GEOGRAPHY
PAPER 1
Instructions to candidates
- This paper contains two sections: A and B.
- Answer ALL the questions in section A. In section B, answer question 6 and any other TWO questions.

Questions
SECTION A
Answer all the questions in this section
-
- Define Physical Geography. (2 marks)
- State three importance of studying Geography. (3 marks)
-
- Distinguish between weather and climate. (2 marks)
- Give three characteristics of ITCZ. (3 marks)
-
- List three sources of sedimentary rocks. (3 marks)
- Give two examples of mechanically formed sedimentary rocks. (2 marks)
-
- Describe two ways in which biological weathering takes place. (2 marks)
- Identify three benefits of weathering to human activities. (3 Marks)
-
- What is a river confluence? (2 marks)
- List three processes of river erosion. (3 marks)
SECTION B
Answer question 6 and any other two questions in this section
- Study the map of Yimbo 1: 50000 (sheet 115/1) provided and answer the following questions.
-
- Give the latitudinal extent of the map. (2 marks)
- What is the highest point of Usengi Hill? (2 marks)
- Measure the length of the provincial boundary to the North West of the area covered by the map. Give your answer in kilometers. (2 marks)
- What is the area of Western Province in the area covered by the map? (2 marks)
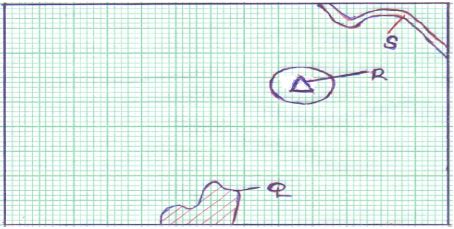
- The rectangle below represents the area in the map extract bounded by Eastings 30 and 39 and Northings 90 and 96.
Name the features marked Q, R and S. (3 marks) - Describe the characteristics of River Yala. (6 marks)
-
- Describe the relief of the area covered by the map. (4 marks)
- Explain two factors which have influenced the distribution of Settlement in the area covered by the map. (4 marks)
-
-
-
- What is folding? (2 marks)
- State three factors that influence folding. (3 marks)
-
- Apart from over thrust fold, name four other types of rocks. (4 marks)
- With the aid of well-labelled diagrams, describe the formation of an Overthrust fold. (8 marks)
- Explain four significance of Fold Mountains to human activities. (4 marks)
-
-
- Give three ways in which the shape of landmasses may influence the Movement of ocean waters. (3 marks)
- Distinguish between Constructive waves and the Destructive waves. (2 marks)
- Describe three processes of wave erosion along the coast. (9 marks)
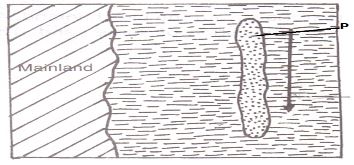
- The diagram below shows a wave deposition feature.
- Identify the feature labelled P. (1 mark)
- State two factors that favors the formation of the feature named in (i) above (2 marks)
- Students from Gedi Secondary School conducted a field study on coastal landforms.
- Identify three objectives for their study. (3 marks)
- Give three preparations they made for their study. (3 marks)
- Mention two methods they might have used to collect information before the actual field study. (2 marks)
-
-
- Define underground water. (2 marks)
- Explain how the following factors influence availability of Underground water. (2 marks)
- Slope of the land
- Vegetation cover
-
- State three conditions that are necessary for the formation of an Artesian well. (3 marks)
- State three problems that are associated with an artesian well. (3 marks)
-
- Differentiate between a Karst scenery and Karst region. (2 marks)
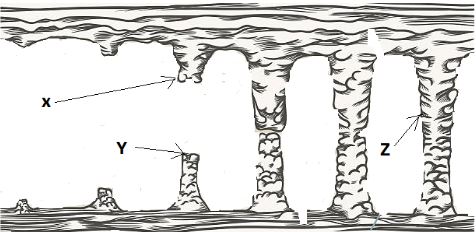
- The diagram below shows the underground features in limestone areas.
Identify the features marked X, Y and Z. (3 marks)
- Form four students of a school are planning to carry out a field study on a Karst landscape around their school.
