Instructions to Candidates
- This paper has TWO Sections: A and B.
- Answer all questions in Section A.
- In Section B, answer Question 6 and any other two

Questions
SECTION A (25marks)
-
- What is a habitat. (2mks)
- Name disciplines related with the following areas of study.
- Geomorphology (1mk)
- Biogeography (1mk)
-
- State three characteristics of summer solstice. (3mks)
- Give two ways in which sea breezes influences the adjacent lands. (2mks)
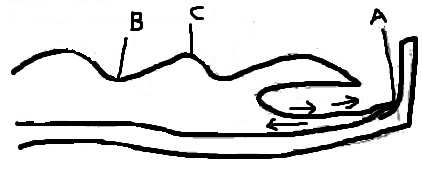
- The diagram below shows a breaking wave
- Name the parts labelled A, B, C (3mks)
- Give three conditions for the formation of a beach. (3mks)
-
- Outline three reasons why some lakes have fresh water. (3mks)
- Name two lakes formed as a result of crustal warping. (2mks)
-
- What is soil catena? (2mks)
- Outline three characteristics of halmorphic soils. (3mks)
SECTION B (All questions carry equal marks)
-
- Study the map of Kijabe 1:50,000 sheet 134/3 provided and answer the following questions.
- Give the six – figure grid reference of the water tank at Bathi near the cattle dip. (2mks)
- Measure the distance of the regional boundary North West of the area covered by the map. (2mks)
- What is the longitudinal extend of the area covered by the map. (2mks)
- Describe the relief of the area covered by the map. (5mks)
- Explain three factors that have influenced the distribution of settlement in the area covered by the map. (6mks)
- Students of St. Monica secondary school went for a field study in the area covered by the map.
- Name three social functions they may have identified. (3mks)
- Giving evidence, show any one agricultural activity they identified. (2mks)
- Give three problems they are likely to experience during the study. (3mks)
- Study the map of Kijabe 1:50,000 sheet 134/3 provided and answer the following questions.
-
-
- Define folding (2mks)
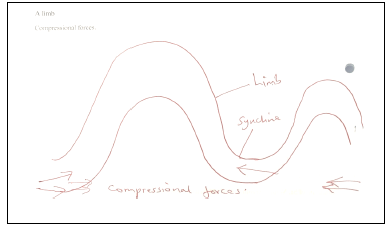
- Draw a diagram to show a simple fold. On it mark and name the following;
A syncline A limb Compressional forces (3mks)
-
- Describe how Fold Mountains are formed.
By geosyncline theory. (7mks) - A part from Fold Mountains, name any other three features resulting from folding.(3mks)
- Describe how Fold Mountains are formed.
- Name two fold mountains in Africa. (2mks)
- Explain four negative effects of folding to human activities. (8mks)
-
-
-
- Define desertification. (2mks)
- Name three major deserts in Africa. (3mks)
- Describe three processes of wind erosion. (6mks)
- Describe how the following desert features are formed.
- Yardang’s (4mks)
- Seif dunes (4mks)
- Explain any three positive effects of desert features to human environment. (6mks)
-
-
-
- Differentiate between a valley glacier and an ice sheet. (2mks)
- Explain two processes of glacial movement (4mks)
-
- State three causes of glacial deposition. (3mks)
- List four erosional features of glacier in the highland areas. (4mks)
- Describe how a drumlin is formed. (4mks)
- You are supposed to carry a field study of a glaciated low land.
- Give three reasons why you need a map of the area of study. (3mks)
- Give two methods you will use to collect data. (2mks)
- List three problems that you are likely to experience during the field study. (3mks)
-
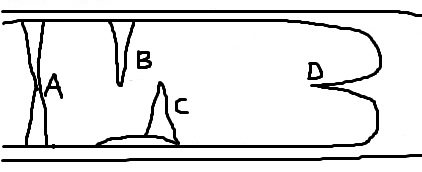
- The diagram represents underground features in a limestone area. Use it to answer question (a)
-
- Name the features marked B, C, and D. (3mks)
- Describe how the feature marked A is formed. (6mks)
- What are the ideal conditions for the formation of artesian basin? (4mks)
- Explain how the following factors influence the existence of underground water.
