Instructions to candidates:
- Answer all questions in the spaces provided in the question paper.
- KNEC mathematical tables and electronic calculators may be used for calculations.
- All working MUST be clearly shown where necessary.
- Candidates should answer the questions in English.
- You are provided with:
Solid P – 3.6 g of hydrated oxalic acid with the formula H2C2O4. X H2O. Solution W – 0.2 M sodium hydroxide solution.
You are required to determine:- Solubility of solid P.
- The value of X in H2C2O4. X H2O.
Procedure I:
- Fill the burette with distilled water.
- Transfer 4 cm3 of distilled water from the burette in to a boiling tube containing solid P.
- Heat the mixture while stirring carefully with a thermometer until all the solid dissolves.
- Cool the mixture by dipping it in cold water contained in a beaker while stirring with the thermometer. Record the temperature at which crystals start to form in table 1 below.
- Add a further 2 cm3 of distilled water from a burette to the mixture. Repeat step (iii) and (iv) above and record the crystallization temperature. Complete table 1 below.
(RETAIN THE CONTENTS OF THE BOILING TUBE FOR USE IN PROCEDURE II)
- Table 1
(5marks)Volume of distilled water in boiling tube. Crystallization temperature. Solubility of solid A in g/100g of water. 4 6 8 10 12 - On the grid provided, plot a graph of solubility of solid P against crystallization temperature. (3marks)
- From the graph, determine:
- The solubility of solid P at 60ºC. (1mark)
- The temperature at which 40 g of solid P would dissolve in 50 g of water. (2marks)
Procedure II:
Transfer all the contents of the boiling tube in procedure I into a clean 250 ml volumetric flask. Rinse the boiling tube and the thermometer with distilled water and add the contents into the volumetric flask. Add 100 cm3 of distilled water to the volumetric flask; shake until all the solid dissolves. Add more distilled water to the mark. Label this as solution Q. Drain the burette of any distilled water and then fill it with solution Q. Pipette 25 cm3 of solution W into a clean conical flask, add 3 drops of phenolphthalein indicator. Titrate solution Q against solution W. Record your reading in table 2 below. Repeat the titration two more times and complete the table below.
- Table 2
(4marks)I II III Final burette reading (cm3) Initial burette reading (cm3) Volume of solution Q used (cm3) - Calculate the average volume of solution Q used. (1mark)
- Calculate the:
- Number of moles of solution W used. (1mark)
- Number of moles of solution Q used given the equation below. (1mark)
2NaOH(aq) + H2C2O4. X H2O (aq) Na2C2O4.XH2O(aq)+ H2O (l) - Concentration of solution Q in moles per litre. (1mark)
- Determine the value of X in the formula H2C2O4. X H2O.(C = 12, H = 1, O = 16).(2mks)
- You are provided with solid E. Carry out the tests below. Write your observations and inferences in the spaces provided. Place all solid E in a boiling tube. Add about 10 cm3 of distilled water and shake until all the solid dissolves. Use about 2 cm3 portions of the solution in a test tube for the tests below.
- To the first portion, add sodium hydroxide solution dropwise till in excess.
Observations Inferences - To the second portion, add aqueous ammonia dropwise till in excess.
Observations Inferences - To the third portion, add 3 drops of sodium chloride solution.
Observations Inferences - To the fourth portion, add 3 drops of barium nitrate solution.
Observations Inferences - To the fifth portion, add 3 drops of acidified lead (II) nitrate solution.
Observations Inferences
- To the first portion, add sodium hydroxide solution dropwise till in excess.
- You are provided with solid F. Carry out the tests below. Write your observations and inferences in the spaces provided.
- Place half of solid F on a metallic spatula and ignite it over a Bunsen burner.
Observations Inferences - Place the remaining portion of solid F in a boiling tube. Add 5 cm3 of distilled water and shake. Preserve the resulting mixture for test (i) and (ii) below.
