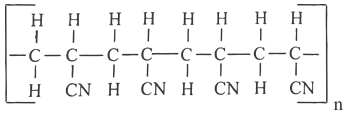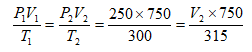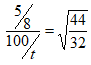INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
- Answer all questions in the spaces provided in the question paper.
- KNEC Mathematical tables and silent non-programmable electronic calculators may be used.
- All workings must be clearly shown where necessary.
- Candidates should answer the questions in English.
- Silicon and carbon are both group IV elements. Silicon (IV) oxide is a solid at room temperature which melts at 1973K while carbon (IV) oxide is a gas and melts at 217K. In terms of structure and bonding, explain the difference. (2 marks)
- When sodium carbonate is added to a solution containing Al3+(aq) ions, effervescence is observed. Explain (2 marks)
- An element Q can be represented as
(Q is not the actual symbol of the element)
- Write the electron configuration of Q (1 Mark)
- To which group and period does Q belong? (1 Mark)
- Write the formula of the ion of Q. (1 Mark)\
-
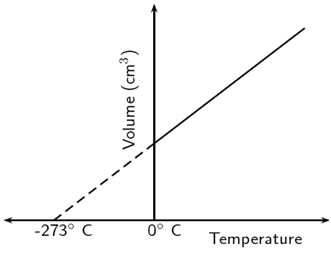
- Sketch a graph demonstrating Charles’ law. (2 Marks)
- A fixed mass of a gas has a volume of 250cm3 at a temperature of 27°C and 750mmHg pressure. Calculate the volume the gas would occupy at 42°C and 750mmHg. (2 Marks)
- Sketch a graph demonstrating Charles’ law. (2 Marks)
- The table below shows the trend in ionization energy for elements M, N and L. Use it to answer the questions that follows.
Element First Ionization energy (kJ) M 494 N 519 L 418 - Define ionization energy. (1 Mark)
- Which element has the smallest atomic radius? (1 Mark)
- Which is the most reactive element? Explain. (2 Marks)
- Identify acids and bases in the following reaction using Bronsted-Lowry theory. (2 Marks)
NH4+(aq) + OH- (aq)NH3(aq) + H2O(l)
Acids:……………………………………………………………Bases:……………………………………………… -
- State Graham’s law of diffusion. (1 Mark)
- 50cm3 of oxygen gas diffused through a porous plug in 80 seconds. How long will it take 100cm3 of carbon (IV) oxide gas to diffuse through the same plug? (3 Marks)
- When hydrogen sulphide gas was bubbled into an aqueous solution of iron (III) chloride, a yellow precipitate was formed.
- State another observation that was made. (1 Mark)
- Explain the observation above. (1 Mark)
- Write an equation for the reaction that took place. (1 Mark)
- Using equations, explain the observations made at the electrodes when an electric current is passed through molten Aluminium oxide. (3 Marks)
- In a titration experiment, a student was provided with the following:-
- Solution R which was 0.408M HCl
- Solution S containing 6.9g of a metal carbonate M2CO3 in 250cm3 solution
Upon titration, 24.5cm3 of solution R was required to completely neutralize 25cm3 of solution S. Determine the following.- Molarity of solution S (2 Marks)
- Formula mass of M2CO3 (2 Marks)
- Relative atomic mass of M (1 Mark)
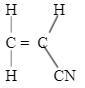
- Compounds A and B have the same molecular formula C3H6O2. Compound A liberates carbon (IV) oxide gas on addition of aqueous sodium carbonate while compound B does not. Compound B has a pleasant smell. Name and draw the structural formulae of A and B. (4 Marks)
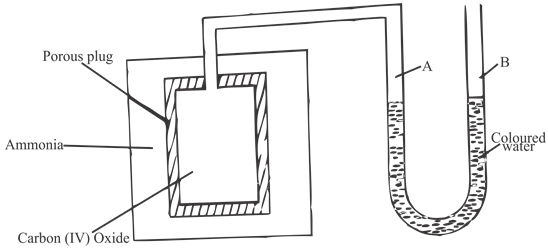
- The set up below was used by a form 3 student to study the difference in rates of diffusion between ammonia (NH3) and carbon (IV) oxide(CO2) gases. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
State and explain the observation made on the level of coloured water in the arms A and B on the U tube as the experiment progressed. (3 Marks) - 2.1g of a compound of carbon and hydrogen burns to form 6.6g of carbon (IV) oxide and 2.7g of water.
