INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
- Write your name and admission number in the spaces provided above
- Sign and write the date of examination in the spaces provided.
- Answer allthe questions in the spaces provided.
- Mathematical table and silent electronic calculators may be used.
- All working must be clearly shown where necessary.
- The apparatus shown below was used to investigate the effect of carbon(II) oxide on copper(II)oxide.
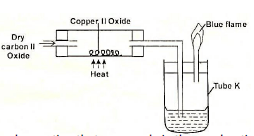
- State the observation that was made in the combustion tube by the end of the experiment. (1 mark)
- Write an equation for the reaction that took place in the combustion tube. (1mark)
- Why is it necessary to burn gas coming out of tubeK? (1mark)
- Name the process which takes place when:
- Iodine changes directly from solid to gas (1mk)
- The process of hardening rubber by heating it together with sulphur(1mk)
- White sugar changes to black solid when mixed with excess concentrated sulphuric (VI)
acid (1mk)
- A student was asked to prepare dry lead (II) sulphate salt using the following reagents; dilute nitric (V) acid, lead (II) carbonate and magnesiumsulphate solution. Describe how the salt can be prepared.(3 mks)
- In a reaction 20cm3 of 0.1M sodium carbonate completely reacted with 12.5cm3 of dilute sulphuric (VI) acid. Find the concentration of suphuric (VI) acid in moles per litres. (3mks)
- Whencalcium carbonate is placed in a solution of hydrogen chloride gas in water, there is effervescence while there is no effervescence when placed ina solution of hydrogen chloride gas dissolved in methylbenzene .Explain this observation (2mk)
- Study the chart below for the Contact process and other extensions.
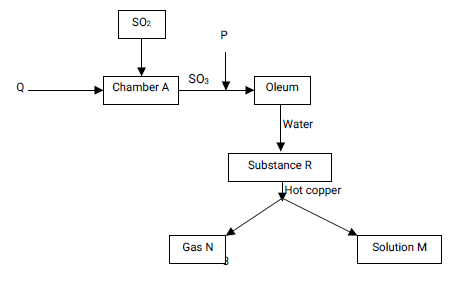
- Identify the substances: (2 mks)
Q ……………………………………………………………………………………………………
P …………………………………………………………………………………………..………….
R……………………………………………………………………..…………………………………
N………………………………………………………………………………………………………. - Name solution M and state its colour. (1 mk)
- Identify the substances: (2 mks)
- Use the reaction scheme below to answer the questions that follow.
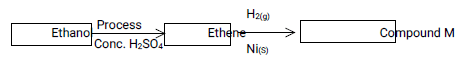
- Give one necessary condition for process P
- Name the Process P. (1/2 mark)
- Draw and name the structure of compound M (11/2 mark)
- Use the bond energies given below to answer the questions that follow.
Bond Bong energy (KJ /mole)
C – H 414
Cl – Cl 244
C – Cl 326
H – Cl 431- Calculate the heat change for the reaction. (3mks)
CH4(g) + Cl2(g) CH3Cl(g) + HCl(g) - State the condition necessary for the above reaction to occur. (1 mk)
- Calculate the heat change for the reaction. (3mks)
- Using dots (.) and crosses (x) to represent electrons, show:
- bonding in sodium chloride (1 mk)
- the structure of an ion illustrated by the formula
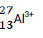 (1 mk)
(1 mk)
- On complete combustion of a hydrocarbon; 1.257g of carbon (IV) oxide and 0.514g of water were produced. If the relative molecular mass of the hydrocarbon is 84, determine the molecular formula of the hydrocarbon (C=12,H=1,O=16) (4mks)
- Below is a diagram of set-up of apparatus that is used to investigate the effect of electric current on a binary electrolyte, lead (II) bromide.