Observations Inferences - To about 2 cm3 of the solution in a test tube, add 3 drops of acidified potassium manganate (VII) solution.
Observations Inferences - To another 2 cm3 portion of the solution, add 3 drops of acidified potassium dichromate (VI) solution.
Observations Inferences
- Place half of solid F on a metallic spatula and ignite it over a Bunsen burner.
CONFIDENTIAL
The information contained here is to help the teacher in charge of chemistry and head of the institution to prepare adequately before the start of the practical. This information should therefore not be disclosed to anyone else, as that will constitute an exam irregularity.
In addition to the other apparatus found in the laboratory, each candidate should have the following:
- Complete stand and clamp.
- 50 ml burette.
- 25 ml pipette.
- A white tile.
- A spatula.
- Means of heating.
- 2 boiling tubes.
- 100 cm3 of solution W.
- 3.6 g of accurately weighed solid P.
- A conical flask.
- 500 ml distilled water in a wash bottle.
- 100 ml beaker.
- Means of labeling.
- 250ml volumetric flask.
- 6 dry test tubes.
- About 0.5 g of solid E.
- One thermometer (-10ºC to 110ºC).
- About 0.5 g of solid F.
Access to each of the following solutions:
NB: Each solution to be supplied with a dropper.
- 2 M aqueous ammonia.
- 2 M sodium hydroxide solution.
- Sodium chloride solution.
- Barium nitrate solution.
- Acidified lead (II) nitrate solution.
- Acidified potassium manganate (VII).
- Acidified potassium dichromate (VI).
- Phenolphthalein indicator.
Preparations.
Solid P is hydrated oxalic acid.
Solution W is 0.2 M sodium hydroxide solution.
Solid E is hydrated aluminium sulphate.
Solid F is maleic acid.

MARKNG SCHEME
Instructions to candidates:
- Answer all questions in the spaces provided in the question paper.
- KNEC mathematical tables and electronic calculators may be used for calculations.
- All working MUST be clearly shown where necessary.
- Candidates should answer the questions in English.
- You are provided with:
Solid P – 3.6 g of hydrated oxalic acid with the formula H2C2O4. X H2O. Solution W – 0.2 M sodium hydroxide solution.
You are required to determine:- Solubility of solid P.
- The value of X in H2C2O4. X H2O.
Procedure I:
- Fill the burette with distilled water.
- Transfer 4 cm3 of distilled water from the burette in to a boiling tube containing solid P.
- Heat the mixture while stirring carefully with a thermometer until all the solid dissolves.
- Cool the mixture by dipping it in cold water contained in a beaker while stirring with the thermometer. Record the temperature at which crystals start to form in table 1 below.
- Add a further 2 cm3 of distilled water from a burette to the mixture. Repeat step (iii) and (iv) above and record the crystallization temperature. Complete table 1 below.
(RETAIN THE CONTENTS OF THE BOILING TUBE FOR USE IN PROCEDURE II)
- Table 1
10×½ = 5 mksVolume of distilled water in boiling tube. Crystallization temperature. Solubility of solid A in g/100g of water. 4 6 8 10 12
Complete table: (1 Mark) Conditions:
5 readings (1 mark)
3-4 readings (½mark)
Less than 3 readings (0mark)
Penalties:
Penalize ½ mark once for unrealistic temperature readings of above 100ºC. and below 10ºC.
Decimals (1 mark)
Accept temperature readings given as whole numbers, 1 d.p (.0 or .5) or 2 d.p of .00, .25, .50, .75
Trend (1 mark).
Accept only a decreasing trend of temperature, otherwise penalize fully. Solubility calculations in column II (2 marks):
5 correctly worked out solubility values (2 marks)
3-4 correctly worked out solubility values (1 mark)
Less than 3 correctly worked out solubility values (0mark) - On the grid provided, plot a graph of solubility of solid P against crystallization temperature. (3marks)
Graph (3 marks)- Axis (2 correctly labelled) = ½ mk.