- Determine the empirical formula of this compound (C=12, H=1, O=16) (2 Marks)
- Given that the molecular mass of the compound is 42, determine its molecular formula (1 mark)
- To which group of organic compounds does the compound belong? (1 Mark)
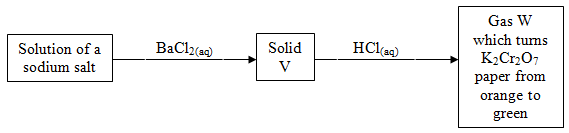
- Study the diagram below and answer the questions that follow.
- Name
- Solid V ………………………………………………………....................... (1 Mark)
- Gas W ………………………………………………………………………. (1 Mark)
- Write an equation for reaction between solid V and dilute hydrochloric acid. (2 Marks)
- Name
- Starting with solid aluminium sulphate, describe how a solid sample of aluminium hydroxide could be prepared.
(3 Marks) -
- A burning magnesium ribbon continues to burn in a jar of nitrogen gas but a burning splint is extinguished. Explain (1 Marks)
- Using equations explain what happens when concentrated nitric (V) acid is reacted with wood charcoal. (2 Marks)
-
- State Gay Lussac’s law. (1 Mark)
- 10cm3 of a gaseous hydrocarbon were mixed with 33cm3 of oxygen gas which was in excess. The mixture was exploded and after cooling to room temperature, the residual volume of gas occupied 28cm3. On adding concentrated potassium hydroxide the volume decreased to 8cm3.
Work out the molecular formula of the hydrocarbon (3 Marks)
-
- What are isotopes? (1 Mark)
- Lithium has two isotopes
and
Determine the number of neutrons in
. (1 Mark)
- If the relative atomic mass of lithium is 6.94. Which of the two isotopes is more abundant. Give a reason. (2 Marks)
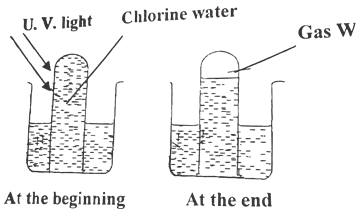
- The diagram below represents a set of apparatus used to study properties of chlorine water.
- Name two components of chlorine water. (1 Mark)
- Write an equation for the reaction that produces gas W. (1 Mark)
- The following test was carried out on chlorine water contained in a test tube. A piece of blue flower was dropped in the test tube. Explain why the flower was bleached. (2 Marks)
- The diagram below shows part of a synthetic polymer. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
- Draw the structural formula of the monomer from which the polymer is made. (1 Mark)
- A sample of the polymer has a molecular mass of 63600. Calculate the number of monomers in the sample.
(2 Marks) - Methanol has molecular mass of 32 while ethane has a molecular mass of 30. The boiling point of methanol is 65°C while that of ethane is -89°C. Explain (2 Marks)
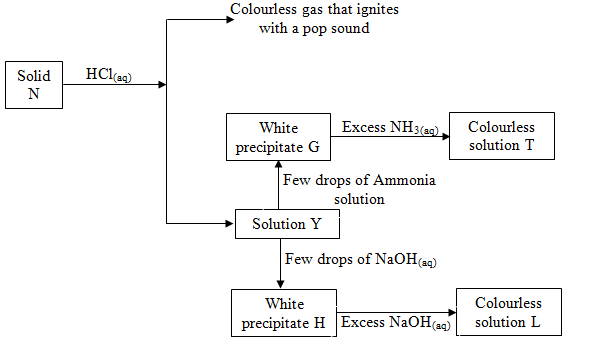
- Study the reaction scheme below and answer the question that follows:-
- Name solid N. (1 Mark)
- State the observation that would be made if solution Y is mixed with lead (II) nitrate solution. (1 Mark)
- Write an ionic equation for the formation of the colourless solution T. (1 Mark)
- Name the ion present in colourless solution L. (1 Mark)
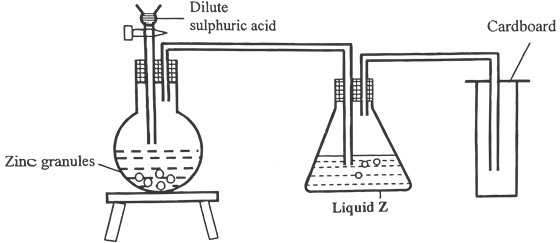
- The setup below was used to prepare dry hydrogen gas. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
- Identify one mistake in the setup above. (1 Mark)
- What is the role of liquid Z? (1 Mark)
- Using an equation give one chemical property of hydrogen gas. (1 Mark)
-
- Define solubility. (1 Mark)
- In an experiment to determine the solubility of solid W in water at 40°C, the following results were obtained.
