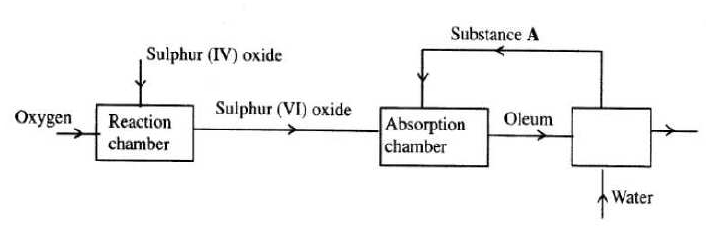
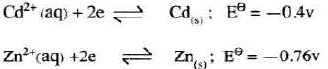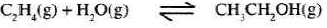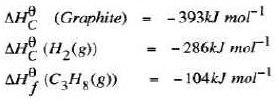- The flowchart below shows some of the process involved in large scale production of sulphuric (VI) acid. Use it to answer the question that follow.
- Describe how oxygen is obtained from air on a large scale. (2 marks)
- Name substance A. (1 mark)
- Write an equation for the process that takes place in the absorption chamber. (1 mark)
- Vanadium (V) oxide is a commonly used catalyst in the contact process. (2 marks)
- Name another catalyst which can be used in this process. (1 mark)
- Give two reasons why vanadium (V) oxide is the commonly used catalyst. (2 marks)
- State and explain the observations made when concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid is added to crystals of copper (II) sulphate on a beaker.(2 marks)
- The reaction of concentrates sulphuric(VI) acid with sodium chloride produces hydrogen chloride gas . State the property of concentrated sulphuric (VI)acid illustrated in this reaction. (1 mark)
- Name four uses of sulphuric (VI) acid. (2 marks)
- Describe how oxygen is obtained from air on a large scale. (2 marks)
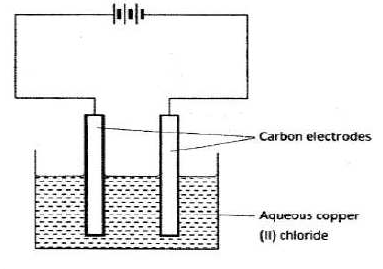
- The setup below was used by a student to investigate the products formed when aqueous copper(II) chloride was electrolyzed using carbon electrodes.
- Write the equation for the reaction that takes place at the cathode. (1 mark)
- Name and describe a chemical test for the product initially formed at the anode when a highly concentrated solution of copper (II) chloride is electrolysed.( 3 marks)
- How would the mass of the anode change if the carbon anode was replaced with copper metal? Explain. (2 marks)
- Write the equation for the reaction that takes place at the cathode. (1 mark)
- O.6g of metal B were deposited when a current of 0.45A was passed through an electrolyte for 72 minutes . Determine the change on the ion of metal B. (relative atomic mass of B =59, Faraday =96500 coulombs). (3 marks)
- The electrode potentials for cadmium and zinc are given below;
Explain why it is not advisable to store a solution of cadmium nitrate in a container made of zinc. (2 marks)
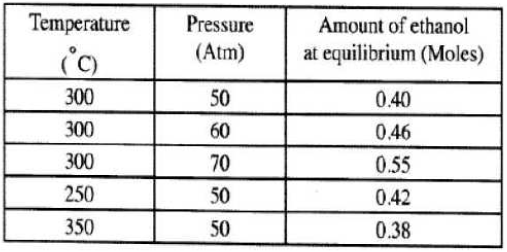
- Ethanol can be manufactured from ethane and steam as shown in the equation below;
Temperature and pressure will affect the position and equilibrium of the above reaction. Name the other factor that will affect the position of equilibrium of the above reaction. (1 mark) - The data in the table below was recorded when one mole of ethane was reacted with excess steam. The amount of ethanol in the equilibrium mixture was recorded under different conditions of temperature and pressure. Use the data to answer the questions that follow.
- State whether the reaction between ethene and steam is exothermic or endothermic. Explain your answer. (3 marks)
- State and explain one advantage and one disadvantage of using extremely high pressure in this reaction.
