SECTION A
Answer all the questions in this section
- The diagram below represents the structure of the earth. Use it to answer question (a).
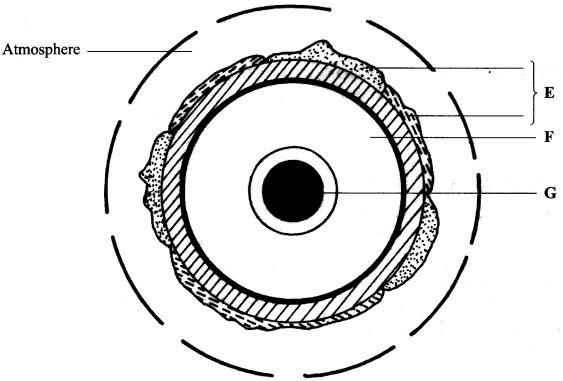
- Name:
- The layers marked E and F. (2 marks)
- The minerals that make up the layer marked G. (2 marks)
- Give two effects of the rotation of the earth on its axis. (2 marks)
- Name:
-
- What is a metamorphic rock? (2marks)
- Give three examples of metamorphic rocks. (3 marks)
-
- Name two types of boundaries according to the plate tectonic theory. (2 marks)
- Give three effects of the movement of tectonic plates. (3 marks)
-
- What is an earthquake? (2 marks)
- Identify the scale used to measure:
- Intensity of earthquakes; (1 mark)
- The magnitude of earthquakes. (1 mark)
-
- Give three characteristics of a river in its middle stage. (3 marks)
The diagram below shows a Bird’s foot delta. Use it to answer question (b).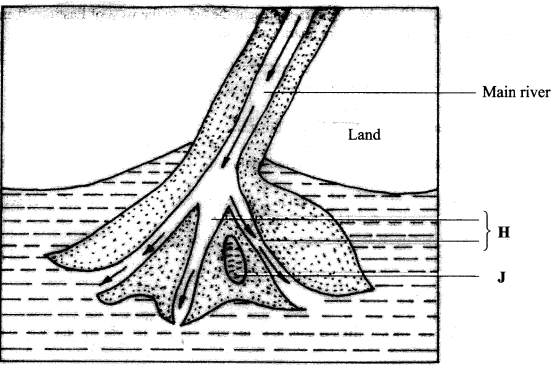
- Identify the features marked H and J. (2 marks)
- Give three characteristics of a river in its middle stage. (3 marks)
Section B
Answer question 6 and any other two questions from this section
- Study the map of Busia 1:50,000 (sheet 101/1) provided and answer the following questions.
-
- Convert the ratio scale of the map extract into statement scale. (2 marks)
- What is the general direction of the flow of river Sio? (1 mark)
- Identify two dominant types of natural vegetation shown in the area covered by the map. (2 marks)
- Draw a square 10 cm by 10 cm to represent the area to the west of Easting 30 and north of Northing 40. On the square, mark and label:
- an international boundary.
- an air photo principal point;
- river Sio;
- the area above 1200 meters above sea level; (5 marks)
- Describe the relief of the area covered by the map. (5 marks)
-
- Explain how the following factors have influenced the distribution of settlements in the area covered by the map:
- drainage;(2 marks)
- transport.(2 marks)
- Citing evidence from the map, state three functions of Funyula town. (6 marks)
- Explain how the following factors have influenced the distribution of settlements in the area covered by the map:
-
-
-
- Define the term weather. (2 marks)
- Explain how the following factors influence weather.