- Mass of empty evaporating dish = 36.2g
- Mass of evaporating dish + saturated solution = 52.4g
- Mass of evaporating dish + dry solid W = 40.4g
Use this data to calculate the solubility of W at 40°C. (2 Marks)

MARKING SCHEME
- Silcon and carbon are both group IV elements. Silcon (IV) oxide is a solid at room temperature which melts at 1973K while carbon (IV) oxide is a gas and melts at 217K. In terms od structure and bonding, explain the difference. (2 Marks)
- Carbon (IV) oxide has a simple molecular structure with weak van der waals forces which require little energy to break while silcon (IV) oxide has a giant atomic structure with strong covalent bonds which require more energy to break.
- When sodium carbonate is added to a solution containing Al3+(aq) effervescence is observed. Explain (2 Marks)
- The solution is acidic containing which reacts with the CO32-
CO32-(aq) + H+(g) → CO2(g) + H2O(l)
[Al(H2O6)3+(aq) → [Al(H2O)5 OH]2+(aq) + H+(aq)
- The solution is acidic containing which reacts with the CO32-
- An element Q can be represented as
(Q is not the actual symbol of the element)
- Write the electron configuration of Q. 2.8.8.2 (1 Mark)
- To which group and period does Q belong? Group II Period 4 (1 Mark)
- Write the formula of the ion of Q. Q2+ (1 Mark)
-
- Sketch a graph demonstrating Charles’ law. (2 Marks)
- A fixed mass of a gas has a volume of 250cm3 at a temperature of 27°C and 750mmHg pressure. Calculate the volume the gas would occupy at 42°C and 750mmHg. (2 Marks)
27 + 273 = 300K 42 + 273 = 315K
V2 = 250 × 750 × 315 = 262.5cm3
750 × 300
- Sketch a graph demonstrating Charles’ law. (2 Marks)
- The table below shows the trend in ionization energy for elements M,N,L. Use it to answer the questions that follows.
- Define ionization energy. (1 Mark)
- Minimum amount of energy required to remove electron from atom in its gaseous state
- Which element has the smallest atomic radius? (1 Mark)
- N
- Which is the most reactive element? Explain. (2 Marks)
- L- Requires the least energy to lose an electron
- Define ionization energy. (1 Mark)
- Identify acids and bases in the following reaction using Bronsted-Lowry theory. (2 Marks)
ACID BASES NH4+
H2OOH−
NH3 -
- State Graham’s law of diffusion. (1 Mark)
- Under the same conditions of temperature and pressure, the rate of diffusion of a gas is inversely proportional to the square root of its density.
- 50cm3 of oxygen gas diffused through a porous plug in 80 seconds. How long will it take 100cm3 of carbon (IV) oxide gas to diffuse through the same plug? (3 Marks)
Ro2 = 50/80 = 5/8
Rco2 = 100/t
100/t = 0.533
T = 100 = 187.617
0.533
- State Graham’s law of diffusion. (1 Mark)
- When hydrogen sulphide gas was bubbled into an aqueous solution of iron (III) chloride, a yellow precipitate was formed.