- Precipitation. (2mks)
- Nature of rocks (2mks)
- Vegetation cover. (2mks)
- Explain three significance of Karst scenery to human activities. (6mks)
-

Marking Scheme
SECTION A (25marks)
Instructions: answer all questions in this section.
-
- What is a habitat. (2mks)
A home that provides the physical conditions under which certain plants or animals live. - Name disciplines related with the following areas of study.
- Geomorphology (1mk)
Geology - Biogeography (1mk)
Biology
- What is a habitat. (2mks)
-
- State three characteristics of summer solstice. (3mks)
- The sun is overhead at the tropic of cancer.
- Days are longer in the northern hemisphere
- The area has higher temperatures
- Nights are shorter in the northern hemisphere and shorter in southern hemisphere
- Give two ways in which sea breezes influences the adjacent lands. (2mks)
- Lowers temperature of adjacent land.
- Increases rainfall
- Increases humidity
- Lead to convectional rainfall
- Moderate diurnal range of temperature.
- State three characteristics of summer solstice. (3mks)
- The diagram below shows a breaking wave
- Name the parts labelled A, B, C (3mks)
- Shore
- Trough
- Wave crest
- Give three conditions for the formation of a beach. (3mks)
- Gently sloping shore
- The shore should be shallow
- Breaking waves should have a strong swash and a weak backwash.
- Waves should carry a large load of materials to be deposited.
- Name the parts labelled A, B, C (3mks)
-
- Outline three reasons why some lakes have fresh water. (3mks)
- Some lakes are situated in areas of high rainfall which keeps the water fresh.
- Some have surface outlets which drain the salts that accumulates in the lakebeds.
- Some lakes have regular inflow of freshwater from rivers.
- Some are situated in places of low temperature thus low rate of evaporation.
- Some have subterranean outlets which drain the salts that accumulates in the lake beds.
- Some of lakebeds were covered by recent volcanic eruptions covering the salt in them
- Name two lakes formed as a result of crustal warping. (2mks)
- L. Victoria
- L. Kyoga
- L. Chad
- L. Wamala
- L. Nakivali
- L. Kakira
- L. Amboseli
- Outline three reasons why some lakes have fresh water. (3mks)
-
- What is soil catena. (2mks)
Soil catena is the arrangement of soil along a slope from the top to the bottom/sequence of different soils on a slope from top to bottom. - Outline three characteristics of halmorphic soils. (3mks)
- They are saline
- They are thin
- Low in moisture content
- Light in colour.
- Loosely held.
- What is soil catena. (2mks)
-
- Study the map of Kijabe 1:50,000 sheet 134/3 provided and answer the following questions.
- Give the six – figure grid reference of the water tank at Bathi near the cattle dip. (2mks)
363926 - Measure the distance of the regional boundary North West of the area covered by the map. (2mks)
4.1±1 KM - What is the longitudinal extend of the area covered by the map. (2mks)
36º30E – 36º45ºE
- Give the six – figure grid reference of the water tank at Bathi near the cattle dip. (2mks)
- Describe the relief of the area covered by the map. (5mks)
Relief- There is a saddle/col/pass
- Hills
- Escarpment
- River valleys occupied by rivers
- Rolling plains in the NW
- Highest point 2680
- Lowest point 1780
- The area slopes from North to South
- The area has valleys – Ewaso Kidong
- Explain three factors that have influenced the distribution of settlement in the area covered by the map. (6mks)
- There is settlement along rivers for easy access of water
- Kidong valley has discouraged settlement because it is hot and dry.
- Settlement along railway line and roads/transport lines for easy movement
- Thicket has discouraged settlement because they are insecure
- Forests have discouraged settlement because they are insecure/government policy
- steep slopes discourage settlement because it is difficult to construct
- Plantations discourage settlement.
- Students of St. Monica secondary school went for a field study in the area covered by the map.
