QUESTIONS
-
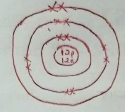
- Draw a labelled diagram showing the atomic structure of 2412 mg. (2 marks)
- The atomic number of phosphorus is 15. Draw a dot (•) and cross (x) diagram for the compound formed when phosphorus reacts with chlorine, atomic number 17. (1 mark)
-
- State the condition under which a Bunsen burner produces a luminous flame. (1 mark)
- Write an equation for the reaction that takes place in a luminous flame assuming the laboratory gas is butane. (1 mark)
- One of the regions in the non-luminous flame is the unburnt gas region. Describe how the presence of this region can be shown using a wooden splint. (1 mark)
-
- The elements sodium, magnesium and aluminium belong to group I, II and III respectively. Select the element with the highest electrical conductivity and give a reason. (1 mark)
- Complete Table 1 to show the products of electrolysis for concentrated sodium chloride and molten sodium chloride.
Table 1
(2 marks)Compound Anode Cathode Concentrated sodium chloride Molten sodium chloride
- A small piece of sodium metal was placed in a beaker containing pure water revision.
- State two observations made during the reaction. (1 mark)
- State and explain another observation made when a drop of phenolphthalein is added to the mixture in the beaker. (1 mark)
- Explain why it is not advisable to carry out this experiment using potassium metal. (1 mark)
- Describe how a pure sample of copper(II) nitrate crystals can be prepared using recycled copper wire. (3 marks)
- The following apparatus and chemicals are used to investigate the percentage of air used when iron rusts: iron filings, 100 ml measuring cylinder, trough and water.
- Draw a setup of the experiment. (2 marks)
- Write an expression to show how the percentage of air used is calculated at the end of the experiment (1 mark)
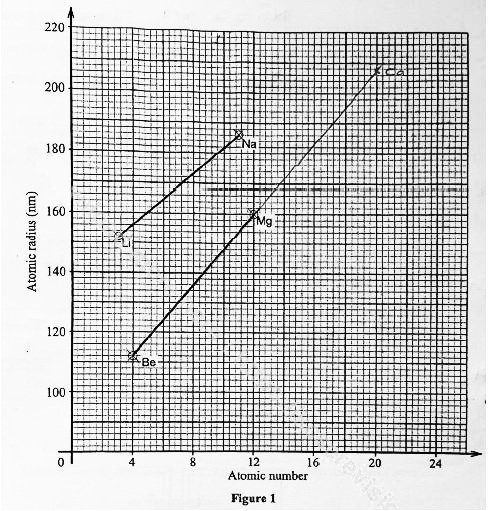
- Figure I shows a graph of atomic radius of some group I and group II elements.
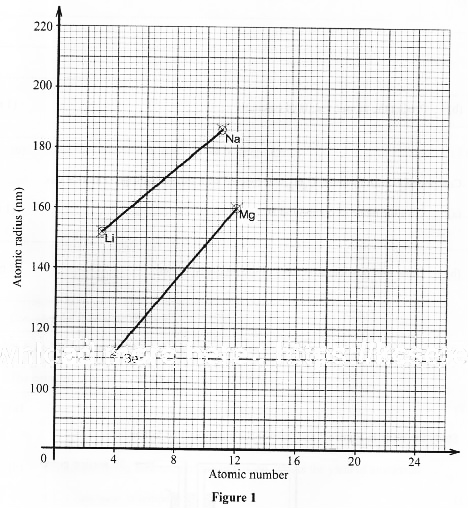
- Explain why the atomic radius of sodium is higher than that of:
- lithium (1 mark)
- magnesium (1 mark)
- Predict the atomic radius of calcium. (1 mark)
- Explain why the atomic radius of sodium is higher than that of:
- Compound D with formula, C3H4 was reacted with excess hydrogen chloride gas.
- Give the name of compound D. (1 mark)
- Draw two possible structures of the products formed. (2 marks)
- Study the setup in Figure 2 and answer the questions that follow.
