QUESTION 1
- The grid below represents part of the periodic table. Study it and answer the questions that follow: The letters do not represent the actual symbols of the elements.

- What name is given to the group of elements to which C and F belong? (1mk)
- Explain the difference in reactivity between element C and D (2mks)
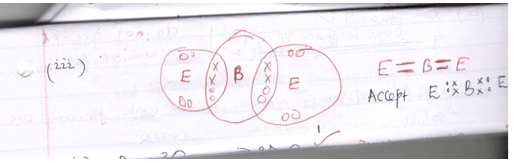
- Using( .) and cross (x) illustrate the bond between B and E (2mks)
- Write a balanced chemical equation for a reaction between element D and oxygen gas (1mk)
- On the grid indicate a tick(√) the position of element G which is in the third period of the periodic table and forms G3- ions (1mk)
- Study the information in the table below and answer the questions that follow: (The letters do not represent the actual symbols of the substance)
Substance Melting point ºC Boiling points ºC Solubility in water Density at room temp in g/cm3 H -117 78.5 Very Soluble 0.8 J -78 -33 Very Soluble 0.77 x 10-3 K -23 77 Insoluble 1.6 L -219 -183 Slightly Insoluble 1.33 x 10-3 - Which substance would dissolve in water and could be separated from the solution by fractional distillation in the school laboratory (1mk)
- Which substance is a liquid at room temperature and when mixed with water two layers would be formed. (1mk)
- Which letter represents substance that is a gas at room temperature and which can be collected (density of air is 1.225x10-3 g/cm3)
- Over water (1mk)
- By downward displacement of air (1mk)
QUESTION 2
- Propane can be changed into methane as shown below:
2CH3CH2 CH3(g) high temperature CH4(g) + C2H4(g) + CH3CHCH2(g) +H2(g)- Name the process undergone by propane (1mk)
- Write the equation of reaction between ethene and chlorine gas and name the product.(2mks)
- The diagram below shows an incomplete set-up of the laboratory preparation and collection of Ethene gas:
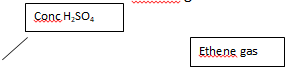
- Complete the diagram to show how Ethene gas is collected. (2mks)
- Name substances X and Y (2mks)
- Apart from being colourless and odourless, state another physical property of ethene.(1mk)
- the table below gives information about the major components of crude oil. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
Components Boiling pointsºC Gases Below 40 Petrol 40-175 Kerosene 175-250 Diesel oil 250-350 Lubricating oil 350-400 Bitumen Above 400 - Which of the compounds of crude oil has molecules with the highest number of atoms? Explain. (2mks)
- Explain the condition that could cause a poisonous gas to be formed when kerosene is burnt? (2mks)
QUESTION 3
- Air is a mixture of gases that can be classified as active and inactive part. The diagram below represents an experiment that can be carried out to determine the active part of air.
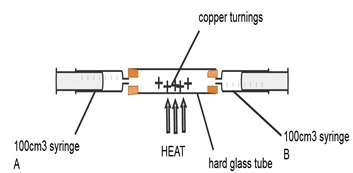
Describe how this set-up can be used to determine the active part of air (4mks) - When magnesium ribbon is heated in air the mass of the product is more than the mass of magnesium ribbon used. Explain (1mks)
- Carbon (IV) oxide and sulphur (IV) oxide are some of the gases that are common pollutant in the atmosphere. Explain two measures that are taken to reduce atmospheric pollution of the two gases. (2mks
- Oxygen is obtained on large scale by the fractional distillation of air as shown on the flow chart.
