Questions
INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
- Answer ALL questions in the spaces provided
- Mathematical tables and electronic calculators may be used.
- All working MUST be shown clearly where necessary.
- Study the information given below and use it to answer the questions that follow;
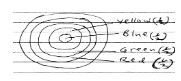
Red dye is more soluble than green dye, green is more soluble than yellow whereas blue dye is the least soluble.- Represent the three dyes on a round paper chromatography. (2marks)
- Name one industrial application of chromatography. (1mark)
-
- What is a fuel? (1mark)
- Calculate the heat value of ethanol if its molar enthalpy of combustion is-1360kjmol-1
(C=12.0, O=16.0, H=1.0) (2marks)
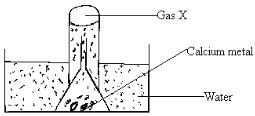
- Study the set up below and use it to answer the questions that follow.
- What physical property of calcium metal is demonstrated in the diagram above? (1mark)
- What would be observed if water was replaced with dilute Sulphuric (VI) acid? (2marks)
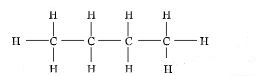
- A hydrocarbon decolorizes chlorine gas in presence of ultra violet light but does not decolorize acidified potassium manganate (VII) solution.
- Name the homologous series to which the hydrocarbon belongs. (1mark)
- Draw the structural formula and name the fourth member of the homologous series to which the hydrocarbon belongs? (2marks)
- Explain why a solution of hydrogen chloride in water turns blue litmus paper red but a solution of hydrogen chloride in methylbenzene has no effect on litmus papers. (2marks)
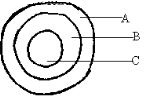
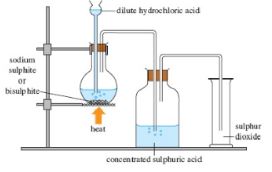
- The diagram below represents a cross section of the apparatus used to extract sulphur from its deposits. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
- State the role of the substance that is passed through;
- A(1mark)
- C(1mark)
- Give one reason why the method shown in the diagram is suitable for extraction of sulphur. (1mark)
- State the role of the substance that is passed through;
- Explain how you would obtain magnesium carbonate from a mixture of magnesium carbonate and sodium carbonate. (2mark
- 20g of potassium carbonate were dissolved in 50cm3 of water in a conical flask. Lemon juice was then added drop wise while shaking until there was no further observable change.
- Explain the observation that was made in the conical flask when the reaction was in progress. (1mark)
- What observation would be made if lemon juice had been added to copper turnings in a conical flask? Give a reason. (2marks)
- Explain why a burning magnesium continues to burn in a gas jar full of carbon (IV) oxide while a burning candle would be extinguished. (2marks)
- 8.4g of carbon (IV) oxide and 3.42g of water are formed when a hydrocarbon is burnt completely in oxygen. Determine the empirical formula of the hydrocarbon. (H=1.0; C=12.0; O=16.0) (3marks)
- The melting point of nitrogen is -196°C while that of sodium is 98°C, in terms of structure and bonding explain the differences in the melting points of nitrogen and sodium. (2marks)
-
- What is an amphoteric substance? (1mark)
- Identify the reagent that acts as a base in the equation below. Give a reason for your answer.
H2O2(aq) + H2O(I) → H3+O(aq) + HO2(aq) (2marks)
- In the industrial manufacture of ammonia gas by Harber process, Nitrogen and hydrogen gases are reacted together.
- State any two conditions necessary for ammonia to be formed in the Harber process. (1mark)
- Nitrogen and hydrogen must be purified before they are reacted. Give a reason. (1mark)
- Other than manufacture of fertilizers state one use of ammonia. (1mark)
- Describe how you would prepare crystals of potassium sulphate starting with 100cm3 of 0.5M potassium hydroxide. (3marks)
- Distinguish between atomic mass and relative atomic mass. (2marks)
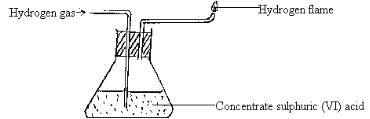
- Study the diagram below and answer the questions that follow:
- Name one chemical and one physical property of hydrogen being demonstrated in the set-up above.
- Chemical property. (1mark)
- Write a chemical equation for the reaction taking place. (1mark)
- Name any other substance that can be used in place of concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid. (1mark)
- Give a reason why it is necessary to burn the hydrogen gas as shown in the set-up. (1mark)
- Name one chemical and one physical property of hydrogen being demonstrated in the set-up above.
