INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
- This paper has two sections, A and B.
- Answer question 6 and any other TWO questions.
FOR EXAMINERS USE ONLY
|
SECTION |
QUESTION |
MARKS |
SCORE |
|
A |
1-5 |
25 |
|
|
B |
6 |
25 |
|
|
7 |
25 |
||
|
8 |
25 |
||
|
9 |
25 |
||
|
10 |
25 |
||
|
TOTAL MARKS |
100 |
||
|
TOTAL SCORE |
|||

QUESTIONS
SECTION A:
Answer all the questions in this section
- The diagram below shows the internal structure of the earth.
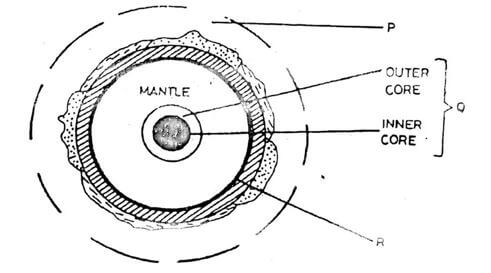
- Name the parts labelled P, Q and R. (3marks)
- State the characteristics of the inner core. (3marks)
-
- Give two local winds that are found in Kenya. (3 marks)
- State three conditions that are necessary for formation of dew. (3 marks)
- Explain how the following factors influence climate.
- Oceans currents (2marks)
- Forests (2marks)
-
- Define a lake (2marks)
- State three reasons why some rift valley lakes are fresh water. (2marks)
-
- Give two main components of soils (2marks)
- List three factors that influence soil erosion (3marks)
SECTION B
Answer question 6 and any other two questions from this section.
- Study the map of Kijabe 1:50,000 (sheet 134/3) provided and answer the following questions.
-
- Identify the type of map provided (1 mark)
- Give the longitudinal extent of the area covered by the map. (2 marks)
- Convert the scale of this map into statement scale. (2 marks)
- Draw a rectangle 10cm by 20cm to represent part of the area between the northings 90 and 00 and easting 25 and 30 on it mark and name: (6 marks)
- Kijabe
- Road A 104
- Power line
- Provincial boundary
-
- Identify four types of natural vegetation in the area covered by the map. (4 marks)
- Describe the drainage of the area covered by the map (5 marks)
- Identify five economic activities and their evidences in the areas covered by the map. (5 marks)
-
-
-
- Distinguish between minerals and rocks. (2 marks)
- Describe the following characteristics of minerals:
- Colour. (2 marks)
- Tenacity. (2 marks)
- Hardness. (2 marks)
-
- What are sedimentary rocks? (2 marks)
- State three characteristics of sedimentary rocks. (3 marks)
- Explain two reasons why sedimentary rocks are widespread in the coastal plain of Kenya. (4 marks)
- Describe how the following sedimentary rocks are formed.
- Mechanically formed. (4 marks)
- Organically formed. (4 marks)
-
-
-
- Name two types of earth movements. (2 marks)
- State three causes of earth movement. (2 marks)
- Describe the plate tectonics theory. (5 marks)
-
- Define faulting. (2 marks)
- State three factors that may influence faulting processes. (3 marks)
- Name four types of faults. (4 marks)
- With the aid of well-labelled diagrams, describe the formation of rift Valley by compressional forces. (7 marks)
-
-
-
- Name two types of hot desert landscapes. (2 marks)
- State two reasons why wind erosion is very effective in hot deserts. (2 marks)
-
- A part from Yadangs, name three features that result from wind action in deserts. (3 marks)
- Using well-labelled diagrams, describe how Yadangs are formed. (7 marks)
- Explain three ways in which winds transport in desert areas. (6 marks)
- State the significance of desert features to human environment. (5 marks)
-
-
-
- What is glacier? (2 marks)
- Describe how glacier is formed. (4 marks)
- Describe two processes of ice erosion on a glaciated highland. (6 marks)
-
- Apart from Crag and Tail, name two other features formed by ice erosion in lowlands. (2 marks)
- Describe how a crag and tail is formed. (5 marks)
- Explain three positive effects of glaciation in the lowland areas. (6 marks)
-

MARKING SCHEME
SECTION A: 25 marks
Answer all the questions in this section
- The diagram below shows the internal structure of the earth.