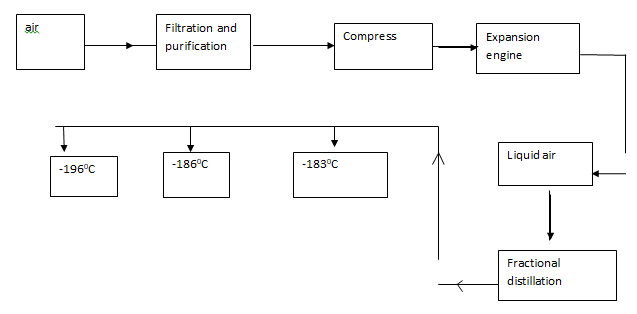
- Explain how carbon (IV) oxide and water are removed before liquification of air. (2mks)
- Identify the component that is collected at -186ºC (1mk)
- State one commercial use of oxygen gas apart from its use in hospital by patient with difficult breathing (1mk)
QUESTION 4
- Rhombic and Monoclinic are allotropes of sulphur. They are interconvertible as shown below:
96ºC
Rhombic ⇄ Monoclinic- What does the temperature 96ºC represent (1mk)
- State the differences in crystalline appearances between rhombic and monoclinic crystals. (1mk)
- The chart below shows some process involved in large scale production of sulphuric (VI) acid. Use it to answer the question that follows:

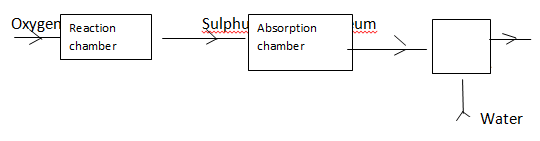
- Name substance A (1mk)
- Write an equation that takes place in the absorption chamber (1mk)
- Vanadium (V) oxide is commonly used as an catalyst in the contact process:
- Name another catalyst that can be used in this process.(1mk)
- Give two reasons why vanadium V oxide is the commonly used catalyst. (2mks)
- State and explain the Observation made when concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid is added to crystals of copper (II) sulphate in a beaker.(2mks)
- If 100kg of sulphur( IV) oxide is used in one day by this plant, determine the mass of oleum produced in one day. (S=32. O=16 H=1) (3mks)
QUESTION 5
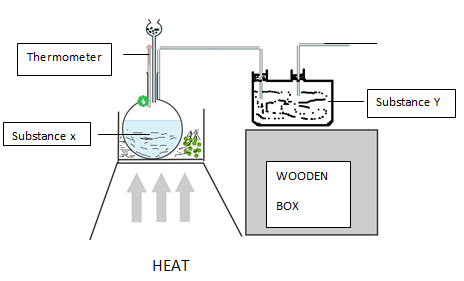
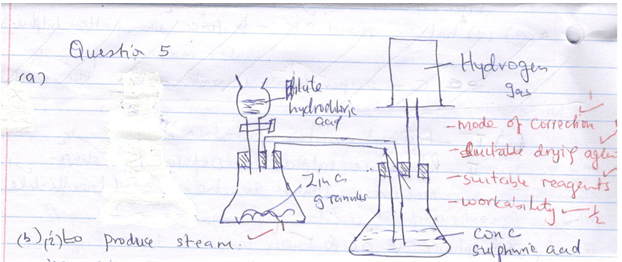
- Draw a well labeled diagram of set-up that can be used to prepare dry hydrogen gas in the laboratory. (3mks)
- The experiment below was carried out to investigate the reaction between steam and magnesium. Use it to answer the questions that follow:
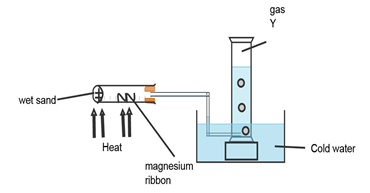
- Explain why wet sand is heated. (1mk)
- State and explain what was observed in the combustion tube. (2mks)
- Name the gas Y and state how it is tested in the laboratory. (1mk)
- Distinguish between:
Drying and dehydration. (2mks) - A student found two liquids labeled A and B placed on the bench in the laboratory. The liquids were colourless and did not have a smell. One liquid was water.
Describe a test that you would carry out to determine the beaker that contained water. (3mks)
QUESTION 6
- Give the name of the process involved in each of the following:
- Crystals of hydrated sodium carbonate(Na2CO3.10H2O) when left in open air change to white powder. (1 mk)
- When anhydrous calcium chloride is used to dry hydrogen gas for a long time, it changes to a solution. (1mk)
- Complete the table below by indicating the observations, type of change (permanent or temporary) and name of new compound formed. (6 mks)
Experiment Observations Type of change Name of product Heating solid zinc oxide in a test tube. Anhydrous cobalt (II) chloride is left exposed overnight. Iron wool is soaked in tap water for two days - The diagram below shows a sample of hard water being passed through a vertical column to remove its hardness.
