QUESTIONS
- How is support provided for in herbaceous plants? (1mk)
- Briefly explain the role of the Pinna in the hearing process. (2 marks)
- Using Lamarck’s theory, explain why ducks have webbed feet (4 marks)
- State two main differences between a millipede and centipede. (2 marks)
- Explain the immediate reaction of the body bathed in cold water. (2 marks)
-
- Name one enzyme present in all living cells (1mk)
- In a certain part of the gut, large fats are broken down into small fatty acid droplets, name two salts involved in the process? (2 marks)
-
- what is a habitat? (1mk
- Differentiate between population and a community. (2mks
- 600 flies were caught and marked. After 24 hrs 400 flies were caught out of which 120 had the marks.
Estimate the population size of the flies in that house. (3 marks)
-
- State three importance of DNA molecule. (3mks
- Give two causes of discontinuous variations. (2mks)
- The sequence below is a portion of a nuclei acid
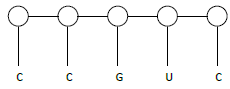
With a reason, identify the nucleic acid to which the portion belongs (2mks)
- The diagram below shows a mature pollen grain
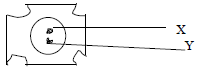 State the function of the structure labelled. (2marks)
State the function of the structure labelled. (2marks)
X……………………………………………………………………………..
Y……………………………………………………………………………. - The diagram below shows some changes in the external views of the mammalian eye. Study them and answer the question that follows.
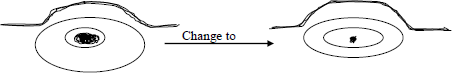
- Name the stimulus that resulted into the change above (1mark)
- Explain the events that led to the change above. (3marks)
-
- In the Savannah, hyenas have been known to kill and eat lion cubs (young ones of lions). With reference to trophic levels, the hyenas in this case may be referred to as (1mk)
- In terms of biotic factors in Savannah ecosystem, the hyena act as (1mk)
- In some terrestrial ecosystem, 10% of energy is normally transmitted to the next trophic level. If a sample of potatoes contained 100,000 kJ , how much energy would you expect to be passed on to weaver birds that feed on 20% of larvae that ate all the potatoes? Show your working (2mks)
- State three adaptations of aquatic plants to photosynthesis. (3 marks)
- Explain why tadpoles in a certain fishpond failed to become adults throughout their cycle? (2mks)
- Name the type of response exhibited by:
- Movement of termites from dry soil towards moist soil (1mark)
- Tendrils of Pisum sativum twinning on another plant (1mk)
- State the significance of the response you named in (b) above (1mk)
- State the structural difference between sensory and motor neurons (1mk)
- State two reasons why the class Insecta in the phylum Arthropoda has the largest number of individuals (2mks)
- Explain why the shortest food chains are always the most efficient (1mk)
- Give a reason why the breakdown of pyruvic acid in the mitochondria occurs in a series of enzyme controlled reaction (1mk)
- A patient whose pancreatic duct had blocked was found to have normal blood glucose but the process of digestion was impaired. Explain this observation? (2mks)
- The diagram below shows the internal structure of the mammalian ear
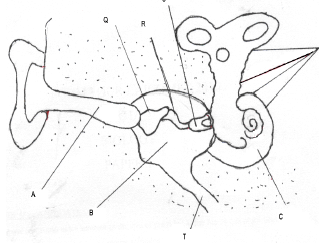
- What is the function of the parts labelled Q and S (1mk)
- Explain what would happen if the part labelled T is blocked (2mks)
- A teacher set-up the apparatus below to investigate a certain phenomenon. The cobalt (II) chloride paper was placed on the upper and lower surfaces of the leaf as shown.
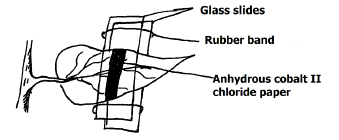
- What was the aim of the experiment? (1mk)
- What observations were made after 2hrs? (2mks)
-
- What is sex-linkage (1mk)
- Name two genes located on the Y chromosome (2mks)
- The diagram below shows the articulation of bones of the left fore-limbs of a rabbit.
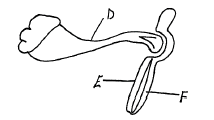
- On the diagram, identify the bones labelled E and F (2mks)
E …………………………………………………………………………
F ………………………………………………………………………… - Name the type of joint found at the distal end of the bone labelled D (1mk)
- On the diagram, identify the bones labelled E and F (2mks)
- Name the organelle that:
- Manufacture and transport lipids and steroids in a cell. (1mk)
- Contain enzymes that are capable of destroying old damaged cells. (1mk)
- The scheme below shows a process that takes place in the human gut.
