-
- Place 2ml of bicarbonate indicator in a clean test tube. Add dilute hydrochloric acid drop by drop and shake after each drop till there is a permanent color change.
- State the resulting color 1mk
- To the mixture obtained above, now add sodium hydroxide solution dropwise until there is a permanent color change. Record your observations 1mk
- From your observations in a) i) and a) ii) above, what is the nature of the bicarbonate indicator 1mk
- Place 10ml of a fresh bicarbonate indicator in boiling tube. Using a drinking straw, bubble air through the bicarbonate indicator until there is color change
- Record your observation 1mk
- What does the color obtained in b) i) above suggest about the nature of the gas breathed out 1mk
- Rinse the measuring cylinder and use it to place 2ml of lime water solution in a clean test tube. Rinse the drinking straw in (b) above and use it to bubble air through lime water solution
- Record your observation 1mk
- Suggest the identity of the gas that give rise to the observations above 1mk
-
- Name the physiological process in cells that leads to formation of gas named in (c)( ii) above 1mk
- Write down a word equation for the process named in (d) (i) above 1mk
- What is the importance of the identified process in cells of living organisms 1mk
- Place 2ml of bicarbonate indicator in a clean test tube. Add dilute hydrochloric acid drop by drop and shake after each drop till there is a permanent color change.
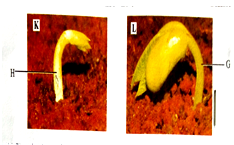
- Below are photographs of two seedlings labeled K and L. Examine them.
- Given that the two plants belongs to the same class, name the class and give a reason based on the observable features in any of the two seedlings or both. 2mks
Class
Reason(s)- State giving a reason, the type of germination that occurs in each of the two seedlings 4mks
K
L - Explain how the two types of germination you have stated in (b) (i) above occur 2mks
K
L
- State giving a reason, the type of germination that occurs in each of the two seedlings 4mks
- Name the parts labelled H and G on the seedling 2mks
- As germination progresses, both seedlings straightens. Explain how this occurs. 4mks
- Name the type(s) of root system that will develop in the two seedlings 1mk
- State another observation that will be made as seedling L straightens 1mk.
- Given that the two plants belongs to the same class, name the class and give a reason based on the observable features in any of the two seedlings or both. 2mks
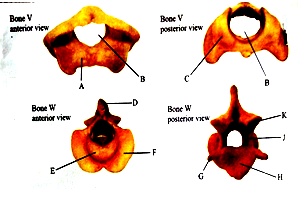
- The photographs below are specimens from the same animal of two different bones each shown in two views. Examine them.
- Identify the two specimens 2mks
Specimen V
Specimen W - Give four observable differences between bones V and W 4mks
Bone V
Bone W
- Name the structure that articulates with part labeled A 1mk
- State two roles of opening labeled B 2mks
- Name the part labelled E and state its role 2mks
Name
Role - Which of the labelled part(s) are used for articulation with adjacent vertebra 1mk
- State a common role of the parts labelled H and J 1mk
- Which of the labeled part(s) is(are) used for muscle attachment 1mk
- Identify the two specimens 2mks

MARKING SCHEME
-
-
- yellow
- red
- acid-base indicator
-
- color change from red to yellow
- the gas is acidic
-
- white precipitate formed
- carbon iv oxide
-
- respiration(aerobic)
- Glucose + oxygen→carbon iv oxide + water + energy
- for provision of energy
-
-
- class- Dichotyledonae
Reasons - presence of two cotyledons in specimen L
Net venation on plumule/leaves of specimen L(reticulate) -
- K- hypogeal; cotyledon remains in the ground
L- epigeal ; cotyledons brought above the ground - K- epicotyl elongates pulling the plumule leaves and the shoot tip out of the cotyledons and out of the ground leaving the cotyledons in the soil.
L- Hypocotyl elongates pulling the cotyledons enclosing the plumule above the ground
- K- hypogeal; cotyledon remains in the ground
- H –Epicotyl
G- hypocotyls - As the bent parts exposed to sunlight, more light on the upper side causes auxins to migrate to the lower side; the increased auxin concentration on the lower side , stimulates faster elongation of cells; on the lower side leading to straightening og the seedling
- Both will develop a taproot system
- the cotyledons will part and the leaves will expand and spread out
- class- Dichotyledonae
-
- V- Atlas
W- Axis -
Bone V
Bone W
Has a wider neural canal
Narrower neural canal
Has a very small centrum
Prominent centrum
Has a greatly reduced neural spine
Has a broad neural spine
Lack odontoid process
Has an odontoid process
- occipital condyles of the skull
- passage of the spinal cord and fitting of odontoid process of the axis
- name- odontoid process
role- it fits into the canal of the atlas and allows for rotational movements of the head - C,F and K ( mark any one)
- protection of the spinal cord
- D and G ( mark any one)
- V- Atlas
Download BIOLOGY PAPER 3 - KCSE 2019 ALLIANCE MOCK EXAMINATION.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students