Q1. You are provided with:
- Solution A: dibasic acid H2C2O4●XH20 containing 2.52g in 250cm3 of solution.
- Solution B: 0.2MNaOH.
You are required to determine the value of X in the formula H2C2O4●XH20 (H=1, C=12, O=16)
Procedure
Fill the burette to the mark with solution A, pipette 25cm3 of solution B into a clean dry conical flask. Titrate solution A against solution B using phenolptherine as indicator. Repeat the titration to obtain consistent results and fill table below.
|
|
I |
II |
III |
|
Find burette readings |
|||
|
Initial burette reading |
|||
|
Volume of solution A used (cm3) |
- Calculate the average volume of solution A. (5mks)
- Calculate the Molarity of the solution A. (2mks)
- Calculate the relative formula mass of the acid solution A and hence the volume X in H2C2O4XH2O. (3mks)
Q2. You are provided with;
- Solution C: 0.2M potassium iodide solution
- Solution D: 0.2M sodium thiosulphate solution
- Solution E: Hydrogen peroxide
- Starch indicator solution.
You are required to determine the effect of concentration on rate of a reaction.
Procedure
Transfer 10cm3 of potassium iodide into test tube labeled C using a burette 5xm3 of sodium thiosulphate into test tube labeled D and 2cm of hydrogen peroxide into test tube labeled E. Using 10ml measuring cylinder and clean it before using it to measure next solution.
Transfer solution B into clean conical flask followed by 5cm3 of fleshly prepared starch solution. Simultaneously add solution C and solution E to the conical flask and immediately start to turn blue black. Record your results in the table that follows. Repeat the process using different volumes of solution E and complete table below.
|
set |
Volume of solution C (cm3) |
Volume of solution D (cm3) |
Volume of solution E (cm3) |
Volume of starch (cm3) |
Time for |
1/t sec-1 |
|
1 |
10 |
5 |
2 |
5 |
||
|
2 |
10 |
5 |
3 |
5 |
||
|
3 |
10 |
5 |
4 |
5 |
||
|
4 |
10 |
5 |
2 |
5 |
||
|
5 |
10 |
5 |
6 |
5 |
- Plot the graph of 1/t sec -1 versus volume of H2O2 (6mks)
- From the graph determine the time taken for the black to appear if volume of hydrogen peroxide solution E and cm is 4.5cm3. (3mks)
- Explain the effect of concentration to rate of reaction. (1mks)
Q3. you are provided with solid F. Carry out the following tests and record the observations and inferences in the space provided.
- Place about one third solid F into clean dry test tube and heat it strongly.
Observation
Inference
(1mk)
(1mk)
- Place the remaining solid F in a boiling tube. Add about 10cm3 of distilled water. Shake the mixture thoroughly for about one minute. Filler and divide the filtrate into four portions.
Observation
Inference
(1mk)
(1mk)
- To the first portion add two drops of phenolphthalein indicator.
Observation
Inference
(1mk)
(1mk)
- To the second portion, add two drops of hydrochloric acid.
Observation
Inference
(1mk)
(1mk)
- To the third portion, add about three drops of sodium sulphate solution.
Observation
Inference
(1mk)
(1mk)
- To the last portion, add drops of sodium hydroxide drop wise until is excess.
You are provided with solid G. Carry out the following tests and record observation and inferences in space provided.
- Place about one third of sodium G into clean metallic spatula and burn it in a Bunsen burner flame.
Observation
Inference
(1mk)
(1mk)
- Place the remaining Place the remaining of solid G in a boiling tube. Add about 10cm3 of distilled water and shake. Divide the mixture four portions.
Observation
Inference
(1mk)
(1mk)
- To the first portion of mixture in test tube and solution NaHCO3 provided.
Observation
Inference
(1mk)
(1mk)
- To the second portion add three drops of acidified potassium manganate VII.
Observation
Inference
(1mk)
(1mk)
- To the last portion add three drops of bromine water.