Trypsinogen + substance K Trypsin- Name substance K (1mk
- In which part of the gut does the process occur. (1mk)
- Name the substrate that is acted upon by trypsin and the product formed. (2mks)
Substrate…………………………………………………………………………………
Product……………………………………………………………………………………
- State the characteristics that can separate the following organisms into respective classes;
Millipedes, tsetse fly and spider (2mks) -
- During which phase of meiosis does crossing over occur? (1mk)
- How do identical and fraternal twins arise?
- Identical twins (2mks)
- Fraternal twins (2mks)
- Which one of the cell organelles would be found in large numbers in;
- An enzyme secreting cell (1mk)
- A rapidly respiring cell in comparison to other cells in the same organism (1mk)
- A mature red blood cell lacks the nucleus for packaging of more haemoglobin. Name one other organelle present in other animal cells but absent in a red blood cell? (1mk

MARKING SCHEME
- Cell sap:
- Offers turgidity of the cell contributing to mechanical support;
- Regulates the osmotic pressure of the cell, of the plant;
- Contains sugars ions and waste products.
- Pinna, 1. It collects and direct/concentrates; sound waves into the auditory meatus;
- originally all ducks had unwebbed feet; because of competition for food they started using feet as peddlers in water; in search of food the feet later developed acquired webs; the subsequent generation were all born with webbed feet/inherited webbed feet.
Millipede Centipede Body divided into three head, thorax and trunk Body divided into two head and trunk (has fifteen segment) Have two pairs of limps on each segment hence diplopoda Have one pair of limbs in each segment. Two pairs of simple eyes One pair of simple eyes Have cylindrical bodies Have elongated dorso-ventrally flattened bodies Feed on dead organic matter detritivorers / herbivores Carnivores - Sweating decrease; Hair is raised; blood kept from the surface and metabolic rate increases. body temperature raises shivering to generate heat by contraction of muscles.
-
- catalase;
- Sodium glycocholate;
Sodium taurocholate;
-
- Habitat refers to the specific place (locality) where an organism lives in an ecosystem;
- Population: Refers to members of one species occupying a particular habitat at a given time while Community constitutes two or more populations i.e. (Many species) occupying and
Interacting in the same habitat. - P = FM x SC 600 x 400; 2,000
MR 120
-
-
- stores genetic information in a coded form.
- Enables transfer of genetic information unchanged to daughter cells through replication.
- Translates the genetic information into the characteristics of an organism through protein synthesis.
- DNA duplication making exact copies of itself.
- RNA. Presence of uracil
-
- X- Tube nucleus: Facilitates in growth of pollen tube and assist in piercing the embryo sac.
Y- Generative nucleus: divides mitotically to give rise to two male nuclei. -
- Light amount / Intensity
- Circular muscles of the iris contract; while radial muscles relax; and the pupil becomes smaller, This
prevent damage of the retina by excessive light.
-
- Tertiary consumers.
- Predators.
- 100KJ
-
- Have stomata on the upper leaf surface large leaf surface to increase surface area for light absorption.
- Presence of aerenchyma tissue that allows them to float on water; Hence accessing sunlight
-
- positive Hydrotaxis
- Thigmotropism
- Thigmotropism enables herbaceous plants to get mechanical support; expose leaves to light for photosynthesis.
Sensory neurone Motor neurone Cell body off the axon
terminal dendrites located inside the CNScell body at one end of the axon
Receptor dendrites inside the CNS-
- ability to fly
- inhabit all types of habitats
- feed on variety of foods
- Low energy losses by respiration, excretion, defaecation hence the end consumer receive a lot of energy
- so that heat energy is released in small quantities and in stages to avoid bursting of the cell
- Insulin and glucagon for controlling blood glucose are secreted directly into the blood, pancreatic juice contain digestive enzymes conveyed to the duodenum by pancreatic duct stopped;
-
- Q- malleus (hammer)
S- stapes (stirrup)
Both Q, S and incus amplifies and transmits the vibrations from tympanic membrane to the oval window. - Hearing impaired since the pressure on both sides of the eardrum would not be equalized, hence the eardrum would not vibrate / distorted
- Q- malleus (hammer)
-
- Transpiration / loss of water through leaves
- The lower cobalt II chloride paper turned pink faster than the upper cobalt II Chloride paper.
-
- Location of Genes on the sex-chromosomes.
- Premature baldness, hairy pinna/hairy ears.
-
- E – radius
F – Ulna - Hinge joint
- E – radius
-
- Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
- Lysosome
-
- Enterokinase
- Doudenum
- Proteins
peptides
-
- Body parts / Division;
- no. of limbs/ walking legs;
- body segment;
-
- prophase I;
-
- An ovum is fertilized; and later cells separate in early stages of cell division;
- Two ova are released; and fertilized by two different sperms;
-
- golgi bodies/apparatus rej Golgi body/ apparator
- mitochondria rej Mitochondorion
- Mitochondrion
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download Biology Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Butere Mock Exams 2021.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students