- Name two surface features are likely to identify.(2 marks)
- Give three reasons why they needed a working schedule. (3 marks)
- Why was it necessary for them to divide into groups during their study? (3 marks)
-
-
- What is soil? (2 marks)
-
- Name three components of soil. (3 marks)
- Describe how the following factors influence the formation of soil.
- Topography (3 marks)
- Nature of the parent rock (3 marks)
-
- Define soil profile. (2 marks)
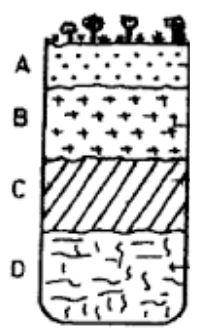
- The diagram below represents a well-developed soil profile. State the characteristics of horizon A. (4 marks)
- Explain four ways in which farming practices may lead to loss of soil fertility. (8 marks)

Marking Scheme
-
- Define Physical Geography. (2 marks)
- It is a branch of Geography that deals with the study of the natural physical environment of human kind.
- It is a branch of Geography that deals with the study of the natural physical environment of human kind.
- State three importance of studying Geography. (3 marks)
- It helps to develop skills.
- It enables learners to understand/appreciate different environmental influences.
- It encourages international awareness/co-operation.
- It helps learners to appreciate important social values.
- It promotes positive attitudes towards protection/conservation of the environment.
- It leads to development of career opportunities
- It enables learners manage time properly.
- It enables learners to explain the origin of the earth and landforms.
- Define Physical Geography. (2 marks)
-
- Distinguish between weather and climate. (2 marks)
- Weather refers to the atmospheric conditions of a place at a specific time while Climate is the average weather conditions of a place over a long period of time.
- Weather refers to the atmospheric conditions of a place at a specific time while Climate is the average weather conditions of a place over a long period of time.
- Give three characteristics of ITCZ. (3 marks)
- It is a region of low pressure belt.
- Moves with the apparent movement of the midday sun.
- Associated with high temperatures.
- It is a zone of convergence where trade winds meet. (NE and SE trade winds)
- It receives high rainfall.
- Distinguish between weather and climate. (2 marks)
-
- List three sources of sedimentary rocks. (3 marks)
- Pre-existing weathered rock.
- Mineral compounds.
- Remains of organisms (dead plants and animals.
- Give two examples of mechanically formed sedimentary rocks. (2 marks)
- Conglomerate
- Breccia
- Boulder clay
- Sandstone
- Mudstone
- Shale
- Claystone
- Siltstone
- Loess
- List three sources of sedimentary rocks. (3 marks)
-
- Name two ways in which biological weathering takes place. (2 marks)
- Through the action of plants
- Through the action of animals
- Through the action of people.
- Identify three benefits of weathering. (3 marks)
- Weathering leads to formation of soil used in Agriculture.
- Weathering produces other natural resources e.g. clay used in brick making and pottery.
- Weathering weakens rocks making them easier for people to exploit e.g. Quarrying or mining.
- Weathered rocks like the granitors are fascinating therefore act as tourist attraction.
- Name two ways in which biological weathering takes place. (2 marks)
-
- What is a river confluence? (2 marks)
- It is the point at which a tributary joins the main river.
- It is the point at which a tributary joins the main river.
- List three processes of river erosion. (3 marks)
- Hydraulic action/Quarrying process
- Corrasion/abrasion
- Solution
- attrition
- What is a river confluence? (2 marks)
- Study the map of Yimbo 1 : 50000 (sheet 115/1) provided and answer the following questions.
-
- Give the latitudinal extent of the map. (2 marks)
- 0000' to 0°15'S/15'
- 0000' to 0°15'S/15'
- What is the highest point of Usengi Hill? (2 marks)
- 1269m above sea level
- 1269m above sea level
- Measure the length of the provincial boundary to the North West of the area covered by the map. Give your answer in kilometers. (2 marks)
- 6.1 km
- 6.1 km
- What is the area of the Western Province in area covered by the map? (2 marks)
- Complete squares – 5
- Incomplete squares – 11
Area = 5+ 11/2
= 5+5.5
=10. 5 km2
- Give the latitudinal extent of the map. (2 marks)
- The rectangle below represents the area in the map extract bounded by Eastings 30 and 39 and Northings 90 and 96.