- Advantage. (2 marks)
- Disadvantage. (2 marks)
- State whether the reaction between ethene and steam is exothermic or endothermic. Explain your answer. (3 marks)
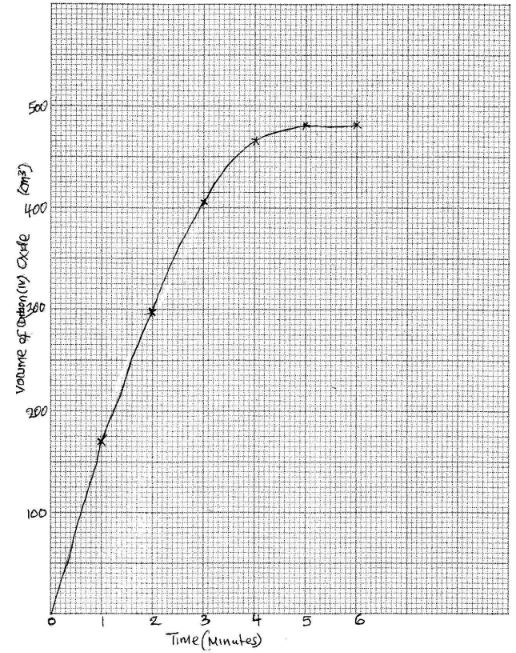
- In an experiment to determine the rate of reaction between calcium carbonate and dilute hydrochloric acid, 2g of calcium carbonate were reacted with excess 2M hydrochloric acid. The volume of Carbon(IV) oxide evolved was recorded at regular intervals of one minute for six minutes. The results are as shown in the table below.
- Plot a graph of time in minutes on the horizontal axis against volume of Carbon (IV) oxide on the vertical axis. (3 marks)

- Determine the rate of reaction at 4 minutes. (2 marks)
- Plot a graph of time in minutes on the horizontal axis against volume of Carbon (IV) oxide on the vertical axis. (3 marks)
- Ethanol can be manufactured from ethane and steam as shown in the equation below;
- When excess calcium metal was added to 50cm3 of 2M aqueous copper (II) nitrate in a beaker, a brown solid and bubbles of gas were observed.
- Write two equations for the reactions which occured in the beaker. (2 marks)
- Explain why it is not advisable to use sodium metal for this reaction. (2 marks)
- Calculate the mass of calcium metal which reacted with copper(II)nitrate solution. (Relative atomic mass of Ca =40). (2 marks)
- The resulting mixture in (a) above was filtered and aqueous sodium hydroxide added to the filtrate drop wise until in excess. What observations were made? (1 mark)
- Starting with calcium oxide, describe how a solid sample of calcium carbonate can be prepared. (3 marks)
- Name one use of calcium carbonate. (I mark)
- When excess calcium metal was added to 50cm3 of 2M aqueous copper (II) nitrate in a beaker, a brown solid and bubbles of gas were observed.
- Other than their location in the atom, name two other differences between an electron and a proton. (2 marks)
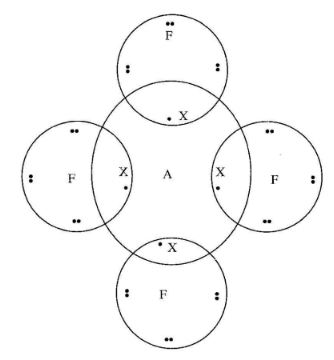
- The table below gives the number of electrons, protons and neutrons in particles A,B,C,D.E.F and G.
