QUESTIONS
- Explain how the hotness of a Bunsen burner flame can be increased. (1 mark)
- When dilute hydrochloric acid was reacted with solid B, a colourless gas which extinguished a burning splint was produced. When an aqueous solution of solid B was tested with blue litmus paper, the paper turned red/ pink.
- Identify the anion present in solid B. (1 mark)
- Write an ionic equation for the reaction between solid B and dilute hydrochloric acid. (1 mark)
- Identify the anion present in solid B. (1 mark)
- Dry ammonia gas was passed over heated lead (II) oxide and the products passed over anhydrous copper (II) sulphate as shown in the diagram below.
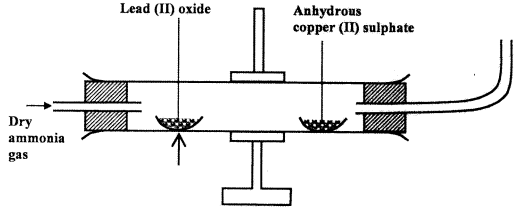
State:- Two observations made in the combustion tube. (2 marks)
- The property of ammonia gas shown in the experiment. (1 mark)
- Two observations made in the combustion tube. (2 marks)
- Starting with zinc sulphate solution, describe how a sample of zinc oxide can be obtained. (3 marks)
- Explain how conduction of electricity takes place in the following:
- Iron metal. (1 mark)
- Molten lead (II) iodide (1 mark)
- Iron metal. (1 mark)
- 100 cm3 of a sample of ethane gas diffuses through a porous pot in 100 seconds. What is the molecular mass of gas Q if 100 cm3 of the gas diffuses through the same porous pot in 121 seconds under the same conditions? (3 marks)
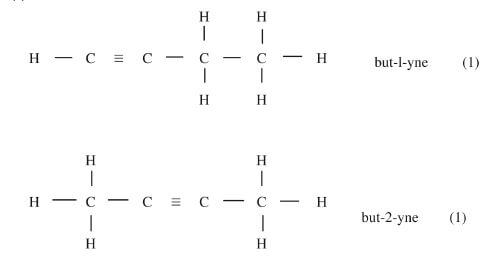
(C = 12.0, H = 1.0) - Draw and name the isomers of butyne. (2 marks)
- State one use of polystyrene. (1 mark)
- Draw and name the isomers of butyne. (2 marks)
- Complete the nuclear reaction below:
(a)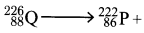 (1 mark)
(1 mark)
(b) State two uses of radioisotopes in health. (2 marks) - The table below shows the relative molecular masses and boiling points of pentane and ethanoic acid.
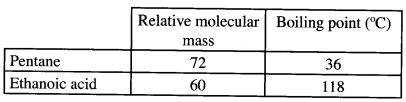
Explain the large difference in boiling points between ethanoic acid and pentane. (2 marks) - One of the ores of copper has the formula, CuFeS2.
- Describe how iron in the ore is removed during extraction of copper metal. (1 mark)
- State two environmental problems associated with extraction of copper metal. (2 marks)
- Describe how iron in the ore is removed during extraction of copper metal. (1 mark)
- Study the flow chart below and answer the questions that follow.
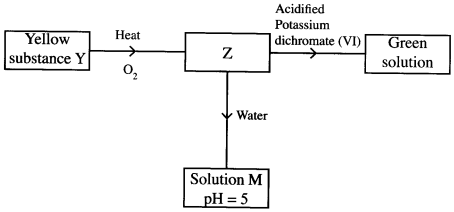
Identify Z and M. (2 marks)
Z
M - The table below shows the pH values of solutions A, B, C and D.
