INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
- Write your name and index number in the spaces provided above.
- Sign and write the date of examination in the spaces provided above.
- This paper consists of two sections A and B
- Answer all the questions in section A in the spaces provided
- In section B answer question 6 (compulsory) and either question 7 or 8 in the spaces provided after question 8.
SECTION A (40 MARKS)
Answer all the questions in this section in the spaces provided
- The cells shown below were obtained from two different plant cells which were immersed in 2% and 25% salt solutions.
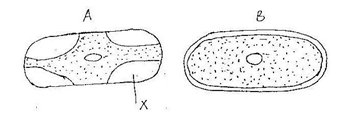
- Which of the two cells A and B, was immerse in 2% salt solution? Give a reason for your answer(2mks)
- Name the substance present in part marked x in cell a explain your answer(2mks)
- Comment on the nature of the 25% salt solution in relation to the cell sap (2mks)
-
- What biological phenomenon leads to the observations made in A (1mk)
- State one importance of osmosis in plants (1mks)
- Study the diagram below and answer the following questions.
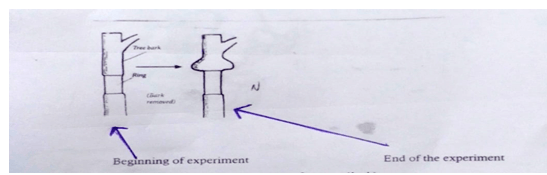
- What is the aim of the experiment? (1mk)
- Account for the observed results. (3mks)
- Does the set up shown in the experiment above affect the flow of water up the plant?
Give reason for your answer. (2mks) - What would you expect to eventualy happen to the tree that had a complete ring of the bark removed. Give a reason for your answer. (2mks)
- Study the graph below representing the growth of an organism
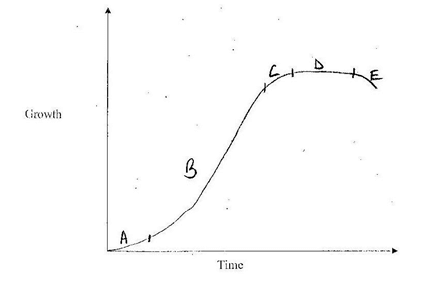
- Identify the type of growth curve represented by the graph (1mk)
- Suggest the parameters that might have been used to come up with the above graph (1mk)
- Account for the following phases
- Phase A (2mks)
- Phase B (2mks)
- Phase D (2mk)
- The diagram below represents some hormones, their sources and functions in a mammal
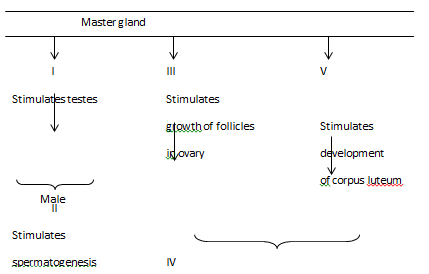
- Identify the gland described as master gland. (1mk)
- Name the hormones: (4mks)
II _______________________________________________________________
III ____________________________________________________________
V ____________________________________________________________
VI _______________________________________________________________ - Describe the consequences of deficiency of hormone II in man. (2mks)
- Other than stimulate development of uterine wall, suggest one other functions of hormone VI. (1mks)
-
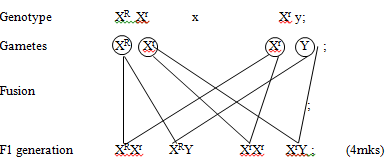
- Eye colour in fruit flies is sex-linked. Red eye colour R is dominant to white eye colour .A heterozygous red –eyed female fly was crossed with a white eyed male.
- Show the parental genotypes (1mk)
- By means of a genetic cross, determine the genotypic ratio of the offsprings (4mks)
- Explain why the actual phenotype ratio obtained from this cross could differ from the Expected (1mk)
- Name two disorders due to non-disjunction (2mks)
SECTION B (40 MARKS)
Answer question 6(compulsory) and either question 7 or 8 in the spaces provided after question 8.
- Eye colour in fruit flies is sex-linked. Red eye colour R is dominant to white eye colour .A heterozygous red –eyed female fly was crossed with a white eyed male.