- What particle is likely to be a halogen? (1 mark)
- What is the mass number of E? (1 mark)
- Write the formula of the compound formed when E combines with G. (1 mark)
- Name the type of bond formed in (iii) above. (1 mark)
- How does the radii of C and E compare? Give a reason . (2 marks)
- Draw a dot (.)and cross(x) diagram for the compound formed between A and F. (1 mark)
- Why would particle B not react with particle D? (1 mark)
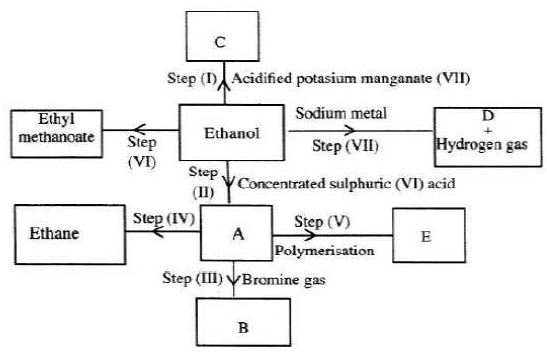
- Study the flowchart below and answer the questions that follow.
- What observation will be made in step I? (1 mark)
- Describe a chemical test that can be carried out to show the identity of compound C. (2 marks)
- Give the names of the following; (2 marks)
- E…………………………………………………….
- Substance D…………………………………………
- Give the formula of substance B. (1 mark)
- Name the type of reaction that occurs in: (1 mark)
- Step (II)…………………………………………………………….
- Step (IV)……………………………………………………………
- Give the reagent and conditions necessary for step (VI). (2 marks)
- Name the following structure. (1 mark)
- Draw the structure of an isomer of Pentene. (1 mark)
- Name the following structure. (1 mark)
- Study the flowchart below and answer the questions that follow.
- What is meant by molar heat of combustion? (1 mark)
- State the Hess’s law. (1 mark)
- Use the following standard enthalpies of combustion of graphite, hydrogen and enthalpy of formation of propane.
- Write the equation for the formation of propane. (1 mark)
- Draw an energy cycle diagram that links the heat of formation of propane with its heat of combustion and the heats of combustion of graphite hydrogen. (3 marks)
- Other than the enthalpy of combustion, state one factor which should be considered when choosing a fuel. ( 1 mark)
- The molar enthalpies of neutralization for dilute hydrochloric acid and dilute nitric (V) acid are -57.2kJ/mol while that of ethanoic acid is -55.2kJ/mol. Explain this observation. (2 marks)
- What is meant by molar heat of combustion? (1 mark)
MARKING SCHEME
-
- Purify to remove dust, bubble in NaOH or KOH to remove CO2 reduce tem perature to remove water as ice, compress to liquify the remaining air then fraction ally distill to obtain Oxygen at –183°C. (3 marks)
-
- 98% concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid (1 mark)
- SO3(g) + H2SO4(l) → H2S2O7(l) (1 mark)
-
- Platinum or platinised asbestos (1 mark)
- It is cheap and not easily poisoned. (2 marks)
- They turn from blue to white and form a powder. (1 mark)
The sulphuric (VI) acid dehydrates the copper (II) (1) sulphate crystals forming copper (II) sulphate powder. (1 mark) - H2SO4 is less- volatile (1) (1 mark)
-
- Manufacture fertilizers eg. Super phosphate
- Production of rayon fibres
- Car batteries as electrolyte . Sulphur detergents
- Cleaning of metals (Pickling)
- Paints etc.
any four (12) mark each
(2 marks)
-
-
- Cu2+(aq) + 2e Cu(s) (1) (1 mark)
- It decreases . The anode is not inert so it dissolves (1) (2 marks)
- Chlorine gas . Use moist blue litmus paper. It will change from blue to pink then to white or is bleached. (3 marks)
- Quantity of electricity = 0.45 x 72 x 60
= 1944 coulombs
0.6g require 1944 1944 x 59
59 require ? 0.6
191116 Q
1 Faraday = 96,500 Q
? = 191160 Q
Number of Faradays/Charge = 191160/ 96500
1.98
2
∴ B2+ (3 marks) - From the electrode potentials, zinc is more reactive than cadmium.(1) Therefore zinc will displace cadmium ions from solution hence the metal container will dissolve. (1) (2 marks)
-
-
- Increase or change in amount of reagent either reactants or products. (Concentration). (1 mark)
-
- Exothermic (1) increase in temperature from 250 - 350 at constant pressure the amount of ethanol formed at equilibrium decreases. (1) (3 marks)
-
- Advantage - it would increase the yield of ethanol (1/2); since increase in pressure will favour side with less moles i.e. the products.
