INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
- Answer all the questions in the spaces provided.
- Mathematical tables and electronic calculators may be used.
- All working must be clearly shown where necessary.
- An oxide of element G has the formula as G2O3.
- State the valency of element G. (1 mark)
……………………………………………………………………………………………………… - In which group of the periodic table is element G? (1 mark)
……………………………………………………………………………………………………
- State the valency of element G. (1 mark)
- The set-up below was used to separate a mixture.
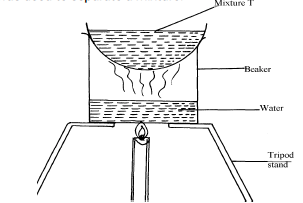
- Name the apparatus missing in the set-up. (1 mark)
……………………………………………………………………………………………………... - Give one example of mixture T. (1 mark)
……………………………………………………………………………………………………... - What is the name of this method of separation? (1 mark)
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
- Name the apparatus missing in the set-up. (1 mark)
- Name the process which takes place when:
- Solid Carbon (IV) oxide (dry ice) changes directly into gas. (1 mark)
……………………………………………………………………………………………………... - A red litmus paper turns white when dropped into chlorine water. (1 mark)
……………………………………………………………………………………………………… - Propene gas molecules are converted into a giant molecule. (1 mark)
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
- Solid Carbon (IV) oxide (dry ice) changes directly into gas. (1 mark)
- The information below gives pH values of solutions V, W, X, Y Z.
Solution pH values V
W
X
Y
Z2
6.5
11
14
4.5- Which solution is likely to be?
- Calcium hydroxide? (1 mark)
……………………………………………………………………………………………………… - Rain water? (1 mark)
……………………………………………………………………………………………………...
- Calcium hydroxide? (1 mark)
- Which solution would react most vigorously with Zinc carbonate? (1 mark)
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
- Which solution is likely to be?
- Explain why very little Carbon (IV) oxide gas is evolved when dilute sulphuric (VI) acid is added to lead (II) carbonate. (1 mark)
……………………………………………………………………………………………………… - Air was passed through several reagents as shown below:
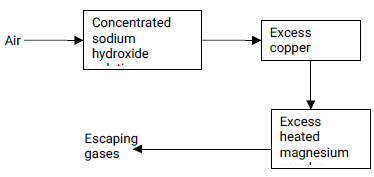
- Write an equation for the reaction which takes place in the chamber containing magnesium powder. (1 mark)
……………………………………………………………………………………………………… - Name one gas which escapes from the chamber containing magnesium powder.
Give a reason for your answer. (2 marks)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………
- Write an equation for the reaction which takes place in the chamber containing magnesium powder. (1 mark)
- The set-up below was used to study some properties of air.
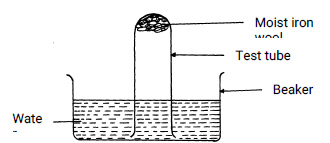
State and explain two observations that would be made at the end of the experiment. (2 marks) - Below is a list of oxides.
MgO, N2O, K2O, CaO and Al2O3
Select:-- A neutral oxide. (1 mark)
- A highly water soluble basic oxide. (1 mark)
- An oxide which can react with both sodium hydroxide solution and dilute hydrochloric acid. (1 mark)
-
- Hydrogen can reduce copper (II) Oxide but not aluminium oxide. Explain. (1 mark)
- When water reacts with potassium metal, the hydrogen produced ignites explosively on the surface of water.
- What causes this ignition? (1 mark)
- Write an equation to show how this ignition occurs. (1 mark)
- In an experiment an unknown mass of anhydrous sodium carbonate was dissolved in water and the solution made up to 250 cm3. 25cm3 of this solution neutralized 20 cm3 of 0.25 M nitric acid. Calculate the mass of unknown sodium carbonate used. (3 marks)
(Na = 23.0, C = 12.0, O = 16.0) - An element M has two naturally occurring isotopes, 63M and 65M. Calculate the percentage of each isotope if the relative atomic mass of M is 63.55. (2 marks)
- Carbon and silicon belong to the same group of the periodic table, yet Carbon (IV) oxide is a gas while silicon (IV) oxide is a solid with a high melting point. Explain this difference (2 marks)
- The table below gives information about the ions T+ and Z2-.