- Name the parts labelled P, Q and R. (3marks)
- P- Atmosphere
- Q- Core/Centrosphere and Barysphere
- R- Mohorovicic discontinuity / Moho
- State the characteristics of the inner core (3marks)
- Is made of iron minerals
- It has very high temperatures estimated to be between 45000c to 5,500
- Average density 16-17gm/cc/very high density
- It is solid in nature
- Name the parts labelled P, Q and R. (3marks)
-
- Give two local winds that are found in Kenya (3 marks)
- Anabatic winds
- Katabatic winds
- Sea breeze
- Land breeze
- State three conditions that are necessary for formation of dew. (3 marks)
- Daytime should be warm.
- The air should be calm
- Low temperature below dew point
- Cloudless nights.
- Give two local winds that are found in Kenya (3 marks)
- Explain how the following factors influence climate.
- Oceans currents (2 marks)
- Onshore winds blowing over a warm ocean current causing a warming effect raising the temperature of the adjacent coast.
- Onshore winds blowing over a warm ocean current picks up moisture causing rainfall on the adjacent coastal lands.
- Forests (2 marks)
- Temperature is lowered by the shade of the trees.
- Rainfall is higher duet to thigh rate of evapotranspiration.
- Friction between trees and the wind reduces the speed of wind.
- High humidity due to high rate of evapotranspiration.
- Oceans currents (2 marks)
-
- Define a lake (2 marks)
- It is a body of water which occupies a basin, depression or hollow on the earth’s surface.
- State three reasons why some rift valley lakes have fresh water. (2 marks)
- It has surface and subterranean outlets through which excess salt deposits are carried away.
- It has regular inflow of fresh water from rivers, which dilutes the salts, keeping the water fresh.
- It is situated in an area of high rainfall, which keeps the water fresh.
- It is located in an area of low temperatures, resulting in low rates of evaporation, therefore low salt concentration.
- Define a lake (2 marks)
-
- Give two main components of soils. (2 marks)
- Inorganic Matter
- Organic Matter
- Soil Water/moisture
- Soil Air
- State three factors that influence soil erosion. (3 marks)
- Nature of slope
- Nature of soil
- Prevailing climate conditions
- Vegetation cover
- Give two main components of soils. (2 marks)
- Study the map of Kijabe 1:50,000 (sheet 134/3) provided and answer the following questions.
-
- Identify the type of map provided (1 mark)
- Topographical map
- Give the longitudinal extent of the area covered by the map. (2 marks)
- 360 300’E- 360 450’E
- Convert the scale of this map into statement scale (2 marks)
- 1cm represents 0.5km
- Identify the type of map provided (1 mark)
- Draw a rectangle measuring 10cm by 20cm to represent part of the area between the northings 90 and 00 and easting 25 and 30 on it mark and name:
- Kijabe hill
- Road A 104
- Power line
- Provincial boundary. (6 marks)
-
- Identify four types of national vegetation in the area covered by the map. (4marks)
- Bamboo vegetation
- Forest vegetation
- Thick vegetation
- Woodland vegetation
- Scattered vegetation
- Describe the drainage of the area covered by the map (5marks)
- The main drainage features are rivers
- There are many rivers
- Most of rivers are permanent
- Some of the rivers are disappearing
- Some rivers form parallel drainage pattern
- Some rivers have their source from hills
- Some rivers have their source from forests.
- Identify five economic activities in the area covered by the map. (5 marks)
- Trade – trading /shops /markets/petrol station
- Transports- many roads and railway lines
- Forestry – forests/forest guards post/ saw mills
- Quarrying – marram pit
- Livestock – Dairy cattle dip
- Manufacturing / processing – Kagwe cardboard factory / saw mill
- Identify four types of national vegetation in the area covered by the map. (4marks)
-
-
-
- Distinguish between minerals and rocks. (2marks)
- A mineral is an inorganic homogenous substances which occurs naturally on or beneath the surface of the earth.
- A rock is a naturally occurring solid material composed of one or more minerals and form the solid part of the earth.
- A rock is a substance made up of a mineral or a combination of mineral particles cemented together and form the solid part of the earth’s crust.
- Describe the following characteristics of minerals. (2marks)
- Colour (2marks)
- Different mineral display different colours.
- Tenacity (2marks)
- Minerals have different degrees of tenacity.
- Hardness (2marks)
- Some minerals such as diamond have a high resistance while others such as talc are soft.
