QUESTIONS
-
- What is a universal indicator? (1mark)
- State one advantage of universal indicator over other commercial indicators. (1mark)
- Complete the diagram below on identification and uses of some laboratory apparatus.
Diagram 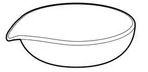
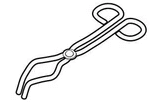
Name (a) (c) Purpose (b) (d) -
- In an experiment, sulphur was heated in a deflagrating spoon until it begins to burn then lowered into a gas jar. Explain the observations made. (2 marks)
- Explain the role of oxygen in steel making. (2 marks)
-
- State Graham’s law of diffusion. (1mark)
- At what temperature, in K, assuming constant pressure, is the volume of a fixed mass of gas at 127ºC doubled? (2 marks)
-
- Distinguish between a temporary physical change and temporary chemical change. (2 marks)
- In an experiment, the following substances were heated in separate test tubes. Complete the table to state the observations and classifying the type of change that occurs. (3 marks)
Solid Observation on heating Type of change CuSO4.5H2O KMnO4
- Explain how you would distinguish between ethane and ethyne. (2 marks)
- Explain how solid calcium sulphate can be prepared from solid samples of calcium carbonate and sodium sulphate. All other reagents and apparatus are provided. (3 marks)
-
- A metal reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid to produce a gas. Explain how to identify the gas. (1mark)
- The diagram below shows the set up used for the reaction between magnesium and steam.
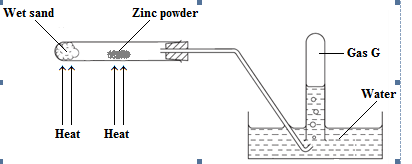
- Explain the observations made. (2 marks)
- Explain why the wet sand must be heated first before the zinc powder is heated. (1mark)
-
- Distinguish between covalent bond and co-ordinate bond. (2 marks)
- The diagram below shows the structure of a covalent compound containing the element hydrogen, H, and the unknown elements X, Y and Z.
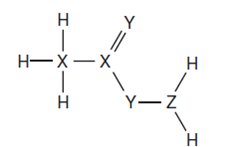
To which groups of the Periodic Table do these three elements, X, Y and Z, belong? (1½ marks)
- In an experiment silicon (IV) chloride is dissolved in water in a boiling tube.
- Write an equation for the reaction that occurs. (1mark)
- Explain the observations that were made during the experiment. (3 marks)
- A standard solution of potassium hydroxide (KOH) is prepared in a 250 cm3 volumetric flask. During a titration, 12.5 cm3 of this solution neutralizes 25 cm3 of a 0.16 moldm-3 ethanoic acid solution.
The balanced equation for the reaction is: CH3COOH(aq) + KOH(aq) → CH3COOK(aq) + H2O(l)
Calculate the mass of potassium hydroxide used to prepare the solution above in the 250 cm3 volumetric flask.
(K = 39, O = 16.0, H = 1.) (3 marks) - Ammonia gas was burnt in oxygen as shown in the diagram below.
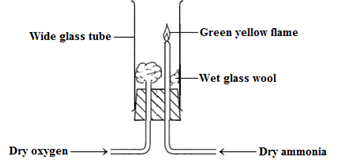
- State the role of the glass wool. (1mark)
- State the observations made during the experiment. (1mark)
- Write an equation for the reaction that occurs. (1mark)
- Study the following reaction at equilibrium at a certain temperature.
2SO3(g) ⇌ O2(g) + 2SO2(g) ΔH > 0- State two optimum conditions for this reaction. (1mark)
- State two ways of increasing the yield of SO3(g). (2 marks)
-
- Write the equation for the reaction between chlorine and cold dilute sodium hydroxide. (1mark)
- When chlorine gas reacts with hot concentrated calcium hydroxide, one of the products formed is calcium hypochlorite (CaOCl2). This commonly referred to as bleaching powder.
Explain the bleaching action of calcium hypochlorite. (2 marks)
- The diagram below shows an apparatus for the laboratory preparation of carbon (II) oxide.