Solution A B C D pH 2 7 11 14
Select solutions in which a sample of lead (II) hydroxide is likely to dissolve. Give reasons for each solution selected. (3 marks) - 100 cm3 of 0.05M sulphuric (VI) acid were placed in a flask and a small quantity of anhydrous sodium carbonate added. The mixture was boiled to expel all the carbon (VI) oxide. 25 cm3 of the resulting solution required 18 cm3 of 0.1 M sodium hydroxide solution to neutralise it. Calculate the mass of sodium carbonate added. (Na = 23; O = 16.0; C = 12.0) (3 marks)
- When 20 cm3 of 1 M sodium hydroxide was mixed with 20 cm3 of 1 M hydrochloric acid, the temperature rose by 6.70C. Assuming the density of the solution is 1 g/cm3 and the specific heat of the solution is 4.2 Jg-1 k-1;
- Calculate the molar heat of neutralization. (2 marks)
- When the experiment was repeated with 1 M ethanoic acid, the temperature change was found to be lower than with 1 M hydrochloric acid. Explain. (1 mark)
- Calculate the molar heat of neutralization. (2 marks)
- Study the set-up below and answer the questions that follow.
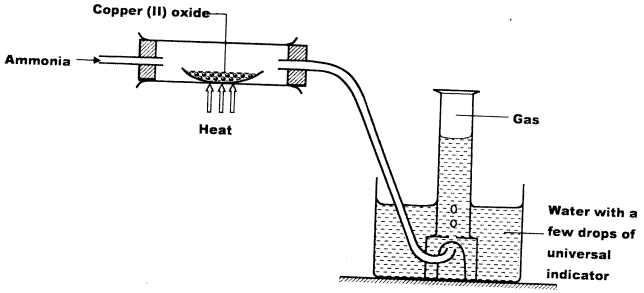
- Write an equation for the reaction between ammonia and copper (II) oxide. (1 mark)
- During the experiment, the colour of the contents in the water trough changed. State the colour change observed and give an explanation. (2 marks)
- Write an equation for the reaction between ammonia and copper (II) oxide. (1 mark)
- A measuring cylinder fitted with moist steel wool was inverted in a trough of water as shown in the diagram below.
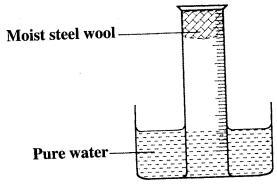
- State and explain the observations made in:
- Moist steel wool after four days. (1 mark)
- Water level in the measuring cylinder after four days. (1 mark)
- What would be the effect of the steel wool moistened with salty water? (1 mark)
- State and explain the observations made in:
- In an experiment of rates of reaction, potassium carbonate was reacted with dilute sulphuric (VI) acid.
- What would be the effect of an increase in the concentration of the acid in the rate of the reaction? (1 mark)
- Explain why the rate of reaction is found to increase with temperature. (2 marks)
- What would be the effect of an increase in the concentration of the acid in the rate of the reaction? (1 mark)
- Use the part of the periodic table given below to answer the questions that follow. (Letters are not the actual symbols of the elements.)
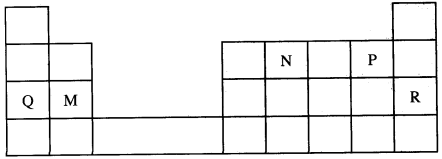
- Identify the element that forms giant covalent structures. (1 mark)
- Identify one element that does not form compounds. (1 mark)
- Write the formula for the nitride of M. (1 mark)
- Identify the element that forms giant covalent structures. (1 mark)