- Explain what is meant by a ‘binary electrolyte’. (1mark)
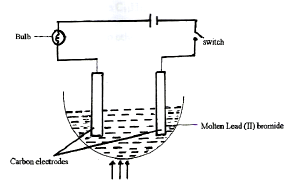
- State the importance of heating in the above experiment. (1mark)
- Give an observation made at the cathode (1 mark)
- Explain what is meant by a ‘binary electrolyte’. (1mark)
-
-
- Name the following organic compounds. (2marks)
- CH3 – CH=C – CH2– CH2–CH3
I
CH3 - CH3 CH2CH2CH2CH3
- CH3 – CH=C – CH2– CH2–CH3
- Describe one chemical test that can be used to distinguish between substances (a) and (b) above. (1 mark)
- Name the following organic compounds. (2marks)
-
-
- Define the term solubility. (1mk)
- 35g of salt W were added to 60cm3 of water at 25ºC.After stirring 5g of crystals of salt W were filtered out. Determine the solubility of salt W at 25ºC. (2mks)
- Temporary water hardness can be removed by boiling
- What is hard water? (1 mk)
- Name the anion responsible for temporary hardness of water. (1 mk)
- State one advantage of hard water. (1mk)
-
- State Graham’s law. (1mark)
- 60cm³ of oxygen gas diffused through a porous hole in 50 seconds. How long will it take 80cm³ of sulphur (IV) oxide, SO2 to diffuse through the same hole under the same conditions. (S = 32, O=16). (2marks)
- The set-up below shows laboratory preparation of hydrogen gas, use it to answer the questions that follow.
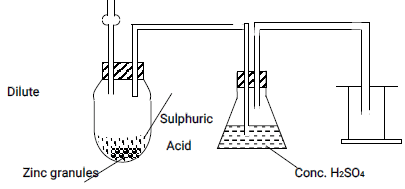
- Identify two mistakes in the set-up (2 mks)
- Why is itnot advisable to use potassium metal as an alternative of zinc for the preparation of hydrogen gas? (1mks)
- The apparatus below was set up to show the catalytic oxidation of ammonia. Study the diagram and answer the questions that follow
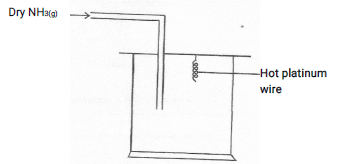
- Write an equation for the reaction that takes place in the gas jar
- What is the role of hot platinum wire?
- Write the formula of the complex ion formed when excess ammonia gas is passed through a solution containing Zn2+ ions. (1mk)
- The diagram below shows the set-up that was used to prepare and collect sulphur (iv) oxide gas.
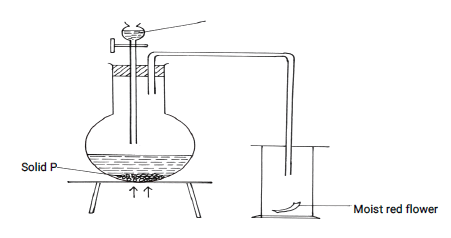
- Identify solid P (1mk)
-
- Why is it possible to collect sulphur (IV) Oxide as shown? (1mk)
- What happened to the red flower? (1mk)
- Hydrogen sulphide gas was passed through a solution of iron(III) chloride
- State and explain the observations made (2mks)
- Write an ionic equation for the reaction taking place in (i) above (1mk)
- A Certain mass of a metal reacted with excess dilute hydrochloric acid at 25ºC. The volume was recorded after every 30secs. The results were presented as shown below.
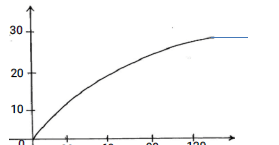
- Name one piece of apparatus that may be used to measure the volume of the gas liberated. (1mk)
-
- On the same axis, sketch the curve that would be obtained if the experiment was repeated at 35ºC (1mk)
- Explain how increase in temperatureaffects the rate of a chemical reaction. (2mks)
- The set up below was used to prepare dry hydrogen chloride gas.
