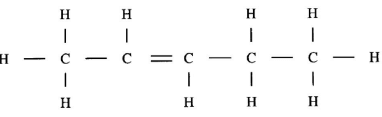-
-
- Carbon (IV) oxide is present in soft drinks. State two roles of carbon (IV) oxide in soft drinks. (1 mark)
- Explain the observation made when a bottle containing a soft drink is opened. (2 marks)
- Carbon (IV) oxide dissolves slightly in water to give an acidic solution. Give the formula of the acid. (1 mark)
- Zinc oxide can be obtained by heating zinc nitrate. A student heated 5.76 g of zinc nitrate.
- Write an equation for the reaction that occured. (1 mark)
- Calculate the total volume of gases produced.
(Molar gas volume is 24 dm3; Zn = 65.4; O = 16.0; N = 14.0). (4 marks) - Identify the element that is reduced when zinc nitrate is heated. Give a reason. (2 marks)
-
-
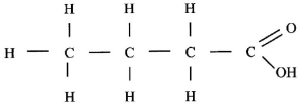
- Draw the structure of the following compounds. (2 marks)
- Butanoic acid;
- Pent-2-ene.
- Explain why propan-1-ol is soluble in water while prop-1-ene is not.
(Relative molecular mass of propan-1-ol is 60 while that of prop-1-ene is 42). (2 marks) - What would happen if a few drops of acidified potassium manganate (VII) were added to oil obtained from nut seeds? Explain. (2 marks)
- State one method that can be used to convert liquid oil from nut seeds into solid. (1 mark)
- Describe how soap is manufactured from liquid oil from nut seeds. (3 marks)
- 0.44g of an ester A reacts with 62.5 cm3 of 0.08M potassium hydroxide giving an alcohol B and substance C. Given that one mole of the ester reacts with one mole of the alkali, calculate the relative molecular mass of the ester. (2 marks)
- Draw the structure of the following compounds. (2 marks)
-
- Name the method that can be used to obtain pure iron (III) chloride from a mixture of iron (III) chloride and sodium chloride. (1 mark)
- A student was provided with a mixture of sunflower flour, common salt and a red dye. The characteristics of the three substances in the mixture are given in the table below.

The student was provided with ethanol and any other materials needed.
Describe how the student can separate the mixture into its three components. (3 marks) - The diagram below shows part of a periodic table. The letters do not represent the actual symbols of the elements. Use diagram to answer the questions that follow.
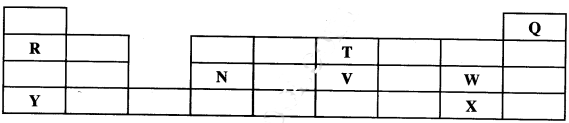
- Explain why the oxidising power of W is more than that of X. (2 marks)
- How do the melting points of R and T compare? Explain. (2 marks)
- State an element that could be used:
- in weather baloons; (1 mark)
- for making a coking pot. (1 mark)
-
- Classify the substances water, iodine, diamond and candle wax into elements and compounds. (2 marks)
Elements Compounds - Give one use of diamond. (1 mark)
- Classify the substances water, iodine, diamond and candle wax into elements and compounds. (2 marks)
-
- The diagram below represents a dry cell. Use it to answer the questions that follow.
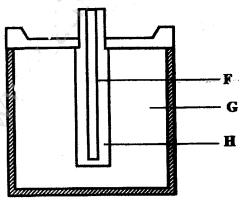
- Which of the letters represent:
- carbon electrode? (1 mark)
- The electolyte? (1 mark)
- One of the substances used in a dry cell is manganese (IV) oxide. State two roles of manganese (IV) oxide in the cell. (2 marks)
- Which of the letters represent:
- Below is a simplified electorolytic cellused for purification of copper. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
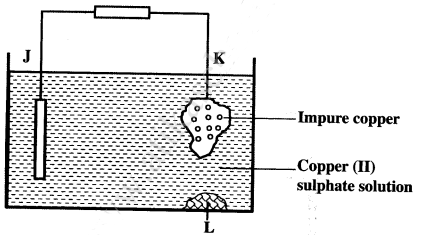
- Identify the cathode. ( 1 mark)
- Write the equation for the reaction at the anode. (1 mark)
- What name is given to L? (1 mark)
- A current of 0.6 A was passed through the electrolyte for 2 hours. Determine the amount of copper deposited.
(Cu = 63.5; Faraday = 96,500 coulombs). - State two uses of copper metal. (1 mark)
- The diagram below represents a dry cell. Use it to answer the questions that follow.
- The set-up below can be used to generate a gas without heating. This occurs when substance M reacts with solid N.