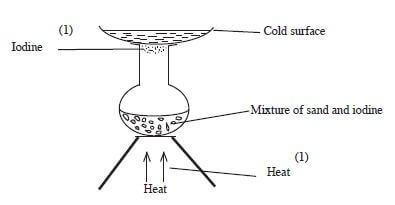
- Draw a set-up that can be used to separate a mixture of sand and iodine. (3 marks)
- In the contact process, during the production of sulphur (VI) oxide, a catalyst is used. Give two reasons why vanadium (V) oxide is preferred to platinum. (2 marks)
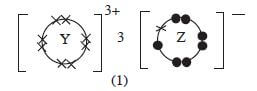
- Given that the atomic number of Y is 13 and that of Z is 9:
- Write the electronic arrangement of Y and Z; (1 mark)
- Draw the dot (.) and cross (x) diagram for the compound formed by Y and Z. (1 mark)
- Write the electronic arrangement of Y and Z; (1 mark)
- The set up below was used to separate a mixture of methanol and propanol. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
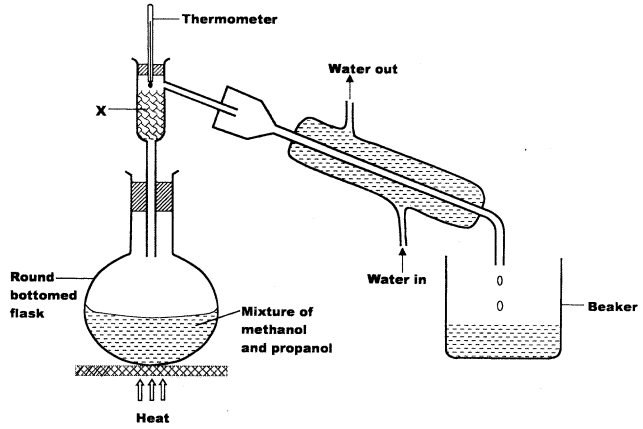
- State the function of X. (1 mark)
- Which liquid will collect first in the beaker? Give a reason. (1 mark)
- State the function of X. (1 mark)
- Study the flow chart below and answer the questions that follow.
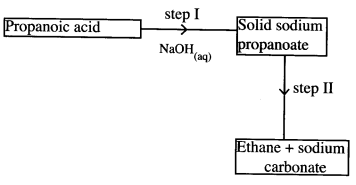
- Name the process in step I. (1 mark)
- Identify the reagent in step II. (1 mark)
- Give one use of ethane. (1 mark)
- Name the process in step I. (1 mark)
- A student electrolysed dilute sodium chloride solution using inert carbon electodes.
Name the products at: (2 marks)- Anode;
- Cathode.
- If the experiment was repeated using concentrated sodium chloride instead of dilute sodium chloride solution, write the half equation at the anode. (1 mark)
- A student electrolysed dilute sodium chloride solution using inert carbon electodes.
- An organic compound had the following composition 37.21% carbon, 7.75% hydrogen and the rest chlorine. Determine the molecular compound of the formula mass of the compound is 65. (C = 12.0; H = 1.0; Cl = 35.5). (3 marks)
- Cotton is a natural polymer. State one disadvantage and one advantage of this polymer. (2 marks)
- Name a suitable solvent for extracting an indicator from flowers; (1 mark)
- Give a reason why the indicator named in (a) above is used. (1 mark)
- Name a suitable solvent for extracting an indicator from flowers; (1 mark)
- A student used the set up below to prepare a sample of nitrogen gas.
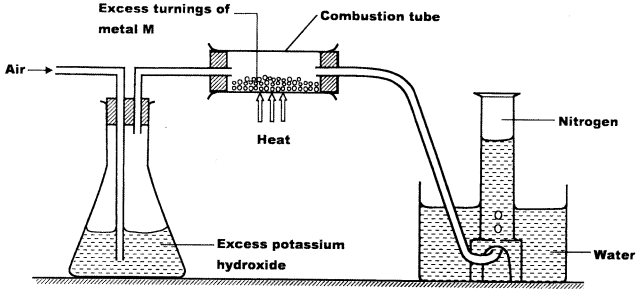
- State the function of potassium hydroxide in the set up. (1 mark)
- Give a suitable metal M for use in the combustion tube. (1 mark)
- Give a reason why the nitrogen gas obtained is not pure. (1 mark)
- State the function of potassium hydroxide in the set up. (1 mark)
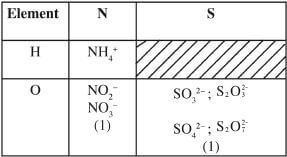
- What is meant by the term radical? (1 mark)
- The table below contains atoms that form common radicals. Complete the table to show radicals formed from various atoms.
