SECTION A (40MKS)
Answer all the questions in these section
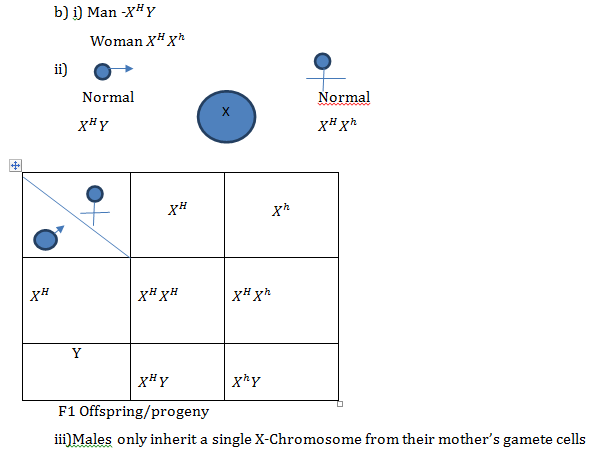
- Haemophilia is a sex linked characteristic caused by a recessive gene located on one of the sex chromosomes.
- Name the chromosome onto which the gene for haemophilia is linked to (1mk)
- A normal man for the condition marries a normal woman for the condition but sadly one of their sons develop this condition from birth.
- What are the likely genotypes of this couple? (2mks)
- Using a punnet square, carry out a cross to show why the couple gave birth to haemophiliac son (4mks)
Use (H),to represent the gene for normal condition and (h) to represent the gene for haemophilia - Why is this haemophiliac condition very common in males than in female (1mk)
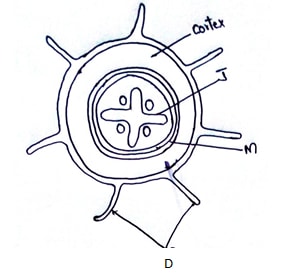
- The figure below represents an organ obtained from a section of a plant. Use it to answer questions that follow.
-
- Name the organ from which the above section was obtained. Give a reason for your answer (2mks)
- Structure labelled J is described as a mechanical tissue. Explain (1mk)
-
- Name the process by which water passes across structure M (1mk)
- Explain two ways by which cells with structures Dare adapted to their functions (2mks)
- Name two strengthening materials that strengthen the collenchyma tissue (2mks)
-
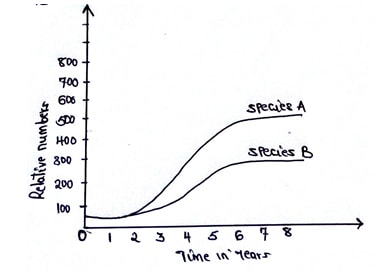
- The herbivorous mammalian species were introduced into an ecosystem at the same time and in equal numbers. The graph below represents their populations during the first seven years. Study the graph and answer the questions that follow.
-
- Which species has a better competitive ability (1mk)
- Give reason for your answer (1mk)
- Account for the shape of the curve of species A between
- One year and three years (2mks)
- Three years and seven years (2mks)
- A natural predator for species A was introduced into the ecosystem. With a reason state how the population of each species would be affected (2mks)
-
- A student from Abogeta secondary set up an experiment as illustrated below.
The visking tubing was left in iodine solution for 4 hours.- State the physiological process being investigated (1mk)
- What were the expected results in the visking tubing and in the beaker (2mks)
- Account for your expected result in visking tubing (2mks)
- Mention three factors that influences the rate of active transport (3mks)
- State the physiological process being investigated (1mk)
- An experiment was set up to investigate a factor in autotrophism in green plants.