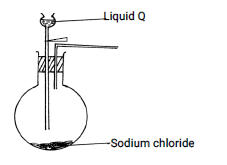
- Complete the diagram to show how dry hydrogen chloride gas is collected. (2marks)
- Identify liquid Q (1mark)
- Write a balanced equation for the reaction that produces hydrogen chloride gas in the above experiment (1mark)
- The relative atomic mass of an elementR is 10.28; it has two isotopes 10 R and 11R.Calculate the relative percentage abundance of each isotope. (3marks)
- Below is a sketch of a reaction profile.
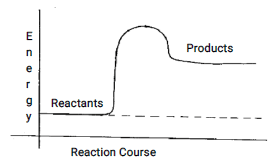
- On the diagram show the heat of reaction ∆H (1mk)
- State and explain the type of reaction represented by the profile (2mks)
- Describe how you would obtain oil from groundnuts. (2mks)
- State any two differences between luminous and non-luminous flames (2mks)
- A sample of water is suspected to contain some dissolvedchloride ions. Describe a chemical test for establishing the presence of the chloride ions in the water sample. (2mks)
- Sketch a graph of temperature against time for a pure substance A with a melting point of 10ºC and boiling point of 80ºC and it is heated from 0ºC to 90ºC. (3marks)

MARKING SCHEME
- The apparatus shown below was used to investigate the effect of carbon(II) oxide on copper(II)oxide.
- State the observation that was made in the combustion tube by the end of the experiment. (1 mark)
Brown solid is formed - Write an equation for the reaction that took place in the combustion tube. (1mark)
CuO(s) + CO(g) → CO2(g) + Cu(s) - Why is it necessary to burn gas coming out of tubeK? (1mark)
The gas is poisonous/toxic
- State the observation that was made in the combustion tube by the end of the experiment. (1 mark)
- Name the process which takes place when:
- Iodine changes directly from solid to gas (1mk)
Sublimation - The process of hardening rubber by heating it together with sulphur(1mk)
Vulcanisation - White sugar changes to black solid when mixed with excess concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid (1mk)
Dehydration
- Iodine changes directly from solid to gas (1mk)
- A student was asked to prepare dry lead (II) sulphate salt using the following reagents; dilute nitric (V) acid, lead (II) carbonate and magnesiumsulphate solution. Describe how the salt can be prepared.(3 mks)
Add excess lead (II) carbonate to the dilute nitric(IV) acid. Filter the mixture to get Pb(SO3). React the filtrate with magnesium sulphate solution. Filter the mixture to obtain lead(II) sulphate as the residue. Rinse the residue with distilled water and dry between filter papers - In a reaction 20cm3 of 0.1M sodium carbonate completely reacted with 12.5cm3 of dilute sulphuric (VI) acid. Find the concentration of suphuric (VI) acid in moles per litres. (3mks)
Moles of Na2CO3 used:
If 1000cm3 → 0.1moles
therefore 20cm3 →20/100 x 0.1 = 0.002 moles
Equation:
Na2CO3 aq+ H2SO4aq → Na2SO4 aq + H2O(I) + CO2(g)
Mole ratio of Na2CO3 : H2SO4 is 1:1:
Moles of H2SO4 acid used:
If 1 mole of Na2CO3 = 1 mole of H2SO4
therefore 0.002 moles of Na2CO3 = 0.002/1 x 1 = 0.002moles
Molarity of H2SO4 :
If 12.5cm3 = 0.002 moles
therefore 1000cm3 = 1000/12.5 x 0.002
= 0.16M - When calcium carbonate is placed in a solution of hydrogen chloride gas in water, there is effervescence while there is no effervescence when placed ina solution of hydrogen chloride gas dissolved in methylbenzene .Explain this observation (2mk)
Water is a polar solvent which enables hydrogen chloride gas to dissolve and ionise into free hydrogen and chloride ions. The hydrogen ions are responsible for the acidity of the solution while methylbenzene is a non-polar solvent therefore HCl does not ionise in it after dissolving - Study the chart below for the Contact process and other extensions.
