INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
- Write your Name, Index Number and School in the spaces provided above.
- Sign and write the Date of Examination in the spaces above.
- Answer all the questions in the spaces provided in the question paper.
- Mathematical tables and non-programmable electronic calculators may be used.
- ALL working must be clearly shown where necessary.
FOR EXAMINER’S USE ONLY
|
QUESTIONS |
MAX SCORE |
CANDIDATE’S SCORE |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
13 11 12 12 10 15 08 |
|
|
TOTAL |
80 |
|

QUESTIONS
- Study the information in the table below and answer the questions that follow.
The letters do not represent the actual symbols of the elements.
Elements
Electronic configuration
Ionization energy kJmol-1
P
2:1
519
C
2:8:1
494
R
2:8:8:1
418
- What is the general name given to the group which elements P, C and R belong? (1mk)
- What is meant by ionization energy? (2mks)
- Explain why element P has the highest ionization energy. (2mks)
-
- When a piece of element “C” is placed on water, it melts and hissing sound is produced as it moves on the surface of the water. Explain these observations. (2mks)
- Distinguish between a strong and a weak base. Give an example of each. (2mks)
- Neutralization is one of the methods of preparing salts.
- What is meant by neutralization? (1mk)
- Describe how you would prepare crystals of sodium nitrate starting with 200cm3 of 2M sodium hydroxide. (3mks)
- Write an equation for the reaction that takes place when a solid sample of sodium nitrate is heated. (1mk)
-
- The diagram below represents a set-up that was used to obtain dry nitrogen from air. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
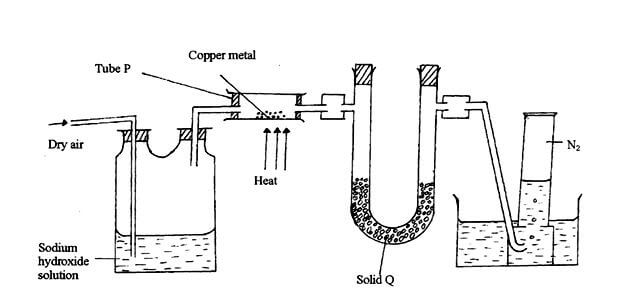
- Name solid Q. (1mk)
- What is the purpose of NaOH(aq)? (1mk)
- Write an equation for the reaction which took place in tube P. (1mk)
- Give the name of one impurity in the nitrogen gas obtained. (1mk)
- Why is liquid nitrogen used for storage of semen for artificial insemination? (1mk)
- The set-up below was used to prepare nitric acid.
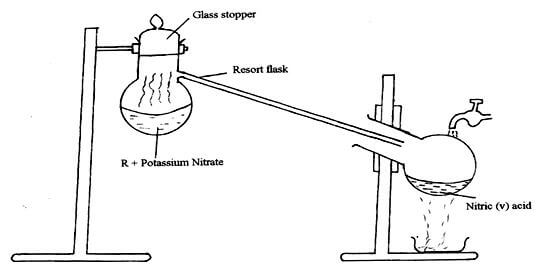
- Give the name of liquid R. (1mk)
- Write an equation for the reaction which took place in the retort flask. (1mk)
- Explain the following:-
- Nitric acid is not stored in clear / transparent glass. (2mks)
- The reaction between copper metal with 50% nitric acid (one volume of acid added to an equal volume of water) in an open test tube produces brown fumes. (2mks)
- The diagram below represents a set-up that was used to obtain dry nitrogen from air. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
- Chlorine is a member of group VII.
- What is the family name of group VII elements? (1mk)
- Explain why the reactivity of Iodine is lower than that of Bromine. (2mks)
- Chlorine gas used for industrial purposes is obtained by electrolysis of brine.