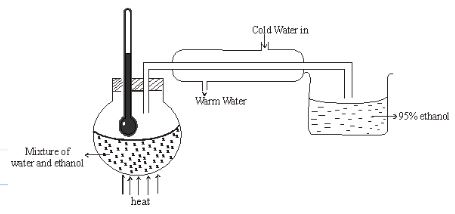
- The diagram below shows a simple distillation to separate water and ethanol.
- State one of the conditions for the above process to take place. (1mark).
- Ethanol collected is 95% pure. Secondary distillation is carried out in which calcium metal is placed in ethanol to react with water. Give a reason why the following cannot be used. (2marks)
- Sodium
- Copper
- A solution of potassium chloride was added to a solution containing a lot of lead (II) nitrate. A precipitate that weighed 5.56g was formed. Find the amount of potassium chloride in the solution (3marks)
- 1.9g of Magnesium chloride was dissolved in water. Silver nitrate solution was added till excess. Calculate the mass of silver nitrate that was added for complete reaction. (3marks)
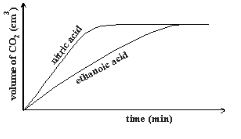
(MgCl2= 95, N=14, O=16, Ag = 108) - In an experiment 40cm3 of 0.5M nitric acid was reacted with excess Sodium Carbonate and the volume of Carbon (IV) Oxide produced recorded with time. In another experiment, the same volume and concentration of ethanoic acid was reacted with excess Sodium Carbonate and the volume of Carbon (IV) Oxide produced recorded with time.
- Why was Sodium Carbonate used in excess? (1marks)
- On the graph below sketch and label the curves of the volumes of Carbon (IV) Oxide produced against time. (2marks)
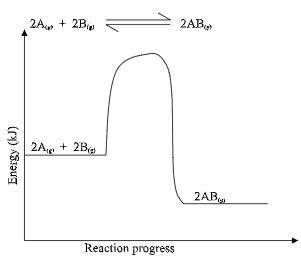
- The figure below is an energy level diagram for the reaction.
Explain how the following conditions would affect the yield of AB.- Increase in pressure. (2marks)
- Decrease in temperature. (2marks)
- A white solid K was heated. It produced a brown gas A and another gas B which relights a glowing splint. The residue left was yellow even after cooling.
- Identify gases A and B. (2marks)
- Write a balanced chemical equation for the decomposition of solid K. (1mark)
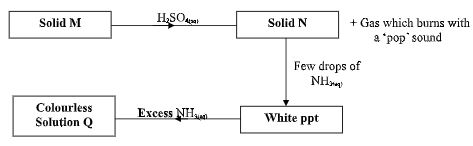
- The scheme below shows some reaction sequence starting with solid M.
- Name solid M. (1mark)
- Write the formula of a complex ion present in solution Q. (1mark)
- Write an ionic equation of the reaction between barium nitrate and solution N. (1mark)
-
- What is meant by a saturated solution? (1mark)
- In an experiment to determine the solubility of solid Y in water at 300C the following results were
obtained.
Mass of evaporating dish = 26.2g
Mass of evaporating + saturated solution = 42.4g
Mass of evaporating dish + dry solid Y = 30.4g
Using the information, determine the solubility of solid Y at 300C. (2marks)
- Compare the electrical conductivity of dilute Sulphuric (VI) acid and concentrated Sulphuric (VI) acid. Explain your answer. (2marks)
- Draw a well labelled diagram of a setup used to prepare and collect dry Sulphur IV oxide. (3marks)
- The molar heat of formation of carbon (II) oxide is -105kJmol-1, molar heat of combustion of carbon is -393kJmol-1.
By using an energy cycle diagram, determine the molar heat of combustion of carbon (II) oxide. (3marks) - In an experiment, a small amount of charcoal was added into a test tube and 5cm3 of concentrated nitric (V) acid added, then warmed.
- State the observation that was made. (1mark)
- Explain the observation made in (i) above. (1mark)
- Write an equation for the reaction that took place. (1mark)
Marking Scheme
- Study the information given below and use it to answer the questions that follow; Red dye is more soluble than green dye, green is more soluble than yellow whereas blue dye is the least soluble.