- Identify the substances: (2 mks)
Q - Air/Oxygen
P - Conc sulphuric(VI) Acid
R - Sulphuric (VI) acid
N - Sulphur (IV) oxide - Name solution M and state its colour. (1 mk)
Name - Copper(II) sulphate
Colour - Blue
- Identify the substances: (2 mks)
- Use the reaction scheme below to answer the questions that follow.
- Give one necessary condition for process P
Heat of beteween 160ºC and 180ºC , Reject a range of temperatures - Name the Process P. (1/2 mark)
Dehydration - Draw and name the structure of compound M (11/2 mark)
- Give one necessary condition for process P
- Use the bond energies given below to answer the questions that follow.
Bond Bong energy (KJ /mole)
C – H 414
Cl – Cl 244
C – Cl 326
H – Cl 431- Calculate the heat change for the reaction. (3mks)
CH4(g) + Cl2(g) CH3Cl(g) + HCl(g)
Bonds broken:
Four H-C bonds = +1656
One CL-Cl bond = 1 x 244 = +244
Total heat absorbed = + 1900
Bonds formed:
Three H-C bonds = 3 x 414 = -1242
One C-CL bond = 1 x 325 = -326
One H-Cl bond = 1 x 431 = -431
Total bonds released = -1999
ΔH = +1900 +(-1990)
= -99kJmol - State the condition necessary for the above reaction to occur. (1 mk)
Sunlight or U.V light
- Calculate the heat change for the reaction. (3mks)
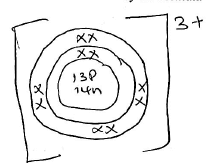
- Using dots (.) and crosses (x) to represent electrons, show:
- bonding in sodium chloride (1 mk)
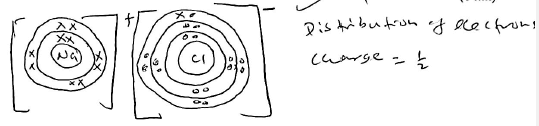
- the structure of an ion illustrated by the formula Al3+ (1 mk)
- bonding in sodium chloride (1 mk)
- On complete combustion of a hydrocarbon; 1.257g of carbon (IV) oxide and 0.514g of water were produced. If the relative molecular mass of the hydrocarbon is 84, determine the molecular formula of the hydrocarbon (C=12,H=1,O=16) (4mks)
Mass of carbon in the Co2 :
12 x 1.257 = 0.3428g
12+(2 x 16)
Mass of H in H2O
12 x 0.514 = 0.0571g
1 x 2(+16)
Empirical formula isElement C H Mass 0.3428 0.0571 Moles 0.3428 = 0.0286
120.0571 = 0.0571
1Mole Ratio 0.0286 = 1
0.02860.0571 = 1.99≈ 2
0.0286
CH2
(CH2)n = 84
{12 + (1 x 2)}n = 84
14n = 84
n = 6
Molecular formular is (CH2)6 = C6H12 - Below is a diagram of set-up of apparatus that is used to investigate the effect of electric current on a binary electrolyte, lead (II) bromide.
- Explain what is meant by a ‘binary electrolyte’. (1mark)
An electrolyte which has only one type of anion and cation - State the importance of heating in the above experiment. (1mark)
To melt the solid lead(II) bromide so that the ions become free and mobile - Give an observation made at the cathode (1 mark)
Grey beads are formed
- Explain what is meant by a ‘binary electrolyte’. (1mark)
-
-
- Name the following organic compounds. (2marks)
- CH3 – CH=C – CH2– CH2–CH3
I
CH3
3 methyl hex-2-ene - CH3 CH2CH2CH2CH3
Pentane
- CH3 – CH=C – CH2– CH2–CH3
- Describe one chemical test that can be used to distinguish between substances (a) and (b) above. (1 mark)
Add sew drops of orange/yellow bromine water to each separately: Brown bromine water will be decolorised by a substance (a) while in substance(b), the brown colour remains brown.