- Cloud cover; (4 marks)
- Local winds. (4 marks)
The diagram below represents a weather measuring instrument. Use it to answer question (b)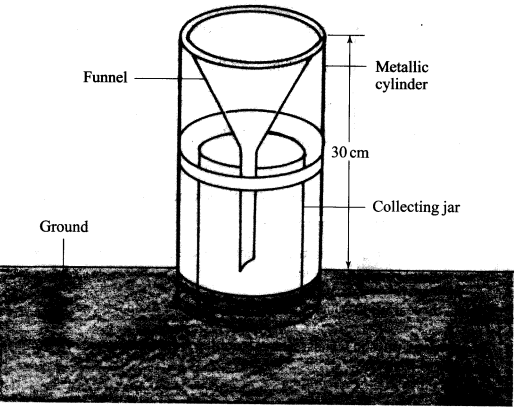
-
- What element of weather is measured using the instrument shown above? (1 mark)
- Describe how the above instrument is used. (3 marks)
The table below shows the temperature and rainfall readings for station T in one week. Use it to answer question (c).
Day Mon Tue Wed Thu Fri Sat Sun Temperature °C 23 23 24 21 25 25 23 Rainfall in mm 50 49 55 45 60 60 49
-
-
Calculate:
-
the range of temperature for the week.(1 mark)
-
the mean weekly rainfall." (2 marks)
-
-
State four characteristics of the weather in station T. (4 marks)
-
- Give four characteristics of the stratosphere. (4 marks)
-
-
-
-
Apart from the Rift Valley, name three other relief features formed as a result of faulting. (3 marks)
-
With the aid of diagrams, describe how the Great Rift Valley may have been formed by tensional forces. (8 marks)
-
-
Explain three ways in which faulting may influence drainage systems. (6 marks)
-
Describe four ways in which features resulting from faulting are of significance to the economy of Kenya.
(8 marks)
-
-
-
-
Apart from alternate wetting and drying, name three other processes of mechanical weathering. (3 marks)
-
Describe the following processes of weathering:
-
alternate wetting and drying; (3 marks)
-
hydrolysis; (2 marks)
- carbonation.(3 marks)
-
-
-
-
State three conditions that influence the process of solifluction in mass wasting.(3 marks)
-
Give three negative effects of mass wasting on the physical environment.(3 marks)
-
-
You are planning to carry out a field study on types of mass wasting.
-
Identify three methods you would use to collect data (3 marks)
- Give three types of rapid mass wasting that you are likely to observe during the field study. (3 marks)
-
State two ways in which the information collected during the field study would be useful to the local community. (2 marks)
-
-
- The diagram below represents an artesian basin. Use it to answer question (a). Rain
- Identify:
- the layers marked X and Y. (2 marks)
- the process marked Z. (1 mark)
- Explain how the following factors influence the amount of underground water in limestone areas:
- rainfall; (4 marks)
- vegetation cover (4 marks)
-
- Apart from stalagmites, name three other underground features formed in limestone areas.(3 marks)
- With the aid of a diagram, describe how a stalagmite is formed. (8 marks)
- Give three reasons why there are few settlements in Karst landscapes. (3 marks)
- Identify:

MARKING SCHEME
SECTION A
- The diagram below represents the structure of the earth. Use it to answer question (a).

- The layer marked:
- E - Lithosphere/crust/sima/sial/hydrosphere/scal
- F - Mantle/Asthenosphere
- The minerals that make up the layer marked G.
Iron and Nickle
- Give two effects of the rotation of the earth on its axis.
- The daily rise and fall of tides.
- The occurrence of day and night.
- A difference of 1 hour between two longitudes 15o apart.
- The deflection of winds/ocean currents.
any 2 x 1 (2 marks)
- The layer marked:
-
- What is a metamorphic rock?
This is a rock formed when the original/igneous sedimentary rock is subjected to chemically active fluids/pressure/intense heat which changes its form/structure/ composition. (2 marks) - Give three examples of metamorphic rocks.
- Schist/homblende/mica;
- Slate;
- Marble;
- Quartzite;
- Gneiss;
- Graphite.
- Serpentnite (from peridolite)
Any 3 x 1 (3 marks)
- What is a metamorphic rock?
-
- Name two types of boundaries according to the Plate Tectonic theory.
- Constructive/extension/divergent boundary.
- Destructive/compressional/ convergent boundary.
- Transform fault/conservative boundary.
Any 2 x 1 (2 marks)
- Give three effects of the movement of tectonic plates.
- Causes folding/related features of folding.
