
ACIDS, BASES AND INDICATORS
In a school laboratory:
- An acid may be defined as a substance that turns litmus red.
- A base may be defined as a substance that turns litmus blue.
Litmus is lichen found mainly in West Africa. It changes its colour depending on whether the solution it is in, is basic/alkaline or acidic. It is thus able to identify/show whether another substance is an acid, base or neutral. - An indicator is a substance that shows whether another substance is a base/alkaline,acid or neutral
Common naturally occurring acids include:
Name of acid | Occurrence |
1.Citric acid | Found in ripe citrus fruits like passion fruit/oranges/lemon |
2.Tartaric acid | Found in grapes/baking powder/health salts |
3.Lactic acid | Found in sour milk |
4.Ethanoic acid | Found in vinegar |
5.Methanoic acid | Present in ants, bees stings |
6.Carbonic acid | Used in preservation of fizzy drinks like coke, Lemonade, Fanta |
7.Butanoic acid | Present in cheese |
8.Tannic acid | Present in tea |
Most commonly used acids found in a school laboratory are not naturally occurring. They are manufactured.
They are called mineral acids.
Common mineral acids include:
Name of mineral acid | Common use |
Hydrochloric acid (HCl) | Used to clean/pickling surface of metals Is found in the stomach of mammals/human beings |
Sulphuric(VI) acid (H2SO4) | Used as acid in car battery, making battery, making fertilizers |
Nitric(V)acid (HNO3) | Used in making fertilizers and explosives |
Mineral acids are manufactured to very high concentration. They are corrosive (causes painful wounds on contact with the skin) and attack/reacts with garments/clothes/metals.
In a school laboratory, they are mainly used when added a lot of water. This is called diluting. Diluting ensures the concentration of the acid is safely low.
Bases are opposite of acids. Most bases do not dissolve in water.
Bases which dissolve in water are called alkalis.
Common alkalis include:
Name of alkali | Common uses |
Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) | Making soaps and detergents |
Potassium hydroxide(KOH) | Making soaps and detergents |
Ammonia solution(NH4OH) | Making fertilizers, softening hard water |
Common bases (which are not alkali) include:
Name of base | Common name |
Magnesium oxide/hydroxide | Anti acid to treat indigestion |
Calcium oxide | Making cement and neutralizing soil acidity |
Indicators are useful in identifying substances which look-alike.
An acid-base indicator is a substance used to identify whether another substance is alkaline or acidic.
An acid-base indicator works by changing to different colors in neutral, acidic and alkaline solutions/dissolved in water.
Experiment: To prepare simple acid-base indicator
Procedure
- Place some flowers petals in a mortar. Crush them using a pestle. Add a little sand to assist in crushing.
Add about 5cm3 of propanone/ethanol and carefully continue grinding.
Add more 5cm3 of propanone/ethanol and continue until there is enough extract in the mortar.
Filter the extract into a clean 100cm3 beaker. - Place 5cm3 of filtered wood ash, soap solution, ammonia solution, sodium hydroxide, hydrochloric acid, distilled water, sulphuric (VI) acid, sour milk, sodium chloride, toothpaste and calcium hydroxide into separate test tubes.
- Put about three drops of the extract in (a) to each test tube in (b). Record the observations made in each case.
Sample observations
Solution mixture | Colour on adding indicator extract | Nature of solution |
wood ash | green | Base/alkaline |
soap solution | green | Basic/alkaline |
ammonia solution | green | Basic/alkaline |
sodium hydroxide | green | Basic/alkaline |
hydrochloric acid | Red | Acidic |
distilled water | orange | Neutral |
sulphuric(VI)acid | Red | Acidic |
sour milk | green | Basic/alkaline |
sodium chloride | orange | Neutral |
Toothpaste | green | Basic/alkaline |
calcium hydroxide | green | Basic/alkaline |
Lemon juice | Red | Acidic |
The plant extract is able to differentiate between solutions by their nature. It is changing to a similar colour for similar solutions.
- Since lemon juice is a known acid, then sulphuric (VI) and hydrochloric acids are similar in nature with lemon juice because the indicator shows similar colors. They are acidic in nature.
- Since sodium hydroxide is a known base/alkali, then the green colour of indicator shows an alkaline/basic solution.
- Since pure water is neutral, then the orange colour of indicator shows neutral solutions.
In a school laboratory, commercial indicators are used. A commercial indicator is cheap, readily available and easy to store. Common indicators include: Litmus, phenolphthalein, methyl orange, screened methyl orange, bromothymol blue.
Experiment:
Using commercial indicators to determine acidic, basic/alkaline and neutral solutions
Procedure
Place 5cm3 of the solutions in the table below. Add three drops of litmus solution to each solution.