- Name three social functions they may have identified. (3mks)
- Administration - PS
- Education - School
- Medication/Health services -Hospital
- Provision of water - pump house
- Religion – church
- Giving evidence, show any one agricultural activity they identified. (2mks)
- Crop farming – plantation
- Livestock -Cattle dip/scrub vegetation/dairy
- Give three problems they are likely to experience during the study. (3mks)
- Steep slope that make movement difficult
- Thick forest that makes it difficult to penetrate through
- Numerous rivers that may slow movement
- The forest may have wild animals
- Name three social functions they may have identified. (3mks)
- Study the map of Kijabe 1:50,000 sheet 134/3 provided and answer the following questions.
-
-
- Draw a diagram to show a simple fold. On it mark and name the following; (3mks)
- Folding – is the process of crustal distortion which causes the rocks to bend upward or downloads
-
- Describe how Fold Mountains are formed. By geosyncline theory. (7mks)
- An extensive shallow depression called a geosyncline is formed on the surface of the earth.
- It is filled with water and sediments eroded from the surrounding highlands
- The weight of the sediments causes the floor of the geosyncline to subside/sink.
- The continents are pulled towards the geosyncline by sagging motion of the geosyncline.
- This movement triggers off compressional forces in the rocks.
- Deposited materials are folded upwards to form Fold Mountains.
- A part from Fold Mountains, name any other three features resulting from folding. (3mks)
- Escarpments
- Valley and ridge landscapes
- Rolling plains
- Inter – montane plateaus
- Inter – montane basins
- Depressions
- Synclinal
- Describe how Fold Mountains are formed. By geosyncline theory. (7mks)
- Name two fold mountains in Africa. (2mks)
- Cape ranges
- Atlas
- Drakensberg
- Explain four negative effects of folding to human activities. (8mks)
- Folding process may lead to loss of live
- The leeward slopes of Fold Mountains receive low rainfall discouraging farming.
- Fold Mountains act as barriers during the construction of transport lines
- Ruggedness of folded areas discourages settlement.
- Cold descending winds may cause stunted growth in crops
-
-
-
- Define desertification. (2mks)
This is the slow but steady encroachment of desert like conditions onto potentially productive agricultural land. - Name three major deserts in Africa. (3mks)
- Define desertification. (2mks)
-
- Sahara
- Kalahari
- Namib
-
- Describe three processes of wind erosion. (6mks)
Abrasion- It involves materials carried by wind scraping, grinding and polishing the rock surface thus removing materials from it.
Deflation - Process through which wind removes loose unconsolidated materials by rolling them on the ground and lifting them up in the air.
Attrition - The materials carried by wind hit each other or against the rock surface and they reduce in size.
- It involves materials carried by wind scraping, grinding and polishing the rock surface thus removing materials from it.
- Describe how the following desert features are formed.
- Yardang’s (4mks)
- They are formed when a rocklandscape of different resistance /heterogeneous occur in vertical bands parallel to the direction of prevailing wind.
- The regions of soft rocks are eroded faster than hard resistant rocks.
- Layers of less resistant rocks form furrows while layers of resistant rocks are left standing as ridges called yardangs.
- Seif dunes (4mks)
- They are formed when barchans are stretched and straightened by wind action to form ridges of sand.
- Cross winds interrupt prevailing winds to drive sand from side to side.
- This breaks the crescent shape of barchans into longitudinal ridges called seif dunes
- Yardang’s (4mks)
- Explain any thee positive effects of desert features to human environment. (6mks)
- Loess regions have fertile soils which are used for crop cultivation
- Features eg sand dunes, rock pedestal attract tourist’s thus earning foreign exchange.
- Oasis contain water which is used for domestic’s purposes.
- Salty flats and salina’s / sebkhas are used for salt production
- Deserts have low population hence ideal for military training.
-
-
-
- Differentiate between a valley glacier and an ice sheet. (2mks)
Valley glacier is the glacier that flows down a slope in a pre – existing valley from an area of accumulation while an ice sheet is a continuous mass of ice covering a wide surface - Explain two processes of glacial movement (4mks)
Basal slip
- Weight of ice causes ice layer which is in contact with the rock beneath to melt slightly. The ice above slides over the rock.
Plastic flowage - Weight of glacier exerts pressure on the layers of ice at the bottom.
- The pressured ice particles melt slightly and move downhill before they freeze again.