- Occurrence of vulcanicity/features related to vulcanicity.
- Subduction/oceanic trench.
- Occurrence of earthquakes.
- Causes faulting/features related to faulting causes continental drift.
Any 3 x 1 (3 marks)
- Name two types of boundaries according to the Plate Tectonic theory.
-
- What is an earthquake?
It is sudden earth movement that causes vibrations within the earth's crust. (2 marks) - Identify the scales used to measure:
- The intensity of earthquakes - Mercalli scale.
- The magnitude of earthquakes - The Ritcher scale.
- What is an earthquake?
-
- Give three characteristics of a river in its middle stage.
- the river flow is moderate.
- Lateral erosion is dominant.
- The river begins to meander.
- The river has a gentle gradient.
- The river deposits material in the convex banks
- The river has several tributaries.
- The volume of water is high.
- The main features are river bluff/slip off slopes/open V shaped valley.
- Flood plains begin to form.
The diagram below shows a Bird's Foot delta.
- Identify the features marked H and J.
H - distributaries
J - Lagoon
- Give three characteristics of a river in its middle stage.
SECTION B
Answer question 6 and any other TWO questions from this section.
- Study the map of Busia 1:50,000 (sheet 101/1) provided and answer the following questions.
-
- Convert the ratio scale of the map extract.into a statement scale. 1 cm on the map represents 5 km/0.5 km on the ground.
- What is the general direction of flow of river Sio? North East to South West.
- Identify the two dominant types of natural vegetation shown in the area covered by the map. (2 marks)
- Scrub;
- Papyrus swamp/vegetation;
- Scattered trees;
- Thicket;
- Three swamp vegetation;
- Riverine trees;
- Woodlands
Any 2 x 1 (2 marks)
- Draw a square 10 cm by 10 cm to represent the area west of Easting 30 and north of Northing 40. On the square mark and label:
- An International boundary.
- An air Phot Principal Point.
- River Sio.
- The area above 1200 metres sea level.
- Correct drawing.
Diagram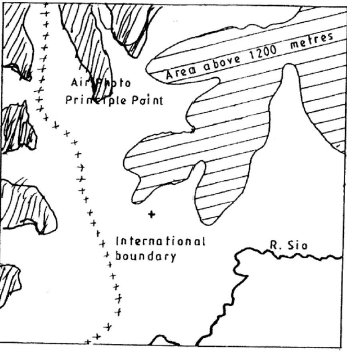
- Describe the relief of the area covered by the map. (5 marks)
- The northern part of the area covered by the map is low lying, broad, flood plain.
- The land lies between 1160 metres and 1568 metres above sea level.
- The area towards the south western part is hilly/has numerous conical hills.
- The south western area has an elongated ridge.
- The area towards the east/west/North is gently sloping.
- There are several river valleys.
- There are steep slopes in the south western part of this area covered by the map.
- There are several passes/saddles/cors
Any 5x1 (5 marks)
-
- Explain how the following factors have influenced the distribution of settlements in the area covered by the map.
Drainage- Areas that are well-drained have many/nucleated settlements.
- Areas that are poorly drained/swampy have few/no settlements.
- There are no settlements near most rivers because they may be prone to flooding.
Any 1x2 (2 marks)
Transport - Along the roads/motorable tracks there are linear settlements.
- At road junctions, there ar nucleated settlements.
Any 1 x 2 (2 marks)
- Citing evidence from the map, state three functions of Funyula town. (6 marks)
Function
it is a residential centre
it is an administrative centre
it is a transport centre
it is a recreation centre
it is a commercial/trading centre
Evidence
huts/built up areas
Chief's camp/chief's house, Police post
All weather/loose surface road/motorable tracks
Rest house
Market
Any 3 x 2(6 marks)
- Explain how the following factors have influenced the distribution of settlements in the area covered by the map.
-
-
-
- Define the term weather. (2 marks)
Weather is the daily atmospheric conditions of a place at particular time. - Explain how the following factors influence weather.