- Represent the three dyes on a round paper chromatography. (2marks)
- Name one industrial application of chromatography. (1mark)
- Detecting/identifying poisonous substances present in food substances// purifying natural pigments (1)
- Represent the three dyes on a round paper chromatography. (2marks)
-
- What is a fuel? (1mark)
- A substance that produces a substantial amount of energy when burnt. (1)
- Calculate the heat value of ethanol if its molar enthalpy of combustion is-1360kjmol-1 (C=12.0, O=16.0, H=1.0) (2marks)
- RFM of C2H5OH. = 12 x 2 + 1 x 6 + 16 = 46 ( ½ )
Heat value = ΔHc/RFM = -1360/46 ( ½ )
= 29.5652kJ(1) penalize ½ mk for wrong/missing units
- RFM of C2H5OH. = 12 x 2 + 1 x 6 + 16 = 46 ( ½ )
- What is a fuel? (1mark)
- Study the set up below and use it to answer the questions that follow.
- What physical property of calcium metal is demonstrated in the diagram above? (1mark)
- Denser than water (1
- What would be observed if water was replaced with dilute Sulphuric (VI) acid? (2marks)
- Effervescence/gas bubbles ( ½ ) which stops immediately ( ½ )// white precipitate with evolution of gas bubbles/effervescences
- Calcium reacts with sulphuric acid to form an insoluble calcium sulphate and hydrogen gas (1)
- What physical property of calcium metal is demonstrated in the diagram above? (1mark)
- A hydrocarbon decolorizes chlorine gas in presence of ultra violet light but does not decolorize acidified potassium manganate (VII) solution.
- Name the homologous series to which the hydrocarbon belongs. (1mark)
- Alkanes (1)
- Draw the structural formula and name the fourth member of the homologous series to which the hydrocarbon belongs? (2marks)
(1) Butane (1)
- Name the homologous series to which the hydrocarbon belongs. (1mark)
- Explain why a solution of hydrogen chloride in water turns blue litmus paper red but a solution of hydrogen chloride in methylbenzene has no effect on litmus papers. (2marks)
- HCL(g) ionizes (1) in water to form acidic solution ( ½ ) while in methylbenzene, HCl(g) gas remains molecular (1) hence neutral ( ½ )
- The diagram below represents a cross section of the apparatus used to extract sulphur from its deposits. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
- State the role of the substance that is passed through;
- A – Superheated water is used to melt sulphur deposits (1) (1mark)
- C – Hot air used to force the mixture of molten sulphur (1mark)
- Give one reason why the method shown in the diagram is suitable for extraction of sulphur. (1mark)
- The soil structure is weak and can cave incase of open mining (1)
- State the role of the substance that is passed through;
- Explain how you would obtain magnesium carbonate from a mixture of magnesium carbonate and sodium carbonate. (2mark
- Add water to the mixture (1) filter (1) wash the residue with distilled water ( ½ ) Dry between filter papers (½)
- 20g of potassium carbonate were dissolved in 50cm3 of water in a conical flask. Lemon juice was then added drop wise while shaking until there was no further observable change.
- Explain the observation that was made in the conical flask when the reaction was in progress. (1mark)
- Lemon reacted with the carbonate to produce carbon (IV) oxide gas (effervesnces ) (1)
- What observation would be made if lemon juice had been added to copper turnings in a conical flask? Give a reason. (2marks)
- No observable change/effervescence/gas bubbles (1); lemon juice is not an oxidizing agent
- Explain the observation that was made in the conical flask when the reaction was in progress. (1mark)
- Explain why a burning magnesium continues to burn in a gas jar full of carbon (IV) oxide while a burning candle would be extinguished. (2marks)
- The intense heat of reaction (1) of magnesium decomposes CO2(g) into carbon and oxygen.(1)
- The oxygen formed further combine with magnesium to form magnesium oxide (1)
- 8.4g of carbon (IV) oxide and 3.42g of water are formed when a hydrocarbon is burnt completely in oxygen. Determine the empirical formula of the hydrocarbon. (H=1.0; C=12.0; O=16.0) (3marks)
- CxHy + O2(g) XCO2(g) + H2O(l)✔ (1)
Mass moles 8.4/44 3.42/18
Moles 0.1909 : 0.19( ½ )
Mole ration : 0.1909: 019
0.19 0.19
X = 1; = 1 y=2✔ ( ½ )
E.F = CH2 (1)
- CxHy + O2(g) XCO2(g) + H2O(l)✔ (1)
- The melting point of nitrogen is -1960C while that of sodium is 980C, in terms of structure and bonding explain the differences in the melting points of nitrogen and sodium. (2marks)
- Nitrogen has a simple molecular structure ( ½ ) with weak van der waals/ intermolecular forces (½ ) which are easily overcome by heat ( ½ ) while sodium metal has a metallic structure (½) with stronger metallic bonds (1)// which require a lot of heat to break.
