
Introduction
- A binomial is an expression of two terms
Examples
(a + y), a + 3, 2a + b
- It easy to expand expressions with lower power but when the power becomes larger, the expansion or multiplication becomes tedious. We therefore use pascal triangle to expand the expression without multiplication.
- We can use Pascal triangle to obtain coefficients of expansions of the form( a + b) n

Pascal's Triangle
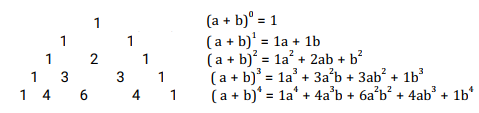
Note;
- Each row starts with 1
- Each of the numbers in the next row is obtained by adding the two numbers on either side of it in the preceding row
- The power of first term (a ) decreases as you move to right while the powers of the second term (b) increases as you move to the right
Example
Expand (p + q)5
Solution
The terms without coefficients are;
p5, p4q, p3q2, p2q3, pq4, q5
From Pascal triangle, the coefficients when n =5 are; 1, 5, 10, 10, 5, 1
Therefore (p +q)5 = p5 +5p4q + 10p3q2 + 10q2q3 + 5pq4 + q5
Example
Expand (x − y)7
Solution
(x−y) 7 = (x + (−y)7
The terms without the coefficient are;
x7, x6(−y), x5(−y)2, x4(−y)3, x3(−y)4, x2(−y)5, x(−y)6, y7
From Pascal triangle, the coefficients when n =7 are; 1, 7, 21, 35, 35, 21, 7, 1
Therefore (x−y)7= x7 − 7x6y + 21x5y2 − 35x4y3 + 35x3y4 − 21x2y5 + 7xy6 − y7
Note;
When dealing with negative signs, the signs alternate with the positive sign but first start with the negative sign.
Applications to Numeric Cases
Example
Use binomial expansion to evaluate (1.02)6 to 4 S.F
Solution
(1.02) = (1+0.02)
Therefore (1 .02)6 = (1 + 0.02)6
The terms without coefficients are
16, 15(0.02)1, 14(0.02)2, 13(0.02)3, 12(0.02)4, 11(0.02)5, (0.02)6
From Pascal triangle, the coefficients when n = 6 are; 1, 6, 15, 20, 15, 6, 1
Therefore;
(1.02)6 = 1 + 6 (0.02) + 15 (0.02)2 + 20(0.02)3 + 15(0.02)4 + 6(0.02)5 + (0.02)6
=1 + 0.12 + 0.0060 + 0.00016 + 0.0000024 + 0.0000000192 + 0.000000000064
=1.1261624
=1.126 (4 S.F)
Note;
- To get the answer just consider addition of up to the 4th term of the expansion. The other terms are too small to affect the answer.
Example
Expand (1 + x)9 up to the term x3. Use the expansion to estimate (0.98) 9 correct to 3 decimal places.
Solution
(1 + x)9
The terms without the coefficient are;
19, 18(x), 17x2, 16(x)3, 15(x)4
From Pascal triangle, the coefficients when n =9 are; 1, 9, 36, 84, 126, 126, 84, 36, 9, 1
Therefore (1 + x)9= 1 + 9x + 36x2 + 84x3………………..
(0.98)9= 1 + 9(-0.02) + 36 + (-0.02)2 + 84 (-0.02)3
= 1 – 0.1 8 + 0.0144 – 0.000672
= 0.833728
= 0.834 (3 d.p)
Example
Expand (1 + ½x)10 upto the term in in ascending powers of hence find the value of (correct to four decimal places.)
Solution
= 1 + 10(1/2x) + 45(1/2 x)2 + 120(1/2x)3
= 1 + 10 × 1/2x + 45 × 1/2x2 + 120 × 1/8x3
= 1 + 5x + 45/4x2 + 15x3
(1.005)10 = (1+0.005)10
Here 1/2 x = 0.005
x = 0.010
Substituting for x = 0.01 in the expansion
[1+ 1/2 (0.01)]10 = 1 + 5 ×0.01 + 45/4 ×(0.01)2 + 15(0.01)3
= 1 + 0.05 +0.001125 +0.00001 5
= 1.051140
= 1.0511 (4 decimal places)

Past KCSE Questions on the Topic.
- Write down the simplest expansion (1 + x)6
Use the expansion up to the fourth term to find the value of (1.03)6 to the nearest one thousandth. - Use binomial expression to evaluate (0.96)5 correct to 4 significant figures.
- Expand and simplify (3x – y)4 hence use the first three terms of the expansion to proximate the value of (6 – 0.2)4
- Use binomial expression to evaluate
(2 + 1/√2)5+ (2 − 1/√2)5 - Expand the expression (1 + 1/2x)5 in ascending powers of x, leaving the coefficients as fractions in their simplest form.
-
- Expand (a − b)6
- Use the first three terms of the expansion in (a) above to find the approximate value of (1 .98)6
- Expand (2 + x)5 in ascending powers of x up to the term in x3 hence approximate the value of (2.03)5 to 4 s.f
-
- Expand (1 + x)5
Hence use the expansion to estimate (1 .04)5 correct to 4 decimal places - Use the expansion up to the fourth term to find the value of (1 .03)6 to the nearest one thousandth.
- Expand (1 + x)5
- Expand and Simplify (1 − 3x)5 up to the term in x3
Hence use your expansion to estimate (0.97)5 correct to decimal places. - Expand (1 + a)5
Use your expansion to evaluate (0.8)5 correct to four places of decimal -
- Expand (1 + x)5
- Use the first three terms of the expansion in (a) above to find the approximate value of (0.98)5
Download Binomial Expansion - Mathematics Form 3 Notes.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students

