QUESTIONS
-
- Define the term fuels (1mk)
- State two reasons why hydrazine is used as rocket propellant (2mks)
- Hydrogen can be placed in group VII and group I of the periodic table respectively. Use equations to explain (3mks)
- Study the set-up below and answer the questions that follow:-
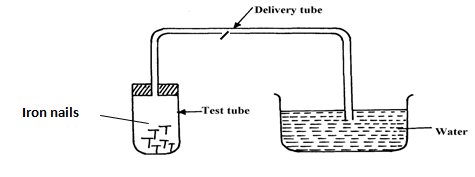
- Name the process being investigated (1mk)
- State two observations that would be made after one week. Explain (2mks)
-
- Apart from water softening list two other uses of sodium carbonate (2mks)
- Using an ionic equation show how sodium carbonate is used to soften hard water (1mks)
- A form four student from Orawa secondary school found a white solid in a beaker that had two labels of zinc sulphate and aluminium sulphate respectively. Briefly explain how the student would test whether it was a compound of zinc or aluminium (3mks)
- The set-up below was used to prepare a carbon (II) oxide gas.
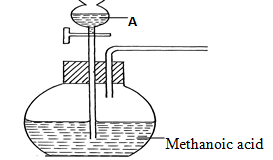
- Give the name of substance A ……………………………………………….(1⁄2mk)
- Complete the diagram to show how the gas can be collected (11⁄2mks)
- Write the equation for the reaction (1mk)
- A certain gas A was passed over a hot black metal oxide B, a brown solid was formed and a colorless liquid C that boiled at 105 oC, the liquid also changed a blue anhydrous cobalt (II) chloride paper to pink.
- Name
- Gas A…………………………………………………………………………………..(1⁄2mk)
- Metal oxide B…………………………………………………………………………..(1⁄2mk)
- Colourless liquid C………………………………………………………………………(1⁄2mk)
- State and explain a reason why the colourless liquid C boiled at 105oC (1mk)
- Name
- The following elements belong to the same group of the periodic table. (Letters do not represent the actual symbols)
Element Atomic radius (nm) Ionic radius (nm) First ionization Energy (KJ mol-1) A 0.136 0.065 736 B 0.089 0.031 900 C 0.174 0.099 590 - Are the elements metals or non-metals? Explain (2mks)
- Which of the elements is the most reactive? (1mk)
- Zinc reacts with HCl according to the equation below.
Zn(s) + 2HCl(aq) → ZnCl2(aq) + H2(g)
Complete the table to show how the factors given affect the rate of reaction above and give explanation (2 mks)
Factors Effect on rate Explanation Using Zinc powder instead of granules Heat the reactants - Which allotrope of sulphur:
- Is stable at room temperature ………………………………………………………..(1mk)
- Has prismatic crystals ……………………………………………………………….(1mk)
- Has higher density ………………………………………………………………..…(1mk)
- A certain flower was suspected to contain red and yellow pigments. Describe how the pigments could be separated (3mks)
- A certain element has two isotopes with atomic mass 6 and 7 respectively. Given that the relative atomic mass is 6.94. Calculate the relative abundance of each isotope (2mks)
- The set up below was used to collect gas K, produced by the reaction between water and calcium metal.
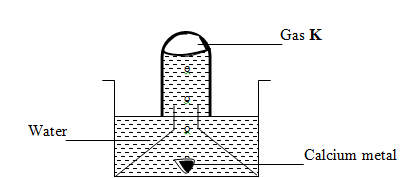
- State two observations made during the experiment (2mks)
- Write an equation for the reaction taking place. (1mk)
- State the properties of concentrated sulphuric (vi) acid demonstrated in the following reactions
- Reacts with sodium chloride to form hydrogen chloride gas (1mk)
- Reacts with copper metal to form sulphur (iv) oxide (1mk)
- 1.0g sample of limestone was allowed to react with 100cm3 of 0.2M hydrochloric acid. The excess acid required 24.8cm3 of 0.1M sodium hydroxide solution for complete neutralisation. Calculate the percentage of calcium carbonate in the limestone (3mks)
- In an experiment, dry chlorine gas was reacted with aluminium as shown in the diagram below
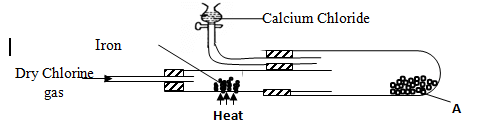
- State two properties of substance A (2mk)
- Write an equation for the reaction that took place in the combustion tube (1mk)
- State one use each of the following apparatus in the laboratory (3mks)
- Desiccator
- Crucible
- Deflagrating spoon
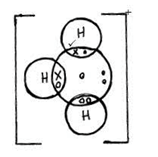
- Using dots and crosses to represent electrons draw diagrams to represent bonding in (2mks)
