- Question six is compulsory.
- Choose either question 7 or 8
SECTION A
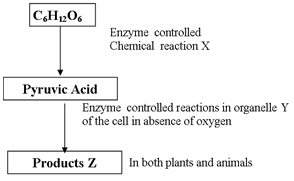
- Study the flow chart below of a process that takes place in both plants and animals.
- Name the above process. (1mk)
-
- In the above process name the chemical reaction represented by X. (1mark)
- Name the part of the cell where the enzyme controlled reactions in b(i) above takes place. (1mark)
- Name the products Z in
- Plants…………………………………………. (1mark)
- Animals…………………………………………………………. (1mark)
- What would be the fate of pyruvic acid if oxygen supply is availed in the mitochondria of an animal cell (2marks)
- Define the term oxygen debt (1mark)
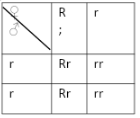
- In a certain bird species red flight feathers is controlled by gene R while white flight feather is controlled by gene r. The heterozygous condition Rr results into pink flight feathers.
- Using a punnet square, find the genotype of a cross between pink flight feathered bird and white flight feathered bird. (4 marks)
- Which type of dominance is illustrated here? (1 mark)
-
- Identify the nuclei acid whose base sequence is shown below. (1 mark)
G - A - C - U - A - G - C - G - U - Give a reason for your answer in (i) above (1 mark)
- If this nucleic acid was involved in protein synthesis, how many amino acid would be present in the protein synthesized. (1 mark)
- Identify the nuclei acid whose base sequence is shown below. (1 mark)
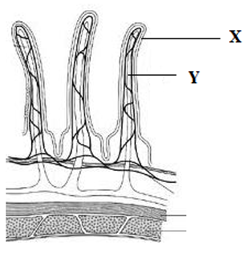
- The diagram below represents a longitudinal section through the ileum wall.
- Identify the structures labeled X and Y (2 marks)
- State one function of X and Y (2 marks)
- State two functions of the ileum (2 marks)
- Explain the role of the liver in digestion (1 mark)
- State the endocrine (hormonal) role of pancreas in a mammal (1 mark)
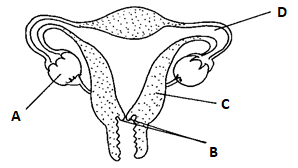
- The diagram below represents the female reproductive system.
- Name the structures labeled A and C (2 marks)
- State the conditions that results if implantation occurs at point labeled D. (1 marks)
- Name the hormone secreted by the part labeled A and for each give one function (4 marks)
- What role does part labeled B play during pregnancy? (1 mark)
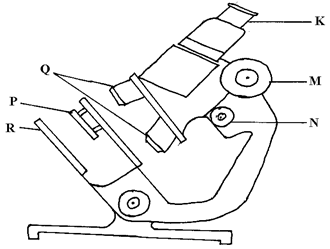
- The diagram below shows some components of a light microscope.
- Name the parts labeled (2 marks)
K ………………………………………………………………………………………………
M ……………………………………………………………………………………………… - State the functions of (2 marks)
P ………………………………………………………………………………………………
Q ……………………………………………………………………………………………… - A student was viewing a prepared slide of a plant cell under high power microscope. The features of the cell were blurred. Which one of the labeled parts of the microscope would the student use to obtain:-
- A sharper outline of the features. (1 mark)
- Give the formula used to calculate magnification in a light microscope. (1 mark)
- A student was preparing a section of a plant cell to be viewed on a light microscope. Give a reason for each of the following steps:-
- Cutting a very thin section……………………………………………...... (1 mark)
- Staining the section……………………………………………………………...... (1 mark)
- Putting the section in water…………………………………………………………………. (1 mark)
- Name the parts labeled (2 marks)
SECTION B
Answer question 6 (compulsory) and either question 7 or 8 in the spaces provided after question
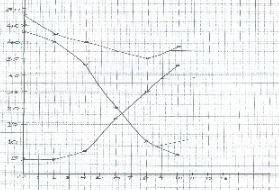
- During germination and growth of a cereal, the dry weight of the endosperm, the embryo and total dry weight were determined at two day intervals. The results are shown in the table below.
Time after planting (Days) Dry weight of endosperm (mg) Dry weight of embryo (mg) Total dry weight (mg) 0 43 2 45 2 40 2 42 4 33 7 40 6 20 17 37 8 10 25 35 10 6 33 39 - On the same axes, draw graphs of dry weight of endosperm, embryo and the total dry weight against time. (7marks)
- What was the total dry weight on day 5? ………………………………………… (1mark)
- Account for:
- Decrease in dry weight of endosperm from day 0 to day 10. (2marks)
- Increase in dry weight of embryo from day 0 to day 10. (2marks)
- Decrease in total dry weight from day 0 to day 8. (1mark)
- Increase in dry weight after day 8. (1mark)
- State two factors within the seed and two outside the seed that cause dormancy.
