- Skin
- The Urinary system
- Facts about urine
- Diseases and conditions that cause chronic kidney disease include:
- Signs and symptoms of Kidney Diseases
- To reduce your risk of developing kidney disease:
- How can I protect my skin?
- Effects of cosmetics on health

Human Excretory system
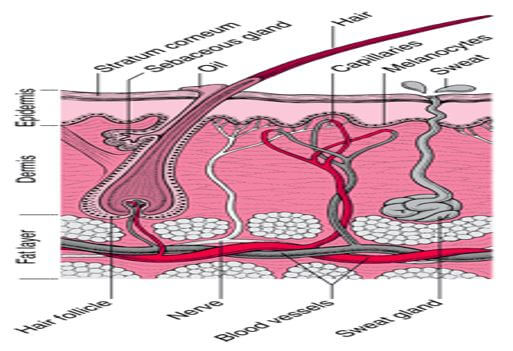
The skin is the largest organ of the body, with a total area of about 20 square feet. The skin protects us from microbes and the elements, helps regulate body temperature, and permits the sensations of touch, heat, and cold.
Skin has three layers:
- The epidermis, the outermost layer of skin, provides a waterproof barrier and creates our skin tone.
- Acts as a protective barrier: The epidermis keeps bacteria and germs from entering your body and bloodstream and causing infections. It also protects against rain, sun and other elements.
- Makes new skin: The epidermis continually makes new skin cells. These new cells replace the approximately 40,000 old skin cells that your body sheds every day. You have new skin every 30 days.
- Protects your body: Langerhans cells in the epidermis are part of the body’s immune system. They help fight off germs and infections.
- Provides skin color: The epidermis contains melanin, the pigment that gives skin its color. The amount of melanin you have determines the color of your skin, hair and eyes. People who make more melanin have darker skin and may tan more quickly.
- The dermis, beneath the epidermis, contains tough connective tissue, hair follicles, and sweat glands.
- Has collagen and elastin: Collagen is a protein that makes skin cells strong and resilient. Another protein found in the dermis, elastin, keeps skin flexible. It also helps stretched skin regain its shape.
- Grows hair: The roots of hair follicles attach to the dermis.
- Keeps you in touch: Nerves in the dermis tell you when something is too hot to touch, itchy or super soft. These nerve receptors also help you feel pain.
- Makes oil: Oil glands in the dermis help keep the skin soft and smooth. Oil also prevents your skin from absorbing too much water when you swim or get caught in a rainstorm.
- Produces sweat: Sweat glands in the dermis release sweat through skin pores. Sweat helps regulate your body temperature.
- Supplies blood: Blood vessels in the dermis provide nutrients to the epidermis, keeping the skin layers healthy.
- The deeper subcutaneous tissue (hypodermis) is made of fat and connective tissue.
- Cushions muscles and bones: Fat in the hypodermis protects muscles and bones from injuries when you fall or are in an accident.
- Has connective tissue: This tissue connects layers of skin to muscles and bones.
- Helps the nerves and blood vessels: Nerves and blood vessels in the dermis (middle layer) get larger in the hypodermis. These nerves and blood vessels branch out to connect the hypodermis to the rest of the body.
- Regulates body temperature: Fat in the hypodermis keeps you from getting too cold or hot.
The skin’s color is created by special cells called melanocytes, which produce the pigment melanin. Melanocytes are located in the epidermis.
Front view of the urinary tract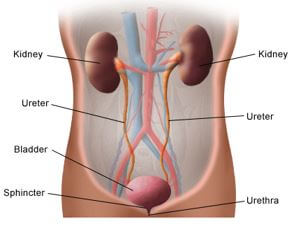
The body takes nutrients from food and converts them to energy. After the body has taken the food components that it needs, waste products are left behind in the bowel and in the blood.
The kidney and urinary systems help the body to eliminate liquid waste called urea, and to keep chemicals, such as potassium and sodium, and water in balance. Urea is produced when foods containing protein, such as meat, poultry, and certain vegetables, are broken down in the body. Urea is carried in the bloodstream to the kidneys, where it is removed along with water and other wastes in the form of urine.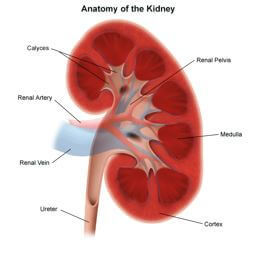
- Two kidneys. This pair of purplish-brown organs is located below the ribs toward the middle of the back. Their function is to:
- Remove waste products and drugs from the body
- Balance the body's fluids
- Release hormones to regulate blood pressure
- Control production of red blood cells
- Two ureters. These narrow tubes carry urine from the kidneys to the bladder. Muscles in the ureter walls continually tighten and relax forcing urine downward, away from the kidneys.
- Bladder. This triangle-shaped, hollow organ is located in the lower abdomen. It is held in place by ligaments that are attached to other organs and the pelvic bones. The bladder's walls relax and expand to store urine, and contract and flatten to empty urine through the urethra. The typical healthy adult bladder can store up to two cups of urine for two to five hours.
- Urethra. This tube allows urine to pass outside the body. The brain signals the bladder muscles to tighten, which squeezes urine out of the bladder. At the same time, the brain signals the sphincter muscles to relax to let urine exit the bladder through the urethra. When all the signals occur in the correct order, normal urination occurs.