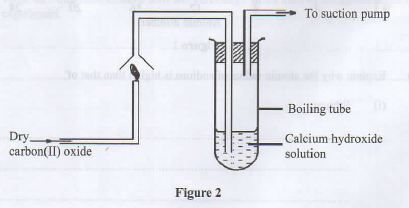
- State the precaution that should be taken in carrying out the experiment. Give a reason. (1 mark)
- State the observations made in the boiling tube. (2 marks)
- Consider the following reaction:
N2(g) + 3H2(g) ⇌ 2NH3(g)
The enthalpy change is 92.4 kJ per mole of nitrogen.- Give the enthalpy change per mole of ammonia. (1 mark)
- State and explain how each of the following affects the yield of ammonia:
- Increase in temperature. (1 mark)
- Finely divided iron. (1 mark)
- Study the flow chart in Figure 3 and answer the questions that follow.
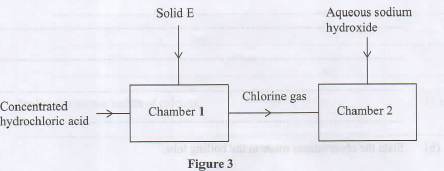
- Identify solid E. (1 mark)
- Name the type of reaction that takes place in chamber 1. (1 mark)
- Write an equation for the reaction that takes place in chamber 2. (1 mark)
- Compounds H and J have the following structures.
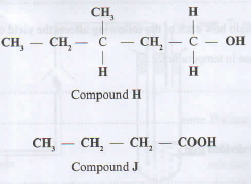
- Give the names of:
- Compound H. (1 mark)
- Compound J. (1 mark)
- State the conditions necessary for H and J to react. (1 mark)
- Give the names of:
- Rhombic sulphur is one of the allotropes of sulphur
- Draw the structure of rhombic sulphur. (1 mark)
- Describe the observations made when rhombic sulphur is heated from room temperature until it boils. (1 mark)
- The molar enthalpy of solution for potassium sulphate (K,SO) is +23.8 kJ.
- On the axes provided, draw a labelled energy level diagram for the dissolution process of potassium sulphate in water. (2 marks)

- Calculate the enthalpy change when 5:12 gof potassium sulphate is completely dissolved in water (K = 39:0;5=32,0; 0 - 16.0)(1 mark)
- On the axes provided, draw a labelled energy level diagram for the dissolution process of potassium sulphate in water. (2 marks)
-
- State Gay-Lussac's law. (1 mark)
- 180 cm3 of nitrogen(II) oxide gas was reacted with 400 cm3 of oxygen gas.
- Write an equation for the reaction. (1 mark)
- Calculate the total volume of the gases at the end of the reaction. (3 marks)
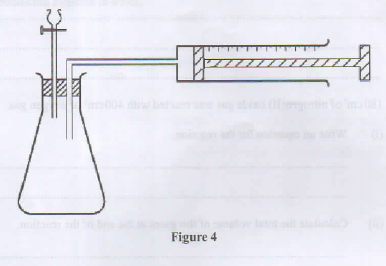
- Describe how the setup in Figure 4 can be used to distinguish between 50.0 cm of 0.2M hydrochloric acid and 50.0 cm of 0.2 M ethanoic acid using pieces of 6 m length of magnesium ribbon and a stop watch. (3 marks)
- Describe how dilute nitrie(V) acid and blue litmus papers can be used to distinguish between solid samples of sodium carbonate and sodium sulphite. (3 marks)
-
- Describe how propanone can be used to extract a pure sample of sunflower oil. (2 marks)
- State why sodium hydroxide solution is not suitable for the extraction of sunflower oil. (1 mark)
- 31.5 cm3 of concentrated nitric(V) acid was diluted to 500 cm3. 10.0 cm3 of the dilute acid required 25.0 cm3 of 0.4M sodium hydroxide for neutralisation.
- Calculate concentration of the:
- dilute acid. (1 mark)
- concentrated acid. (1 mark)
- Calculate concentration of the:
- Figure 5 shows part of a radioactive decay series.