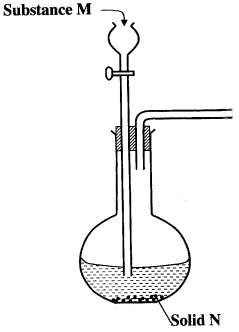
-
- Complete the table below giving the names of substance M and solid N if the gases generated are chlorine and sulphur (IV) oxide. (2 marks)
- Complete the diagram above to show how a dry sample of sulphur (IV) oxide can be collected. (3 marks)
- Complete the table below giving the names of substance M and solid N if the gases generated are chlorine and sulphur (IV) oxide. (2 marks)
- Describe two chemical methods that can be used to test the prescence of sulphur (IV) oxide. (3 marks)
- Other than the manufacture of sulphuric (VI) acid, state two uses of sulphur (IV) oxide. (2 marks)
-
-
- Other than concerntration, state two factors that determine the rate of reaction. (2 marks)
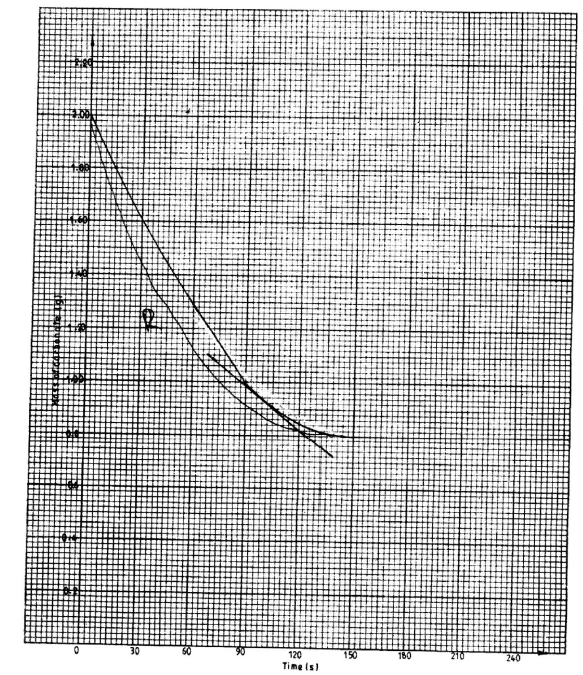
- In an experiment to determine the rate of reaction, excess lambs of calcium carbonate were added to 2 M hydrochloric acid. The mass of calcium carbonate left was recorded after every 30 seconds. The results are shown in the table below.
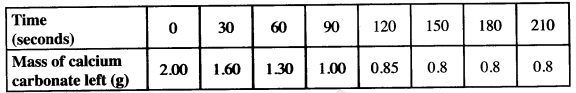
- Write the equation of the reaction that took place. (1 mark)
- On the grid provided, plot a graph of mass of calcium carbonate vertical axis against time. (3 marks)

- Determine the rate of reaction at the 105th second. (3 marks)
- Why does the curve level off after some time? (1 mark)
- On the same grid, sketch a curve for the same reaction using 4 M hydrochloric acid and label the curve R. (2 marks)
-
- Naturally occurring magnesium consists of three isotopes. 78.6% 24Mg; 10% 25Mg and 26Mg. Calculate to one decimal place, the relative atomic mass of magnesium. (2 marks)
- When magnesium burns in air, it forms a white solid and a grey-green solid. When a few drops of water are added to the mixture, a gas that turns red litmus paper blue is evolved.
Identify the:- white solid. (1 mark)
- gas evolved and state its use.
- Name of the gas. (1 mark)
- Use of the gas. (1 mark)
- Two different samples of water (I and II) were tested with soap solution. Sample II was further subjected to two other processes before adding soap. 20 cm3 of each sample of water was shaken with soap solution in a boiling tube until a permanent lather was obtained. The results are shown in the table below.
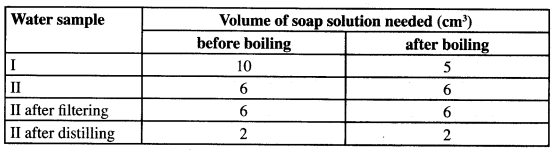
- Identify the water sample that had temporary hardness. Explain your answer. (2 marks)
- Explain why the results for sample II are different after distilling but remain unchanged after filtering. (2 marks)
- State two advantages of using both water samples for domestic purposes. (2 marks)

MARKING SCHEME
-
-
- It acts as a preservative (+).
It gives it taste/adds flavour/sweetens ( 2 ). - Effervescence/ fizzing/bubbles/sound (1) CO2 is dissolved under pressure in the soft drink. On opening, the pressure is released the pressure is decreased (1).
- H2CO3 (1)
- It acts as a preservative (+).
-
- 2Zn(NO3)2(s) → 2ZnO(s) + 4NO2(g) +O2(g)
- Moles of Zn(NO3)2 = 5.76 = 0.03 moles (1)
189.4
Moles of NO2 = 2 x 0.03
=0.06
Moles of O2 = 0.03
2
= 0.015
Total no. of moles of gases = 0.06 +0.015
= 0.075
Volume of gases = 0.075 x 24 = 1.8 dm3 - Nitrogen (1). Its oxidation state decreases/oxidation state changes from +5 to +4.
