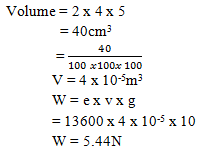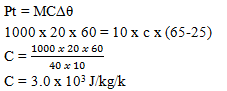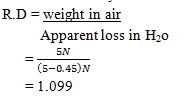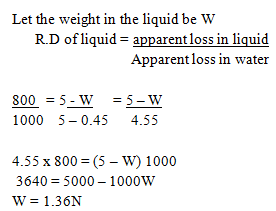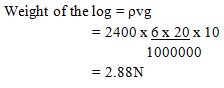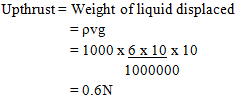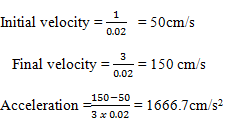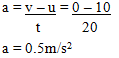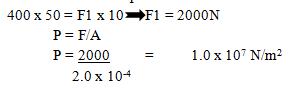SECTION A (25 Marks)
Answer all the questions in this section
- Figure 1(a) below shows a micrometer screw gauge when closed and Figure 1(b) shows the same micrometer screw gauge measuring the thickness of a wire.

Figure 1a and Figure 1b
Determine the thickness of the wire (2mks)- Zero error - 0.08mm
Thickness of the wire = (1.62 – 0.08)mm
= 1.54mm
- Zero error - 0.08mm
- A form two student was provided with two springs to make a spring balances, she sets up two designs as shown below in Figure 2(a) and Figure 2(b)
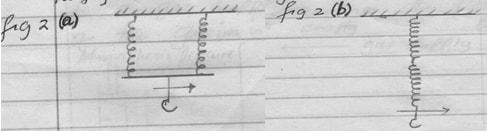
Figure 2a and Figure 2b
With reason(s) state which two designs you would use to measure the weight of a heavy load? (2mks)- Set a. Because the weight is shared by the two springs
- A rectangular container measures 2 cm by 4cm by 5cm. What is the weight of the mercury that will fill the container to the brim? (3mks)
- Figure 3 below shows a U-tube connected to a gas supply. Determine the pressure of the gas in cmHg
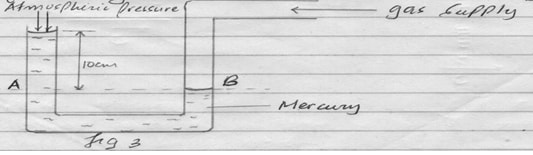
Figure 3- Pressure at A = pressure at B (pressure of the gas)
= (76 + 10) cm Hg
Gas Pressure = 86cm Hg
- Pressure at A = pressure at B (pressure of the gas)
- Three iron sheets meant for construction in hot regions have oval- shaped holes. Bolts are used to fix them on the roof through the oval holes. Explain the importance of the shape of the holes. (1mk)
- They provide room for expansion and contraction
- Figure 4 below shows paper kite
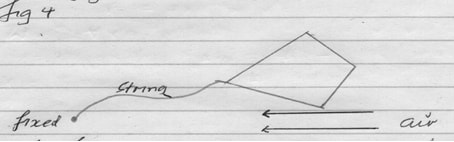
Figure 4
Fast moving air is blown horizontally under the kite as shown in the diagram. State and explain the observation made. (2mks)- When the air is blown, the kite moves downwards. This is because a region of low pressure is created below the kite due to fast moving air and excess atmospheric pressure above the kite processes it downwards
- Figure 5 below shows a light rod balanced by the forces shown. M is a magnet of weight 5N and P is a permanent magnet fixed on the bench. (2mks)
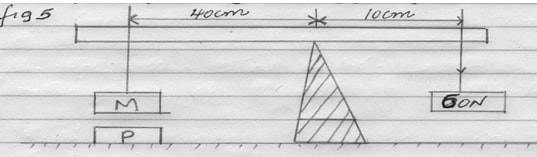
Figure 5
Find the attraction force between M and P.- Anticlockwise movements = clockwise movements
40 × (5 + x) = 60 x 10
200 + 40x = 600
40x = 400
x = 10N
- Anticlockwise movements = clockwise movements
- A heating coil rated 1000w takes 20 minutes to heat 10kg of a liquid from 25oC to 65o Determine the specific heat capacity of the liquid. (Assume no heat is lost to the surroundings).
- Figure 6 below shows 3 identical masses m1, m2 and m3 placed on a smooth rotating
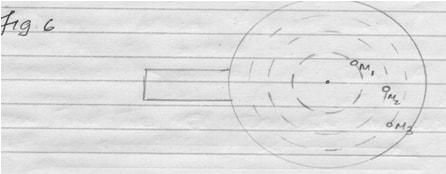
Figure 6
State the factors that determine whether a particular mass slides off table or not. (1mk)- Distance from the centre/Radius
- Angular Velocity of the rotating table
- Ice is in a beaker which is placed in a table as shown in Figure 7 below.