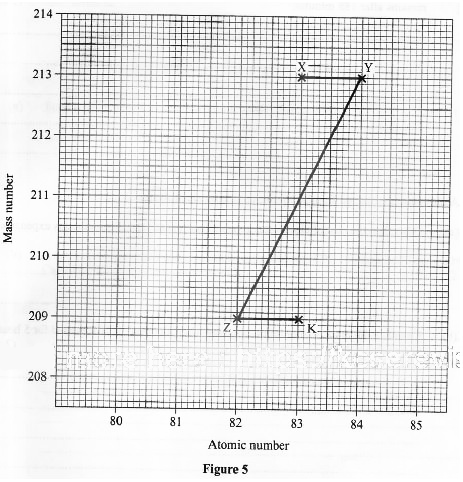
- Write a nuclear equation for the formation of nuclide K from nuclide X. (1 mark)
- The half-life of nuclide X is 47 minutes. Determine the percentage of nuclide X that remains after 188 minutes. (2 marks)
- Aluminium is extracted from aluminium oxide by electrolysis.
- Other than the cost of electricity, give another reason why this method is expensive. (1 mark)
- Calculate the mass of aluminium obtained when a current of 20A is used for 5 hours.
(1 Faraday - 96500 C; Al - 27.0)(2 marks)
- Explain each of the following observations:
- Articles made of copper turn green when left exposed in air over a long period of time. (1 mark)
- Addition of aqueous ammonia to a solution containing copper(II)ions produces a deep blue solution (1 mark)
-
- State what is meant by relative atomic mass of an element. (1 mark)
- A compound of carbon and element X with formula, CX, contains 3.6% carbon by mass. Calculate the relative atomic mass of X. (2 marks)
- Carbon(II) oxide can be prepared by dehydration of ethanedioic acid
- Complete the following equation to show the reaction that takes place. (1 mark)
H20204 - Name another reagent that can be used to prepare carbon(II) oxide by dehydration (1 mark)
- Complete the following equation to show the reaction that takes place. (1 mark)
- Figure 6 shows an incomplete diagram of a setup for laboratory preparation of nitrogen gas.
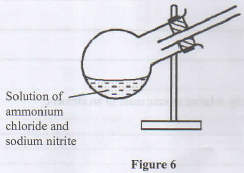
- Complete the setup in Figure 6 to show how nitrogen gas can be collected. (2 marks)
- The nitrogen prepared using this setup is purer than that obtained from air. Give a reason. (1 mark)
- Hydrazine, is used as a fuel in rockets. Using the bond energies in Table 2, calculate the enthalpy change for combustion of hydrazine.
N2H4 (1) +02(g) → N2(g) + 2H2O(g)
Table 2
(3 marks)Bond Bond Energy kJ/mol N-H 388 N-N 163 O=O 496 N≡N 944 O-H 463 -
- Table 3 gives the standard reduction potentials of some group VII elements.
Table 3
State and explain the reactions that take place when aqueous bromine is added to a sample of sea water containing both chloride and iodide ions. (2 marks)Reduction equations Eº/V CI2 + 2e→2CI- +1.36 Br2 +2e→2Br- +1.07 I2 + 2e→21- +0.54 - Give a reason why potassium iodide is added to table salt
- Table 3 gives the standard reduction potentials of some group VII elements.