Name the features marked Q, R and S. (3 marks)- Q - River Yala
- R - Usire Hill
- S - Thicket
- Describe the characteristics of River Yala. (6 marks)
- It has many tributaries
- River Yala flows from the South-eastern/River Yala flows westwards.
- The river has many meanders.
- The river flows on a wider river valley.
- The river is permanent.
- There are swamps/papyrus swamps and marshes in some part of the river valley.
-
- Describe the relief of the area covered by the map. (4 marks)
- There are many hills in the area covered by the map.
- There are many wide river valleys in the area covered by the map.
- There is a depression occupied by Lake Sare/ L. Victoria.
- The land is flat in the area occupied by papyrus swamp.
- The land rises from the West towards the East.
- There are steep slopes on the slopes of Usengi hill.
- The highest point on the map is 1318m above sea level and the lowest point is 1140m above sea level.
- Lake Victoria has many islands.
- Explain two factors which have influenced the distribution of settlement in the area covered by the map. (4 marks)
- There are no settlements in the swampy areas because it is difficult to construct houses/waterlogged which pose a health hazard to human life.
- There are no settlement on the steep slopes/hills because it is difficult to construct houses.
- There are many settlements/clustered around market centres due to easy access to social amenities/goods and services/economic activities.
- There are few/no settlements in the area covered by thickets because it is difficult/expensive to build houses.
- There are linear settlement along the roads/motorable/main tracks because of ease of movement.
- There are clustered/nucleated settlements at road junctions in order to access social amenities/to engage in trade activities.
- There are many/clustered settlements on the gently sloping/undulating land because it is easy to construct houses.
- Describe the relief of the area covered by the map. (4 marks)
-
-
-
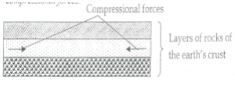
- What is folding? (2 marks)
- The process of crustal rocks distortion that causes rocks to bend upwards and downwards due to compressional forces.
- The process of crustal rocks distortion that causes rocks to bend upwards and downwards due to compressional forces.
- State three factors that influence folding. (3 marks)
- The age of the sedimentary rocks
- The flexibility or elasticity of the rocks.
- The strength or intensity of compressional forces.
- The temperature within the rocks.
- What is folding? (2 marks)
-
- Apart from overthrust fold, name four other types of rocks. (4 marks)
- Symmetrical fold
- Asymmetrical fold
- Overfolds
- Isoclinal folds
- Recumbent folds
- Anticlinorium folds
- Synclinorium folds
- With the aid of well-labelled diagrams, describe the formation of an overthrust fold. (8 marks)
- Earth’s crustal rocks are subjected to compressional forces.
- Increased compressional forces lead to formation of an overfold.
- Increased compressional forces on the overfold from a recumbent fold.
- Greater compressional forces lead to formation of a fracture along the axis of the recumbent fold to form a thrust plane.
- Compressional forces pushes the upper limb which will formed over the lower limb along the thrust plane to form an overthrustfold or nappe.
Diagram : ✓ 3 marks
Text : ✓ 5 marks
- Earth’s crustal rocks are subjected to compressional forces.
- Apart from overthrust fold, name four other types of rocks. (4 marks)
- Explain four significance of Fold Mountains to human activities.(4 marks)
- Fold Mountains may form unique scenery that may attract tourists; encouraging tourism which earn the country foreign exchange.
- The windward slopes of Fold Mountains receives high rainfall/encourages human settlement.
- The windward slopes of Fold Mountains may support the growth of forest encouraging forestry/wildlife.
- Windward slopes requires high rainfall which support arable farming/agriculture.
- Some Fold Mountains have exposed valuable materials encouraging mining.
- High rainfall on Fold Mountains or melting ice makes sources of rivers that provide water for domestic use/irrigation./industrial use.
-
-
- Give three ways in which the shape of the landmasses may influence movement of the ocean waters. (3 marks)
- May change direction of flow.
- May force ocean currents to flow along the coastline of the landmass.
- May split currents into two parts and flow in different directions.