-
- What is an amphoteric substance? (1mark)
- A substance that displays both acidic and basic properties(1)
- Identify the reagent that acts as a base in the equation below. Give a reason for your answer.
- H2O2(aq)(1) has accepted protons/H+(1)
- What is an amphoteric substance? (1mark)
- In the industrial manufacture of ammonia gas by Haber process, Nitrogen and hydrogen gases are reacted together.
- State any two conditions necessary for ammonia to be formed in the Haber process. (1mark)
- Temperature of 4500C - 5000C
- Pressure of 200 atmospheres
- Iron catalyst Any 2 correct @ ½ mk each
- Nitrogen and hydrogen must be purified before they are reacted. Give a reason. (1mark)
- Impurities will poison the iron catalyst (1)
- Other than manufacture of fertilizers state one use of ammonia. (1mark)
- Make nitric acid; Refrigerates; softening water; make hydrazine (rocket fuel) Any 1 correct @ 1mk
- State any two conditions necessary for ammonia to be formed in the Haber process. (1mark)
- Describe how you would prepare crystals of potassium sulphate starting with 100cm3 of 0.5M potassium hydroxide. (3marks)
- React the 100cm3 of potassium hydroxide with 50cm3 of 0.5M H2SO4(aq) (or 100ml of 0.25 H2SO4) (1)
- Evaporate/heat ( ½ )the resulting solution to saturation ( ½ ) leave in air the saturated solution to form crystals/cool in air for crystals top form ( ½ ) Dry the crystals by pressing a filter paper on them ( ½ )
- Distinguish between atomic mass and relative atomic mass. (2marks) Atomic mass- refers to the total number of protons and neutrons in an atom of an element (1)
- Relative atomic mass – the average mass of an atom of the element compared with an atom of carbon – 12 (1)
// RAM = Average mass of one atom of an element
1/2 of the mass of one atom of C-12
- Relative atomic mass – the average mass of an atom of the element compared with an atom of carbon – 12 (1)
- Study the diagram below and answer the questions that follow:
- Name one chemical and one physical property of hydrogen being demonstrated in the set-up above.
- Chemical property. (1mark)
- Burns in air/Reacts with air when burnt ( ½ )
- Write a chemical equation for the reaction taking place. (1mark)
- 2H2(g) + O2(g) → 2H2O(g)
- Chemical property. (1mark)
- Name any other substance that can be used in place of concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid. (1mark)
- Anhydrous calcium chloride/calcium oxide lamps (1)
- Give a reason why it is necessary to burn the hydrogen gas as shown in the set-up. (1mark)
- Explodes in air/when mixed with air (1)
- Name one chemical and one physical property of hydrogen being demonstrated in the set-up above.
- The diagram below shows a simple distillation to separate water and ethanol.
- State one of the conditions for the above process to take place. (1mark).
- Two liquids must be miscible √1mk or two liquids must have different boiling points.
- Ethanol collected is 95% pure. Secondary distillation is carried out in which calcium metal is placed in ethanol to react with water. Give a reason why the following cannot be used. (2marks)
- Sodium
- React with both water and ethanol √1mk
- Copper
- Copper cannot react with water √1mk
- Sodium
- State one of the conditions for the above process to take place. (1mark).
- The table below shows tests carried out on a sample of water and the results obtained.
Test Results Addition of sodium hydroxide solution White precipitate which dissolves in excess Addition of excess aqueous ammonia Colourless solution obtained Addition of dilute hydrochloric acid and barium chloride White precipitate - Identify the anion present in the water. (1mark)
- SO42-√1mk
- Write an ionic equation for the reaction in III (1mark)
- Ba2+(aq) + SO42-(aq) → BaSO4(s) √1mk
- Write the formula of the complex ion formed in II (1mark)
- Zn(NH3)4 2+ √1mk
- Identify the anion present in the water. (1mark)
- 1.9g of Magnesium chloride was dissolved in water. Silver nitrate solution was added till excess. Calculate the mass of silver nitrate that was added for complete reaction. (3marks) (MgCl2= 95, N=14, O=16, Ag = 108)|
- In an experiment 40cm3 of 0.5M nitric acid was reacted with excess Sodium Carbonate and the volume of Carbon (IV) Oxide produced recorded with time. In another experiment, the same volume and concentration of ethanoic acid was reacted with excess Sodium Carbonate and the volume of Carbon (IV) Oxide produced recorded with time.