MARKING SCHEME
-
-
Nuclear composition
12p
12n
Electrons
OR
3energy levels
Nuclear with occupied protons and neutrons 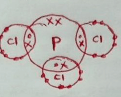
1 or 0
Use of only dots or crosses (penalise fully)
-
-
- When airhole/collar is closed or fully closed
- CH4(g) + 4O2(g) → C(s) + 3CO(g) + CO(g) +5H2O(I)
OR
CH4(g) + 4O2(g) → C(s) + CO(g) + CO(g) +5H2O(I) - Slip a wooden splint across the middle part of the flame. The central part remains unburnt / uncharred while the outer part burns
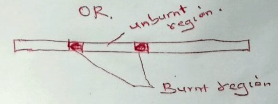
-
- Aluminium
It has 3 delocalised electrons while sodium and magnesium has one and two respectively -
Compound Anode Cathode Concentrated sodium chloride Chlorine or CL2 Hydrogen H2 Molten sodium chloride Chlorine or CL2 Sodium Na
- Aluminium
-
-
- The piece of metal darts/floats
- Melts into silvery ball
- Production of effervescence/hissing sound
- The beaker becomes warm
- Solution turns pink because sodium hydroxide/alkaline solution is formed
- Potassium reacts explosively with water/ more vigorously/ more violent
-
-
- Heat the copper wire in air to form copper
- Add excess copper(II) oxide to dilute nitric acid
- Filter to remove unreacted copper(II) oxide
- Heat the resulting solution to saturation
- Allow it to cool to form crystals
- Dry/filter the crystals
-
-
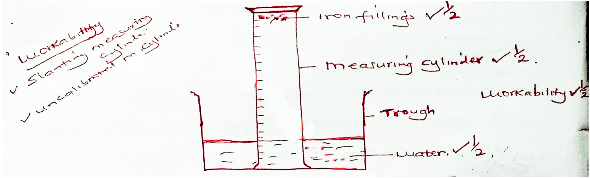
- Initial height of air column - Final height of air column
Initial height of air column
OR
Initial height of water - Final height of water
Initial height of water
-
-
-
- Na = 2.8.1
Li = 2.1
Sodium has 3 energy levels while lithium has two
or
Li = 2
Na = 2.8.1 - Mg = 2.8.2
Na = 2.8.1
The effective nuclear charge is higher in magnesium than sodium. Mg has a higher number of protons
- Na = 2.8.1
- 208± 2
Ithout showing on the graph
Extrapolate to 20 on x-axis and mark to value
-
-
- Propyne
prop 1 -yne
prop -1,2-iodene - ,,
- Propyne
-
- The experiment should be carried out in a fume chamber out in open since carbon(II) oxide is poisonous
- A white percipitate is formed which dissolves to form a colourless solution
-
- - 92.4 ⇒ =46.2 KJmol-1
2 -
- It lowers the yield of ammonia since the forward reaction is exothermic or backward reaction is endothermic
- No effect
A catalyst has no effect on the position of the equilibrium
- - 92.4 ⇒ =46.2 KJmol-1
-
- Potassium magnate VII or maganese(iv) oxide lead(vi) oxide
- Red ox/oxidation
- CI2(g) + 2NaOH → NaCl(aq) + NaOCl(aq) + H2O
-
-
- 3-methylpentanol/ 3-methylpentanol
- Butanoic acid
-
- Concentrated sulphuric VI acid/ sulphuric acid
- Warm/heat/ temperature between 3-6ºC
-
-
-
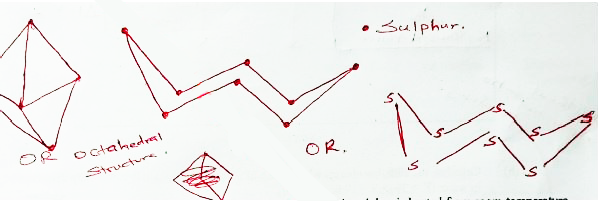
- Yellow solid forms amber liquid
As the temperature increases the liquid becomes darker and vicious
Then it turns dark red/brown and less vicious
-
-
-
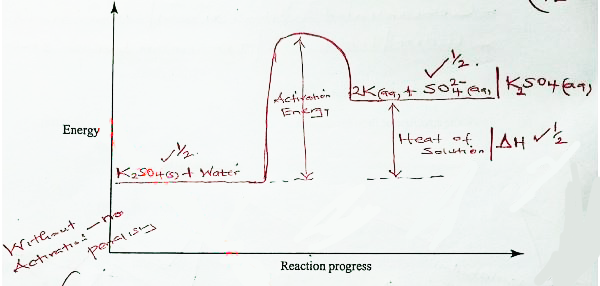
OR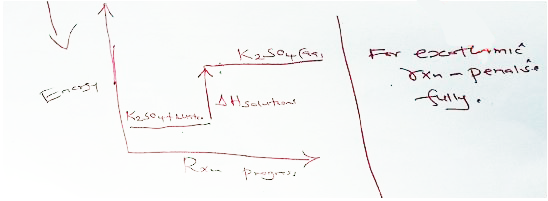
- RFM of K2SO4 = 174
moles of K2SO4 = 5.22/174 = 0.03
ΔH = 0.03 x 23.8 = 0.714KJ
-
-
