SECTION A
- A young scientist observed a bird laying her eggs in a nest and later the eggs hatched into chicks. Name three characteristics shown by the chicks that show a chick is a living thing but an egg is not (3mks)
- Which organelles should be abundant in;
- Skeletal muscle (1mk)
- Palisade tissue (1mk)
- A form 1 student was preparing temporary slides in the laboratory, in the course of preparation he carried out the following processes;
- Sectioning
- Fixation
- Staining
State the importance of the above processes (3mks)
- Why are lysosomes many in phagocytic cells (2mks)
- Differentiate between guttation and transpiration (2mks)
-
- Give a reason why xylem vessel should be dead (1mk)
- What is the role of lignin in the wall of the xylem vessel (1mk)
- Name the disease of the blood characterized by,
- Abnormally large number of white blood cells (1mk)
- Cresent –shaped haemoglobin (1mk)
- The chart below is a summary of blood clotting mechanism in a man.
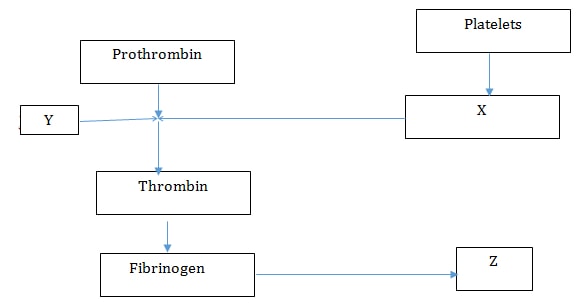
Name;- The metal ion represented by Y (1mk)
- The end product of the mechanism represented by Z (1mk)
- The graph below represents the growth of animals in a certain phylum. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
- Name the type of growth pattern shown on the graph (1mk)
- Identify the process represented by letter B (1mk)
- Name the hormone responsible for the process in (b) above (1mk)
- Explain why a mule is infertile (1mk)
- Phylum Arthropoda is the most successful of invertebrates. Explain two characteristics that make them most successful (2mks)
- Name phylum whose members possess a notochord (1mk)
-
- Define evolution and homologous structures (2mks)
- State three limitations of using fossil records as an evidence that supports organic evolution (3mks)
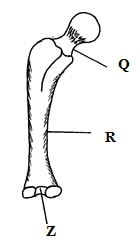
- The following is part of a kidney nephron
-
- Name the process represented by the arrows (1mk)
- Name the conditions necessary for the process named in (a) (i) above to take place (1mk)
- Identify with a reason vessel A (1mk)
- Name any two blood components that are present in vessel (A) but are absent in vessel B (2mks)
-
- The diagrammatic representation below illustrates one of the process that occurs in mammals during feeding. Carefully study it and answer the following questions
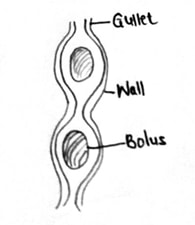
-
- Identify the process (1mk)
- State two structural adaptations of gullet to its functions (2mks)
- Name one enzyme already present in the food bolus within the gullet in man (1mk)
- State two functions of mucus secreted by the intestines (2mks)
-
- Explain each of the following;
- Variegated plants accumulates less food than non-variegated plants under similar conditions. (2mks)
- Most leaves are thin with broad leaf surface (2mks)
- State the economic importance of the following plant excretory products (3mks)
- Papain
- Caffein
- Colchicine
-
- State two processes which occurs during anaphase of mitosis (2mks)
- What is the significance of first meiotic division (1mk)
- State two ways in which HIV/AIDS is transmitted from mother to child (2mks)
- State the function of the following during pregnancy (3mks)
- Amnion
- Amniotic fluid
- Umblical cord
- Name the process by which;
- Producers convert sunlight energy into chemical energy (1mk)
- Chemical energy is converted into heat energy by consumers (1mk)
- Students from Mpesa foundation academy wanted to investigate the population of crabs in their school pond. They caught 50 crabs, marked them with white paint on the cephalothorax and then released them back into the pond. After three days, they came back and caught 50 crabs of which 3 had the white mark.
- Using the data above, calculate the population of crabs in the pond (2mks)
- Suggest three assumptions the students made during this study (3mks)
- State any two methods that can be used at home to properly manage domestic effluents(2mks)
-
- Explain how the following factors increase the rate of diffusion (3mks)
- Temperature
- Diffusion gradient
- Size of diffusing particles
- Diffusion is a passive process while active transport is an active process. Explain (2mks)
- Explain how the following factors increase the rate of diffusion (3mks)
-
- Waterlogging in terrestrial plants inhibit uptake of certain mineral ions from the soil by the plants. Explain (3mks)
- State two illustrations of Osmosis in plants (2mks)
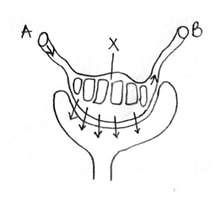
- The diagram below represents a gill of a fish
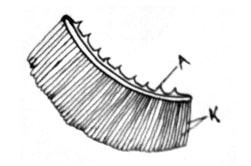
- State two ways in which a large surface area is created in structures labelled K (2mks)
- Name the type of flow system that occurs between water and blood in the capillaries present on structures K (1mk)
- Name an organ in human beings that also display the flow system named in (ii) above (1mk)
- Identical twins were separated after birth and were then raised in different environments. One in Kenya and the other in U.S.A. They rejoined after 18 years and they looked slightly different.
