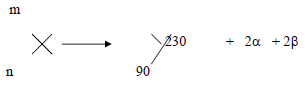 m = _____________________________________________________
m = _____________________________________________________
n = _____________________________________________________ - Fig. 6 below shows an expansion cloud chamber.
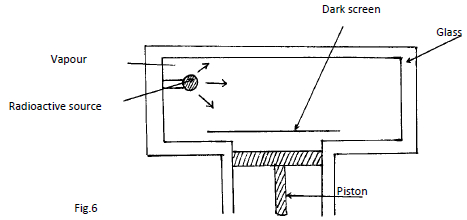
- State the purpose of the vapour. (1mk)
- Explain how the radiations emitted by the radioactive source in the chamber are detected (4mks)
- A radio active element has an initial count rate of 3200 counts per minute on a scaler.
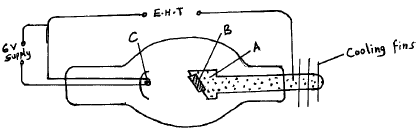
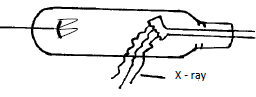
- Fig 7 shows the structure and circuit of a modern x-ray tube.
-
- Show on the diagram, the path of x-rays produced. (1mk)
- Name and state the use of the parts marked A, B & C; (6mks)
- Briefly describe how the tube produces the x-rays. (3mks)
- State how the setting of the tube would be done to facilitate:
- production of x –rays with higher penetration ability. (1mk)
- production of x-rays in larger quantity. (1mk)
- State energy changes that occur in the tube during x-ray production. (1mk)
- State the reason why it is necessary to evacuate the tube. (1mk)
-

MARKING SCHEME
SECTION A
-
- Secondary cells are renewed/re-charged whereas primary cells are not;
- Secondary cells generate higher electromotive force than primary cells;
- Earth’s North – South direction
- Negatively charged
- Few –ve charges are attracted at the cap; More –ve charges are attracted to the cap inducing positive charge on leaf and plate hence more divergence.;
- Mag = v/u;
= 45/30 ;
= 1.5
But hi/ho = mag hi/10 = 1.5
hi = 15cm
hi = 0.15m; -
-
- doping tetravalent element with trivalent element;
- During the bonding there is a deficit of electron – hole
- 1/25 + 1/(2 +3) = 1/25 + 1/5
1/C = 1 + 5/25
1/C = 6/25
= 4.167μF; - Np = Vp;
Ns Vs
Ns = 480 x 9; = 18;
240 -
- (infra-red) Photography;
- Heat sensors ( thermocouple detectors, bolo meter and heat seeking missiles );
- cooking
- heating
- (to warm) green houses ( any 2)
- P = VI
I = P/V
= 3 x 100 + 10 x 40 + 8 x 60
240 240 240
= 1.25 + 1.667 + 2.0
= 4.917 A
Suitable fuse in circuit = 5 A fuse; -
- Virtual;
- Upright;
- Diminished (Any 2)
- Sin i = 4 ;
Sin r 3
Sin 30 = 4 ;
Sin r 3
¾ x 0.5 = Sin r
r = 22.02º
SECTION B
-
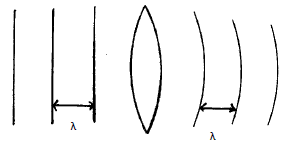 Shape ;
Shape ;
Same wavelength;-
- Constant phase difference / same C frequency ;
- Approximately same amplitude
-
- V = fλ
λ = v/f
= 334/256
= 1.305m -
- Temperature ; (Any two correct)
- Direction of wind
- Humidity
- V = fλ
-
-
- Emission of electrons from a surface when irradiated with radiation of sufficient frequency;
-
 Workability of set up
Workability of set up
Labelling- Irradiate the Zinc plate with uv light ; Electrons are ejected and hence leaf diverge reduces.
Nature of emission is thus electrons
-
-
- Work function of metal ;
- Freq. of radiation ;
- h = grad x e;
h = ( 3.6 – 0); x -1.6 x 10-19;
(14 – 5.2) x 1014
h = 6.545 x 10-34;
ø/e = y – intercepts ;
ø = -2.1 x -1.6 x 10-19
= 3.36 x 10-19 J
h = Grad; xe
Extract;
Subst ;
Ans;
Ø = extract;
-
-
-
-
- Both axes labelled with appropriate units;
- Simple and uniform scale;
- Correctly plotted point ½ mark each maximum of 4 points
- straight line with positive gradient passing through at least 3 correctly plotted points
TOTAL = 5MKS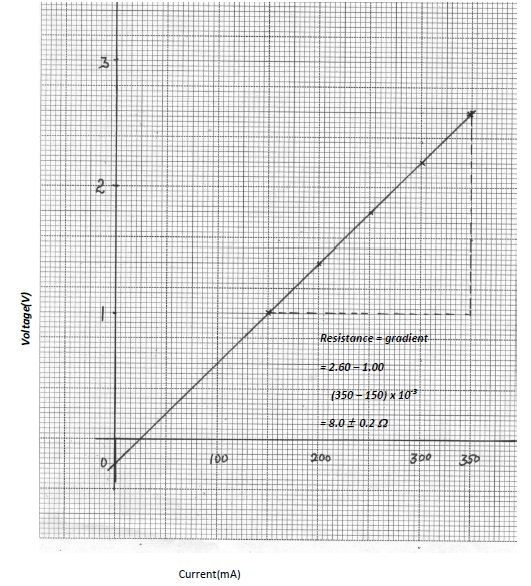
- Resistance = slope of Graph ;
= 2.2 – 1.4
0.3 – 0.2
= 8Ω;
-
-
-
- 3200x ½ x ½ x ½x ½ = 400;
:half life = 40/4 hrs
= 10hrs: - NO half – lifes = 30/10 or 3 half lives ;
No. undecayed = ½ x ½ x ½ x 4.0x 1023
= 0.5x1023
= 5.0x 1022 atoms
No decayed = ( 4.0 - 0.5) x 1023
= 3.5 x 1023
- 3200x ½ x ½ x ½x ½ = 400;
- m = 238;
n = 92; -
- They condense on air ions caused by radiations at low temperature
- Piston is moved down suddenly making air to expand suddenly too and thus causing cooling 1at low temperature vapour is saturated radiation ionizes airy and ionized air act as nuclei on which the vapour condenses forming tracks,
-
-
-
-
-
- Copper anode; conduct heat away from target;
- Tungsten or molybdenum ( or hard target); stops fast moving electronic in a short time;
- Concave focusing cathode;
Focus electrons onto target B;
-
-
- Cathode is heated electrically to emits electrons;
- E.H.T between anode and cathode accelerate electrons to very high speed;
- Fast moving electrons bombard hard target and x – rays are produced;
-
- Increase accelerating potential;
- Increase cathode current;
- Electrical energy ; heat energy K.e x-rays Heat (filament cathode)
Any two correct - To minimize possible loss of electron energy by collision with air particles;
-
Download Physics Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Butere Mock Exams 2021.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students