Only one axis labelled or axes completely unlabeled = 0 mk. - Scale (½mk)
Penalize fully for nonlinear / inconsistent interval on any of the axis. Penalize fully if plotting is on less than half of the grid space provided. - Plotting (1 mark)
All five points correctly plotted = 1 mark. 3 – 4 correctly plotted points = ½mk
Less than 3 correctly plotted points = 0 mks - Curve (1 mark).
Accept a smooth curve passing through atleast 3 correctly plotted points, otherwise penalize fully.
- Axis (2 correctly labelled) = ½ mk.
- From the graph, determine:
- The solubility of solid P at 60ºC. (1mark)
Award 1 mark for correctly read solubility value. - The temperature at which 40 g of solid P would dissolve in 50 g of water. (2marks)
40 g dissolve in 50 g of water
? dissolve in 100g of water.
40 × 100
50
= 80 g√1mark
Then read the temperature that gives a solubility of 80g/100g of water. √1mark
- The solubility of solid P at 60ºC. (1mark)
Procedure II:
Transfer all the contents of the boiling tube in procedure I into a clean 250 ml volumetric flask. Rinse the boiling tube and the thermometer with distilled water and add the contents into the volumetric flask. Add 100 cm3 of distilled water to the volumetric flask; shake until all the solid dissolves. Add more distilled water to the mark. Label this as solution Q. Drain the burette of any distilled water and then fill it with solution Q. Pipette 25 cm3 of solution W into a clean conical flask, add 3 drops of phenolphthalein indicator. Titrate solution Q against solution W. Record your reading in table 2 below. Repeat the titration two more times and complete the table below.
- Table 2
I II III Final burette reading (cm3) Initial burette reading (cm3) Volume of solution Q used (cm3) - Complete table = 1 mark.
Complete table with three titrations = 1 mark.
Incomplete table with two titrations = ½mark.
Incomplete table with one titration = 0 mark.
Penalties.- Wrong arithmetic.
- Inverted table.
- Burette readings beyond 50 ml and below 1.0 ml.
For any of the above penalties, penalize ½mark each upto a maximum of ½mark.
- Use of decimals = 1 mark
- 1 d.p used consistently.
- If 2 decimal places are used, the second decimal place MUST be a 0 or 5.
Penalize FULLY for any other use of decimal place.
- Accuracy = 1 mark.
- Compare any of the candidates reading with the school value.
- If atleast one titre value is within ±0.1 cm3 of the school value = 1 mark.
- If none is within ±0.1 cm3 of s.v but within ±0.2 cm3 of s.v = ½mark.
- If none is within ±0.2 cm3 of the s.v, award 0 mark.
- In case of wrong arithmetic in the table, cored the correct titre with the s.v and award accordingly.
- Principles of averaging = 1 mark.
- 3 consistent values averaged = 1 mark.
- 3 titrations done, only two consistent and averaged = 1 mark.
- Only two titrations done, are consistent and averaged = ½mark.
- Final answer = 1 mark.
- Compare the school value with the candidate’s averaged titre.
- If within ± 0.1 cm3 of the s.v award 1 mark.
- If not within ± 0.1 cm3 but within ±0.2 cm3 of the s.v award ½mark.
- If beyond, ±0.2 cm3 award 0 mark.
- Compare the school value with the candidate’s averaged titre.
- Complete table = 1 mark.
- Calculate the average volume of solution Q used. (1mark)
- Tied to (V) above.
- Calculate the:
- Number of moles of solution W used. (1mark)
0.2×25 √½mk
1000
= 0.005 moles. √½mk
The above expression MUST be given as it is, otherwise penalize fully for any strange value used. - Number of moles of solution Q used given the equation below. (1mark)
2NaOH (aq) + H2C2O4. X H2O (aq) Na2C2O4.X H2O (aq) + H2O (l)
From the equation, mole ratio is 2:1
0.005 √½mark
2
= 0.0025 moles. √½mark - Concentration of solution Q in moles per litre. (1mark)
Answer in c(ii) above ×1000 √½mark
Average titre.
