- Introduction
- Examples of Three Dimensional Figures
- Angle Between a Line and a Plane
- Angle Between Two Planes
- Past KCSE Questions on the Topic

Introduction
- Geometrical properties of common solids
- A geometrical figure having length only is in one dimension
- A figure having area but not volume is in two dimension
- A figure having vertices ( points),edges(lines) and faces (plans) is in three dimension

Examples of Three Dimensional Figures
Rectangular Prism

- A three-dimensional figure having 6 faces, 8 vertices, and 1 2 edges
Triangular Prism
- A three-dimensional figure having 5 faces, 6 vertices, and 9 edges.
Cone

- A three- dimensional figure having one face.
Sphere

- A three- dimensional figure with no straight lines or line segments
Cube
- A three- dimensional figure that is measured by its length, height, and width.
- It has 6 faces, 8 vertices, and 12 edges
Cylinder

- A three- dimensional figure having 2 circular faces
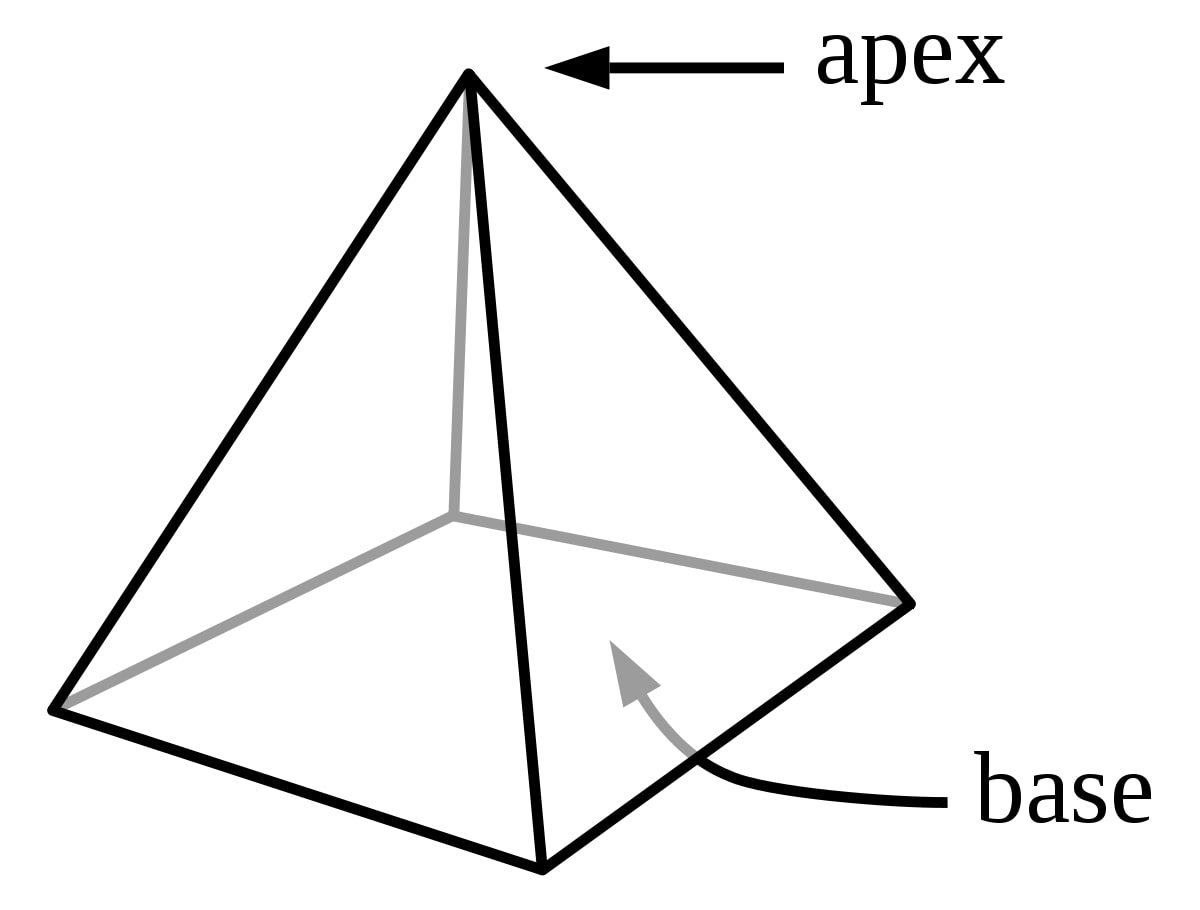
Rectangular Pyramid
- A three-dimensional figure having 5 faces, 5 vertices, and 8 edges
- It has a rectangilar base