- Write the formula of the two cations present in the sample of hard water. (2mks)
- What name is given to the above method of softening hard water. (1 mk)
- Write an ionic equation to show how the hard water is softened. (1 mk)
- Study the table below and answer the questions that follow.
A solution 9g of P and 14g of Q in 100g of water at 200 C is warmed while stirring up to 5o0C. State and explain the observations made. (2 mks)Salt Solubility (g/100g of water) at 20ºC Solubility (g/100g of water) at 50ºC P 10 20 Q 15 12
QUESTION 7
- A student set out to prepare iron (III) chloride using the apparatus shown in the diagram below:
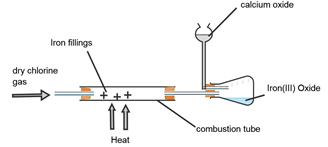
- Explain why
- It’s necessary to pass chlorine gas through the apparatus before heating begins. (2mks)
- Explain why
- Calcium oxide is used in the guard tube. (1mk)
- The total mass of Iron III chloride formed was found to be 0.5g. Calculate the volume of chlorine gas that reacted with Iron.
(Fe=56.0 Cl=35.5 and molar gas volume at 298k is 24,000cm3) (3mks) - What property of Iron (III) chloride makes it possible to be collected as shown in the diagram? (1mk)
- In the large scale production of hydrogen chloride gas, hydrogen gas burned in chlorine gas. State the source of the two gases. (1mk)

MARKING SCHEME
Question 1
-
- Alkaline earth metals (1mk)
- C is more reactive than D, (1mk) Element C has less nuclear charge than D (1/2mk) which make it easier to loose electrons. (1/2mk)
(2mks)- 4D + 3O2 → 2D2O3(s) (1mk) penalize (1/2mk) if no state symbol or wrong state .
(s) (g) (s) symbol are used
OR
4AL + 3O2 → 2Al2O3 Award Zero mark if equation is not balanced.
(s) (g) (s)
(1mk)C D √ E
-
- H (1mk)
- K (1mk)
-
- L (1mk)
- J (1mk)
QUESTION 2
-
- Thermal cracking (1mk) (accept cracking)
- C2H4 + Cl2 → CH2Cl CH2Cl Accept structural formula (1mk)
1,2- dichloroethane
-
-
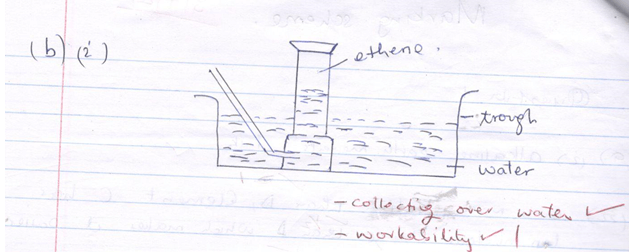
- X – ethanol (1mk)
Y –Sodium hydroxide (Accept chemical formular.) -
- Slightly soluble in water
- Soluble in organic substance low M.P and B.P Award 1mk for any one correct.
-
- Bitumen (1mk)
Has the highest boiling point (1mk) - Burning in limited of air and carbon( II) oxide gas is produced.
Question 3
- Ensure one of syringe A or B contains 100cm3(1/2mk) of air and the other syringe has no air. Heat the (1/2mk) copper turnings as you slowly (1/2mk) pass air from one syringe to the other. Continue passing the air (1/2mk) for several times until there is no further change in volume of air and stop heating. Allow apparatus to cool. (1/2mk) Take the final volume (1/2mk) of air in the syringe and Subtracts the final volume of air from 100cm3.
- Magnesium combine with oxygen in air to form magnesium oxide(1/2mk) Combining with oxygen increase the mass (1/2 mk)
- Introduce better and more efficient filter system in industries.
- Improvement of combustion of fuel in petrol and diesel engine.
- Introduce smokeless solid fuels or fuels like hydrogen.
- Make sulphur free fuels.
- Lining chimneys with CA(OH)2 in the scubbing process (any correct 2)
-
- H2O solidify at low temperature (-10ºC) (1mk)
Pass CO2 in NaOH/KOH or Co2 Solidifies at -78.5ºC before N2, O2 and argon liquefies. (1mk) - Argon
-
- Used in arch welding.