- Name two other products of this electrolysis. (2mks)
- Write the equation for the reaction at the anode. (1mk)
- Sodium chlorate (NaClO3) is used as a herbicide. It is formed according to the following equation:
6NaOH(aq) + 3Cl2(g) →NaClO3(aq) + 5NaCl(g) + 3H2O(l)
Sodium chloride is less soluble than sodium chlorate and crystallizes out first. Sodium chlorate is obtained from the remaining solution by crystallization of saturated solution.- State one condition necessary for this reaction. (1mk)
- Calculate the maximum mass of sodium chlorate in kilograms that can be formed from 206m3 of chlorine gas. (1 mole of gas = 24dm3, Na = 23.0, Cl = 16.0).(3mks)
- Name two other uses of chlorine. (2mks)
-
- The table below contains information from the measurements made of the radioactivity in counts per minutes from a radioisotope iodine – 128.
Counts per min
240
204
180
156
138
122
108
Time (min)
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
- Plot a graph of counts per minute against time. (3mks)
- Use the graph to determine the half-life of iodine – 128. (1mk)
- What is the counts rate after 22 minutes? (1mk)
- After how many minutes were the counts rate 160 counts per minute? (1mk)
- Plot a graph of counts per minute against time. (3mks)
- If isotope 232Th decays to 216Bi as a result of X alpha-particles and Y-beta particles emission
90 83- Find the numerical value of X and Y. (2mks)
- Write the nuclear equation. (1mk)
- A radioactive material emitted radiations as shown below.
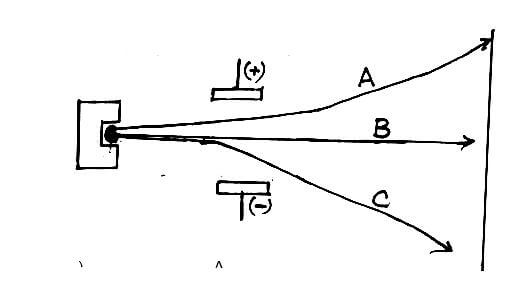
- Identify: (1½mks)
A _______
B _______
C _______ - Which radiation: (1½mks)
- Has no mass?
- Has the lowest ionizing power?
- Contains Helium particles?
- Identify: (1½mks)
- The table below contains information from the measurements made of the radioactivity in counts per minutes from a radioisotope iodine – 128.
- The raw material for extraction of aluminum is bauxite.
- Name the method that is used to extract aluminium from bauxite. (1mk)
- Write the chemical formula for the major components of bauxite. (1mk)
-
- Name the major impurities in bauxite. (2mks)
- Explain how the impurities in bauxite are removed. (1mk)
- Crayolite is used in the extraction of aluminium from bauxite. State its function. (1mk)
- Describe how carbon (IV) oxide is formed during the extraction of aluminium. (2mks)
- Aluminum is a reactive metal yet utensils made from aluminium do not corrode easily. Explain this observation. (2mks)
- Standard electrode potentials for half cell reactions are shown below.
A2+(aq) + 2e A(s) - 0.76V
B2+(aq) + 2e B(s) - 0.13V
C+(aq) + e C(s) +0.80V
D2+(aq) + 2e D(s) +0.34V
The cell below was set-up using A and B electrodes.-
- Give the half-cell equations for each half cell. (1mk)
- Write the overall cell equation. (1mk)
- Calculate the e.m.f. of the cell above. (1mk)
- Describe how the salt bridge helps in maintaining the change balance in each half cell when the cell is in operation. (2mks)
- It is not advisable to use potassium chloride salt bridge when Lead (II) nitrate solution is used as an electrolyte in the above set-up. Explain. (2mks)
- Sodium hydroxide is a chemical that can be prepared industrially in a mercury cell.
- Give the name of the main raw material used. (½mk)
- In the cell, graphite is used as anode electrode. Name another substance that can be used in place of graphite (carbon). (½mk)
- Give two uses of sodium hydroxide. (2mks)
- Give two reasons why mercury is recycled. (2mks)
- Write the equation in which sodium hydroxide is produced. (1mk)
- If the volume of hydrogen produced in the mercury cell is 100 litres. Calculate the mass of sodium hydroxide formed at room temperature.