-
-
-
- Propan - 1 - ol dissolves in water because it is polar v Prop-l-ene is non-polar.
- The purple colour would be decolourised (1) because oil from nuts is unsaturated (1) / contains a
double bonds..
- Hydrogenation (1).
- Add NaOH/KOH to the oil , stir, boil the mixture. Add NaCl solution, skim off or filter
- Moles of KOH = 62.5 x 0.08
1000
= 0.005 moles (1)
0.44 = 0.005 (1)
R.M.M
-
-
- Sublimation (1 mark)
- Add ethanol to the mixture. Filter and evaporate filtrate to obtain red dye . Add water to the residue. Filter to obtain sunflower flour. Evaporate filtrate to obtain salt (2).
Add 4,0 to mixture , filter, residue is sunflower, evaporate the water; add ethanol to the residue filter. The filtrate is red dye. (3 marks) -
- W accepts electrons more readily than X. W has small atomic radius/ W has less energy levels than X/ W has less screening effect than X/ W has greater effective nuclear attraction than X. W is more electro negative than X.
- T has a lower melting point than R because it exists in simple molecular form with weak Van der Waals forces while R has strong metallic bonds
- Q
- N
- Elements
iodine
diamond
Compounds
Water
Candle wax- making drilling bits/making glass cutters
- Jewellery
-
-
-
- F
- G(1)
-
- Manganese (IV) oxide oxidises hydrogen to water /depolariser (1).
- It increases the surface area of the electrolyte (1).
-
-
- Cathode J (1).
- Cu(s) → Cu2+(aq) + 2e(s)
- Slag /impurity / sludge
- Q = It Quantity of electricity = 60 x 2
Q = 0.6 x 60 x 60 x 2
Cu → Cu2+ + 2e
IF = 96500 x 2
0.6 x 60 x 60 - ?
0.6 x 60 x 60 =0.01119 x 2
96500 x 2
Mass = 0.02238 x 63.5 = 1.42 g (3 marks) - Uses of copper metal - soldering bits / wires
- Electrical cables and alloys - coins, ornaments/lightening arrestors/ diodes/
- calorimeters. (1 mark)
-
-
-
- Chlorine
Solid N - Potassium manganate (VII).
M - Conc HCl.
SO2 -N is sodium sulphite / Potasium sulphite
Mis dilute HCI / H2SO4 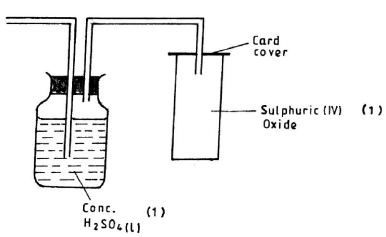
- Chlorine
- Presence of SO2
- Use of acidified potassium dichromate (VI) which turns from orange to green
- Bubble gas through acidified potassium manganate (VII) which decolourises/changes i.e from purple to colourless.
- Iron (III) sulphate solution - yellow/brown changes to green
- Bromine water colour changes from yellow/brown / orange to colourless
-
- Fumigation (1)
- Preservative (1).
- Antioxidant
- Bleaching agent
- Disinfectant
-
-
- Factors, temperature, catalyst, surface area, particle size, pressure, light intensity. (2 marks)
-
- Equation:
CaCO3(s) + 2 HCl(aq) → CaCl2(aq) + CO2(g) + H2O(I) (1 mark) - Graph
- Plotting
- scale
- curve-which levels towards the end
- Equation:
- Determine the rate of reaction at 105 sec. (Use the graph)
Draw a tangent at 105 - Curve levels off, because all the acid has been used up. (1 mark)
- Sketching a curve.(2 marks)
-
- % Mg = 78.6 + 10.0
= 88.6
100 - 88.6 = 11.4% (1)
RAM for Mg = 24 x 78.6 + 10 x 25 + 11.4 x 26
100
1886.4 + 250 + 296.4
100
RAM of Mg = 24.3 (1) -
- White solid = Magnesium oxide (1 mark)
Ammonia. (1 mark) - Making ammonium fertilizers /manufacture of Na, CO /laundry/refregirant. (1 mark)
- White solid = Magnesium oxide (1 mark)
-
-
- Water sample with temporary hardness is I
- It uses less soap after boiling
- On filtering there is still soluble cations of Ca2+ and Mg2+ present which contribute to water hardness. Distilling, the Ca2+ and Mg2+ ions are left behind as insoluble salts.
Filterning does not remove hardness in water/does not remove Ca2+ and Mg2+ ions. Distillation removes hardness in H,O/ removes Ca2+ and Mg2+. - Clogs water pipes, waste soap formation of scum/Boiler scales
Dirty marks/stains on clothes.
-
- % Mg = 78.6 + 10.0
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download KCSE 2015 Chemistry Paper 2 with Marking Scheme.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students