- Colour (2marks)
- Distinguish between minerals and rocks. (2marks)
-
- What are sedimentary rocks? (2 marks)
- These are rocks which are composed of sediments which are laid down in water or land depressions.
- What are sedimentary rocks? (2 marks)
-
- State three characteristics of sedimentary rocks. (3 marks)
- They are found in layers.
- They have bedding planes.
- Most are non-crystalline.
- Some contain fossils
- Explain two reasons why sedimentary rocks are widespread in the coastal plain of Kenya. (4 marks)
- The coata region is a lowland which has facilitated deposition of sediments.
- The shallow continental shelf has conducive environment for the formation of coral rocks.
- Much of the coastal plain emerged from the sea where sedimentation occurred.
- Describe how the following sedimentary rocks are formed.
- Mechanically formed. (4 marks)
- Pre-existing rocks are weathered and eroded to form sediments.
- The sediments are transported by wind, water or moving ice.
- Such sediments get deposited in a stratified order to form layers on land or under water.
- The sediments are compressed by the weight of the overlying layers which cements and compacts them into a solid rock.
- Organically formed. (4 marks)
- They are formed from the organic remains of dead plants and animals.
- The remains are deposited on lakes or ocean beds and other buried underground by layers of sediments.
- These remains accumulate to form layers.
- Over time, the materials get compressed by weight of the overlying materials to form compact solid rocks.
- Mechanically formed. (4 marks)
- State three characteristics of sedimentary rocks. (3 marks)
-
-
-
- Name two types of earth movements. (2 marks)
- Lateral/ horizontal/ orogenic.
- Vertical/ epeirogenic
- State three causes of earth movements. (3marks)
- Movement of magma within the crust.
- Conventional currents in the mantle.
- Isostatic adjustment of the crust.
- Gravitational pressure.
- Name two types of earth movements. (2 marks)
-
- Define faulting (2 marks)
- It is the cracking/ fracturing of the crustal rocks as a result of tectonic forces.
- State three factors that may influence faulting processes (3 marks)
- Intensity or strength of the tectonic forces.
- The nature of crustal rocks.
- Direction of the forces involved.
- Name four types of faults (4 marks)
- Normal faults
- Reversed faults
- Tear / shear faults
- Thrust/over thrust faults
- Anticlinal faults
- Define faulting (2 marks)
- With the aid of well-labelled diagrams describe the formation of rift Valley by compressional forces. (7 marks)
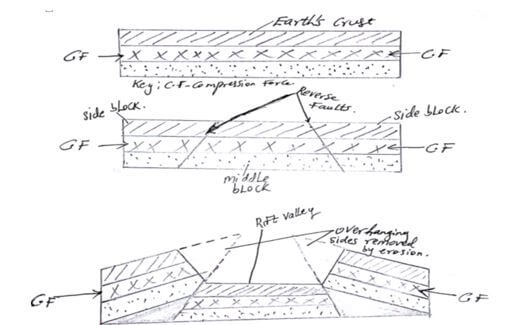
- the crustal rock layers are subjected to forces of compression
- This leads to formation forces to formation of parallel reversed faults towards each other.
- The compressional forces push the outer blocks towards each other
- The outer blocked one force upwards uplift or hung over the middle block.
- The middle block sinks or may remain at the lower level.
- The sunken middle block form a depression having sleep fault scarps called rift valley.
-
-
-
- Name two types of hot desert landscapes (2 marks)
- Sandy/ Erg/ Koum.
- Stony/Reg/ Serrir
- Rocky/ Hamada.
- Badlands.
- State two reasons why wind erosion is very effective in hot deserts. (2 marks)
- Presence of loose unconsolidated dry masses of mud, sand and gravel
- Occurrence of strong tropical storms.
- Absence of vegetation leading to high wind velocity due to little frictional force.
- Name two types of hot desert landscapes (2 marks)
-
- A part from Yadangs, name three features that result from wind action in deserts. (3marks)
- Rock pedestals
- Mushroom blocks
- Zeugens
- Deflation hollows
- Ventifacts
- Using well labelled diagrams, describe how Yadangs are formed. (7 marks)
Diagrams (3 marks)
Text (4 marks)- Rocks made up of vertical alternating layers of hard and soft rocks lie parallel to prevailing winds in deserts.
- Wind abrasion erodes the soft rocks and the particles are removed by deflation
- This leads to formation of large furrows.