- Distinguish between constructive waves and the destructive waves. (2 marks)
- Construction waves; a wave whose swash is more powerful than backwash leading to deposition of materials at the shore while Destructive wave; a wave whose backwash is more powerful than swash leading to more removal of materials/erosion from the shore than is being deposited.
- Construction waves; a wave whose swash is more powerful than backwash leading to deposition of materials at the shore while Destructive wave; a wave whose backwash is more powerful than swash leading to more removal of materials/erosion from the shore than is being deposited.
- Describe three processes of wave erosion along the coast. (9 marks)
- ✓P
- Abrasion / Corrasion
- When the waves breaks, the swash carries pebbles, sand, boulder and other rock fragments from the shore.
- The materials are then hurled against the base of the cliff/the foot and the face of a rock by a breaking wave.
- The leads to under cutting and rocks break up.
- Some of these materials are dragged back into the water by backwash of the wave.
- Such materials, the heave ones also erode by scratching the ocean floor while the suspended materials in the back wash hit the rock face causing particles to break off. (3X1 =3 Marks)
- Solution✓P
- Sea water has both corrosive and dissolving effects.
- Some oceans have coasts with soluble rocks which simply dissolve directly in ocean water.
- They are carried away in solution leaving hollows/cavities in the rocks/cliffs.
- Some oceans have coasts made of rocks that reacts with sea water to form soluble products that are washed away by the sea water.
- Carbon (IV) oxide dissolves in sea water forming weak carbonic acid.
- The weak carbonic acid reacts with minerals in some rocks in the ocean coast i.e. limestone.
(3X1 =3 Marks)
- Hydraulic action ✓P
- This is the erosion action caused by the force of moving water.
- In a breaking wave, large amount of water crush against the rock face/surface.
- Water continuously pound the rock face/cliff surface at intervals.
- This weakens the rock causing it to break into small particles which are carried by water.
- As water pounds the cliff/rock surface it may also force air into the cracks/crevices.
- Once inside the cracks, the air becomes compressed and increasing in pressure.
- This pressure causes widening of the cracks.
- As water retreats, the pressure is suddenly released causing the trapped air to suddenly expand explosively.
- This causes the rocks to fracture and the cracks to enlarge.
- When this process occurs repeatedly, it causes the shattering of rocks.
(3X1 =3 Marks)
- The diagram below shows a wave deposition feature.
- Identify the feature labelled P. (1 mark)
- Off shore bar
- Off shore bar
- State two factors that favour the formation of the feature named in (i) above (2 marks)
- Very gently sloping coasts
- The coasts extends deep into the sea/ocean
- Presence of sand
- Identify the feature labelled P. (1 mark)
- Students from Gedi Secondary School went out for a field study on coastal landforms.
- State three objectives for their study. (3 marks)
- To find out the wave erosional features at the coast.
- To find out the importance of coastal land forms
- To find out processes of wave transport along the coast.
(Any 3x1 = 3 marks)
- Give three preparations they made for their study. (3 marks)
- Seeking permission
- Conducted reconnaissance/pre-visit.
- Preparing work schedule
- Divided themselves into groups
- Formulated/adjusted objectives and the hypothesis
- Identify two methods they might have used to collect information before the actual field study. (2 marks)
- Observing films/photographs in the library
- Reading written materials about oceans/coasts from the internet.
- State three objectives for their study. (3 marks)
- Give three ways in which the shape of the landmasses may influence movement of the ocean waters. (3 marks)
-
-
- Define underground water. (2 marks)
- It is the water that exists beneath the earth’s surface in pore spaces in soils and rocks.
- It is the water that exists beneath the earth’s surface in pore spaces in soils and rocks.
- Explain how the following factors influence availability of underground water. (2 marks)
- Slope of the land
- There is more underground water in flat and gently sloping areas because rain water has ample time to infiltrate while steeply sloping area have little underground water.
- Vegetation cover
- Areas with thick vegetation have more underground water because plants break the speed of surface run-off of rain water, while areas with scanty vegetation cover have little underground water.
- Define underground water. (2 marks)
-
- State three conditions that are necessary for the formation of an artesian well. (3 marks)
- Aquifer to be sandwiched between impermeable rocks to prevent evaporation and percolation.
- Aquifer to be exposed in a region which is a source of water e.g. rainy area or lake.