Cloud cover:- Thick cloud cover reduces the amout of solar radiation reaching the earth surface thus decreasing the atmospheric temperature.
- Absence of cloud cover leads to an increase in diurnal range of temperature.
- Thick cloud cover blocks terestial radiation from leaving the earth surface lower atmosphere thereby increasing the atmospheric temperature.
- The type of cloud determines type/amount of rainfall.
- The amount of cloud cover determines the intensity of sunshine received on the earth surface.
- Shape/height/movement of clouds determines the type of weather that is likely to occur.
Any 2 x 2 (4 marks)
Local winds: - Warm winds blowing over an area bring the warming effect thereby raising the temperature of the place
- Cold winds blowing over an area bring the cooling effect hence lowering the temperature of the place.
- Moist winds passing over a region drop moisture as precipitation/increase humidity.
- Dry winds passing over a region bring a drying effect/aridity/lower humidity.
Any 2 x 2 (4 marks)
The diagram below represents a weather measuring instrument. Use it to answer question (b).
- Define the term weather. (2 marks)
-
- Which element of weather is measured using the instrument shown?
Rainfall. (1 mark) - Describe how the above instrument is used.
- The instrument is placed in an open area and rain water collects in the jar.
- The metal collecting jar is removed from the metal holder.
- The water is poured into a measuring/graduated cylinder.
- The reading is taken/recorded.
- The water is emptied and the instrument is placed outside to collect more water for measuring the following day.
Any 3 x 1 (3 marks)
The table below shows the temperature and rainfall readings for station T in one week. Use it to answer question (C).
Day Mon Tue Wed Thu Fri Sat Sun Temperature °C 23 23 24 21 25 25 23 Rainfall in mm 50 49 55 45 60 60 49
- Which element of weather is measured using the instrument shown?
-
- Calculate:
- The range of temperature for the week.
25° C - 21° C = 4°C (1 mark) - The Mean weekly rainfall. (2 marks)
50 +49 +55 + 45 +60 +60 + 49
7
368 = 52.57 mm
7
= 52.6 mm (2 marks)
- The range of temperature for the week.
- State four characteristics of the weather in station T.
- The lowest temperature of the station is 21° C.
- The highest temperature of the station is 25° C.
- The Mean weekly temperature of the station is 23.4° C./moderate
- The highest amount of rainfall for the station is 60 mm/Friday/Saturday.
- The lowest amount of rainfall for the station is 45 mm/Thursday.
- There is rainfall throughout the week.
- There is low weekly temperature range /4° C.
- It is hot and wet throughout the week.
- There is high rainfall /368 mm.
Any 4 x 1 (4 marks)
- Calculate:
- Give four characteristics of the stratosphere.
- It extends from 15 - 50 km (equator) and (8 - 50 km) at the poles.
- The lower part of it has constant temperature/is othermal layer.
- It has little/no water vapour.
- Temperature increase with increase in height at the upper layer/negative lapse rate/ temperature inversion.
- Temperature ranges from 80°C -0°C
- It is mainly composed of O-zone gas.
-
-
-
- Apart from the Rift Valley, name three other relief features formed as a result of faulting.
- Escarpments/scarp slopes.
- Tilt blocks.
- Fault steps.
- Block mountains/horst/fault block.
Any 3 x 1 (3 marks)
- With aid of diagrams, describe how the great Rift Valley may have been formed by tensional forces.
Layers of rocks are subjected to tensional forces when there is some instability within the earth's crust.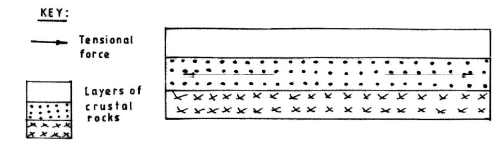
Parallel normal faults/parallel lines of weakness develop.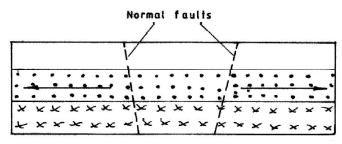
With time, the middle part sinks/subside as the side blocks are pulled apart.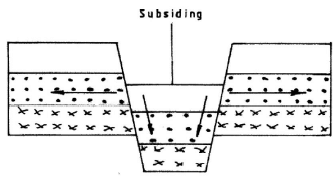
The sunken middle part forms a depression/trough known as the Rift Valley.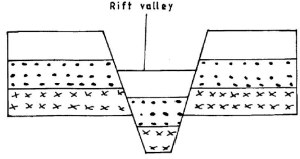
Diagram 4x1 (4 marks)
Text 4x1 (4 marks)
- Apart from the Rift Valley, name three other relief features formed as a result of faulting.