- Why was Sodium Carbonate used in excess? (1marks)
- To ensure all the acid has reacted ✔1
- On the graph below sketch and label the curves of the volumes of Carbon (IV) Oxide produced against time. (2marks)
- Why was Sodium Carbonate used in excess? (1marks)
- The figure below is an energy level diagram for the reaction.
Explain how the following conditions would affect the yield of AB.- Increase in pressure. (2marks)
- The yield of AB √ 1 mk is increased.
- The forward reaction is accompanied by a decrease in volume √ ½ mk. Equilibrium shifts to the right following the forward reaction. √ ½ mk
- Decrease in temperature. (2marks)
- The yield of AB √ 1 mk is increased.
- The forward reaction is exothermic. √ ½ mk
- Decrease in temperature favours the forward reaction, equilibrium shifting to the right. √ ½ mk
- Increase in pressure. (2marks)
- A white solid K was heated. It produced a brown gas A and another gas B which relights a glowing splint. The residue left was yellow even after cooling.
- Identify gases A and B. (2marks)
- A – nitrogen (IV) oxide √ 1 mk / NO2(g)
- B – Oxygen / O2(g)√ 1 mk
- Write a balanced chemical equation for the decomposition of solid K. (1mark)
- 2Pb(NO3)2(s) → 2PbO(s)+ 4NO2(g) √ 1 mk
- Identify gases A and B. (2marks)
- The scheme below shows some reaction sequence starting with solid M.
- Name solid M. (1mark)
- Zinc Metal √ 1 mk
- Write the following of a complex ion present in solution Q. (1mark)
- Zn(NH3)42+ √ 1 mk
- Write an ionic equation of the reaction between barium nitrate and solution N. (1mark)
- Ba2+(aq) + SO42 -(aq) → BaSO4(s) √ 1 mk
- Name solid M. (1mark)
-
- What is meant by a saturated solution? (1mark)
- a solution in which no more solute can be dissolved in the solvent.
- In an experiment to determine the solubility of solid Y in water at 300C the following results were obtained.
Mass of evaporating dish = 26.2g
Mass of evaporating + saturated solution = 42.4g
Mass of evaporating dish + dry solid Y = 30.4g
Using the information, determine the solubility of solid Y at 300C in grams per 100g of water. (2marks)- Mass of solid Y = 30.4 - 26.2g = 4.2g√ ½ mk
Mass of water in the solution = 42.4 – 30.4g = 12g √ ½ mk
12g of water dissolves 4.2g
Thus 100g of water dissolves = 100/12 x 4.2g √ ½ mk
= 35g / 100g H2O √ ½ mk
- Mass of solid Y = 30.4 - 26.2g = 4.2g√ ½ mk
- What is meant by a saturated solution? (1mark)
- Compare the electrical conductivity of dilute Sulphuric (VI) acid and concentrated Sulphuric (VI) acid. Explain your answer. (2marks)
- Dilute sulphuric (VI) acid √ 1 mk has a higher electrical conductivity than concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid.
- Reason;
Dilute sulphuric (VI) acid has more ions in solution than conc. Sulphuric (VI) acid. √ 1 mk
- Draw a well labelled diagram of a setup used to prepare and collect dry Sulphur IV oxide. (3marks)
- The molar heat of formation of carbon (II) oxide is -105kJmol-1, molar heat of combustion of carbon is -393kJmol-1.
By using an energy cycle diagram, determine the molar heat of combustion of carbon (II) oxide. (3marks)- ΔHθf (CO) + ΔHθc(CO)= ΔHθc(C)
-105 + ΔHθc(C) = -393 √ 1 mk
ΔHcθ = -393 - 105 √ 1 mk
= -188KJmol-1√ 1 mk
- ΔHθf (CO) + ΔHθc(CO)= ΔHθc(C)
- In an experiment, a small amount of charcoal was added into a test tube and 5cm3 of concentrated nitric (V) acid added, then warmed.
- State the observation that was made. (1mark)
- Brown fumes √ 1 mk of nitrogen (iv) oxide
- Explain the observation made in (i) above. (1mark)
- Nitric (v) acid is a strong oxidizing agent and thus oxidizes carbon to carbon (iv) oxide √ ½ mk and itself reduced to nitrogen (iv) oxide √ ½ mk
- Write an equation for the reaction that took place. (1mark)
- C(s) +HNO3(l) → 4NO2(g) + CO2(g)+ 2H2O(l) √ 1 mk
- State the observation that was made. (1mark)
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download Chemistry Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Kapsabet Highschool Mock Exams 2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students