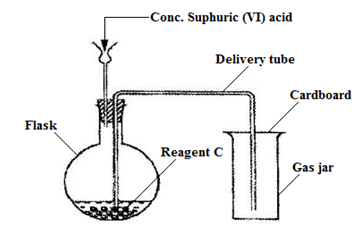
- Identify two mistakes in the set up. (2 marks)
- Write an equation for the reaction between concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid and reagent C. (1mark)
- State one use of carbon (II) oxide. (1mark)
- The structures of four organic compounds are shown.
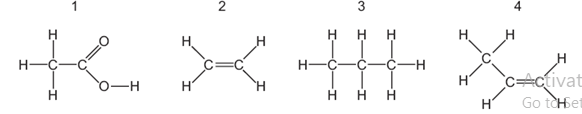
- Which compounds decolourize bromine water? (1mark)
- Explain one chemical test that can be used to distinguish between compounds 1 and 2. (2 marks)
- How does the number of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen atoms in an ester differ from the total number of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen atoms in the alcohol and carboxylic acid from which the compound was derived?(1½ marks)
- The diagram shows a reaction scheme.
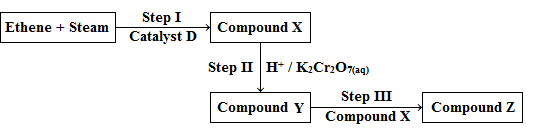
- Name:
- Catalyst D
- Reaction II
- Reaction III
- Compound Z(4 marks)
- State the observations made in step II. (1mark)
- Write an equation for the reaction that occurs in step III. (1mark)
- Name:
- A student performs two reactions.
- reaction 1: 10 g of magnesium ribbon with excess 2.0 mol / dm3 dilute hydrochloric acid
- reaction 2: 5 g of magnesium powder with excess 2.0 mol / dm3 dilute hydrochloric acid
In both experiments, the volume of hydrogen produced, V, is measured against time, t, and the results plotted graphically.- On the grid below, sketch a graph that would be obtained is volume of hydrogen produced is plotted against time for both reactions1 and 2. (2 marks)

- Explain your answers. (2 marks)
- On the grid below, sketch a graph that would be obtained is volume of hydrogen produced is plotted against time for both reactions1 and 2. (2 marks)
- A copper – zinc electrochemical cell is set up as shown below.
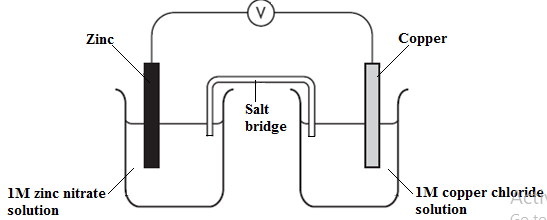
Lead (II) nitrate is used as an electrolyte in the salt bridge.- Initially the cell did not work. Explain. (2 marks)
- Once the mistake identified in (a) above was corrected:
- Write the equation for the reaction at the anode. (1mark)
- Determine the E.m.f of the cell given that: (2 marks)
Zn(s) → Zn2+(aq) + 2e; EƟ + 0.76V
Cu(s) → Cu2+(aq) + 2e; EƟ – 0.34V
- When a solution containing silver ions is added to a solution containing iron (II) ions, an equilibrium is set up.
2Ag+(aq) + Fe2+(aq) ⇌ 2Ag(s) + Fe3+(aq)
(Green) (Yellow)
Explain the effect of addition of silver nitrate to the equilibrium mixture. (2 marks) -
- One of the ores of sodium is saltpetre. Give the formula of saltpetre. (1mark)
- In the Down’s cell, the anode is made of carbon while the cathode is made of steel. Steel is a reactive electrode and would make the electrolytic process faster. Explain why it is not used at the anode despite this advantage. (1mark)
- Write two equations that occur at the anode during the electrolysis process. (2 marks)
-
- What is half life as used in radioactivity? (1mark)
- A certain nuclide has a half-life of 1.5 seconds.