Note: acidified KMnO4 or acidifies K2Cr2O7 can be used in place of bromine water
- Name the following organic compounds. (2marks)
-
-
- Define the term solubility. (1mk)
The maximum mass of the solute required to saturate 100g of the solvent at a particular - 35g of salt W were added to 60cm3 of water at 25ºC.After stirring 5g of crystals of salt W were filtered out. Determine the solubility of salt W at 25ºC. (2mks)
Mass of salt dissolved = (35 - 5)g = 30g
If 60cm3 of water = 30g of salt therefore 100cm3 of water = 100/60 x 30 = 50g
Thus solubility = 50g/100g of water
- Define the term solubility. (1mk)
- Temporary water hardness can be removed by boiling
- What is hard water? (1 mk)
Water that does not readily lather with soap - Name the anion responsible for temporary hardness of water. (1 mk)
Hydrogen Carbonate - State one advantage of hard water. (1mk)
Provides calcium which is essential for strengthening bonds
Used in brewing
Forms a layer of carbonate as lining in lead water pipes preventing lead poisoning
- What is hard water? (1 mk)
-
- State Graham’s law. (1mark)
The rate of diffusion of a gas at a cpnstant temperature and pressure is inversely proportional to the square root of its density - 60cm³ of oxygen gas diffused through a porous hole in 50 seconds. How long will it take 80cm³ of sulphur (IV) oxide, SO2 to diffuse through the same hole under the same conditions. (S = 32, O=16). (2marks)
Time taken by 80cm3 of O2
If 60cm3 of O2 = 50 sec
80 cm3 = 80/60 x 50 = 66.67 secs
TO2 = √MMO2
TSO2 √MMSO2
66.67 = √(16 x 2)
TSO2 √32+(16x2)
66.67 = √32
TSO2 √64
TSO2 x √32 = 66.67 x √64
TSO2 = 94.29sec
- State Graham’s law. (1mark)
- The set-up below shows laboratory preparation of hydrogen gas, use it to answer the questions that follow.
- Identify two mistakes in the set-up (2 mks)
The funnel has not been dipped into the reacting mixture
Wrong method of collecting hydrogen gas - Why is itnot advisable to use potassium metal as an alternative of zinc for the preparation of hydrogen gas? (1mks)
Potassium reacts explosively with dilute acids
- Identify two mistakes in the set-up (2 mks)
- The apparatus below was set up to show the catalytic oxidation of ammonia. Study the diagram and answer the questions that follow
- Write an equation for the reaction that takes place in the gas jar
4NH3(g) + 5O2(g) → 4NO(g) + 6H2O - What is the role of hot platinum wire?
Catalyses the reaction/is a catalyst - Write the formula of the complex ion formed when excess ammonia gas is passed through a solution containing Zn2+ ions. (1mk)

- Write an equation for the reaction that takes place in the gas jar
- The diagram below shows the set-up that was used to prepare and collect sulphur (iv) oxide gas.
- Identify solid P (1mk)
Sodium sulphite or potassium sulphite -
- Why is it possible to collect sulphur (IV) Oxide as shown? (1mk)
SO2 is denser than air - What happened to the red flower? (1mk)
Turned white/got bleached
- Why is it possible to collect sulphur (IV) Oxide as shown? (1mk)
- Identify solid P (1mk)
- Hydrogen sulphide gas was passed through a solution of iron(III) chloride
- State and explain the observations made (2mks)
Yellow/brown solution of iron(II) chloride turns to pale green due to reduction to iron(II) chloride by H2S
Yellow precipitate is formed due to oxidization of H2S to sulphur - Write an ionic equation for the reaction taking place in (i) above (1mk)
H2S(g) + 2Fe3+(aq) → 2Fe3+(aq) + S(s) + 2H+(aq)
- State and explain the observations made (2mks)
- A Certain mass of a metal reacted with excess dilute hydrochloric acid at 25ºC. The volume was recorded after every 30secs. The results were presented as shown below.