H3O+(H=1,O=8) - Carbon powder and copper (ii) oxide are both black in colour. Suggest two reactions that can be used to differentiate them and state the observation in each case. (3mks)
- Starting with sodium metal explain how sodium hydrogen carbonate crystals can be prepared (3mks)
-
- Define the term simple acid base-indicator (1mk)
- State two disadvantages of using simple acid-base indicators (2mks)
- State two applications of complex ions in industries (2mks)
- What do the following abbreviations stand for? (2mks)
IUPAC…………
DDT………… -
- Differentiate between nuclear fission from nuclear fusion (2mks)
- A radioactive cobalt (6128Co) undergoes decay by emitting a beta particle and forming Nickel atom. Write a balanced decay equation for the above change (1mk)
- The following are heats of combustion of carbon, hydrogen and ethanol the following substances calculate the heat of formation of ethanol
C(s) + O2 (g) → CO2 (g); ΔH = -393KJmol-1
H2 (g) + ½ O2(g) → H2O(l);ΔH = -286KJmol-1
CH3CH2OH(l) + O2 (g) → 2CO2 (g) + 3H2O (l) ;ΔH = 1386KJmol-1- Draw an energy cycle diagram to represent the heat of formation of ethanol (1mk)
- Calculate the heat of formation of ethanol (2mks)
- The diagram below shows an electrochemical cell:
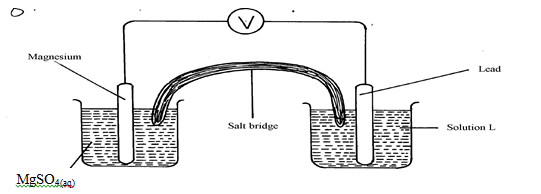
- Give the formula of the possible salt L (1mk)
- On the diagram show the direction of movement of electrons (1mk)
- Write the cell representation (1mk)
-
- State the Graham’s law (1mk)
- 100cm3 of Carbon (IV) oxide gas diffused through a porous partition in 30seconds. How long would it take 150cm3 of Nitrogen (IV) oxide to diffuse through the same partition under the same conditions? (C = 12.0, N = 14.0, O = 16.0) (2mks)
- A compound Q was oxidised by acidified potassium dichromate (vi) to form substance Z. Substance Z reacts with Q to form a pleasantly smelling compound ethylethanoate.
- Name substance Q and Z (1mk)
- Write an equation for the reaction between
- Substance Q and potassium metal (1mk)
- Substance Z and sodium carbonate (1mk)
- State two distinctive features of a dynamic equilibrium. (2mks)
- Explain the effect of increase in pressure on the following equilibrium (1mk)
N2(g) + O2(g) ===== 2NO(g)
- Explain the effect of increase in pressure on the following equilibrium (1mk)

MARKING SCHEME
-
- substance that produces useful energy when it undergoes a chemical or nuclear reaction. 1MK
-
- It burns very rapidly producing large amounts of gases which in turn create a huge thrust as they escape.
- It has a very high heat of combustion (4740 kJ mol–1).
- It ignites easily.
ANY 1MK
- foms positive ions like group I elements½MK
H(g) → H+ (g) + e- 1MK
From negative ions like group VII elements½MK
H(g) + e- → H-(g) 1MK -
- Rusting
- Iron nails CHANGES brown./ RUSTS
Water rises up the delivery tube/water level drops in the trough
-
-
- manufacture of glass, soaps and detergents
- in paper and textile industries(accept any)
- Ca2+(aq) + CO32-(aq) → CaCO3(s)
Mg2+(aq) + CO32–(aq) →CaCO3(s)
-
- Add water to the solid in a boiling tube and divide the solution into two (1mk)
add ammonia solution to the two prepared solutions, until in excess (1mk)
A white ppt that ½MK dissolves in excess shows the presence of Zinc ions while a white ppt that doesn’t dissolve shows the presence of aluminium ½MK ions. -
- Concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid
- Collection over water
drawing and workability
labelling - HCOOH(s) → CO(g) + H2O(g)
-
-
- hydrogen
- copper(ii) oxide
- water
- it is impure and impurities raise the boiling point
-
-
- Metals, the ionic is smaller than the atomic radius
- C
Factors Effect on rate Explanation Using Zinc powder instead of granules increases Powdered zinc offers a large surface area. Heat the reactants increases increases particles collide more -
- Rhombic
- monoclinic
- Rhombic
-
- Place some flowers in the mortar and crush using the pestle while adding propanone a little at time.Decant the extract in a clean beaker
- Place a drop of the extract at the centre of the filter paper and allow it to spread as far as possible.