Repeat with phenolphthalein indicator, methyl orange, screened methyl orange and bromothymol blue.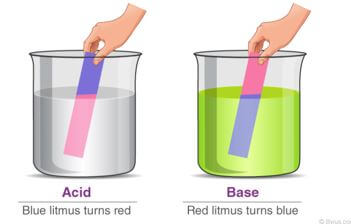
Sample results
Substance/ Solution | Indicator used | ||||
Litmus | Phenolphthalein | Methyl orange | Screened methyl orange | Bromothymol blue | |
wood ash | Blue | Pink | Yellow | Orange | Blue |
soap solution | Blue | Pink | Yellow | Orange | Blue |
ammonia solution | Blue | Pink | Yellow | Orange | Blue |
sodium hydroxide | Blue | Pink | Yellow | Orange | Blue |
hydrochloric acid | Red | Colourless | Red | Purple | Orange |
distilled water | Colourless | Colourless | Red | Orange | Orange |
sulphuric(VI)acid | Red | Colourless | Red | Purple | Orange |
sour milk | Blue | Pink | Yellow | Orange | Blue |
sodium chloride | Colourless | Colourless | Red | Orange | Orange |
Toothpaste | Blue | Pink | Yellow | Orange | Blue |
calcium hydroxide | Blue | Pink | Yellow | Orange | Blue |
Lemon juice | Red | Colourless | Red | Purple | Orange |
The universal indicator is a mixture of other indicator dyes. The indicator uses the pH scale. The pH scale shows the strength of bases and acids. The pH scale ranges from 1-14.These numbers are called pH values:
- pH values 1, 2, 3 shows a substance is strongly acid
- pH values 4, 5, 6 shows a substance is a weakly acid
- pH value 7 shows a substance is a neutral
- pH values 8, 9, 10, 11 shows a substance is a weak base/alkali.
- pH values 12, 13, 14 shows a substance is a strong base/alkali
The pH values are determined from a pH chart. The pH chart is a multicolored paper with each colour corresponding to a pH value.i.e
- red correspond to pH 1, 2, 3 showing strongly acidic solutions.
- Orange/ yellow correspond to pH 4, 5, 6 showing weakly acidic solutions.
- Green correspond to pH 7 showing neutral solutions.
- Blue correspond to pH 8, 9, 10, 11 showing weakly alkaline solutions.
- Purple/dark blue correspond to pH 12,13,14 showing strong alkalis.
The universal indicator is available as:
- Universal indicator paper/pH paper
- Universal indicator solution.
When determining the pH of a unknown solution using
- pH paper then the pH paper is dipped into the unknown solution. It changes/turn to a certain colour. The new colour is marched/compared to its corresponding one on the pH chart to get the pH value.
- universal indicator solution then about 3 drops of the universal indicator solution is added into about 5cm3 of the unknown solution in a test tube. It changes/turn to a certain colour. The new colour is marched/compared to its corresponding one on the pH chart to get the pH value.
Experiment: To determine the pH value of some solutions
- Place 5cm3 of filtered wood ash, soap solution, ammonia solution, sodium hydroxide, hydrochloric acid, distilled water, sulphuric (VI) acid, sour milk, sodium chloride, toothpaste and calcium hydroxide into separate test tubes.
- Put about three drops of universal indicator solution or dip a portion of a piece of pH paper into each. Record the observations made in each case.
- Compare the colour in each solution with the colors on the pH chart provided. Determine the pH value of each solution.
Sample observations
Solution mixture | Colour on the pH paper/adding universal indicator | pH value | Nature of solution |
wood ash | Blue | 8 | Weakly alkaline |
soap solution | Blue | 8 | Weakly alkaline |
ammonia solution | green | 8 | Weakly alkaline |
sodium hydroxide | Purple | 14 | Strongly alkaline |
hydrochloric acid | red | 1 | Strongly acidic |
distilled water | green | 7 | Neutral |
sulphuric(VI)acid | red | 1 | Strongly acidic |
sour milk | blue | 9 | Weakly alkaline |
sodium chloride | green | 7 | Neutral |
toothpaste | Blue | 10 | Weakly alkaline |
calcium hydroxide | Blue | 11 | Weakly alkaline |
Lemon juice | Orange | 5 | Weakly acidic |
Note
- All the mineral acids Hydrochloric, sulphuric (VI) and nitric (V) acids are strong acids
- Two alkalis/soluble bases, sodium hydroxide and potassium hydroxide are strong bases/alkali. Ammonia solution is a weak base/alkali. All other bases are weakly alkaline.
- Pure/deionized water is a neutral solution.
- Common salt/sodium chloride is a neutral salt.
- When an acid and an alkali/base are mixed, the final product has pH 7 and is neutral.
The various uses of acids and bases are listed in this subsection.
- Uses of Acids
- Vinegar, a diluted solution of acetic acid, has various household applications. It is primarily used as a food preservative.
- Citric acid is an integral part of lemon juice and orange juice. It can also be used in the preservation of food.
- Sulphuric acid acid is widely used in batteries. The batteries used to start the engines of automobiles commonly contain this acid.
- The industrial production of explosives, dyes, paints, and fertilizers involves the use of sulphuric acid acid and nitric acid.
- Phosphoric acid is a key ingredient in many soft drinks.
- Uses of Bases
- The manufacturing of soap and paper involves the use of sodium hydroxide. NaOH is also used in the manufacture of rayon.
- Ca(OH)2, also known as slaked lime or calcium hydroxide, is used to manufacture bleaching powder.
- Dry mixes used in painting or decoration are made with the help of calcium hydroxide.
- Magnesium hydroxide, also known as milk of magnesia, is commonly used as a laxative. It also reduces any excess acidity in the human stomach and is, therefore, used as an antacid.
- Ammonium hydroxide is a very important reagent used in laboratories.
- Any excess acidity in soils can be neutralized by employing slaked lime.
Download Acids, Bases and Indicators - Grade 7 Integrated Science Revision Notes.
Tap Here to Download for 30/-
Get on WhatsApp for 30/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students