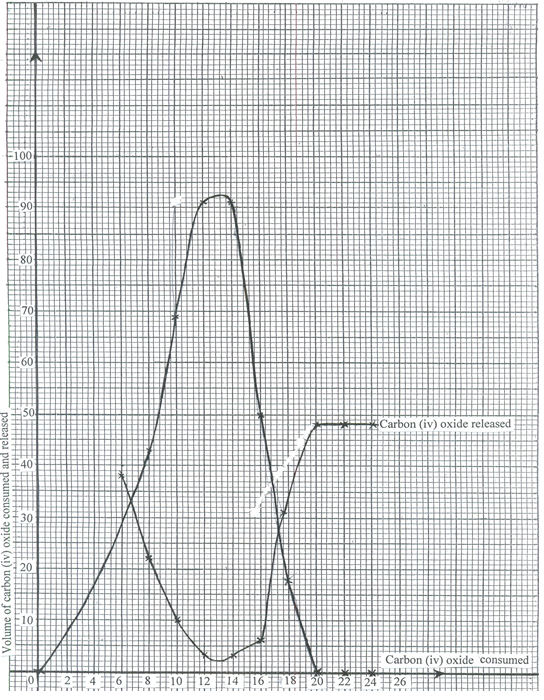
- In an experiment to investigate a certain process in a given plant species, the rate of carbon(iv)oxide consumption and the rate of carbon (iv) oxide released were measured over a period of time of the day. The results of the investigation are shown in the table below.
Time of day (hrs) 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 Carbon (iv)oxide consumption mm3/min 0 43 69 91 91 50 18 0 0 0 Carbon (iv) oxide released mm3/min 38 22 10 3 3 6 31 48 48 48 - On the same axes, draw the graphs of volume of carbon (iv) oxide consumed and released against time (7mks)
- Name the biochemical process represented by
- Carbon (iv) oxide consumption (1mk)
- Carbon (iv) oxide release (1mk)
- Account for the shape of the curve for
- carbon (iv) oxide consumption (3mks)
- Carbon (iv) oxide release. (3mks)
-
- From the graph state the time of the day when the plant attains compensation point (1mk)
- What is made by compensation point? (2mks)
- Explain how temperature affects the rate of carbon (iv) oxide consumption in a plant. (2mks)
- Explain the evidence of organic evolution. (20mks)
-
- State the causes of air pollution (5mks)
- Describe how air pollutants affect organisms hence state how air pollution can be alleviated (15mks)

MARKING SCHEME
SECTION A
- The cells shown below were obtained from two different plant cells which were immersed in 2% and 25% salt solutions.
- Which of the two cells A and B, was immersed in 2% salt solution? Give a reason for your answer. (2mks)
B-gained water by osmosis and become turgid - Name the substance present in part marked X in cell a. Explain your answer (2mks)
25% salt solution molecules moved through the permeable cell wall to fill the space left by receding cell membrane. - Comment on the nature of the 25% salt solution in relation to the cell sap
Hypertonic/highly concentrated. (1mk) -
- What biological phenomenon leads to the observations made in A
Plasmolysis (1mk) - State two importance of osmosis in plants (2mks)
Support in herbaceous plants
Opening and closing of stomata
Absorption of water from the soil
Feeding in insectivorous plants
- What biological phenomenon leads to the observations made in A
- Which of the two cells A and B, was immersed in 2% salt solution? Give a reason for your answer. (2mks)
-
- To demonstrate that translocation occurs through the phloem and that the phloem is located just beneath the bark.
- Ringing breaks the phloem which conducts food to the lower parts including roots.
Food from the leaves accumulated on the upper side of the ring causing swelling. - Water in the stem is conducted through the xylem located at the centre of the stem flow of water not affected.
- The plant will dry up since the roots will lock food to give them energy for active transport which is involved in absorption of minerals and pumping of water across caesarian strip.
- Study the graph representing the growth of an organism
- Identify the type of growth curve represented by the graph (1mk)
Sigmoid - Suggest the parameters that might have been used to come up with the above graph (1mk)
- Length/height
- Width
- Mass
- Account for the following phases
- Phase A (2mks)
- Lag phase-little growth because few cells are dividing
- Cells have not yet adjusted to the surrounding environment
- Phase B (2mks)
Exponential/log phase- rapid growh because – cells have adjusted to the- environment.
- More cells are dividing
- Cell increase is higher than death.
- Phase D (2mks)
Stationary/plateau phase- no more increase in growth because
- Nearly all cells and tissues are fully differentiated
- Cell increase and death is equal.