- Explain three ways in which faulting may influence drainage systems.
- Uplifting of landscape which leads to faulting may cause rivers to reverse their direction of flow/ back tilting.
- Vertical faulting across a river may cause a change in the local base level resulting in the formation of a waterfall.
- Basins/depressions resulting from faulting may be filled with water to form lakes/inland drainage basins.
- Some rivers flow along fault lines forming fault guided drainage patterns.
- Some rivers may disappear into the ground through a fault forming underground streams.
- Uplift of some river channels may cause river rejuvenation.
- Faulting may expose underground water leading to formation of springs.
Any 3 x 2 (6 marks)
- Describe four ways in which features resulting from faulting are of significance to the economy of Kenya.
- Highlands /fault blocks formed through faulting are sources of rivers which provide water for agricultural/domestic/industrial use.
- Faulting leads to formation of features that form beautiful scenery which promote tourism.
- Faulting leads to the formation of lakes that are important fishing grounds/mining sites / irrigation.
- Faulting has led to exposure of minerals that are mined to generate income.
- The highlands formed through faulting influence the formation of relief rainfall on the windward side which favours agriculture/forestry/ settlement.
- Formation of faults scarps creates deep faults which are passages of steam jets that are harnessed to generate geothermal power.
- Fault scarps lead to the formation of natural waterfalls which are suitable sites for HEP production.
Any 4 x 2 (8 marks)
-
-
-
- Apart from alternate wetting and drying, name three other processes of mechanical weathering.
- Exfoliation/onion peeling/spalling
- Block disintegration/block separation
- Pressure release
- Granular disintegration
- Frost action
- Crystal growth
Any 3 x 1 (3 marks)
- Describe the following processes of weathering:
Alternate wetting and drying- During the wet season surface rocks such as clay/shale absorb water causing them to swell.
- During the dry season these rocks dry out causing the outer surface to shrink.
- Repeated wetting and drying weakens the rocks leading to cracking/ slaking.
- These rocks break away from the main rock.
Any 3 x 1 (3 marks)
Hydrolysis - This is a process in which hydrogen ions/hydroxyl ions in water react with mineral ions in a rock.
- This reaction leads to formation of new chemical compounds in the rocks.
- With alteration of the original minerals, the rock becomes weak and disintegrates/decays.
Any 2 x 1 (2 marks)
Carbonation - It involves rain water dissolving carbon 4 oxide in the atmosphere forming a weak carbonic acid.
- The carbonic acid reacts with calcium carbonate in rocks to form calcium bicarbonate solution.
- Calcium bicarbonate solution is removed by running water.
- This leads to the weakening/disintegration of the rock.
Any 3 x 1 (3 marks)
- Apart from alternate wetting and drying, name three other processes of mechanical weathering.
-
- State three conditions that influence the process of solifluction in mass wasting.
- The presence of a gentle slope.
- The occurrence of alternating warm and cold season.
- Presence of a permafrost layer/frozen ground/bedrock.
- Unconsolidated saturated weathered materials/debris.
Any 3 x 1 (3 marks)
- Give three negative effects of mass wasting on the physical environment.
- Destruction of vegetation.
- Blockage of rivers/disruption of flow of rivers.
- Exposure of land to agents of soil erosion.
- Loss of life/property.
- Results in the formation of scars on the land/derelict land.
Any 3 x 1 (3 marks)
- State three conditions that influence the process of solifluction in mass wasting.