Angle Between a Line and a Plane
- The angle between a line and a plane is the angle between the line and its projection on the plane
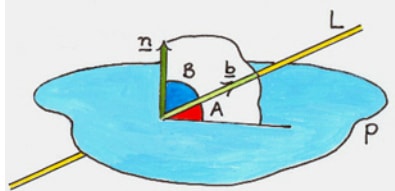
- The angle between the line L and its projection or shadow makes angle A with the plan. Hence the angle between a line and a plane is A.
Example
The angle between a line, r, and a plane, π, is the angle between r and its projection onto π, r'.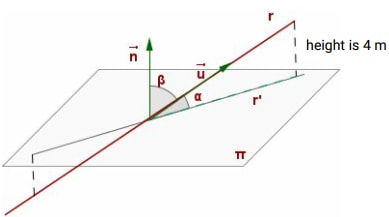
Example
Suppose r' is 10 cm find the angle α
Solution
To find the angle we use tanθ = opposite = 4 = 0.4
adjacent 10
tan-1(0.4) = 21.8o

Angle Between Two Planes
- Any two planes are either parallel or intersect in a straight line.
- The angle between two planes is the angle between two lines, one on each plane, which is perpendicular to the line of intersection at the point
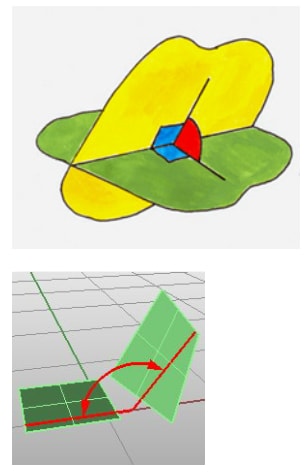
Example
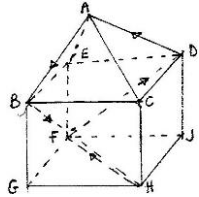
The figure below PQRS is a regular tetrahedron of side 4 cm and M is the mid point of RS;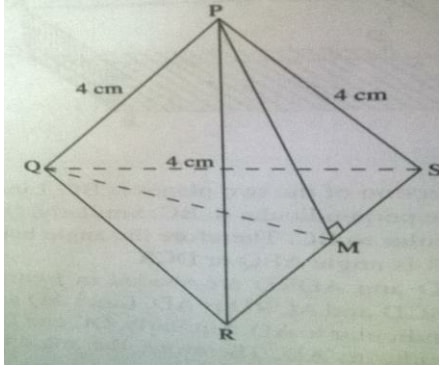
- Show that PM is 2√3 cm long, and that triangle PMQ is isosceles
- Calculate the angle between planes PSR and QRS
- Calculate the angle between line PQ and plane QRS
Solution- Triangle PRS is equilateral. Since M,is the midpoint of RS , PM is perpendicular bisector
PM2 = 42 - 22
= 12
PM = √12 cm
= √(4 x 3) = 2√3 cm
Similar triangle MQR is right angled at M
QM2 = 42 - 22
= 12
QM = √12 cm
= 4 x 3 = 2√3 cm
Since PM = QM = √12 cm Triangle PMQ is isosceleles - The required angle is triangle PMQ .Using cosine rule
42 = (2√3)2 + (2√3)2 - 2(2√3)(2√3)cos m
16 = 12 + 12 - 2 x 12cos m
= 24 - 24cos m
cos m= 24-16 = 0.3333
24
Therefore, m = 70.53o - The required angle is triangle PQM
Since triangle PMQ is isosceles with triangle PMQ = 70.54o;
∠PQM = ½ (180 - 70.54)
= ½(109.46)
= 54.73o

Past KCSE Questions on the Topic
- The diagram below shows a right pyramid VABCD with V as the vertex. The base of the pyramid is rectangle ABCD, WITH ab = 4 cm and BC= 3 cm. The height of the pyramid is 6 cm.
- Calculate the
- Length of the projection of VA on the base
- Angle between the face VAB and the base
- P is the mid- point of VC and Q is the mid – point of VD. Find the angle between the planes VAB and the plane ABPQ
- Calculate the
- The figure below represents a square based solid with a path marked on it. Sketch and label the net of the solid.
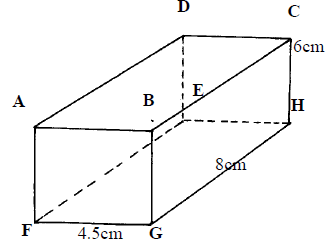
- The diagram below represents a cuboid ABCDEFGH in which FG= 4.5 cm, GH = 8 cm and HC = 6 cm
Calculate:- The length of FC
-
- The size of the angle between the lines FC and FH
- The size of the angle between the lines AB and FH
- The size of the angle between the planes ABHE and the plane FGHE
- The base of a right pyramid is a square ABCD of side 2a cm. The slant edges VA, VB, VC and VD are each of length 3a cm.
- Sketch and label the pyramid
- Find the angle between a slanting edge and the base
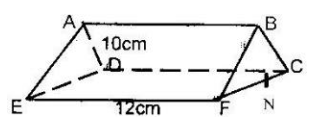
- The triangular prism shown below has the sides AB = DC = EF = 1 2 cm. the ends are equilateral triangles of sides 1 0cm. The point N is the mid point of FC.
Find the length of:-
- BN
- EN
- Find the angle between the line EB and the plane CDEF
-
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download Three Dimensional Geometry - Mathematics Form 4 Notes.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students