- Phase A (2mks)
- Identify the type of growth curve represented by the graph (1mk)
-
- Pituitary gland; (1mk)
- II - Testosterone;
III - Follicle stimulating hormone;
V - Luteinising hormone;
VI - Progesterone; (4mks) - Sterility/lack of spermatogenesis; failure of secondary sexual characteristics; (2mks)
- Inhibit production of FSH/inhibit production of LH; (1mk)
-
-
- XR Xr and Xr Y; (1mk)
Both must be present - Phenotype; Red eyed female White eyed male
- Crossing over;
Mutations; (1mk)
Any one – 1mk - Down’s syndrome; klinefelters syndrome; turners syndrome; (2 mks) first 2 – 2mks
- XR Xr and Xr Y; (1mk)
-
-
- Scale – 1mark
Plotting – 2marks
Curves – 1mark
Identity – 1 mark
Axes – 2 marks
Total 7 marks -
- Photosynthesis;
- Respiration;
-
- Rate of CO2 consumption increases from 6hrs – 12hrs; this is due to increase in light (2mks) intensity; The rate remains the same between 12hrs and 14 hrs which is the period of optimum light intensity; after which it decreases due to increase in light intensity; (3mks)
- Rate of CO2 released decreased from 6hrs to 12hrs; because some of the CO2 is used for photosynthesis; from 14hrs to 20 hrs the rate of carbon (iv) oxide released increased; because the rate of photosynthesis is decreasing as light intensity decreases after which the rate remains constant since no photosynthesis is taking place to consume the CO2 (4mks max 3mks)
-
- 8 hrs and 18 hours
- Point at which rate of photosynthesis; equals to the rate of respiration/rate of CO2 consumption equals to the rate of CO2 released; (2mks)
- Increase in temperature increases the rate of CO2 consumption upto an optimum; because temperature activates enzymes; (2mks)\
- Scale – 1mark
- Explain the evidences of organic evolution.
- Fossil records
Remains of hard parts of organisms preserved in sedimentary rocks over a long period of time. Reveals gradual changes of structures from simple to more complex ones. - Geographical distribution
The theory supposes that the present day continents was once made up of one large mass of land- Pangea
The animals on the land moved freely. Later the continent broke and drifted apart to form the present continents. This lead to isolated animals from common embryonic origin leading to formation of different species. - Comparative anatomy.
When company forms and structures of different organisms, we notice resemblance of structures performing same function /convergent evolution E.g. Wings of insects and birds. Organisms from common ancestral origin have structures that perform different functions.-divergent evolution /homologous structures. - Cell biology /comparative serology.
Structures and functions of cell organelles, cell membranes are similar in all cells suggesting a common origin. - Comparative embryology.
Embryos of vertebrates show great structural similarity suggesting a common ancestry. They have post anal tail; a notochord. Similarly in the mode of formation of embryonic membranes. - Taxonomy /classification.
It is based on evolutionary relationship. Organisms on one taxa have similar features. (20mks)
- Fossil records
-
- Causes of air pollution (5mks)
- Sulphur (iv) oxide, hydrogen sulphide and oxides of nitrogen from industries and emissions of exhaust fumes from motor vehicles;
- Carbon (iv) oxide from combustion of organic fuels;
- Carbon (ii) oxide (CO) from incomplete combustion of fuels in industries and motor vehicles;
- Dust and smoke from quarries and factories;
- Radio active radiations from atomic and nuclear plants;
- Agricultural chemicals used as sprays;
- Noise from factories and vehicles;
- Effects on organisms (8mks)
- Sulphur (iv) oxide, nitrogen (iv) oxide, dust, smoke and carbon (iv) oxide cause respiratory diseases e.g. bronchitis and irritate the respiratory system;
- Nitrogen (iv) oxide and sulphur (iv) oxide combine with atmospheric moisture to form acid rain which is corrosive, poisons plants, lowers metabolic activities/photosynthesis;
- Dust and smoke reduce the amount of light reaching the plant lowering photosynthesis;
- Combines with vapour to form fog which reduce visibility and rate of photosynthesis;
- Carbon (ii) oxide is a respiratory poison – it combines with haemoglobin reducing oxygen carrying capacity of red blood cells;
- Carbon (iv) oxide cause the green house effect that lead to global warming/change in climatic pattern;
- Radioactive radiations cause mutations and cancer;
- Some aerosols release chlorofluorocarbons that lead to depletion of the ozone layer leading to increased penetration of ultra radiations;
- Noise is irritant and cause stress in animals/it affects hearing in animals;
- Methods of alleviating (7mks)
- Erect factories and power generating stations away from residential areas;
- Build factories with chimneys to discharge waste gases up above the ground;
- Government should enforce the legislative act on environment pollution;
- Encourage the use of lead free fuels in motor vehicles;
- Use alternative less polluting fuels, hydroelectric power, solar and wind energy;
- Educate people on dangers of air pollution;
- People working in factories and jua kali that generate loud noises should wear ear muffs;
- Causes of air pollution (5mks)
Download Biology Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Kangundo Subcounty Pre Mock Exams 2021/2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students