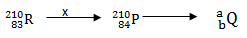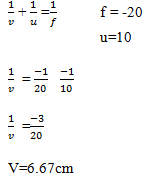SECTION A (25 Marks)
Answer all the questions in this section
- Figure 1 below shows a ray of light incident on a plane mirror at O.
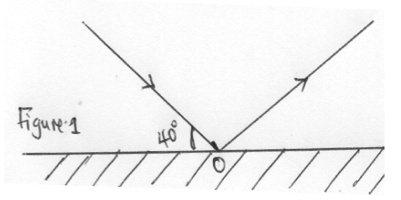
Figure 1
The mirror is rotated through an angle of 250 about an axis perpendicular to the paper .Determine the angle through which the reflected ray is rotated (2mks)- θ=2x25=500
- A car battery requires topping up with distilled water occasionally. Explain why this is necessary and why distilled water is used. (2mks)
- Evaporation on the cell reaction causes loss of water.
- Distilled water is used because it does not introduce impurities to the cell.
- Figure 2 below shows two parallel current carrying conductors A and B cutting through a piece of cardboard.

Figure 2- Sketch the magnetic field pattern produced. (2mks)
- Identify the nature of the force between them (1mk)
- Attractive force
- Distinguish between ultraviolet rays and infrared (1mk)
- UV rays are produced due to large energy charge in the electron of an atom while IR rays are produced due to small energy changes of an electron or molecular vibrations.
- A student synchronizes his watch with a church bell 2km away. The following morning, there is a wind. .He notes that the church bell sounded 0.15s later. Assuming his watch was correct and bell was sounded at the usual time. Determine the direction and the speed of the wind. (Assuming the speed of sound in still air is 340m/s) (3mks)
- Wind is blowing toward the church
Expected time = 2000/340 = 5.882 sec
Actual time =5.882+0.15 = 6.032
Speed of sound = 2000/6.032 =331.55m/s
- Wind is blowing toward the church
- Figure 3 below shows an illustration of a good storage magnets
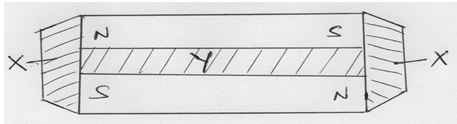
Figure 3
State and explain the material suitable for Y (2mks)- Non-magnetic materials
- To make it sustain its magnetism
- Figure 4 below shows a circular wave approaching a plane barrier in uniform medium.

Figure 4
On the diagram sketch the reflected waves in water (2mks) - A negatively charged rod is brought near the cap of a leaf electroscope. The cap is them earthed momentarily by touching with finger. Finally the rod is withdrawn .State and explain the observation made. (2mks)
- On Earthing negative charges are repelled to the ground .When the rod is withdrawn, the leaf s left with a net positive charge. The leaf rises.
- The following equation represents a decay series
- Identify radiation x. (1mk)
- X - A beta particle
- Determine the values of a & b. (2mks)
- a-206
- b-82
- Identify radiation x. (1mk)
- Figure 5 below shows a circuit where a battery of e.m.f 4.5V, Switches A &B, two capacitors (C1=0.6µF and C2=1.0µF) and a voltmeter are connected.
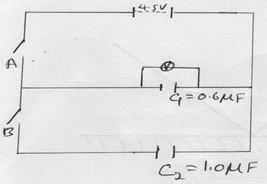
Figure 5- Determine the charge on C1 when the switch A is closed and switch B is open. (2mks)
- Charge Q1 on C1 is given by
Q1=C1V
=0.6 µF x 4.5
=2.7µC
OR
Q1=C1V
=0.6X10-6 x4.5
=2.7X10-6 C
- Charge Q1 on C1 is given by
- What is the effective capacitance C when both switches A and B are closed? (2mks)
- CT=C1+C2
=(0.6+1.0) µf
=1.6µf
- CT=C1+C2
- Determine the charge on C1 when the switch A is closed and switch B is open. (2mks)
- Describe the energy charges that occurs in the cathode ray tube. (1mk)
- Electrical to light energy
SECTION B (55MKS)
Answer all questions in this section
-
- Two coins were placed at the bottom of two jars each containing a different clear liquids as shown in Figure 6 below.