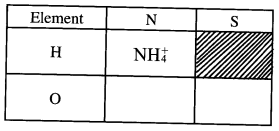
- What is meant by the term radical? (1 mark)
- A gas full of chlorine water was inverted over water and allowed to stand for some time.
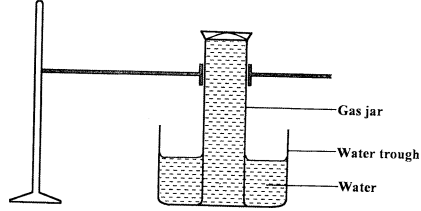
- State and explain two observations made in the gas jar after some time. (2 marks)
- Write the equation for the reaction between chlorine and a hot concentrated potassium hydroxide. (1 mark)
- State and explain two observations made in the gas jar after some time. (2 marks)
MARKING SCHEME
- Increasing the size of the air hole/increase the amount of air/open air holes competely. (1)
-
- HSO-3 (1)
- HSO3-1aq) + H+(aq) → H2O(l) + SO2(g)
or
NaHSO3(s) + H+(aq) → Na+(aq) + H2O(l) + SO2(g)
-
-
- The anhydrous copper (II) Sulphate turns from white to blue. (1)
- A grey solid is formed/droplets of a colourless liquid condense at cool part.(1)
- Reducing property.(1)
-
-
- Add soluble carbonate/Add soluble hydroxide. (1)
- Filter out the zinc carbonate/filter the zinc hydroxide. (1)
- Heat strongly the ZnCO3 to decompose it to form ZnO/Heat strongly the Zn(OH)2 to decompose it to form ZnO. (1)
OR - Heat to evaporate the water. (1)
- Heat ZnSO4 solid to decompose (1) to form ZnO/yellow solid. (1)
-
- delocalised electrons. (1)
- ions in the melt. (1)
-
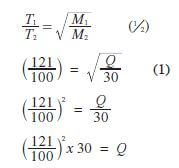
-
-
- Used in packaging - cushions electronics in boxes/insulation/models/ceiling strips/ crates or binding. (1)
-
-
-
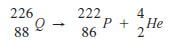 (1)
(1) -
- Cobalt 60 is used to detect the activity of the thyroid gland. (1)
- To sterise equipment/treatment of cancer/radio active Na for disorders in blood circulation/Barium meal for ulcers/detect fractures in bones. (1)
-
- The molecules of ethanoic acid interact through strong hydrogen bonding (1) forming a dimer while molecules of pentane have weak van der waals forces. (1)
NB/ Ethanoic acid has hydrogen bonds while pentane does not have. -
- Roast ore in air/heat in air. (1)
2CuFeS2(s) + 4O2(g) → Cu2S(s) + 2FeO(g) + 3SO2(g) -
- Acid rain that corrodes stone work on buildings/land gulleys/dust pollution. (1)
- SO2 when breathed in causes bronchitis/chlorosis in plants. (1)
- Roast ore in air/heat in air. (1)
- Z is SO2 / sulphur (iv) oxide. (1)
M is H2SO3/ sulphuric (iv) acid. (1) -
- A (1) and D (1)
- A is acidic it will neutralise Pb(OH)2(aq) to form salt and water, ( 1/2 )
- D is a strong base it will react with Pb (OH)2(aq) to form a complex ion. ( 1/2 )
- Lead (II) hydroxide is amphoteric.