Correct answer √½mark
- Number of moles of solution W used. (1mark)
- Determine the value of X in the formula H2C2O4. X H2O. (C = 12, H = 1, O = 16).(2mks)
Molarity = Concentration (g/l)
RFM
Conc in g/l = 3.6 ×1000
250
= 14.4 g/l. √½mark
RFM = 14.4 (g/l) √½mark
Answer in c(iii)
90 + 18X = 14.4 (g/l) √½mark
Answer in c(iii)
X = (14.4 – 90) ÷ 18√½mark
Answer in c(iii)
- You are provided with solid E. Carry out the tests below. Write your observations and inferences in the spaces provided. Place all solid E in a boiling tube. Add about 10 cm3 of distilled water and shake until all the solid dissolves. Use about 2 cm3 portions of the solution in a test tube for the tests below.
- To the first portion, add sodium hydroxide solution dropwise till in excess.
Observations Inferences White precipitate√½mark soluble in excess√½mark Pb2+, Al3+, Zn2+ present.
All 3 mentioned = 1mk
Any 2 correct mentioned = √½mk Only 1 correct mentioned = 0 mk. - To the second portion, add aqueous ammonia dropwise till in excess.
Observations Inferences White precipitate√½mark insoluble in excess√½mark Pb2+, Al3+ present.
Penalize ½mk for any contradictory ion mentioned as present upto a maximum of 1 mark. - To the third portion, add 3 drops of sodium chloride solution.
Observations Inferences No white precipitate.√1mark Al3+ present.√1mark
Award ½mk for Pb2+ mentioned as absent. - To the fourth portion, add 3 drops of barium nitrate solution.
Observations Inferences White precipitate.√1mark SO 2-, SO 2- , CO 2- present.
(1mk)
All 3 mentioned = 2mks
Any 2 correct mentioned = 1mk
Only 1 correct mentioned = 0 mk.
Penalize ½mk for any contradictory ion mentioned as present upto a maximum of 2 marks. - To the fifth portion, add 3 drops of acidified lead (II) nitrate solution.
Observations Inferences White prepitate.√1mark SO 2- present.√1mark
• Accept SO 2- , CO 2- mentioned as
absent for ½mk. Penalize 1mk for
any contradictory ion.
(1mk) (1mk)
NB: Penalize fully for any ion written with a wrong charge.
- To the first portion, add sodium hydroxide solution dropwise till in excess.
- You are provided with solid F. Carry out the tests below. Write your observations and inferences in the spaces provided.
- Place half of solid F on a metallic spatula and ignite it over a Bunsen burner.
Observations Inferences Burns with a yellow / sooty flame.
√1mark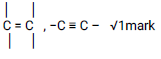
- Place the remaining portion of solid F in a boiling tube. Add 5 cm3 of distilled water and shake. Preserve the resulting mixture for test (i) and (ii) below.
Observations Inferences Solid F dissolves or is soluble. √1mark Polar compound or Q is polar. √1mark - To about 2 cm3 of the solution in a test tube, add 3 drops of acidified potassium manganate (VII) solution.
Observations Inferences Purple color is decolorised changes from purple to colorless 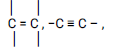
- To another 2 cm3 portion of the solution, add 3 drops of acidified potassium dichromate (VI) solution.
Observations Inferences Orange colour changes to green.√1mark R - OH present √1mark. (1mk)
- To about 2 cm3 of the solution in a test tube, add 3 drops of acidified potassium manganate (VII) solution.
- Place half of solid F on a metallic spatula and ignite it over a Bunsen burner.
Download Chemistry Paper 3 Questions and Answers with Confidential - Kangundo Subcounty Pre Mock Exams 2021/2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students