- State another observation that was made. (1 Mark)
- The yellow solution turns green
- Explain the observation above. (2 Marks)
- Hydrogen sulphide is a reducing agent. It reduces the yellow Fe3+ ions to green Fe2+. H2S is oxidized to Sulphur (yellow deposit)
- Write an equation for the reaction that took place. (1 Mark)
2FeCl2(aq) + H2S(g) → 2FeCl2(aq) + 2HCl(aq) + S(s)
- State another observation that was made. (1 Mark)
- Using equations, explain the observation made at the electrodes when an electric current is passed through molten Alminium oxide. (3 Marks)
Anode
O2− → O + 2e
O2− → O + 2e
2O2− → O2 + 2e
2O2− → O2 + 2e Colourless gas that relights a glowing splint
Cathode
Al3+ + 3e → Al(s) grey solid deposited - In a titration experiment, a student was provided with the following:-
- Solution R which was 0.408M HCl
- Solution S containing 6.9g of a metal carbonate M2CO3 in 250cm3 solution
Upon titration, 24.5cm3 of solution R was required to completely neutralize 25cm3 of solution S. Determine the following.- Molarity of solution S (2 Marks)
2HCl + M2CO3 → 2MCl + H2O + CO2
Moles in 24.5cm3 HCl
24.5 × 0.408 = 0.1
1000
25cm3 → 0.05
1000 →
= 0.05 × 1000 = 0.2M
25 - Formula mass of M2CO3 (2 Marks)
Concentration of M2CO3 in g/l
= 6.9 × 1000 = 27.6g/l
250
= 0.2 → 27.6
1 →
= 27.6 × 1 = 138
0.2 - Relative atomic mass of M (1 Mark)
M2CO3 = 138
2M + 12 + ( 3 × 16) = 138
2M + 60 = 138
2M = 78
M = 39
- Molarity of solution S (2 Marks)
- Compounds A and B have the same molecular formulae C3H6O2. Compound A liberates carbon (IV) oxide gas on addition of aqueous sodium carbonate while compound B does not. Compound B has a pleasant smell. Name and draw the structural formulae of A and B. (4 Marks)
Propanoic acid
Methylethanoate
- The set up below was used by a form 3 student to study the difference in rates of diffusion between ammonia (NH3) and carbon (IV) oxide gases. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
State and explain the observation made on the level of coloured water in the arms A and B on the U tube as the experiment progressed. (3 Marks)
RMM of NH3
RMM of CO2
The level of coloured water in arm A of the U-Tube dropped and rose in arm b. Ammonia has lower density that CO2 as it has a lower RMM and hence it diffused into the porous plug at a higher rate than the rate at which CO2 diffused out of the porous plug creating a region of higher pressure inside the plug. - 2.1g of a compound of carbon and hydrogen burns to form 6.6g of carbon (IV) oxide and 2.7g of water.
- Determine the empirical formulae of this compound (C=12, H-1, O=16) (2 Marks)
RFM of CO2 = 12 + 16 + 12 = 44
RMM of H2O = (1 × 2) + 16 = 18
Mass of C = 12/44 × 6.6 = 1.8
Mass of H = 2/18 × 2.7 = 0.3
EF = CH2ELEMENT C H Mass in grams 1.8 0.3 R.A.M 12 1 Mole ratio 0.15 0.3 Simplest ratio 1 2 - Given that the molecular mass of the compound is 42, determine its molecular formula
14n =42
n=3
MF (CH2)3 = C3H6 - To which group of organic compounds does the compound belong. (1 Mark)
- Alkenes
- Determine the empirical formulae of this compound (C=12, H-1, O=16) (2 Marks)
- Study the diagram below and answer the questions that follow.
- Name
- Solid V - Barium Sulphite (1 Mark)
- Gas W - Sulphur (IV) oxide (1 Mark)
- Write an equation for reaction between solid V and dilute hydrochloric acid. (2 Marks)
BaSO3 + 2HCl → BaCl2SO2 + H2O
- Name
- Starting with aluminium sulphate describe how a solid sample of aluminium hydroxide could be prepared. (3 Marks)
- Add distilled water to aluminium sulphate to dissolve
- Add aqueous ammonium hydroxide to aluminium sulphite solution to precipitate aluminium hydroxide.
- Filter and wash the residue with distilled water
- Dry it between papers
Note: NaOH cannot be used because of the amphoteic Al(OH)3 will dissolve in excess.
-
- A burning magnesium ribbon continues to burn in a jar of nitrogen gas but a burning splint is extinguished. Explain
(1 Marks)- Heat produced by the burning magnesium is strong enough to break the triple bond in the nitrogen molecule forming free nitrogen atoms which react with magnesium. Heat produced by burning wooden splint is not strong enough to break the triple bond.
- Using equations explain what happens when concentrated nitric (V) acid is heated with wood charcoal. (2 Marks)
C(s) + 4HNO3 → CO2(g) + 4NO2(g) + 2H2O(l)
- A burning magnesium ribbon continues to burn in a jar of nitrogen gas but a burning splint is extinguished. Explain
-
- State Gay Lussac’s law. (1 Mark)
- When gases combine they do so in volumes that bear a simple ratio to one another and to the products is gaseous, provided that the temperature and pressure are kept constant.
- 10cm3 of a gaseous hydrocarbon were mixed with 33cm3 of oxygen gas which was in excess. The mixture was exploded and after cooling to room temperature, the residual volume of gas occupied 28cm3. On adding concentrated potassium hydroxide the volume decreased to 8cm3.