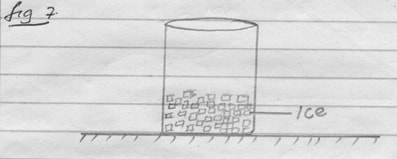
Figure 7
The ice is heated until it melts. Explain what happens to the stability of the beaker (2mks)- The beaker remained stable
- This is because position of c.o.g was lowered
- What is the velocity ratio of the pulley system shown in the figure below? (1mk)
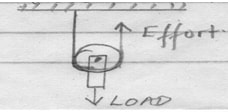
- V.R = 2 i.e. number of strings supporting the load
- Figure 8 below shows how the displacement of a point varies with time as a wave passes it.
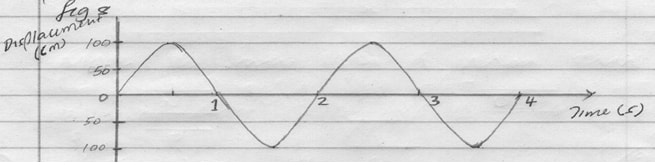
Figure 8
On the same diagram draw a wave which passes the point with half the amplitude and twice the frequency. (2mks)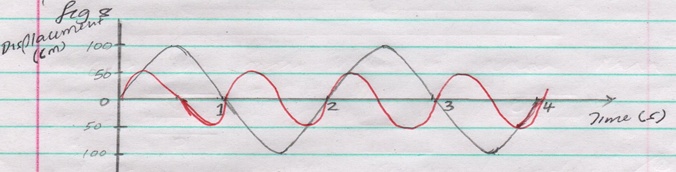
- A part from pressure state another factor that affects the melting point of a substance. (1mk)
- Impurities
SECTION B (55 MARKS)
-
- A piece of wood weighs 5.0N in air and 0.45N when immersed in water
Determine;- its relative density (2mks)
- Its apparent weight in a liquid of density 800kg/m3. (3mks)
- its relative density (2mks)
- Figure 9 shows a cylindrical solid 20 cm long and density2400kg/m3. Its cross-section area is 6cm2 and floats in water of density 1000kg/m3 while partially submerged with 10cm below the surface of water
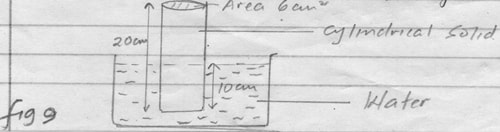
Figure 9
Determine- Weight of the solid (3mks)
- Upthrust on the solid (3mks)
- Weight of the solid (3mks)
- A piece of wood weighs 5.0N in air and 0.45N when immersed in water
-
- Figure 10 below shows a section of a tape pulled through a ticker timer of requency50Hz.

Figure 10- Determine the velocity of the body pulling the tape in cm/s in figure 10 above(3mks)
- T = 1/50 = 0.02(s)
Velocity = displacement/Time
= 10/(8 x 0.02)
= 62.5 cm/s
- T = 1/50 = 0.02(s)
- Find the acceleration of a body in cm/s2 for the tape represented in Figure 11 below. (take the frequency as 50Hz) (4mks)

Figure 11
- Determine the velocity of the body pulling the tape in cm/s in figure 10 above(3mks)
- A lorry of mass 12000kg is travelling at 10m/s and is brought to rest in 20seconds
Determine;- The acceleration of the lorry (2mks)
- The average retarding force (2mks)
- F = ma
= 12000 x (0.5)
= −6000kgm/s2
F = − 6000N
- F = ma
- The acceleration of the lorry (2mks)
- Figure 10 below shows a section of a tape pulled through a ticker timer of requency50Hz.
- Two similar cans are partly filled with equal quantities of paraffin. Each holds a thermometer, is covered with a lid and stands on a wooden bench at the same distance from radiant heat as shown in Figure 12 below.
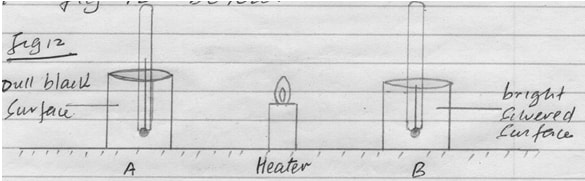
Figure 12
Container A has a dull black surface and container B has bright silvered surface. The following temperatures were recorded.
Time in minutes 0 1 2 3 4 5 Temp oC (dull black) 19 21 23 25 27 29 Temp oC (silvered bright) 19 20 21 22 23 24 - Explain why heat from the heater could not have reached the cans by:-
- Conduction (1mk)
- Air is a poor conductor of heat
- Air is a poor conductor of heat
- Convection (1mk)
- Convection currents moves upwards
- Explain why there is a difference in the thermometer readings in A and B. (2mks)
- The can absorb radiant heat at different rates. Dull black surface absorbs radiant heat more than bright silvered surfaces.