Extrusion flow - Occurs on lowland and gently slopes. Where ice accumulates and builds great weight at the lower part. The weight compresses the lower layers of ice forcing them to spreads out to areas of low pressure.
- Weight of ice causes ice layer which is in contact with the rock beneath to melt slightly. The ice above slides over the rock.
- Differentiate between a valley glacier and an ice sheet. (2mks)
-
- State three causes of glacial deposition. (3mks)
- Excess amount of moraine
- Melting caused by excessive weight of ice
- Gentle slopes
- Friction between the moving ice and the ground over which it is moving.
- Change in climate resulting in warming of the atmosphere.
- List four erosional features of glacier in the highland areas. (4mks)
- Truncated spurs
- Cirque
- Aretes
- Pyramidal peaks
- U – shaped valley
- Hanging valley
- Tarns
- State three causes of glacial deposition. (3mks)
-
- Describe how a drumlin is formed. (4mks)
- As the mass of ice moves in low lands, it thins out as a result of melting.
- It stops moving in the very flat areas and melts
- It deposits boulder clay beneath the ice
- Ice abrasion and plucking reshapes the boulder clay into rounded hills
- Abrasion smoothens the upstream side of the hill.
- This lead to the formation of small rounded or elongated hills called drumlins
- Describe how a drumlin is formed. (4mks)
- You are supposed to carry a field study of a glaciated low land.
- Give three reasons why you need a map of the area of study. (3mks)
- To show direction to be followed during the field study.
- To help in estimation of distance to be covered
- Help in estimation of time required for the study.
- Help in drawing up a work schedule.
- Give two methods you will use to collect data. (2mks)
- Observing
- Photographing/filming/video recording
- Sampling
- List three problems that you are likely to experience during the field study.(3mks)
- Low temperatures that will slow the study
- Sliding on ice
- Inadequate data since not all features may be seen.
- Difficulty in descending the rugged slopes
- Give three reasons why you need a map of the area of study. (3mks)
-
- The diagram below represents underground features in a limestone area. Use it to answer question.
-
- Name the features marked ,B, C, and D. (3mks)
- B – Stalactite
- C – Stalagmite
- D – Cave
- Describe how the feature marked A is formed. (6mks)
- Solution of calcium carbonate trickles down slowly through roof of a cave.
- Solution droplets hang on the roof of the cave
- Water evaporates and calcium carbonate is precipitated
- The precipitated calcium carbonate gradually builds downwards forming stalactite.
- The solution splashes on the floor and evaporates
- Calcium carbonate in it precipitates and gradually build upwards to form a stalagmite.
- Over time the stalactite and stalagmite join to form a pillar/Colum
- Name the features marked ,B, C, and D. (3mks)
- What are the ideal conditions for the formation of artesian basin? (4mks)
- Aquifer must be sandwiched between impermeable rocks so that it can retain water.
- The aquifer must outrage in a region which is a source of water/high rainfall
- The aquifer must dip from a region of water intake and the rock layers must form a broad syncline.
- The mouth of the well must be lower than the intake area.
- Explain how the following factors influence the existence of underground water.
- Precipitation. (2mks)
- Light rain falling over a longer period infiltrates more than heavy down pour which is short.
- Heavy down pour saturate the surface thus blocking the passage that the water would use to infiltrate.
- Nature of rocks (2mks)
- Rocks must have air spaces (pores, cracks or joints) for surface water to infiltrate.
- The aquifer should be porous and underlain by an impermeable rock so that the ground water can accumulate in it.
- Vegetation cover. (2mks)
- Presence of vegetation cover increases infiltration.
- Vegetation break the speed of the rain drops falling. This enable water reach the ground gently thus more infiltration.
- Precipitation. (2mks)
- Explain three significance of Karst scenery to human activities. (6mks)
- Limestone is a raw material for building houses.
- Solution lakes in poljes provide water for domestic use.
- Features e.g caves attract tourist hence foreign exchange
- Limestone landscape discourages settlement.
- Grass in Uvalas form pasture grounds
-
Download Geography Paper 1 Questions and Answers - KCSE Prediction Papers 2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students