Vaseline was applied at joint between the cork and the mouth of glass bottle and set up was left under sunlight for 6 hours.- Why was it necessary;
- To apply Vaseline (1mk)
- To cover the pot with polythene paper (1mk)
- What was the purpose of including the small animals? Give two reasons. (2mks)
-
- What would happen to the small animal if the set up was left over night in darkness
- Account for the answer in b (i) above (1mk)
- State the respiratory surface of the following organism (2mks)
- Amoeba
- Fish
- Why was it necessary;
SECTION B (40MKS)
Answer question 6 (Compulsory) and choose either question 7 or 8
- A hungry person had a meal, after which the concentration of glucose and amino acids in the blood were determined. This was measured hourly as the blood passed through the hepatic portal vein and the iliac vein in the leg. The results were as shown in the table below.
- Using the same axes draw graphs of concentration of glucose in the hepatic portal vein and the iliac vein in the leg against time (7mks)
- Account for the concentration of glucose in the hepatic portal vein from;
- 0-1 hour (2mks)
- 1-2 hours
- 2-4 hours (3mks)
- 5-7 hours (2mks)
- Account for the difference in the concentration of glucose in hepatic portal vein and the iliac vein between 2 and 4 hours (2mks)
- Using the data provided in the table explain why the concertation of amino acids in the hepatic portal vein took longer to increase (1mk)
Essays
-
- Describe the opening and closing of the stomata using the photosynthetic theory (10mks)
- Describe blood sugar regulations in mammals (10mks)
- Describe the adaptation of the following plants to their habitat;
- Xerophytes (15mks)
- Hydrophytes (5mks)

MARKING SCHEME
-
- X –chromosomes
-
-
- Root/dicot root/Dicotyledonous root reject monocot root.
- It contain lignin deposits/it is lignified to provide support.
-
- Active transport; reject osmosis
- – Presence of root hairs
- Contain lignin deposits /lignified to provide support.
Contain a large sap vacuole that has high concentration of soluble to raise its osmotic pressure to that become hypertonic thereby facilitating water uptake by osmosis from the soil.
Thin walled for rapid movement of water and mineral salts into the cell.
Thin & flexible to penetrate between soil particles to reach the water table.
Numerous mitochondria to generate enough energy helped for certain uptake of mineral ion from the soil.
- Cellulose; pectin
-
-
-
- Species A
- Rate of multiplication or growth in A is faster than of species B.
-
- 1-3 yrs – less competition, few or no predators, more suitable environmental conditions such as food, space, resource were not limiting hence population increased exponentially or rapidly.
- 3-7 yrs –shortage of resources like food or space /limiting birth rate equals death rate; population became constant. Environmental resistance has set in.
- Species A would decrease since they are preyed upon, species B would increase because there is less competition with species A and hence more resources available.
-
-
- Diffusion (1mk)
-
- The suspension in visking tubing turned blue black; while in the beaker /iodine colour retained its colour (2mks)
- The iodine molecules are smaller in size hence could diffuse into visking tubing into suspension: starch molecules are large in size, remains in visking tubing, no effect to iodine solution. (2mks)
- Oxygen concentration; change in PH, glucose concentration; temperature (any 3 =3x1=3mks)
-
-
- Prevent entry of gases of respiratory gases. (1mk)
- To ensure soil microbes do not interfere with gas volumes in glass bottle. (1mk)
- – To consume oxygen released from photosynthesizing plant.
To release carbon (IV) oxide from it respiration for photosynthesis by plant (2mks)
-
- Small animal would die. (1mk)
- Lack oxygen gas for respiration (1mk)
-
- Cell membrane
- Gill filament
-
-
- Axis – 1
Scale – 1
Plotting – 2
S/Curve – 2
Labelling - 1 -
- 0-1 hour concentration is constant or low or below normal levels in blood. No digested foods/glucose from the intestines hence no absorption of digested material.
- 1-2 hours – Sharp increase- in concentration of glucose in blood; more absorption of glucose after digestion of the food.
- 2-4 hours Glucose concentration decreasing less glucose bring absorbed; more glucose being converted to glycogen in the liver cells. Some used for tissue respiration), because all the food has been digested.