- What is a nuclide? (1mark)
- What percentage of a given mass of the nuclide will be left after 7.5 hours? (2 marks)
- The potential energy graph for a hypothetical chemical reaction is shown below.
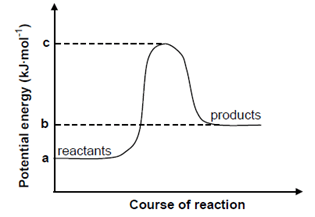
- What type of reaction is taking place? (1mark)
- What are the correct methods to calculate ΔH and Ea? (2 marks)
- The diagram shows the apparatus used to electrolyse lead (II) bromide using inert electrodes.
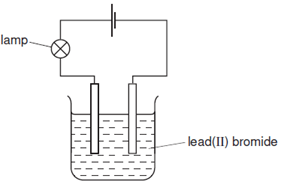
Why does the lamp light up only when the lead (II) bromide is melted? (2 marks)

MARKING SCHEME
-
- A broad range indicator that can give the degree of acidity and alkalinity of a substance;
- Can give the degree of acidify and alkalinity of a substance;
-
- Evaporating dish;
- Evaporating liquids;
- Pair of tongs;
- Used to safely hold hot or corrosive solids;
-
- Blue flame;
White fumes; - Oxygen is bubbled into molten iron; the oxygen reacts with carbon, sulphur and phosphorus impurities; which escape leaving iron more pure;
- Blue flame;
-
- Under same conditions of temperature and pressure, the rate of diffusion of a gas is inversely proportional to the square root of its density;
- Calculation:
V1 = V2
T1 T2
V1 = 1
V2 = 2
T1 = 127 + 273 = 400
T2 = V2T1
V1
= 2 x 400 = 800K
1
-
- Temporary physical change – a reversible reaction in which no new substance is formed;
Temporary chemical change – a reversible reaction in which a new substance is formed;
Owtte - Table
Solid Observation on heating Type of change CuSO4.5H2O Blue solid forms a white solid;
Droplets of a colourless liquid forms in the cooler parts of the test tubeTemporary chemical
KMnO4 Purple solid forms a mixture of a green solid and a black solid;
Evolution of a colourless odourless gas that relights a glowing splint;Permanent chemical
- Temporary physical change – a reversible reaction in which no new substance is formed;
- To separate test tubes of bromine water; bubble each of the gases separately; both decolourise the yellow bromine water but the reaction is faster in ethyne;
Accept the use of KMnO4. -
- Add excess calcium carbonate to dilute nitric (V) acid / dilute hydrochloric acid;
- Filter to obtain a solution of calcium nitrate /calcium chloride;
- Add water to solid sodium sulphate and stir to dissolve;
- Add sodium sulphate to the calcium nitrate / calcium chloride;
- Filter to obtain calcium sulphate and sodium nitrate / sodium chloride;
- Rinse with distilled water and dry between filter papers;
-
- Insert a burning splint into a gas jar of the gas; it extinguishes the burning splint with a pop sound;
-
- Grey solid forms a yellow solid which on cooling changes to white;
Bubbles of a colourless odourless gas; - To drive out atmospheric air; so prevent zinc from being oxidized by the oxygen in the air hence preventing reaction between zinc and air;
- Grey solid forms a yellow solid which on cooling changes to white;
-
- Covalent bond: a chemical bond formed due to sharing of electrons which have been donated by both atoms;
Coordinate bond: a chemical bond formed by sharing electrons, where the electrons shared has been contributed by only one atom; - X – 4
Y – 2
Z – 3;
- Covalent bond: a chemical bond formed due to sharing of electrons which have been donated by both atoms;
-
- SiCl4(aq) + H2O(l) → SiO2(s) + HCl(aq);
- White fumes; silicon (IV) oxide is hydrolysed in water to form HCl(g); the reaction is exothermic sop the resultant HCl is released as white fumes;
- Calculation:
moles of ethanoic acid reacting:
1000 cm3 → 0.16moles
25 cm3 → 25 x 0.16 = 0.004 moles;
1000
Moles of KOH reacting = 0.004 from reaction ratio.