- When gases react, they do so in volumes that bear simple ratios to one another and to the products if gaseous at constant temperature and pressure
-
- 2NO(g) + O2(g) → 2NO2(g)
- 2NO + O2 → 2NO2
using ratio
Volume of oxygen =180 x 1
2
= 90cm3
Volume of oxygen unreacted = 400 - 90
= 310
Volume of NO2 = 18cm3
Total volume = 310 + 180
= 490cm3
-
- Any contact between
- Mg and hydrochloric acid
- Mg and ethanoic acid
- Using a stopwatch to show the difference
- Conclusion - HCl takes a shorter time
- Put a 6cm Mg ribbon in conical flask and add 50cm3 HCl. Using a stopwatch, record the volume of gases collected at a time inferral e.g. 15cm3
- Repeat the experiment using 50cm3 of ethanoic acid
- More/higher volume of gas will be collected when HCl is used than ethanoic acid at same inferral of time
OR
The reaction will take a shorter time to completion when HCl is used than when ethanoic acid used
- To two different test tubes containing the samples add nitric acid
- Place blue items at the mouth of test tubes
- Both turn red
- Thereafter one of them is bleached
- The sample that produces bleaching on the litmus is sodium sulphite
-
-
- Crush the sunflower seeds using motar and pestle
- Add propane and stir
- Decant
- Leave the extract on sunlight for propane to evaporate leaving oil behind
- It will react with oil to form soap
-
-
-
- Moles of NaOH = 0.4 x 25 = 0.01
1000
Moles of HNO3 = 0.01
Molarity of HNO3 = 0.01 x 1000
10 - C1V1 = C2V2
1 x 500 = 15.9M
31.5
- Moles of NaOH = 0.4 x 25 = 0.01
- Add acid to water
-
-
-

- 188 = 4halflives
100 - 50 - 25 - 6.25
OR
x - ½x - ¼x - 1/8x - 1/16x
% = 1/16 x 100 = 6.25%
-
-
- The graphite anode has to be replaced periodically
- Q = It
= 20 x 5 x 60 = 360000
moles = 360000 = 1.244moles
3 x 96500
mass = 1.244 x 27
= 33.588g
-
- Due to formation of copper(II) carbonate. Since copper reacts with carbon(IV) oxide/CO2
- Due to formation of complex ion of tetramine copper(II) ions
OR
due to formation of tetramine copper (II) ions
-
- Is the mass of one atom of an element compound to the mass of carbon - 12
-
Let RAM 7 x be n C X RAM 12
n 96.4 = 4
n
0.3% mass 3.6 96.4 96.4 = 4 x 0.3
nNo. of moles 3.6
1296.4
nn = 96.4
1.20.3 96.4
nRatio 1 4 = 80.3
-
- H2C2O4 → CO(g) + CO2(g) + H2O(I)
-
- Methanoic
- Sodium methanate
-
-
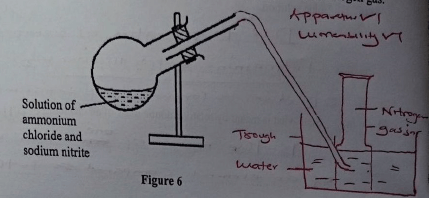
- It has impurities such as noble gases
-
- N2H4 + O2 → N2 + H2O
Bonds broken
4 x 388 = 1552
1 x 163 = 163
1 x 496 = 496
= 2211
Bonds formed
1 x 944 = 944
2 x 463 = 1852
= -2796
Enthalpy of combination = -2796 + 2211
= 585KJmol- -
- Br2(aq) + 2I-(aq) → 2Br-(aq) + I2(aq)
Br2(aq) + 2CI- → No reaction
Bromine will oxidize iodide ions to iodine since it has more positive Eθ
Bromine will not displace chlorine since Eθ for Cl- is more positive - Potassium iodide is a source of iodine is needed to regulate functioning of thyroid gland
- Br2(aq) + 2I-(aq) → 2Br-(aq) + I2(aq)
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download Chemistry Paper 1 Questions and Answers - KCSE 2021 Past Papers.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students