- The layers of hard resistant rocks are left standing as ridges.
- The ridges that are left standing are called Yadangs.
- A part from Yadangs, name three features that result from wind action in deserts. (3marks)
- Explain three ways in which winds transport in desert areas. (6 marks)
- Suspension wind transports by lifting and holding light particles such as dust by air currents above the ground and transporting them over long distances.
- Saltation medium sized particles are carried by a series of jumps and hops. The materials are rolled along the ground, collide with each other and bounce off and are lifted into the air and transported for a short distance.
- Surface Creep wind transported heavy and large unconsolidated materials such as gravel and pebbles by pushing and rolling them along the desert. They are never lifted and are moved only for a short distances due to their weight.
- State the significance of desert features to human environment (5 marks)
- Loess from fertile soils which promote farming
- Desert features such as rock pedestals, Yadangs, zeugens and sand dunes are tourists
- Oasis are sources of water for domestic use / industrial use.
- Deserts are good sites for testing military weapons, military training and experimenting ground for aircraft because they are sparsely populated..
- Salty fats are used economically for salt production
- Oasis water is also used for irrigation.
-
-
-
- What is glacier? (2 marks)
- A mass of ice with limited width that moves outwards from a zone of accumulation
- Describe how glacier is formed (5 marks)
- Due to low temperature water vapour condenses and freezes in the atmosphere to form snow.
- The snow falls and accumulates on higher slopes/mountains tops.
- Snow continues piling and new layers exert pressure on lower layers.
- The lower layers become compressed / compacted as air is expelled space between the snow particles.
- The layers of ice accumulate with time to form huge mass
- The huge mass of ice exerts more pressure on the lower layer leding to thawing.
- With time the ice becomes too thick and its lower layers become plastic, forcing it to flow downwards under the influence of gravity.
- The moving ice moves form the zones of accumulation downslope under the influence of gravity is called glacier.
- What is glacier? (2 marks)
- Describe two processes of ice erosion on a glaciated highland. (6marks)
- Abrasion. (3 marks)
- The rocks embedded in the glacier scrub, scratch and polish the rock surfaces over which the glacier moves.
- This dislodges some rock particles.
- The dislodged rock particles are removed by the moving glacier.
- Plucking / Gouging/Sapping. (3 marks)
- It is the process through which rocks on the valley sides and the floor are pulled away by moving ice.
- It occurs on well jointed rocks / rocks with cracks
- Pressure from overlying layers of ice cause freeze – thaw action
- The melting water fills the cracks in the bedrocks
- The disintegrated rocks within the mass of ice eventually gets embedded and as the ice moves, it pulls/gouges out the ice embedded rock particles from the parent rock through plucking.
- Abrasion. (3 marks)
-
- Apart from crag and tail, name three other features formed by ice erosion in lowlands. (3 marks)
- Roche mountonnee.
- Ice eroded plains.
- Depressions
- Describe how a crag and tail is formed. (5 marks)
- A large block of resistant rock stands on the path of oncoming glacier.
- Ice moves over the rock outcrop.
- Moving ice erodes by plucking the weaker rock fragments on the upper side of the rock.
- Abrasion smoothens the upstream side of the rock.
- The downstream side of the resistant rock experiences no erosion.
- The softer rock on the downstream side is protected from erosion by the resistant rock outcrop.
- As ice moves round and over the resistant rock, it carries the eroded rock materials to the downstream side.
- The soft rock and materials deposited on the downstream side forms a tail while the resistant rock forms a crag.
- Apart from crag and tail, name three other features formed by ice erosion in lowlands. (3 marks)
- Explain four positive effects of glaciation in the lowland areas. (8 marks)
- Till plains provide fertile soils for arable farming.
- Ice sheet scour rocks of the surface which may expose minerals and make it easy to extract.
- Outwash plain has sand and gravel which is used as building and construction materials thus promoting the construction industry.
- Glacial lakes in lowlands can be exploited for fishing and transportation.
- Glaciation forms a scenery such as drumlins and eskers which act as tourists attractions thus earning the country income when tourists visit to see them.
- Glaciated lowlands are generally gently sloping which makes them suitable for settlements and development of transport and communication lines.
-
Download Geography Paper 1 Pre Mock Questions and Answers - Mokasa I Joint Examination July 2021.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students