-
- Moles of NaOH 18 × 0.1 = 0.0018 (1/2)
1000
Moles of acid 18 × 0.1 × 1/2 = 0.0009 (1/2)
1000
Moles in 100 cm3
18 × 0.1 × 1 1004 2= 0.0036 moles
1000 2 25
0.0036 × 100 (1/2)
25
Ratio of acid : Carbonate
1 : 1
Original moles of acid = 100 × 0.05
1000
= 0.005 /0.53g (1/2)
0.005 - 0.0036 = 0.0014 moles / 0.3816g (1/2)
Mass of Na2CO3 = 0.0014 × 106/0.53 - 0.3816
= 0.1484 g = 0.1484 g (1/2)
- Moles of NaOH 18 × 0.1 = 0.0018 (1/2)
-
- Total volume of solution = 40 cm3 / 40 g (1/2)
∆ H = 40 × 6.7 × 4.2 (1/2)
= 1125.6/1000
= 1.1256 KJ
Moles of acid 20 × 1 = 0.02 moles 1125.6 (1/2)
1000 0.02
0.02 moles = = 0.1256 KJ
1 mole = 1.1256 KJ (1/2) -56280j/mol(1/2)
0.02
= -56.28KJ/mol (1/2) - Some energy is used to ionise the weak acid first before it can neutralise. So not all energy is used in neutralisation. (1)
- Total volume of solution = 40 cm3 / 40 g (1/2)
-
- 3CuO(s) + 2NH3(g) → 3Cu(s) + N2(g) + 3H2O(l) (1)
- It changed purple (1)
The excess ammonia makes solution basic which turns purple with universal indicator. (1)
-
-
- It turned brown /blue/violet/green. (1)
- The water level rose up the gas jar/occupy space left by reacted O2. (1)
- The brown colour would be more since the salt accelerates rusting/rust faster. (1)
-
-
- Rate increases. (1)
- Temperature increases the kinetic energy (1) of the particles increasing the number of collisions. (1)
-
- N (1)
- R (1)
- M3N2 (1)
-
- Vanadium (V) oxide is cheaper (1) and is not easily poisoned by impurities. (1)
- Y = 2.8.3 Z = 2.7 (1)
-
- Condensation of alcohol with higher boiling point so that it runs back to the flask as the alcohol with lower boiling point distills over. (1)
- Methanol. (1) It has a lower boiling point due to the size of carbon chain when compared with propanol. (1)
-
- Step 1 is neutralisation. (1)
- Step II is soda lime/ mixture of Naoh and CaO. (1)
- Fuel/making ethene/making hydrogen gas. (1)
-
- Anode - Oxygen /O2 (1)
Cathode - Hydrogen / H2 (1) - 2Cl−aq) → Cl2(g) + 2e
- Anode - Oxygen /O2 (1)
-
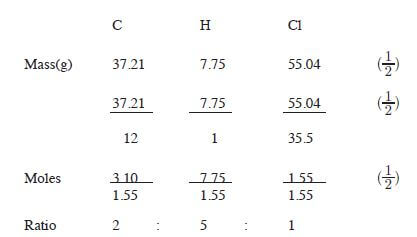
Empirical formula C2H5Cl (1/2)
Empirical mass = 2 x 12 + 5 + 35.5 = 64.5
64.5n = 65
n = 65/64.5
n = 1 (1/2)
therefore: molecular formula = C2H5Cl (1/2) - Natural polymers are biodegradable (1) and are expensive. (1)
Affected by acids/Not easily recyled. -
- Acetone / ethanol / propanone / propanol. (1)
- The solvent dissolves the organic compound indicator present in the flowers / it is an organic solvent. (1)
-
- It absorbs carbon (IV) oxide present in the air. (1)
- Copper /Cu(s) (1)
- It has rare noble gases which have not been removed / Argon. (1)
-
- A radical is a compound formed when elements combine to form ions / free unstable atoms or molecules / a group of free unstable atoms exist in a compound /group of atoms with a common charge. (1)
-
-
- A colourless gas is formed /chlorine water decompose to give oxygen (1/2)
The colour of solution changes from green to colourless / chlorine water becomes hydrochloric acid. (1/2)
The level of solution in the gas jar drops oxgen formed occupies space pushing water downwards. (1/2)
(choose any 2) - 6KOH(aq) + 3Cl2(g) → KClO3(aq) + 5KCl(aq) + 3H2O(l) (1)
- A colourless gas is formed /chlorine water decompose to give oxygen (1/2)
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download KCSE 2014 Chemistry Paper 1 Questions with Marking Scheme.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students