(H = 1.0, Na = 23.0, O = 16.0 MGV = 24 litres) (2mks)
-
-
- Name two advantages of synthetic fibre over natural fibre. (2mks)
- The scheme below shows reactions starting with ethanol. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
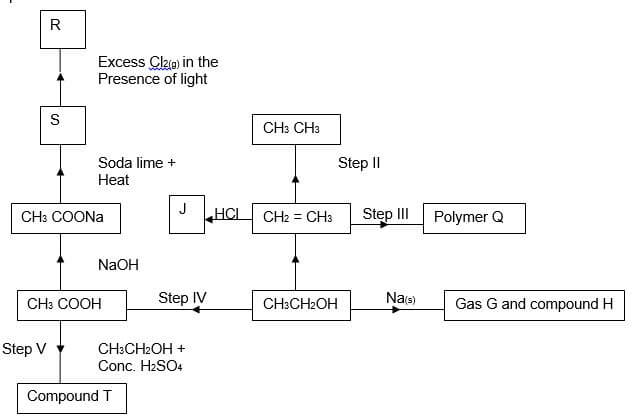
- Name gas G. (1mk)
- Write the structural formulae and names of:
- T (1mk)
- S (1mk)
- Name the homologous series to which T belongs. (1mk)
- Write down the structural formula of compound R. (1mk)
- Name the compound R. (1mk)

MARKING SCHEME
-
-
- Alkali metals
- Energy required to remove an electron from an atom of an element in its gaseous state.
- “P” has the smallest ionic radius therefore, the outermost electrons are most strongly attracted to the nucleus, hence more energy is required to remove this electron.
- Melts because the reaction is exothermic. Hissing sound because of the production of hydrogen gas. Float because it is less dense than water. Moves about due to propelling effect of escaping hydrogen.
- A strong base ionizes completely in water producing more OH- ions e.g. KOH and NaOH. A weak base ionizes slightly producing few OH ions e.g. NH4OH, Ca(OH)2 and Mg(OH)2.
-
- Reaction between H+ ions from the acid and OH ions from bases to form 1 mole of water.
H+(aq) + OH(aq) → H2O(l) - Add 200cm3 of 2M nitric acid to 200cm3 of 2M sodium hydroxide. Heat the mixture so as to make it saturated / concentrated. Allow the mixture to cool for crystals to appear. Filter / decant to obtain the crystals.
- 2NaNO3(s) → 2NaNO2(aq) + O2(g)
- Reaction between H+ ions from the acid and OH ions from bases to form 1 mole of water.
-
-
-
- Anhydrous calcium chloride / silica gel.1
- To remove carbon (IV) oxide from air 1 or free air from CO2.
- 2Cu(s) + O2(g) → 2CuO(S) 1
- Unreacted oxygen, noble gases e.g. Argon. 1
- It has a very low boiling point of -1960C.
-
- Concentrated sulphuric VI acid / H2SO4 reject concentrated sulphuric acid.
- KNO3(s) + H2SO4(l) → HNO3(g) + NaHSO4(aq)
- It is decomposed by light 1 to brown nitrogen (IV) oxide water and oxygen. 1
- The reaction between copper metal and 50% nitric V acid produces colourless nitrogen II oxide gas which is further oxidized by atomospheric oxygen to brown fumes of nitrogen IV oxide.
OR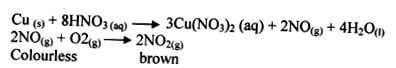
-
-
- Halogens
- They attract electrons into the outer energy level by its nuclear charge during reaction. The atomic radii increase down the group due to the successive additional energy level. Therefore the outer most energy level of iodine increasingly get further away from the nucleus than for bromine hence nuclear attraction for electrons grows weak for iodine than bromine.
-
- NaOH(aq) and H2(g)
- 2Cl-(aq) → Cl2(g) + 2e
-
- Temperature of 60ºC // heat.
- NaClO3 : Cl2 = 1:3
Moles of NaClO3 = 1/3 x moles of Cl2
= 1/3 x 206,000
24
= 2861
NaClO3 = 23 + 35.5 + 48 = 106.5g
Mass of NaClO3 = 2861 x 106.5 = 304.7kg
1000
Or 3047000g
-
- Manufacture of HCl acid.
- Manufacture of Bleachants // or Bleaching agents.
- Manufacture of plastics PVC.