- Name the type of variation the twins exhibited (1mk)
- Give two observable differences likely to be noted between the twins (2mks)

MARKING SCHEME
- Irritability
- Nutrition
- Reproduction
- Locomotion
-
- Mitochondria
- Chloroplast
-
- To make thin sections that allow light to pass through.
- To maintain structure of specimen; make the sections hard enough for thin sections to be cut.
- To make cell structures distinct/clear.
- Contain lytic enzymes that break down foreign materials which can be ingested.
- Guttation is loss of water in form of water droplets through openings called hydathodes, transpiration is loss of water in form of water vapour through stomata, and cuticle of lenticels.
-
- For them not to absorb water being conducted through them
- Its a strengthening tissue/support /mechanical strength.
-
- Leukemia
- Sickle cell anaemia
-
- Calcium ions/Ca2+
- Fibrin
-
- Intermittent growth
- Moulting /ecdysis
- Ecdysone
- It’s an offspring between a donkey and a Horse that belong in different species; hence cannot produce a fertile offspring.
- Phylum Arthropoda is the most successful of invertebrates. Explain two characteristics that make them most successful (2mks)
- Hardened exoskeleton made of chitin which protect them from desiccation and predation.
- Have jointed appendages adapted for different functions (2mks)
- Chordata (1mk)
-
- Gradual change of living organisms from simple life forms to more complex forms over a long period of time-
Homologous structures – structures with common embryonic origin but modified to perform different functions. - Missing links eg some fossils not yet discovered
- Destruction – earth movement /landslides mass movement may have destroyed existing fossils
- Soft bodied parts decay away without forming fossils
- Gradual change of living organisms from simple life forms to more complex forms over a long period of time-
-
-
- Ultrafiltration (1mk)
- Sufficient pressure to force the fluid/filtrate through; pores in the endothelium of glomeruli and epithelium of Bowman’s capsule to allow selective filtration (2mks)
- Afferent arteriole – Reason; has a wider lumen direction of blood flow is towards the glomerulus. (1mk)
- Urea; glucose, amino acids; salts (any two 2 x 1=2mks)
-
-
-
- Peristalsis
- – Have circular and longitudinal muscles
- Epithelial linning has goblet cells (2mks) - Salivary amylase/ptyalin (1mk)
- – Lubricate food movement along the gut.
- Prevents digestion of mucous linning by protease enzymes.
- Helps food to stick together (2x1=2mks)
-
-
- Variegated plants have leaves little chlorophyll hence synthesis less food, non-variegated has leaves that are entirely green-has more chlorophyll hence more synthesis of food (2mks)
- Leaves have thin membrane for easy diffusion of CO2; broad leaves increases surface area for photosynthesis process. (2mks)
-
- Contains proteolytic substance used as food tenderizer.
- Mild stimulant that increases mental activities.
- Used in cancer therapy
-
- Sister chromatids separate
Sister chromatids moves to opposite poles (2mks) - Separation of homologous chromosomes (1mk)
- During birth;
- Through breastfeed (2mks)
- Sister chromatids separate
-
- It secretes the amniotic fluid (1mk)
- – Acts as shock absorber against mechanical shock.
- Connects the embryo and mother where exchange of substances occurs (1mk)
-
-
- Photosynthesis
- Respiration
-
-
- 833 Crabs
- – The marked organisms freely internet with the other organisms
There is no entry of exit of crabs, into the pond.
The mark does not affect the behaviour of the crabs.
This mark does not make the crabs prone to predators.
- Provision of facilities such as toilets and pit latrines for safe and effective disposal of human wastes.
Provision of facilities such as dustbins and composite pits for the disposal of household wastes such as kitchen wastes and papers.
-
-
- An increase in temperature increase the energy content (kinetic energy) in diffusing part times making them to move/diffuse faster.
- A higher differences in centration between two regions increases the rate of diffusion.
- The smaller the diffusingparticles the higher they move father hence faster diffusion.
- Diffusion occurs along a concentration gradient without utilization of energy while in active transport. Ions move against the concentration gradient with the utilization of energy.
-
-
- Waterlogging lowers the concentration of oxygen in the soil; inhibiting active transport process required to uptake of the ions by the root hair cells; respiration process is inhibited
- – Support in herbs
- Closing and opening of stomata
- Feeding in insect feeding plants (insectivorous plants)
- Absorption of water from the soil.
-
- They are numerous
- They are long (elongated) - Counter current flow system
- Kidney /placenta
- They are numerous
-
- Continuous variation
- – Skin colour
Height
Body weight (size)
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download BIOLOGY PAPER 1 - KAPSABET BOYS 2019 TRIAL MOCK EXAMINATION.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students