Ion T+ Z2 Electron arrangement 2.8 2.8.8 Number of neutrons 12 16 - Determine the relative formula mass of the compound formed between T and Z. (2 marks)
- State two conditions under which the compound in (a) above would conduct electricity. (1 mark)
- An ion of oxygen is larger than oxygen atom. Explain. (2 marks)
- A solution of hydrogen chloride gas in methylbenzene has no effect on calcium carbonate while a solution of hydrogen chloride gas in water reacts with calcium carbonate to produce a gas. Explain. (2 marks)
- Starting with Lead (II) carbonate explain how you would prepare a pure sample of Lead (II) sulphate. (3 marks)
- Draw a dot (•) and cross (x) diagram to show bonding in:-
- Ammonium ion, NH + (N = 7.0, H = 1.0) (1 mark)
- Silane, SiH4 (Si = 14.0, H = 1.0) (1 mark)
- Sodium carbonate decahydrate crystals, Na2CO3.10H2O, were left exposed in the atmosphere on a watch glass for two days.
- State the observation made on the crystals after two days. (1 mark)
- Name the property of salts investigated in the above experiment. (1 mark)
-
- What is meant by the term solubility of salts? (1 mark)
- Calculate the solubility of a salt given that 15 g of the salt can saturate 25 cm3 of water. (1 mark)
-
- State the Graham’s law. (1 mark)
- A 100 cm3 of Carbon (IV) oxide gas diffused through a porous partition in 30 seconds.
How long would it take 150 cm3 of Nitrogen (IV) oxide to diffuse through the same partition under the same conditions? (C = 12.0, N = 14.0, O = 16.0) (2 marks)
- The diagram below represents an in complete set-up for preparation of a dry sample of gas R.
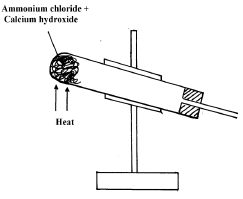
- Complete the set-up to show how a dry sample of gas R is collected. (2 marks)
- Write a chemical equation for the reaction that produces gas R. (1 mark)
- When sulphur powder is heated to over 400ºC the following changes are observed:- At 113ºC it melts into light brown liquid. The liquid then darkens to become red- brown and very viscous at 160ºC. Above 160ºC the liquid becomes almost black. Near the boiling point (444ºC) the liquid becomes mobile. Explain these observations. (3 marks)
- A gas cylinder contains about 1.12dm3 of butane measured at 0º and 1atm. Given that 25% of heat is lost, what is the maximum volume of water at room temperature which can be boiled to 100ºC in order to make some coffee?
C4H10(g) + 6 ½ O2(g) → 4CO2(g) + 5H2O(l); ΔHθ = -3,000 kJmol-1 (3 marks)
(Specific heat capacity of water = 4.2J g-1ºC-1, density of water 1gcm-3 Molar gas volume 22.4 at s.t.p) - Compound W reacted with chlorine to form compound X only. The structural formula of
X is shown below:
CH3 ─ CH ─ CH ─ CH3
│ │
Cl Cl- Give the structural formula and name of compound W. (1 mark)
- Draw the structure of 1-chloro-2, 2-dimethylpropane. (1 mark)
- A weighed sample of crystalline sodium carbonate (Na2CO3.nH2O) was heated in a crucible until there was no further change. The mass of the sample reduced by 14.5%. Calculate the number of moles, n, of water of crystallization. (Na = 23, O = 16.0, C = 12, H = 1). (3 marks)
- In an experiment, soap solution was added to three samples of water. The results below show the volume of soap solution required to lather with 500 cm3 of each water sample before and after boiling.
- Which water samples are likely to be soft? (1 mark)
Sample 1 Sample 2 Sample 3 Volume of soap used before wate rboiled 26.0 14.0 4.0 Volume of soap after water boiled 26.0 4.0 4.0 - Explain the change in volume of soap solution used in sample 2. (1 mark)
- Which water samples are likely to be soft? (1 mark)
- Study the flow diagram below and answer the questions that follow:
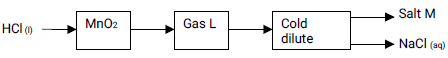
- Name salt M. (1 mark)
- Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction between hydrochloric acid and manganese (IV) oxide. (1 mark)
- Identify another reagent that can be reacted with concentrated hydrochloric acid to produce gas L. (1mark)
- The set-up below was used to prepare and collect hydrogen sulphide gas. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
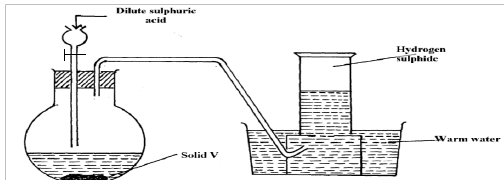
- Name solid V. (1 mark)
- Write chemical equation of the reaction taking place in the flask. (1 mark)
- Give a reason why warm water is used in the set-up. (1 mark)
- The table below gives information on four elements represented by letters K, L, M and N. Study it and answer the questions that follow:
Element Electron arrangement Atomic radius (nm) Ionic radius (nm) K
L
M
N2.8.2
2.8.7
2.8.8.1
2.8.8.20.136
0.099
0.203
0.1740.065
0.181
0.133
0.099- Select the elements with similar chemical properties. (1 mark)
- Explain why the ionic radius of L is greater than its atomic radius. (1 mark)
- Identify the most reactive metal. (1 mark)
- The set up below was used to prepare a solution of hydrogen chloride.