Work out the molecular formular of the hydrocarbon (3 Marks)
CxHy +(x + y/4)O2 → xCO2 + y/2H2O
1mole x+y/4 moles x moles y/2 moles
1Vol x+y/4 Vol xVol
10cm3 25cm3 20cm3
1 2.5 2
x=2
x+y/4 = 2.5
y=2
- State Gay Lussac’s law. (1 Mark)
-
- What are isotopes? (1 Mark)
- Atoms of the same element which have the same atomic number but different mass number
- Lithium has two isotopes
and
determine the number of neutrons in
. (1 Mark)
→ 7 − 3
= 4 neutrons - If the relative atomic mass of lithium is 6.94. Which of the two isotopes is most abundant. Give a reason. (2 Marks)
x% (100−x)%
x × 7 + (100 − x)6 = 6.94
100 100
7x + (600 − 6x) = 6.94
100 100
7x + 600 − 6x = 694
7x − 6x = 694 − 600
x = 94%is the most abundant
94% 6%
- What are isotopes? (1 Mark)
- The diagram below represents a set of apparatus used to study properties of chroline water.
- Name two components of chroline water. (1 Mark)
- Chloric (I) acid
- Hydrochloric acid
- Write an equation for the reaction that produces gas W. (1 Mark)
HOCl → HCl + 'O'
HOCl → HCl + 'O'
2HOCl → 2HCl + O2 - The following was carried out on chroline water contained in test tubes. A piece of blue flower was dropped in the test tube. Explain why the flower was bleached. (2 Marks)\
- Chloric (I) acid HOCl in water decomposes to form atomic oxygen.
- Atomic Oxygen oxidises the coloured flowers to white hence bleaching the
- Name two components of chroline water. (1 Mark)
- The diagram below shows part of a synthetic polymer. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
- Draw the structural formula of the monomer from which the polymer is made. (1 Mark)
- A sample of the polymer has a molecular mass of 63600. Calculate the number of monomers in the sample.
(2 Marks)
RMM of monomer = 3 × 12) + (1 × 3) + 14 = 53
Number of monomers = 63600 = 1200
53 - Methanol has molecular mass of 32 while ethane has a molecular mass of 30. The boiling point of methanol is 65°C while that of ethane is -89°C. Explain (2 Marks)
- Ethane molecules only have the weak van der waals farces while methanol have much stronger hydrogen bonds in addition to the van der waals forces.
- Draw the structural formula of the monomer from which the polymer is made. (1 Mark)
- Study the reaction scheme below and answer the question that follows:-
- Name solid N. Zinc metal (1 Mark)
- State the observation that would be made if solution Y is mixed with lead (II) nitrate solution. (1 Mark)
- White precipitate of Lead (II) chloride; dissolves on warming
- Write ionic equations for the formation of white precipitate G and colourless solution T. (1 Mark)
G Zn2+(aq) + 2OH−(aq) → Zn(OH)2
T Zn(OH)2 + 4NH3(aq) → [Zn(NH3)4]2+ - Name the ion present in colourless solution L. (1 Mark)
Tetrahydroxozinc (II) [Zn(OH)4]2+
- The setup below was used to prepare dry hydrogen gas. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
- Identify one mistake in the setup above. (1 Mark)
- Method of collection is incorrect
- What is the role of liquid Z? (1 Mark)
- Absorb moisture / water from hydrogen gas
- Using an equation give one chemical property of hydrogen gas. (1 Mark)
- Burns in oxygen to form water 2H2(g) + O2(g) → 2H2O(l)
- Reducing agent H2(g) + CuO(s) → Cu(s) + H2O(l)
- Identify one mistake in the setup above. (1 Mark)
-
- Define solubility. (1 Mark)
- Maximum mass of a solute that can saturate 100g of water at a given temperature
- In an experiment to determine the solubility of solid W in water at 40°C, the following results were obtained.
- Mass of empty evaporating dish = 36.2g
- Mass of evaporating dish + saturated solution = 52.4g
- Mass of evaporating dish + dry solid W = 40.4g
Use this data to calculate the solubility of W at 40°C. (2 Marks)
Mass saturated solution = 52.4 − 36.2 = 16.2g
Mass of solute = 40.4 − 36.2 = 4.2g
Mass of water = 16.2 − 4.2 = 12g
Solubility at 40°C of water 100 × 4..2 = 35g/100g of water
- Define solubility. (1 Mark)
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download Chemistry Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Joint Pre-Mock Exams 2021/2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students