- How can the set-up in figure 12 above be adjusted in order to produce same reading of the thermometer. (1mk)
- Move A further or move B closer to the heater.
- Conduction (1mk)
- Two beakers A and B contain equal amounts of warm water initially at 35oC Water at 0oC is added to beaker A while ice cubes at 0oC are added to beaker B. Which beaker will have a lower temperature after a few minutes and why? (2mks)
- lowers more than A
- Latent heat to change ice to water will be supplied by the warm water in beaker B
- In an experiment to determine the specific latent heat of vaporization of water, steam at 100oC was passed into water contained in a well lagged aluminum calorimeter. The following measurements were made;
Mass of calorimeter = 150g
Initial mass of water 100g
Intial temperature of water = 18oC
Final mass of calorimeter + condensed steam = 275g
Final temperature mixture 68oC
(Specific heat capacity of water = 4.2KJkg-1K-1
And C.H.C for aluminium = 400 Jkg-1K-1)
Determine;- Mass of condensed steam (1mk)
- 275 – (100 + 150)
275 – 250 = 25g
- 275 – (100 + 150)
- Heat gained by calorimeter and water (3mks)
Heat gained = McCcϴc + MwCwϴw
= 0.15 x 400 x (68 – 18) + 0.1 x 4200 x (68 – 18)
= 3000 + 21000
= 24000J - Given that Lv is the specific latent heat of vaporization of steam.
- Write an expression for the heat given out by steam. (1mk)
- H = MLV + Mcθ
where m – mass of steam
C – S.H.C of condensed steam
- H = MLV + Mcθ
- Determine the value of Lv. (3mks)
- Mlv + mcθ = 24000
0.0025Lv + 0.025 x 4200 x (100 – 68) = 24000
Lv = 20640/0.025
Lv = 825600 J/kg
- Mlv + mcθ = 24000
- Write an expression for the heat given out by steam. (1mk)
- Mass of condensed steam (1mk)
- Explain why heat from the heater could not have reached the cans by:-
- Figure 13 below shows a hydraulic press used to lift a load L. The effort applied is 400N at the end of the lever 50cm long and pivoted at the other end.
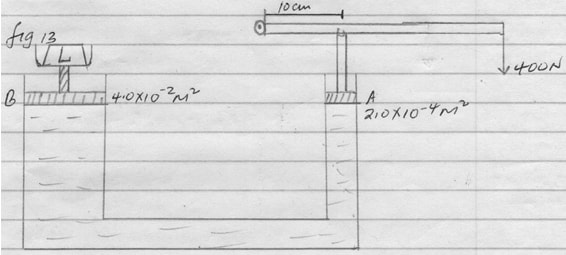
Figure 13
The plunger is 10cm from the pivot. The area of piston A is 2.0 x 2—4m2 and that of piston B is 4.0 x 10-2m2.
Determine;- Pressure exerted at piston A. (3mks)
- Weight of the load L being lifted. (3mks)
- PA = PB = 1.0 x 107 N/m2
L = 1.0 x 107 x 4.0 x 10 -2 m2
= 4.0 x 105 N
- PA = PB = 1.0 x 107 N/m2
- If small piston moves down a distance of 10cm, determine how far upwards the longer piston B moves. (3mks)
- Pressure exerted at piston A. (3mks)
-
- State the differences between temperature measured in Kelvin scale and Celsius scale. (1mk)
- Kelvin scale starts at absolute zero while Celsius scale starts at 273K.
- Figure 14 below shows a simple set up for pressure law apparatus.
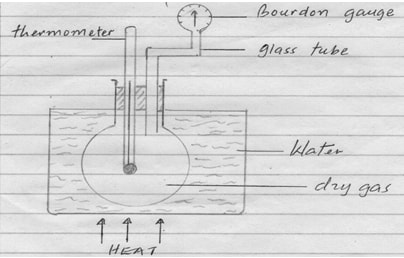
Figure 14- State two measurements that can be recorded using the above apparatus (2mk)
- Pressure of the gas
- Temperature of the gas
- Explain how the measurement above in (i) may be used to verify pressure law. (3mks)
- Measure the value of pressure and temperature
- temperature varies with pressure
- values of temperature and then corresponding values of pressure are recorded
- A graph of pressure against temperature plotted.
- When the graph is interpolated it passes through the absolute zero
- State two measurements that can be recorded using the above apparatus (2mk)
- State one assumptions of real gas laws (1mk)
- Particles of gases do not collide with one another Kinetic Ener is not affected
- At 20oC the pressure of a gas is 50cm of mercury. At what temperature would the pressure of the gas fall to 10cm of mercury. (3mks)
- P/T = constant
P1/T1 = P2/T2
50/293 = 10/T2
T1 = 2930/50
T2 = 58.6K or -214.4oC
- P/T = constant
- State the differences between temperature measured in Kelvin scale and Celsius scale. (1mk)
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download PHYSICS PAPER 1 Marking Scheme - 2019 KCSE Prediction Answers Set 2.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students