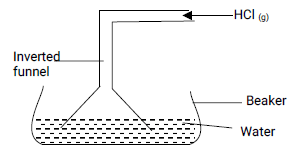
- Explain why an inverted funnel is used. (2 marks)
- Name another gas whose aqueous solution can be prepared in the same way. (1 mark)
- Heated iron can react with both chlorine gas and hydrogen chloride gas.
- Write equations for the two reactions. (2 marks)
- Chlorine gas has no effect on dry blue litmus paper. Explain. (1 mark)

MARKING SCHEME
-
- Valency 3
- Group 3
-
- Wiregauze
- Sodium chloride solution (or any named slat solution)
- Evaporation
-
- Sublimation.
- Bleaching
- Polymerisation
-
-
- X
- W
- V
-
- InsolubleLead(II) sulphate is formed preventing any further reaction.
-
- 3Mg(s)+N2(g) → Mg3N2(s)
- Argon
- It is inert
-
- Water rose up the test-tube to occupy the space of active air or oxygen√½ which has been used in rusting.√½
- Iron wool turned red–brown√½ due formation of hydrated iron(III) oxide√½.
-
- N2O orNitrogen(I)oxide
- K2O (Potassium oxide)
- Al2O3 (Aluminium oxide)
-
- Hydrogen is above Cu√½ and below Al in the reactivity series√½ of elements.
-
- The reaction is too exothermic that alot of heat is produced causing ignition of hydrogen in presence of oxygen.
- H2(g)+O2(g)→ H2O(g)
- Na2CO3(aq)+2HNO3(aq) → 2NaNO3(aq)+CO2(g)+H2O(l)
Mole ratio Na2CO3:HNO3=1:2√½
Moles of HNO3 in 20cm3=20/1000 x 0.25=0.005 moles√½
Moles of Na2CO3 in 25cm3=½ of 0.005=0.0025 moles√½
If 25cm3=0.0025moles
in 250cm3=?
250 x 0.0025=0.025moles√½
25
RFM of Na2CO3 = 106 ½
I mole of Na2CO3=106g
0.025 moles=?
0.025 x 106 =2.65g of Na2CO3 ½
1 - 63x + 65(100–x) = 63.55√½
100
63x + 6500 – 65x = 6355
2x = 6355 – 6500 =145
x=72.5 ½
% abundance of 63M =72.5% ½
65M =100–72.5=27.5% ½ - Silicon(IV) Oxide has giant atomic structure with strong covalent bond holding the atom together. These require alot of energy to break, hence it has high melting point.
Carbon (IV) Oxide has simple molecular structure with weak Van Der Waals forces holding the molecules together which require little energy to break, hence is a gas at room temperature and pressure. -
- Number of protons
T=11protons
Z=16protons
Formula of compound =T2Z
Mass number of T=11+12=23
Mass number of Z = 16+16=32
Formula Mass of T2Z=(23 x 2)+32=78 -
- When molten
- When in aqueous solution
- Number of protons
- The oxide ions has 2 extra electrons that causes greater electron repulsion than in oxygen atom
- HCl(g) is polar.It ionizes/dissociates in water which is a polar solvent to produce H+(aq) that gives the solution acidic properties.HCl(g) doesnotionize/dissociate in methyl benzene which is a non-polar solvent.It remains as molecules hence no H+
ions.1mk -
- Add dilute nitric acid to lead(II) carbonate.
PbCO3(s)+2HNO3(aq) → Pb(NO3)2(aq)+CO2(g)+H2O(l) - React the resulting solution with solution of sodium sulphate or dilute sulphuric acid.
Na2SO4(aq)+Pb(NO3)2(aq) → PbSO4(s)+2NaNO3(aq) - Filter to obtain lead(II) sulphate as residue. Dry the salt of lead(II) sulphate in between the filter papers or in sunshine.
- Add dilute nitric acid to lead(II) carbonate.