Observation
Inference
(1mk)
(1mk)

MARKING SCHEME
- Complete table CTü
Condition – 3 titration doneü
Incomplete table with 2 titration ü½
Incomplete table with 1 titration. 0mk
Decimal Dü
Conditions – Candidate value to be compared with school value.- Value with ± 001 of s.vü
- Value with ±2 of s.v ü½
- Value beyond ±2 of school value. 0mk
- Accuracy A ü - 30.8cm3
- Compare with school value. + or – 0.1ü+ or – 0.2 ü½
Principles of averaging P.Aü
Conditions - Value average must be shown at D within 0.2cm3 of each other. - If 3 titrations done and are within ± 0.2 but only 2 averaged, award 0mk
Find answer F.A ü½
The find answer after averaging must be shown with or without the units.- Moles of NaOH ≡> 24 x 0.2 = 0.005molesü½
1000
Moles of acid (moles ratio 1:2) = 0.005/2 = 0.0025molesü½
Molarity of the acid ≡> 0.0025 X 1000ü½
30.8 (titre value)
=> 0.081mm/Lü½ - 2.52g = 250cm3
? = 1000cm3
2.52 x 1000 = 10.08g/lü
250
Molarity 1- mol/l = g/l
RFM
RFM = 10.08/0.081 = 124.4
H2C2O4 X H2O = 124.4ü
1 x 2 + 12 x 2 + 16 x 4 + x (1 x2 +16) = 124.418x = 34.4
X= 1.9 that is 2ü
- Moles of NaOH ≡> 24 x 0.2 = 0.005molesü½
-
CT (complete table) ü (4mks)Set
Vol of C
Vol of D
Vol of E
Vol of starch
Time (sec)
1/t sec -1
1
2
160
0.006
2
3
94
0.010
3
4
82
0.012
4
5
71
0.014
5
6
60
0.017
D (decimal atleast 3dp for 1/t) ü
T (Trend) ü = (1mks)
Penaties – any unfilled space _ ½
-Values in fractions for 1/t penalize total of 1mk- 1/t = 0.0125 (must be shown on graph paper)
t = 80sec ü½ - When concentration is high the rate of reaction is high since there are more of the reaction particles. ü
- 1/t = 0.0125 (must be shown on graph paper)
-
-
- - White crystal turns to white powder ü½
-Colouless vapour condenses on the cooler part ü½ - Hydrated compound saltü - Colourless fitrates
White residue ü½ - Solid sparingly soluble ü½ or Solid mixture of soluble as insoluble salt - Phenolphthalein turns pinkü - OH-SO2-3 CO32-, HCO-3
NB All 4 ions ü
2 ions ü½
1 ion 0 - No effervescence // no bubbling
CO32- HCO-3 Absentü½ (if OH- present ü)
OH- Present ü (if CO32-, HCO-3 present ü½) - White precipitate ü½ - Ca2+, Ba2+ presentü½
if pb2+ Mentioned or Ag+ ignore - White precipitateü½ Ca2+ or Ba2+ Present ü
Insoluble in excess
- - White crystal turns to white powder ü½
-
- solid melts and burns with sooty /smocky flame. ü C = C or C ≡ Cü
- Solid dissolved forming clourless solutionü - polar organic compound ü
Polar compound.
Effervescenceü½// bubbling
- R-COOH presentü½ (ignore H+ or H3O+present)
- Purple potassium manganate vii turns colourless - C =C or- C≡ C-
R - OHü½
Orange bromine water turns colorless. ü – C = C or C≡ Cü present
Accept yellow bromine turns colourless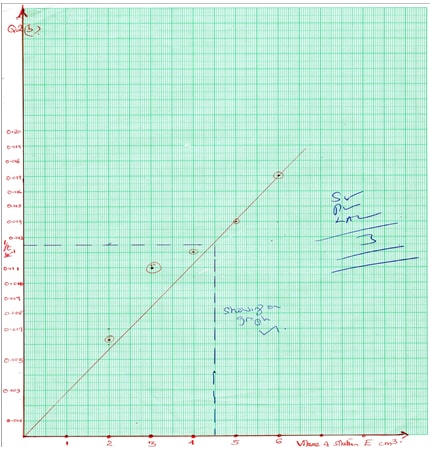
-
Download CHEMISTRY PAPER 3 - 2019 LANJET JOINT MOCK EXAMINATION.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students