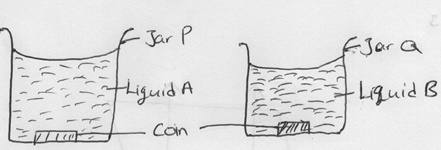
Figure 6
The liquids in the two jars are at the same level. The coin in jar Q appears shallower than in jar P. Explain (2 mk)- They have different refractive index ie refractive index of P is less than that of Q
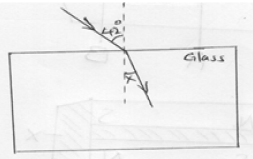
- A ray of light travels from air to glass as shown in Figure 7 below.
Figure 7
Given that the critical angle of glass is 42o, Determine the value of angle X. (4mks)
- n = 1/sin c = 1/sin 42 = 1.5
sin 40/sin x
x = 25.4o
- n = 1/sin c = 1/sin 42 = 1.5
- Figure 8 below shows a ray of eight incident on a triangular prism and a white sources is placed in front of the screen.
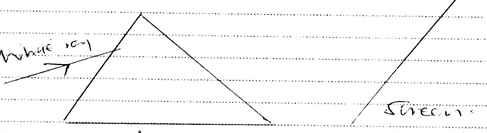
Figure 8
Complete the diagram to show the path followed by the ray up to the screen. (2mks)
- Two coins were placed at the bottom of two jars each containing a different clear liquids as shown in Figure 6 below.
-
- Sate faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction. (1mk)
- The magnitude of the induced emf in a coil is directly proportion to the rate of change of magnetic flux linked with the coil.
- Figure 9 below shows a simple transformer. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
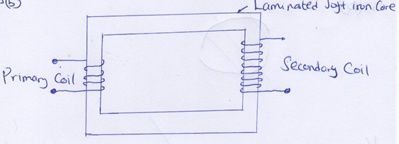
Figure 9- Explain why the core is a continuous loop (1mk)
- It’s continuous so as to maintain closed loops of the magnetic lines of force (circuit)
- Give a reason as to why the cure is laminated. (1mk)
- In order to reduce eddy currents.
- State and explain which coils are thicker. (2mks)
- Primary coils
- Reason: Carry higher current
- Explain why the core is a continuous loop (1mk)
- Sate one difference and one similarity between a step up transformer and induction coil. (2mks)
- Difference:- step up uses A.C and while induction coil uses dc.
- Similarly:-mutual inductance /both step up the voltage
- State two advantages of the use of alternating voltage for the transmission of electrical energy. (2mks)
- Can be stepped up or down
- Can be converted to A.C
- The primary coils of a transformer have 2000 turns and carries a current of 3A. If the secondary coil is designed to carry a current of 30A. Calculate the maximum number of turns in the secondary coil. (3mks)
- Ip/Is =Ns/Np
Ns = (200 × 3)/30 = 200
- Ip/Is =Ns/Np
- Sate faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction. (1mk)
-
- State Ohm’s law (1mk)
- The amount of current flowing through a metallic conductor is directly proportion to the pd across its ends so long as temperature and other physical factor remain constant.
- Figure 10 below shows how a student set up a circuit using 3 identical bulbs X, Y and t each rated 12V, 2.0A
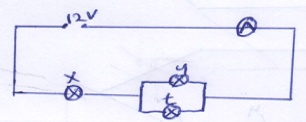
Figure 10- When operating normally calculate the resistance of the bulbs. (2mks)
- V = IR
R = V/I = 12/2 = 6 Ω
- V = IR
- Calculate the effective resistance of the three bulbs. (2mks)
- 1/Rp = 1/6 + 1/6
Rp= 3 Ω
X in series with Rp
RT = 6 + 3 = 9 Ω
- 1/Rp = 1/6 + 1/6
- What will be reading of the ammeter? (2mks)
- I= V/R = 12/9 =1.33 A
- When operating normally calculate the resistance of the bulbs. (2mks)
- When a switch is kept open in the circuit shown in Figure 11 below the voltmeter reads 1.5V, when the switch is closed, the reading drops to 1.3V and the current through the resistor is 0.5A.