12.5 cm3 → 0.004 moles
250 cm3 → 250 x 0.004 = 0.08 moles;
12.5
RMM of KOH = 39 + 16 + 1 = 56
Mass of KOH used = 56 x 0.08 = 4.48g; -
- Reduce the diffusion of oxygen in the glass tube to provide more time for reaction with ammonia;
- Green – yellow flame;
- 4NH3(g) + O2(g) → 2N2(g) + 6H2O(l);
-
- Vanadium (V) oxide catalyst;
Pressure of 2- 3 atmospheres;
400ºC - 500ºC; - Decrease in temperature;
Increase in pressure;
- Vanadium (V) oxide catalyst;
-
- 2NaOH(aq) + Cl2(g) → NaOCl(aq) + NaOCl(aq) + H2O(l);
- CaOCl2 dissociates to liberate oxygen atoms; which oxidizes the dye hence bleaching the dyes;
-
- The thistle funnel is not dipping into the solution;
Wrong method of gas collection; - HCOOH(aq) → CO(g) + H2O(l);
- Extraction of less reactive metals by reducing their oxides;
- The thistle funnel is not dipping into the solution;
-
- Substances 2 and 4;
-
- Add solid sodium carbonate / sodium hydrogen carbonate to separate sample of each; bubbles of a colourless odourless gas with 1but no reaction with 2;
- Bubble or add each separately to bromine water; no reaction with 1 but 2 decolourizes the yellow bromine water;
- Bubble or add each separately to acidified potassium manganate (VII); no reaction with 1 but 2 decolourizes purple acidified potassium manganate (VII);
- Add magnesium / zinc metal to each separately; bubbles of a colourless gas with 1but no reaction with 2;
Consider only the first one
Accept anyone correct
- Carbon – Remains the same
Hydrogen – decreases;
Oxygen – decreases; -
-
- Phosphoric acid;
- Oxidation;
- Esterification;
- Ethylethanoate;
- Orange acidified potassium dichromate (VI) changes from orange to green chromium (III) ions;
- CH3COOH + CH3CH2OH → CH3COOCH2CH3 + H2O;
-
-
- Graph sketches
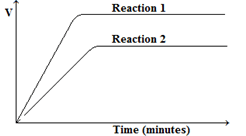
- More volume of gas is produce in reaction 1 because there are more magnesium particles to displace hydrogen ions to form hydrogen gas;
Reaction 1is also faster because the higher mass of magnesium leads to a higher number of reacting particles which leads to more successful collisions;
- Graph sketches
-
- Use of lead (II nitrate in the salt bridge; lead (II) ions migrate to the copper half cell; leading to formation of a precipitate in the salt bridge which stops flow of ions;
-
- Zn(s) → Zn2+(aq) + 2e;
- EMf = Ereduced - Eoxidised
= - 0.34 – (+0.76)
= + 0.42V;
- The green colour fades while the yellow colour intensifies; addition of silver nitrate introduces silver ions which increases concentrations of particles on the right; hence shifting the equilibrium to the right;
-
- NaNO3;
- Still would react with product at the cathode /chlorine due to the high temperatures in the cell;
- Na+(l) + e → Na(l);
Ca2+(l) + 2e → Ca(l);
-
- The time taken for half a given mass/amount of a radioactive substance to decay;
-
- The nucleus of an atom as characterized by the sum total of protons and neutrons therein;
- Total number of half lifes
7.5 = 3
1.5
100 → 50 → 25 → 12.5
Percentage = 12.5%;
-
- Endothermic;
- ΔH = b – a;
Ea= c – b;
- In solid state the ions are held static in the crystal lattice; melting frees the ions leading to free mobile ions for electrical conductivity;
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download Chemistry Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Asumbi Girls Mock Examinations 2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students