- Normal, healthy urine is a pale straw or transparent yellow color.
- Darker yellow or honey colored urine means you need more water.
- A darker, brownish color may indicate a liver problem or severe dehydration.
- Pinkish or red urine may mean blood in the urine.
Diseases and conditions that cause chronic kidney disease include:
- Type 1 or type 2 diabetes
- High blood pressure
- an inflammation of the kidney's filtering units (glomeruli)
- an inflammation of the kidney's tubules and surrounding structures
- other inherited kidney diseases
- Prolonged obstruction of the urinary tract, from conditions such as enlarged prostate, kidney stones and some cancers
- Recurrent kidney infection, also called pyelonephritis
- Heart (cardiovascular) disease
- Smoking
- Obesity
- Being Black, Native American or Asian American
- Family history of kidney disease
- Abnormal kidney structure
- Older age
- Frequent use of medications that can damage the kidneys
Signs and symptoms of Kidney Diseases
Signs and symptoms of chronic kidney disease develop over time if kidney damage progresses slowly. Loss of kidney function can cause a buildup of fluid or body waste or electrolyte problems. Depending on how severe it is, loss of kidney function can cause:
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Loss of appetite
- Fatigue and weakness
- Sleep problems
- Urinating more or less
- Decreased mental sharpness
- Muscle cramps
- Swelling of feet and ankles
- Dry, itchy skin
- High blood pressure (hypertension) that's difficult to control
- Shortness of breath, if fluid builds up in the lungs
- Chest pain, if fluid builds up around the lining of the heart
To reduce your risk of developing kidney disease:
- Follow instructions on over-the-counter medications. When using nonprescription pain relievers, such as aspirin, ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others) and acetaminophen (Tylenol, others), follow the instructions on the package. Taking too many pain relievers for a long time could lead to kidney damage.
- Maintain a healthy weight. If you're at a healthy weight, maintain it by being physically active most days of the week. If you need to lose weight, talk with your doctor about strategies for healthy weight loss.
- Don't smoke. Cigarette smoking can damage your kidneys and make existing kidney damage worse. If you're a smoker, talk to your doctor about strategies for quitting. Support groups, counseling and medications can all help you to stop.
- Manage your medical conditions with your doctor's help. If you have diseases or conditions that increase your risk of kidney disease, work with your doctor to control them. Ask your doctor about tests to look for signs of kidney damage.
How can I protect my skin?
You lose collagen and elastin as you age. This causes the skin’s middle layer (dermis) to get thinner. As a result, the skin may sag and develop wrinkles.
While you can’t stop the aging process, these actions can help maintain healthier skin:
- Apply sunscreen every day (even if you’re mostly indoors). Choose a sunscreen with a broad-spectrum sun protection factor (SPF) of at least 30.
- Don’t tan indoors or outdoors. Tanning causes skin damage. It ages skin and can cause skin cancer.
- Find healthy ways to manage stress. Stress can make certain skin conditions worse.
- Perform regular skin and mole checks to look for changes that may be signs of skin cancer.
- Quit smoking and using tobacco products. Nicotine and other chemicals in cigarettes and electronic cigarettes age skin faster.
- Use gentle cleansers to wash your face in the morning and at night.
- Shower regularly and apply moisturizing lotion to prevent dry skin.
Effects of cosmetics on health
- Headaches
- Hair problems- Extensive use of chemical based hair products could lead to dandruff, scalp redness, thinning of hair, and even loss of hair. Long term use of hair color could also lead to hair discoloration.
- Acne - Some types of makeup which are in the form of liquids and creams clog the pores in your skin. This leads to the formation of blackheads, which when not cleaned regularly can form acne.
- Skin allergies - hemicals known as Parabens which include ethyl-paraben, butyl-paraben, and isopropyl-paraben are used as preservatives to prevent bacterial growth in cosmetics. Parabens can cause various allergic reactions like skin irritation, blotches, and blemishes on the skin.
- Eye infections - Layers of eye makeup can be damaging to your eyes as it also slips into your eyes through the corners causing irritation.
- Premature aging - When you use skin products for a longer period of time, the chemicals present tend to permanently damage your skin. With time, you could begin to see skin ageing signs likes wrinkles or patchiness on your face and body. While makeup does help you hide or cover flaws in your skin, the long term effects could be counterproductive. Also, considering how big the anti-ageing products market is, cosmetic companies have no incentive to reduce the ageing effects of makeup.
- Cancer - Many of the chemical based cosmetics available in the stores today contain toxic ingredients that could cause cancer. With regulations in place, there is testing being done on the ingredients before the products can be sold. ry and avoid products with the following ingredients.
- Formaldehyde and formaldehyde-releasing preservatives
- Phenacetin
- Coal tar
- Benzene
- Untreated or mildly treated mineral oils
- Ethylene oxide
- Chromium
- Cadmium and its compounds
- Arsenic
- rystalline silica (or quartz)
- Skin discoloration- Skin products like sunscreens, moisturizers, toners, and creams contain agents that bleach or darken the skin. Cosmetic products that use poor quality ingredients which have not been regulated can lead to skin discoloration. The effect could be patches, pigmentation, uneven skin tone, redness, and freckles.
Download Human Excretory System - Grade 7 Integrated Science Revision Notes.
Tap Here to Download for 30/-
Get on WhatsApp for 30/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students