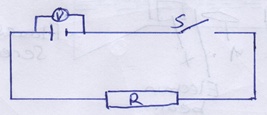
Figure 11- What is the emf of the cell (1mk)
- E.m.f=1.5 V
- What is the terminal voltage of the cell (1mk)
- Terminal voltage =1.3 V
- Calculate the valve of R (2mks)
- R= V/I = 1.3/0.5 = 2.6 A
- What is the emf of the cell (1mk)
- State Ohm’s law (1mk)
-
- Figure 12 below shows an object in front of a lens.
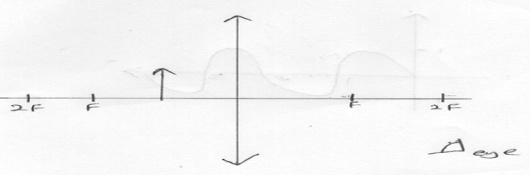
Figure 12- Using rays locate the image as seen by the eye. (2mks)
- Give one application of such a such a dens as used above. (1mk)
- As a magnifying glass
- Figure 13 (a) and (b) shows diagrams of human eye
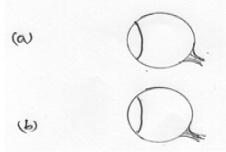
Figure 13- In figure (a),sketch a vary diagram showing long sightedness.(1mk)
- In figure (b) sketch a ray diagram shown how lens is used to correct long sightedness.(2mks)
- An object of height 10.5am stands before a diverging lens of focal length 20cm and a distance of 10cm from the lens.Determine
- The image distance (2mks)
- Height of the image (2mks)
- Magnification (2mks)
- m= v/u = 6.67/10 = 0.67
- The image distance (2mks)
- Figure 12 below shows an object in front of a lens.
-
- State two differences between cathode rays and electromagnetic radiation (2mks)
- Cathode rays have charges but electromagnetic radiation do not have
- Cathode rays are particle and have mass while electromagnetic radiation are waves
- Cathode rays travel with a speed depending on accelerating voltage while electromagnetic radiation travel with the speed of light in vacuum
- Figure 14 below shows the main features of a cathode ray oscilloscope (CRO)
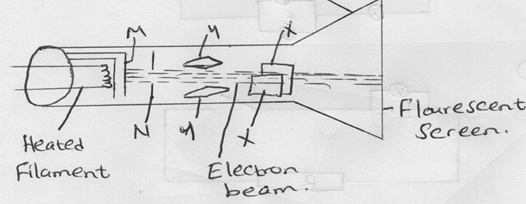
Figure 14- Name the parts labeled M and N. (2mks)
- M-grid
- N-Accelerating anode
- Explain how electrons are produced in the tube (2mks)
- The cathode is heated by filament and electrons are released from cathode by thermionic emission.
- When using the CRO to display waveforms of voltages, state where the following should be connected.
- The voltage to be displayed on the screen (1mk)
- Across Y-Plates
- The time base voltage(1mk)
- Across X-plates
- The voltage to be displayed on the screen (1mk)
- Sate why the tube is highly evacuated(1mk)
- This is to reduce collisions of cathode rays with air molecule in the tube.
- Name the parts labeled M and N. (2mks)
- Figure 15 below shows the waveform of a signal applied at the y-plates of an oscilloscope while time base is switched to the scale of 2milliseconds per minutes.
Determine the frequency of the signal (3mks)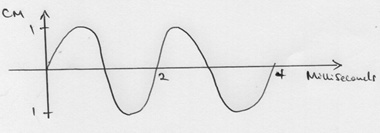
Figure 15- 2 x 2 = 4 Milliseconds for one wave
T= 4/1000 =0.004s
F= 1/T = 1/0.004 = 250Hz
- 2 x 2 = 4 Milliseconds for one wave
- State two differences between cathode rays and electromagnetic radiation (2mks)
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download PHYSICS PAPER 2 Marking Scheme - 2019 KCSE Prediction Answers Set 2.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students