- 5-7 hours concentration of glucose stabilizes digestion has been completed hence no more absorption and excess has been converted to glycogen or respired.
- The concentration of glucose in the iliac vein is lower than in the hepatic portal vein; glucose in hepatic portal vein is not regulated by the liver. Glucose that leaves the liver to iliac vein is regulated.
- Proteins take longer to digest.
- Axis – 1
-
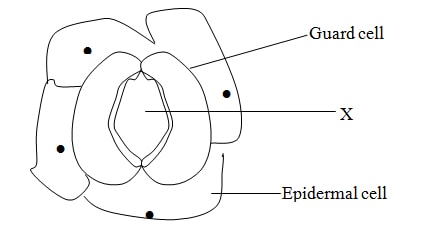
- During the day/in presence of sunlight; guard cells, synthensize glucose /sugar from the photosynthesis process; the synthesizedsugar accumulates in the guard cells, increasing their osmotic pressure (makes them hypertonic to the adjacent cells of the epidermis).By osmosis, guard cells draw in water and bulge outwards opening, the stoma.
During the night / in absence of sunlight; guard cells are unable to carry out photosynthesis hence sugar is converted into starch; starch lowers the osmotic pressure of the guard cell, hence they lose water by osmosis to the neighbouring epidermal cells become fluidhence closing the stomata. (Max =10mks) - When blood sugar rises above normal; the hypothalamusstimulates the pancreatic cells to secrete insulin hormone which travels through the blood stream to the liver when it stimulates the liver cells to;
- Convert excess glucose/sugar into glycogen
- Increase oxidation of sugar /glucose into energy carbon (IV) oxide and water.
- Convert excess glucose/sugar into fats for storage in adipose tissues.
- Inhibits conversion of glycogen into sugar.
When blood sugar/glucose drops below normal; the hypothalamus stimulates the pancreatic cells to secrete hormones glucagon which travels through the blood stream to the liver; where it stimulates the liver cells, to; - Convert stored glycogen into sugar/glucose
- Decrease the oxidation of sugar/glucose
- Convert stored fats into sugar/glucose
Blood glucose is then restored back to normal levels. (MAX=10mks)
- During the day/in presence of sunlight; guard cells, synthensize glucose /sugar from the photosynthesis process; the synthesizedsugar accumulates in the guard cells, increasing their osmotic pressure (makes them hypertonic to the adjacent cells of the epidermis).By osmosis, guard cells draw in water and bulge outwards opening, the stoma.
-
- Adaptation of xerophyte in living in their habitats.
- Leaves modified to needle like structures reducing surface area for transpiration.
- Leaf surface coated with a relatively thick and waxy cuticle.
- Have few stomata located on lower leaf surface
- Xerophytes have their stomata sunken, trapping air around stomata to reduce rate of transpiration.
- Reversed stomatal rhythm to reduce water loss.
- Xerophytes have flattened shoots and succulent tissue for water storage
- Xerophytes have deep and extensive root system for absorbing water from a light shower.
- Some Xerophytes have a short life cycle.
- Some xerophytes produces latex which reduces rate of transpiration and also are distasteful to herbivores.
- Xerophytes sheds their leaves at the onset of droughts to reduce water loss.
- Some have long tap roots to draw water from deep sub-stratum
- Folds their leaves to reduce transpiration.
- Adaptation of hydrophytes to its habitat.
- Have broad leaves to increase surface area for transpiration.
- Have numerous and large sized stomata
- Flowers are held above water to enhance pollination.
- Their root lack root hairs to minimize absorption of water.
- Have large aerenchyma tissues which gives them buoyancy.
- Have reduced root system as they are supported by water.
- Have poorly developed xylem vessel.
- Adaptation of xerophyte in living in their habitats.
Download BIOLOGY PAPER 2 - KAPSABET BOYS 2019 TRIAL MOCK EXAMINATION.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students