-
-
- GRAPH OF COUNTS PER MINUTE AGAINST TIME FOR IODINE – 128
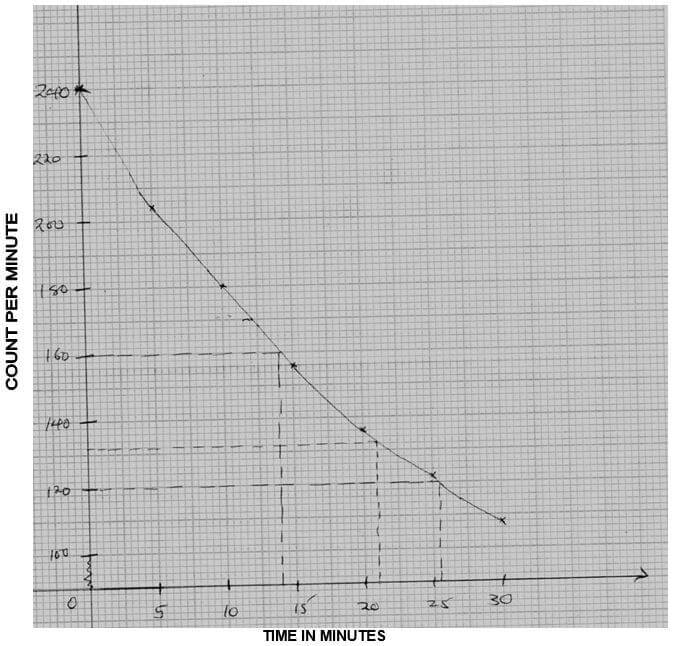
- 26 minutes ± 2 (must be shown on the graph).
- 132 ± 1
- 14 minutes ± 1
- GRAPH OF COUNTS PER MINUTE AGAINST TIME FOR IODINE – 128
-
- Change in mass of isotopes. (1mk)
232 – 216 = 16
4 4
Number of He Particles = 16 = 4 He
2 4 2
4 – particles
Change in atomic number.
90 – (4 x 2) = 90 – 8 = 82 – 83 = -1
o
1 e => an Beta particle.
-1 - 232 216 4 0
TH → Bi + 4 He e
90 83 2 -1
- Change in mass of isotopes. (1mk)
-
- A – Beta (½ mks)
B – Gamma rays (½ mk)
C – Alpha (½mk) - I – Gamma rays (B) (½mk)
II – Beta particle (A) (½mk)
III – Alpha particle (C) (½mk)
- A – Beta (½ mks)
-
-
- Electrolytic 1/Electrolysis
- Al2O3. 2H2O 1
-
- Iron (III) oxide 1
Silicon (IV) oxide 1 - NaOH is added to SiO2
- Iron (III) oxide 1
- To reduce M.P of Al2O3 and to reduce on the cost.
- Oxygen produced at anode react with carbon to form CO2.
- It forms a protective layer of Al2O3 on its surface.
-
-
- A → A2+(aq) + 2e
B2+(aq) + 2e → B(s) - A(s) + B2+(aq) → A2+(aq) + B(s)
- E red – E oxid
-0.13 – (-0.76) = + 0.63 - Introduces K+ and NO3- replace the ions consumed at electrodes.
- Insoluble PbCl2 is formed.
- A → A2+(aq) + 2e
-
- Concentrated sodium chloride / brine.
- Platinum.
- - Soap
- glass
- bleaching agents - - Expensive
- Poisonous - 2Na/Hg + 2H2O → 2NaOH + H2 + Hg
- 24 litres → 2 x 40g of NaOH
100C → 100 x 2 x 40
24
= 333.333g
-
-
- Cotton / silk / cellulose / sisal (any one) – 1mk)
- - Last longer / durable / stronger.
- Less easily attacked by acids and alkalis. -
- Hydrogen gas (1mk)
-
- CH3COOCH2CH3 - Ethylethanoate. (1mk)
- CH4 – Methane
- Alkylalkanoates
-
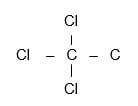
- Tetrachloromethane / Chloroform
Download Chemistry P2 Questions and Answers - Mangu High School Trial Mock Exams 2021/2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students