- When mixed with helium it is used by mountain climbers and deep seadivers
- Used to burn fuels.
- To remove iron impurities during steel making
(any one correct for 1mk)
- H2O solidify at low temperature (-10ºC) (1mk)
Question 4
-
-
- Transition temperature (1mk)
- Rhombic sulphur is Octahedral shape.( 1/2 mk)
Monoclinic sulphur is hexagonal/needle-like/prismatic shaped. ( 1/2 mk)
-
-
- Sulphuric VI acid (1mk)
- SO3 + H2SO4 → H2S2O7 (1mk)
- Platinum (1mk)
- Cheap (1mk) and less easily poisoned (1mk)
Blue crystals turns white ( 1/2 mk)
Concentrated H2SO4 dehydrates ( 1/2 mk) the blue crystals of hydrated copper (II) sulphate ( 1/2 mk) forming anhydrous copper sulphate. - Moles of SO2 used =100000g/64 = 1562.5moles( 1/2 mk)
2SO2 + O2 → 2SO3
(g) (g) (g)
Moles of SO3 formed = 1562.5moles ( 1/2 mk)
SO3 + H2SO4 →H2S2O7 ( 1/2 mk)
Mass of oleum = 178x1562.5 ( 1/2 mk)
= 278,125g ( 1/2 mk) or 278.125kg
QUESTION 5
-
-
- To produce steam.(1mk)
- White powder was formed.
Magnesium ribbon reacts with steam at high temperature to form magnesium Oxide.(1mk)
Or
Mg + H2O → MgO + H2
(s) (g) (s)(white) (g) - Hydrogen gas 1/2 mk) tested using a burning splint it burns with a” pop” sound
-
- Deliquescence – process where some salts when exposed to the atmosphere absorbs enough water to make a solution.(1mk)
Efflorescence- process where some crystals when exposed to the atmosphere loose water of crytallisation and becomes anhydrous. - Drying- removing moisture (1mk) or water.
Dehydration – removing elements of water from a substace(1mk)
- Deliquescence – process where some salts when exposed to the atmosphere absorbs enough water to make a solution.(1mk)
-
- Put a spatulaful of anhydrous Copper (II) sulphate in two separate test-tube.(1mk)
- Using a dropper add few drops of the liquid in the separate test tuber.
- The liquid that turns white powder or copper(II) sulphate to blue crystals is water.
Alternatively
Substitute anhydrous Copper (II) sulphate with anhydrous Cobalt (II) chloride (turns from blue to pink)
Question 6
-
- Efflorescence
- Deliquescence
-
Observations Type of change Name of product Colour changes from white to yellow (1mk) Temporary (1/2mk) Zinc oxide (1/2mk) Colour changes from blue to pink (1mk) Temporary (1/2mk) Hydrated cobalt (II) chloride (1/2mk) Colour changes from grey to brown (1mk) Permanent (1/2mk) Hydrated iron (III) oxide /rust (1/2mk)
-
- Ca2+ and Mg2+
- ion exchange
- Ca2+(aq)+ Na2X(aq) → CaX(s) + 2Na+(aq)
Mg2+(aq) + NA2X(aq) → MgX(s) 2Na+(aq) - mass of crystals= 14g-12g=2g
2g of Q will crystallize
Question 7
-
-
- Expell the air in the combustion tube.
- Absorb moisture
- Reacts with excess chlorine preventing it to escape to the environment as it’s a pollutant
- 2Fe + 3Cl2 → 2FeCl3
(s) (g) (s) (1/2 mk)
Moles FeCl3 = 0.5g = 0.0031 moles
162.5
Moles Cl2 used = 3 x 0.0031= 0.00456moles.
2
1mole Cl2 → 24,000
0.00456 → ??
0.00456 x 24,000 (1/2 mk)= 111.6g(1/2 mk)
1 - It sublimes on heating (1mk)
- Chlorine – electrolysis of brine/molten NaCl (1mk)
Hydrogen – cracking of hydrocarbon (1mk) or electrolysis of brime.
-
Download Chemistry Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Kangundo Subcounty Pre Mock Exams 2021/2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students