- Factors within the seed…………………………………………………………….. (2marks)
- Factors outside the seed. …………………………......................................(2marks)
- Give two characteristics of meristematic cells………………………(2marks)
- Describe how the mammalian skin is adapted to its functions (20 mrks)
-
- Describe how xerophytes are adapted to living in their habitat. (10 mks)
- Explain how an upright position is maintained in herbaceous plants. (10 mks)
MARKING SCHEME
SECTION A
-
- anaerobic;
-
- Glycolysis;
- Cytoplasm;
-
- Alcohol/ ethanol, carbon IV oxide and energy;
(Rej.. if only one product is given) + Energy - Lactic acid, energy
- Alcohol/ ethanol, carbon IV oxide and energy;
- Pyruvic acid will be further oxidized by oxygen (in a series of enzymatic reactions/Krebs cycle) into carbon IV oxide, water and energy;
(reject if all products are not mentioned) - The amount of oxygen required to get rid of the lactic acid that accumulates in the body tissues when supply of oxygen is less than demand;
-
- phenotype pink white
Genotype Rr X rr ;
Gametes
Offspring - Incomplete;
-
- Ribonucleic acid; Rej. RNA
- Has uracil base
- Three (3);
Reason – Has three codons.
- phenotype pink white
-
-
- X – Villas
- Y – Lacteal
-
- X – Increase surface area for absorption;
- Y – Absorption of fatty acids and glycerol;
-
- Digestion;
- Absorption of end products of digestion;
- Produce bile juice which contain bile salts for emulsification of fat/bile salts provide Alkaline medium suitable for enzymes present in pancreatic juice;
- Produce hormones insulin and glycogen;
Rej. if one hormone is mentioned
-
-
-
- A - ovary;
- C - uterine wall;
- Ectopic pregnancy;
-
- Oestrogen
- Repair and healing of endometrium, stimulate pituitary to secrete LH.
- Progesterone
- Proliferation/thickening of endometrium.
- together with oestrogen inhibits production of FSH.
- inhibits production LH
- Oestrogen
- Secrete a thick plug of mucus which prevent entry of air and micro organisms;
-
-
- K- eye piece; M-coarse adjustment knob;
- P-concentrate the light/focuses the light;
Q- magnification of the image; Rej object/specimen for image -
- N ; rej. named part
- Eyepiece magnification X objective lens magnification ; Rej. Length of the drawing
length of the actual
-
- to allow light to pass through ;
- To make the features more clear and distinct; Rej. Without distinct
- For cells to remain turgid/ prevent dehydration;
SECTION B
-
-
- 38.5mg; ±0.5 Rej wrong units , Acc without units
-
- Hydrolysis of starch into simple sugar/glucose; which is translocated to the embryo; oxidation (of simple sugars) respiration to carbon (iv) oxide/energy/Heat
- New cells materials/tissue are synthesized (from proteins); bringing about growth of embryo;
- First leaf carried out photosynthesis (Leading to growth)
-
-
- presence of absiscic acid; Acc presence of germination inhibitors.
- Embryo not fully developed;
- Absence of hormones/enzymes that stimulate germination; impermeable seed coat; (Any two)
-
- Unsuitable temperature/lack of suitable temp/ unfavourable temperature;
- lack of water;
- Absence of light;
- Lack of Oxygen; any 2
-
-
- Dense cytoplasm;
- Thin cell wall
- Absence of vacuoles
-
- Describe the structure and function of the mammalian skin (20marks)
It has a cornified layer made up of dead cells and is tough and impermeable to water; to protect the skin against mechanical damage; bacterial infections and water loss; granular layer; whose cells divide to form the cornified layer; malpighian layer; which is made up of diving cells that give rise to a new granular layer; contains melanin; to protect skin against ultra-violet rays/radiations; Sebaceous glands; which secrete sebum; to make the skin supple/soft and waterproof; sebum is also antiseptic; Blood vessels; dilate during hot weather; increasing blood flow near the skin surface; heat loss is enhanced; constrict; in cold weather; less blood flow; minimize heat loss; Sensory nerve endings and receptors; enable detection of external environmental changes; Highly coiled sweat glands; secrete sweat; to control body temperature; when hot sweat evaporates cooling the body; sweat contains excretory products; subcutaneous fat/adipose tissue in dermis; for insulation; hair; to regulate body temperature; in cold weather erector pili muscles contract; hair is raised, air trapped to insulate the body; in hot weather, erector pili muscles relax; hair lies flat reducing insulation; dense network of blood capillaries; supply nutrients/oxygen to skin tissues; as well as carrying away wastes and carbon (IV) oxide away from the skin tissues; adipose tissue/sub-cutaneous layer; serves as an insulator; helping in temperature control; helps in manufacture of vitamin D;
Max. 20 mks -
-
- Have thick, fleshy (succulent) and green stems; that are modified for water storage and photosynthesis; stomata are reduced in number/located in cavities on the epidermis(sunken stomata) / located mainly on lower part of leaf surface/Exhibit reversed stomata rhythm to minimize transpiration;
- Some are deep rooted; to enable them reach deep water table; others have superficial roots; to absorb surface water after a short shower; In some leaves are permanently folded; to prevent direct exposure of stomata to environmental conditions thus minimizing transpiration; Others shed off their leaves at the onset of dry season to minimize transpiration; in some leaves are small in size/reduced in size to scale-like structures to minimize transpiration; (12 max 10)
- Plant cells have a cellulose cell wall; which is rigid; plants absorb water through osmosis and cells become turgid; which makes the tissues firm and erect; Collenchyma cells have thickened cell walls; to give strength; Xylem vessels have thick and lignified walls; that strengthen plants. Tracheids and fibres; in mature plants have dead thick lignified cells; for strength and support. Parenchyma cells are round and tightly packed together; which maintains shape and firmness; of the plants. (11 max 10)
-
Download Biology Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Eagle II Joint 2021 Mock Exams.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students