-
-
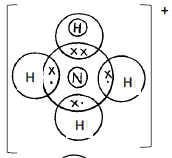
- award 1mk if one Hydrogen has two electrons donated by Nitrogen
- 0mk if all hydrogen atoms
-
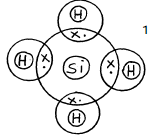
award full mark if Silicon and Hydrogen contributes shared electrons equally
-
-
- They became covered with a white powder
- Efflorescence
-
- This is the maximum mass of a salt that will dissolve in 100g of water at a given temperature
- 15g dissolve in 25cm³ water
x g dissolve in (15 x 100) = 60g/100gwater
25
-
- Grahams law states;
Under the same conditions of pressure and temperature, the rate of diffusion of a gas is inversely proportional to the square root of its density.√ - TimeCO2=MCO2
TimeNO2 MNO2
Where 100cm3 of CO2 takes 30 seconds
150cm3 of CO2 takes 30/100 x 150 = 45 seconds
45 = 44
TNO2 46
45 = 0.975
TNO2
TNO2 = 45 = 46sec
0.97
OR
RCO2=MNO2
RNO2 MCO2
ButRCO2 = 100cm3=3.33cm3per sec
30s
3.33 = 46 =1.0225
RNO2 4
RNO2 = 3.33
1.0225
=3.26cm3 per second
Time for No = 150cm 3
3.26cmsec-1 = 46sec√½
- Grahams law states;
-
- Drying agent which must be CaO
Method of collection 1- upward delivery
Workability - 2NH4Cl(g)+Ca(OH)2(s) → CaCl2(g)+H2O(l)+2NH3(g)
- Drying agent which must be CaO
-
- At 113ºC consists of S8 rings that flow easily;
- Darkens due to breaking of S8 rings and forming long chains consisting of thousands of atoms.The chains also entangle;
- The long chains consisting of thousands of atoms.The chains also entangle;
- The long chains break near b.p. to form shorter one;
- Moles C4H10 = 1.12 = 0.05mol
22.4
Heat produced 0.05 x 3000 = 150kJ√½
Useful heat =75 x 150 =112.5kJ√½
100
Let mass of water =m
Room temperature =25ºC
Boiling point =100ºC
Change in temperature,ΔT =100-25=75
ΔH=ΔT x m x C
75 x m x 4.2 = 112.5
1000
315m =112500
m = 35Kgm-3
Volume=357m3 -
- Formula:CH3CH = CHCH3√½
Name:But-2-ene√½ - H CH3
│ │
Cl─C─C─CH3
│ │
H CH3
- Formula:CH3CH = CHCH3√½
- % of H2O lost =14.5%
5 of anhydrous Na2CO3=85.5% ½
R.F.M of Na2CO3=106 ½
RMM of H2O =18 ½mk
n=1(Na2CO3.H2O) ½NaCO3 H2O 85.5
106
0.8066 = 1
0.805514.5
18
0.8055 = 1
0.8055 -
- Sample 3
- Sample 2 contained ions that caused temporary hardness ,therefore required large volume of soap solution before boiling, but after boiling the temporary hardness was removed thus required very little volume of soap solution to lather.
-
- Sodium chlorite(I)/Sodium hypochlorite
- 4HCl(aq)+MnO2 → MnCl2(aq)+Cl2(g)+2H2O(l)
Penalize ½mk if state symbols are not correct;
Penalize fully if the balancing is incorrect. - Potassium manganate(VII)/KMnO4 or lead(IV)oxide/PbO2
-
- Any suitable metal sulphide e.g.FeS rej.PbS
- FeS(s)+H2SO4(aq) → FeSO4(aq)+H2S(g)
- Hydrogen sulphide is less soluble in warm water compared to cold water
-
- Elements K and N
- Element L is a non-metal and reacts by gaining an electron
- Element M
-
- HCl(g) is extremely soluble in water 1mk. Inverted funnel provides a large surface area for the gas to dissolve in water and prevent suck-back.1mk
- Ammonia gas1mk
-
- 2Fe(S) + 3Cl2(g) → 2FeCl3(g)
Fe(s)+2HCl(g)→ FeCl2(g)+H2(g)√1mk
N.B:Must be balanced
State symbol must be correct
Chemical symbols must be correct - In the absence of moisture, chlorine cannot form HOCl, chloric(I) acid solution, responsible for its bleaching property.√1mk
- 2Fe(S) + 3Cl2(g) → 2FeCl3(g)
Download Chemistry Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Kangundo Subcounty Pre Mock Exams 2021/2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students