- Name one piece of apparatus that may be used to measure the volume of the gas liberated. (1mk)
Graduated syringe/graduated cylinder -
- On the same axis, sketch the curve that would be obtained if the experiment was repeated at 35ºC (1mk)
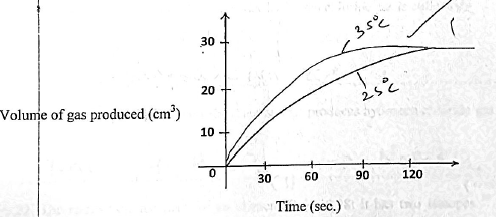
- Explain how increase in temperatureaffects the rate of a chemical reaction. (2mks)
An increase in temperature results in an increase in the kinetic energy of the reacting particles. This makes the particles to move faster and collide more frequently with sufficient energy to cause more successful collissions per unit time. Thus increasing the rate of reaction.
- On the same axis, sketch the curve that would be obtained if the experiment was repeated at 35ºC (1mk)
- Name one piece of apparatus that may be used to measure the volume of the gas liberated. (1mk)
- The set up below was used to prepare dry hydrogen chloride gas.
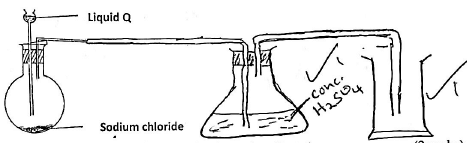
- Complete the diagram to show how dry hydrogen chloride gas is collected. (2marks)
- Identify liquid Q (1mark)
Conc Sulphuric(IV) acid - Write a balanced equation for the reaction that produces hydrogen chloride gas in the above experiment (1mark)
NaCl(s) + H2AO(I) → NaHSO4 + HCl(g)
- The relative atomic mass of an elementR is 10.28; it has two isotopes 10 R and 11R.Calculate the relative percentage abundance of each isotope. (3marks)
Let the abundance of 10R be x%
Hence abundance of "R" will be (100 - x)%
10.28=(x × 10) +11(100 - x)1
100 100
10.28=10x +1100 - 11x
100 100
10.28 = 10x + 1100 - 11x
1028 - 1100 = 10x - 11x
-72 = -x
-72/-1 = x/-1
Thus 10R = 72%
"R = (100 -72) = 28% - Below is a sketch of a reaction profile.
- On the diagram show the heat of reaction ∆H (1mk)
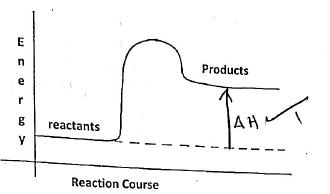
- State and explain the type of reaction represented by the profile (2mks)
Endothermic reaction becasue products have more heat energy than the reactants
- On the diagram show the heat of reaction ∆H (1mk)
- Describe how you would obtain oil from groundnuts. (2mks)
Place the ground nuts in a motor and crush using a pestel. Add propanone or ethanol little by little as crushing continues. Decant the mixture into an evaporating dish. Place the evaporating dish and its contents in the sun for propanone /solvent to evaporate and leave behind the oil - State any two differences between luminous and non-luminous flames (2mks)
Luminous Flame Non-luminous flame Long and wavy
Produces much light
Produces less heat
Produces soot
Burns quietly
Has four zonesShort and steady
Produces less light
Produces more heat
Not sooty
Burns noisily
Has three zones - A sample of water is suspected to contain some dissolvedchloride ions. Describe a chemical test for establishing the presence of the chloride ions in the water sample. (2mks)
To the sample of water in a test-tube add about 3 drops of lead(II) nitrate solution. If a white precipitate is formed which is soluble on warming, then chloride ions are present, confirmed. - Sketch a graph of temperature against time for a pure substance A with a melting point of 10ºC and boiling point of 80ºC and it is heated from 0ºC to 90ºC. (3marks)

Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download Chemistry Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Momaliche Joint Mock Exams 2021/2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students