- You are planning to carry out a field study on types of mass wasting.
- Identify three methods you would use to collect data.
- Observation
- Photographing/video recording
- Interviewing
- Content analysis
Any 3 x 1 (3 marks)
- Give three types of rapid mass wasting you are likely to observe during the field study.
- Mudflow
- Landslide/slump/debris slide/rock slide/rockfall/avalance
- Earthflow
Any 3 x 1 (3 marks)
- State two ways in which the information collected during the field study would be useful to the local community. (2 marks)
- It would be used to plan for precautions/safety
- It would be used in the conservation of land.
- It would be used as a basis for further research.
Any 2 x 1 (2 marks)
- Identify three methods you would use to collect data.
-
- The diagram below represents an artesian basin. Use it to answer question (a).
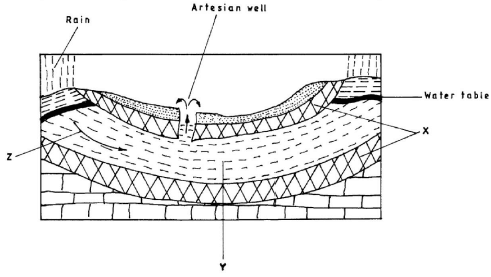
- Identify:
- the features marked x and y.
x - Impermeable rocks (1 mark)
y - Aquifer (1 mark) - the process marked z.
z - Percolation (1 mark)
- the features marked x and y.
- Explain how the following factors influence the amount of underground water in limestone areas.
- Rainfall
- When rains last for long hours it enhances infiltration thereby replenishing the underground water sources.
- Heavy rains saturate the surface blocking air spaces thus reducing the rate of infiltration/leading to low amount of underground water.
- Little rainfall/no rainfall leads to low amount of under ground water.
Any 2 x 2 (4 marks)
- Vegetation cover
- Presence of vegetation cover reduces the speed of surface runoff hence increasing the rate of infiltration/leading to high amount of underground water.
- Presence of vegetation cover breaks the force of raindrops giving water more time to infiltrate hence increasing the amount of underground water.
- In areas of scanty vegetation/on bare ground the surface runoff is high hence reduce rate of infiltration/leading to low amount of underground water.
- Presence of vegetation cover provide shade in the ground reducing direct loss of water through evaporation hence increasing the rate of infiltration leading to high amount of underground water.
Any 2 x 2 marks (4 marks)
- Rainfall
-
- Apart from stalagmites name three other underground features formed in limestone areas.
- Stalactites
- Limestone/pillars/columns
- Caves/caverns
- Underground rivers
Any 3 x 1 (3 marks)
- With aid of a diagram, describe how a stalagmite is formed.
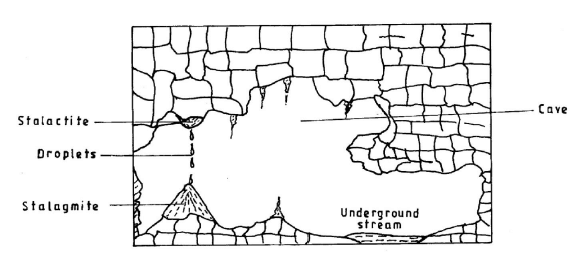
- A solution of calcium hydrogen carbonate drips down slowly through the roof of the cave/hang on the roof of the cave.
- As the solution continues to drip from the roof, it splashes on the floor of the cave.
- Water evaporates and the calcium carbonate precipitates.
- The precipitated calcium carbonate gradually builds upwards to form a Stalagmite.
Diagram (5 marks)
Text(5 marks)
- Apart from stalagmites name three other underground features formed in limestone areas.
- Give three reasons why there are few settlements in Karst landscapes.
- The areas have thin/poor soils.
- The areas are rocky/have rugged surfaces
- There is inadequate surface water supply.
- The areas have poor/scanty vegetation.
Any 3 x 1 (3 marks) - Describe how the above instrument is used. (3 marks)
- Identify:
Download KCSE 2015 Geography Paper 1 with Marking Scheme.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students