- Disadvantage - it would mean investment in equipment to withstand the high pressure(1) and would be expensive.
-
- See graph drawn. (3 marks)
- Drawing tangent
Rate = 525 - 414 = 111 = 30 cm3/min (2 marks)
6 -2.3 3.7
- See graph drawn. (3 marks)
-
-
- Ca (s) + Cu(NO3)2(aq) → Ca(NO3)2(aq) + Cu(s)
Ca(s) + H2O (l) → Ca(OH)2(aq) + H2(g) - Sodium metal is more reactive than calcium. Reaction between sodium and copper nitrate will be explosive as it reacts with water evolving hydrogen gas. (2 marks)
- Ca (s) + Cu(NO3)2(aq) → Ca(NO3)2(aq) + Cu(s)
- Ca (s) + Cu(NO3)2(aq) → Ca(NO3)2(aq) + Cu(s)
1 : 1
moles of copper nitrate 50/1000 x 2 = 0.1 moles
Ratio 1:1
Moles of Ca = 0.1
Mass of Ca = 0.1 x 40 = 4 g (1) (2 marks) - A white precipitate is formed which is insoluble in excess. (1)(1 mark)
-
- Add dilute nitric (V) acid to calcium oxide to form the soluble salt calcium nitrate. Add sodium carbonate (another soluble salt) to form insoluable. Calcium Carbonate and sodium nitrate . Filter out the calcium carbonate, wash it with distilled water to remove traces of sodium nitrate and dry between filter papers (3 marks)
- Manufacture of cement
Manufacture of sodium carbonate. (1 mark)
-
-
-
- electron has 1/1840 mass while proton has mass of one mass unit.
proton is positively charged while electron is negatively charged. (2 marks)
- electron has 1/1840 mass while proton has mass of one mass unit.
-
- F
- 27
- E2G3
- Ionic bond (1) or electrostatic
- E has a smaller atomic radius than C (1)
E has more protons than C :. nucleur attraction stronger. (1) -
- Particle B is inert with a stable electronic configuration :. will not react. (1)
-
-
-
-
- The potasium permanganate is decolurised or changes from purple to colourless. (1)(1 mark)
- C is a ethanoic acid (carboxylic acid) Add sodium carbonate, you will see effervescence, test gas evolved with lime water, it will form a white precipitate. (2 marks)
-
- Polyethene (1)
- Substance D - sodium ethoxide (1) (2 marks)
- Substance B - CH2BrCH2Br. (1) or C2H4Br2 I
-
- Step II - dehydration
- Step IV - hydrogenation.
- Reagent: Methanoic acid (1)
Conditions: Concentrated sulphuric (VI)acid & (1) warm.
-
-
- Hexan - 1 -01 (1 mark)
-
-
-
- The amount of heat liberated when one mole of a substance is burnt in excess oxygen. (1 mark)
- The heat evolved ar absorbed in a chemical change is the same whether the change occurs in one step or through many steps.
-
- 3C(3) + 4H2(g) → C3H8(g)
3C(g) + 4H2(g) → C3H8(g) ΔHc(C3H8)
3CO2(g) + 4 H2O(l) (3 marks) - -104 = 3 x-393 +4 x -286 -ΔHc(C3H8)(l)
ΔHc(C3H8) = 104 + (-1179) + -1144)
= -2219 kJ mol-1
(2 marks)
- 3C(3) + 4H2(g) → C3H8(g)
-
- cost
- effect on environment
- availability
- storage (1 mark)
- Ethanoic acid is a weak acid therefore heat is used to ionise it before neutralization occurs (1). It value is therefore lower than that of hydrochloric acid which is fully ionised(1). (2 marks)
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download KCSE 2011 Chemistry Paper 2 Questions with Marking Scheme.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students