- Month of the well must be at a lower level than the intake area to develop hydraulic pressure to force water out.
- Aquifer to dip from a region of water intake and rock layers must form a bread syncline or basin.
- State three problems that are associated with an artesian well. (3 marks)
- Water may be hot due to high temperatures.
- Water may be salty due to percolation through the salty water rocks.
- Water may fail to come out naturally when it is drawn faster than it is being replaced.
- State three conditions that are necessary for the formation of an artesian well. (3 marks)
-
- Differentiate between a Karst scenery and Karst region. (2 marks)
- A karst region is where surface and the ground is covered with limestone rock while karst scenery are the unique features in karst region that are formed due to action of water.
- A karst region is where surface and the ground is covered with limestone rock while karst scenery are the unique features in karst region that are formed due to action of water.
- The diagram below shows underground features in limestone areas.
- Identify the features marked X, Y and Z. (3 marks)
- Y - Stalagmite
- X - Stalactite
- Z - Limestone pill
- Differentiate between a Karst scenery and Karst region. (2 marks)
- Form four students of a school are planning to carry out a field study on a Karst landscape near their school.
- Give two surface features in a Karst region that they identified. (2 marks)
- Grikes and clints
- Swallow holes
- Dry valleys
- Karst window
- Dolines/dolina
- Uvala
- Polje
- Limestone gorges
- Karst Bridge
- State three reasons why they needed a working schedule. (3 marks)
- To provide an estimate of total time required for study.
- To ensure all important areas are covered and none is forgotten.
- Provides a framework to guide researcher’s to stick to the topic.
- It indicates the specific time when each activity should take place.
- Why was it necessary for them to divide into groups during their study? (3 marks)
- To create order during the study.
- To ease congestion in the area of study.
- To help participants collect data within the time given.
- To reduce fatigue among participants.
- Give two surface features in a Karst region that they identified. (2 marks)
-
-
- What is soil? (2 marks)
- Naturally occurring thin layer of loose unconsolidated materials that overlies crustal rocks forming the earth’s surface.
- The accumulation of minerals, rock particles, organic matter, water and air which found on the surface of the earth on which plants grow.
-
- Name three components of soil. (3 marks)
- Organic matter/humes
- Inorganic matter/minerals
- Soil water/moisture
- Soil air/gases
- Describe how the following factors influence the formation of soil.
- Topography (3 marks)
- Gentle slopes form deep, well drained and mature soils having clear profile.
- Steep slopes are heavily eroded forming thin and immature soils.
- Valley bottoms have deposition of weathered rock materials forming deep soils.
- Flat areas are waterlogged forming poorly drained soils
- Nature of the parent rock (3 marks)
- Rock minerals determine the fertility and chemical characteristics of the soil.
- Hard rocks weather slowly taking long time for formation soil/soft rocks weather faster to form soil.
- Rock texture determines soil structure, such that coarse grained rocks from coarse grained soil/fine grained rocks form fine soils.
- Topography (3 marks)
- Name three components of soil. (3 marks)
-
- Define soil profile. (2 marks)
- The vertical arrangement of soil in layers/horizons from the earth’s surface to the bedrock.
- The vertical arrangement of soil in layers/horizons from the earth’s surface to the bedrock.
- The diagram below represents a well-developed soil profile. State the characteristics of horizon A. (4 marks)
- Have intense chemical and bacterial activities.
- Dark in colour
- Contain humus
- Fine textual soil
- Has two soil layers.
- Zone of eluviation/leaching occurs
- Define soil profile. (2 marks)
- Explain four ways in which farming practices may lead to loss of soil fertility. (8 marks)
- Overgrazing leads to removal of vegetation (over exposing the soil to agents of erosion removing the top fertile soil)
- Continuous irrigation cause soil nutrients to be leached making the top soil deficient of soluble minerals.
- Frequent ploughing weakens the soil structure making the soil easily eroded by agents of erosion.
- Ploughing up and down the slope creates channels for surface run-off which encourage soil erosion.
- Shifting cultivation makes the abandoned land open to erosion and loss of soil fertility.
- Monoculture makes soil nutrients exhausted.
- What is soil? (2 marks)
Download Geography Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Mokasa II Mock Examination 2021/2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students