- Add a drop of propanone at the centre of the filter paper of the filter paper and allow it to spread as far as possible. A chromatogram showing red and yellow colours is seen.
- (6xQ+7xW)=6.94
100
Q+W=100
Elimination
6Q +7W =694
6Q + 6W= 600
W=94%
Q= 6% -
- effervesence/stream of bubbles
- White suspension/ precipitate is formed
Ca(s) + H2O (l) → Ca(OH)2 (aq) + H2(g)
-
- Less volatile,can displace more volatile acids from their salts
- Oxidising agent
- Moles of NaOH that reacted
0.1------------1000
?---------------24.8
= 0.00248moles½MK
Moles of the acid that reacted with the base
NaOH : HCl
1 : 1
0.00248: 0.00248 moles½MK
Moles of the acid in 100cm3
0.2-----------------1000cm3
………………….100cm3 =0.02moles½MK
Moles of the acid that reacted with the carbonate
0.02 moles- 0.00248moles =0.01752moles½MK
Moles of the carbonate that reacted with the acid
CaCO3 : HCl
1 : 2
? : 0.01752
= 0.00876moles½MK
Mass of the carbonate that reacted
Moles x molar mass
0.00876 x 100 = 0.876 g½MK
Percentage of calcium carbonate in limestone
0.876/1 x 100 = 87.6%½MK -
- sublimes on heating
It is deliquescent orange brown, soluble in water - Fe(s) + Cl2(g) FeCl3(s)
- sublimes on heating
-
- Keep substances free from moisture
- Heat substances that require strong heating
- Holding substances being heated
-
-
- Burn in a non-luminous flame, carbon burns in a yellow flame, copper (ii) oxide burns in a green flame
- Add dilute sulphuric (vi) acid, copper (ii) oxide dissolves to form a blue solution while carbon doesn’t dissolve.
- Heat strongly in a boiling tube, carbon forms a colourless gas that forms a white ppt with while lime water copper(ii) oxide doesn’t.
- add copper (ii) oxide to each of them and heat strongly, carbon forms a brown substance while copper(ii0 oxide doesn’t.
-
- Add sodium metal into distilled water, to form sodium hydroxide
- Bubble carbon (iv) oxide gas through sodium hydroxide solution for a long period of time to form sodium hydrogen carbonate.
- Evaporate sodium hydrogen carbonate solution to saturate then cool to crystallize
-
- They are plant extracts that show different colours in acid and base
- Do not have a long shelf life
Do not show consistent results
- used water softening
Extraction of some metals - IUPAC: International union of pure and applied chemistry
DDT: Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane -
- Fission: splitting of a heavy nuclide when bombarded with a fast moving neutron
Fusion: small nuclei combine together when made to collide at high velocity (Both correct) -
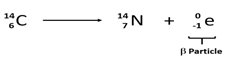
- Fission: splitting of a heavy nuclide when bombarded with a fast moving neutron
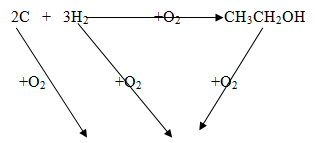
-1674+ 1386 = -290kJ/mol
2 CO2 + 3H2O-
- Pb(NO3)2
-
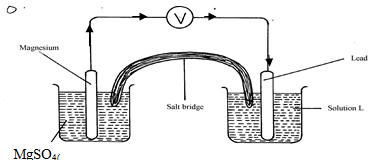
- Mg(s)/Mg2+(aq)//Pb2+(aq)/Pb(s)
-
- At constant temperature and pressure the rate of diffusion of a gas is inversely proportional to the square root of its density.
- 100cm3--------------30sec
150cm3--------------? =45 sec
Ta/Tb = √Da/Db
T2= 2025 x 46/44 = 46.01 sec
-
- Q-Ethanol
Z- Ethanoic acid - 2CH3CH2OH(l) + 2K(s) →2CH3CH2OK(l) + H2(g)
CH3COOH(aq) + Na2CO3(s) → CH3COONa(aq) + CO2(g) + H2O(l)
- Q-Ethanol
-
- The rate of forward reaction is equal to the rate of backward reaction
at equilibrium the concentration of the reactants and products do not change - pressure will have no effect on the equilibrium because, number of molecule on the reactant and products side are equal.
- The rate of forward reaction is equal to the rate of backward reaction
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download Chemistry Paper 1 Questions and Answers - MECS Cluster Joint Mock Examinations 2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students
