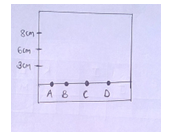
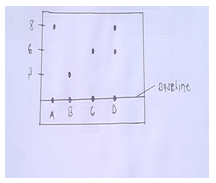
- The diagram below shows spots of pure substance A,B and C on a chromatography paper. Spot D is that of a mixture. After development ,A,B and C were found to have moved 8cm,3cm and 6cm respectively D was separated into two spots which had moved 6cm and 8cm. On the diagram
-
- Label the baseline (origin). [1mk]
- Show the positions of all the spots after development. [3mks]
- Identify the substances present in the mixture D. [2mks]
- Describe how solid ammonium chloride can be separated from a solid mixture of ammonium chloride and anhydrous calcium chloride. [2mks]
- The table below shows liquids that are miscible and those that are immiscible.
liquid
L3
L4
L1
Miscible
Miscible
L2
Miscible
Immiscible
Use the information given to answer the questions that follow- Name the method that can be used to separate L1 and L3 from the mixture of the two.[1mk]
- Describe how a mixture of L2 and L4 can be separated. [2mks]
-
- An ore is suspected to contain mainly iron.
- Describe a method that can be used to confirm the presence of iron in the ore. [3mks]
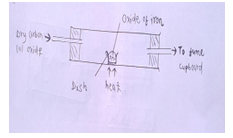
- Excess carbon (ii) oxide gas was passed over a heated sample of an oxide of iron as shown below. Study the diagram and answer the questions that follow.
Mass of empty dish=10.98g
Mass of empty dish +oxide of iron=13.30g
Mass of empty dish +residue=12.66g- Determine the formula of the oxide of iron. (Relative formula mass of iron oxide=232, Fe=56.0, O=16.0) [3mks]
- Write an equation for the reaction which took place in the dish. [1mk]
- Corrosion is a destructive process in which iron is converted into hydrated iron (III) oxide. State:
- Two conditions necessary for rusting to occur. [1mk]
- One method used to protect iron from rusting. [1mk]
- Explain why it is not advisable to wash vehicles using sea water. [2mks]
-
- State the Hess’s law. [1mk]
- The enthalpies of combustion of calcium, carbon and decomposition of calcium carbonate are indicated below:
C[s]+ O [2][g] → CaO[s]: H =-635KJmol-1
C[S]+O2[g] → CO2[g] H =-394KJmol-1
Enthalpy of decomposition of Ca CO3=+178KJmol-1- Draw an energy cycle diagram that links the enthalpy of formation of calcium carbonate to enthalpies of combustion of calcium, carbon and decomposition of calcium carbonate. [2mks]
- Determine the enthalpy of formation of calcium carbonate. [2mks]
- Some average bond energies are given below.
Bond energy in KJmol-1
C-C 348
C-H 414
Cl-Cl 243
C-Cl 432
H-Cl 340
Calculate the energy change for the reaction below. [3mks]
C2H6(g)+Cl2(g) →CH3CH2Cl(g)+HCl(g)
-
- Use the standard electrode potentials for A, B, C, D andF given below to answer the questions that follow.
Eθ (Volts)
A2+[aq] +2e ⇋ A[s] -2.90
B2+[aq]+2e ⇋ B[s] -2.38
C+[aq]+2e ⇋ C2[g] 0.00
D2+[aq]+2e ⇋ D[s] +0.34
F2[g]+e- ⇋ F-[aq] +2.87- Which element is likely to be hydrogen? Give a reason for your answer. [2mks]
- What is Eθfor the strongest reducing agent? [1mk]
- Calculate the e.m.f of the cell that would be formed when half cells of Band D are combined.[1mk]
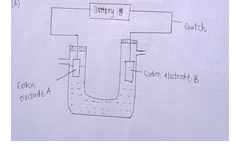
- Aqueous copper (II) sulphate was electrolysed using the set shown below.
- When the switch was closed, a gas was produced at electrode B.Which electrode is the anode?[1mk]
- Write the half equation for the reaction at electrode B. [1mk]
- What happens to the pH of the electrolyte above during electrolysis? Explain. [2mks]
- If carbon electrode were replaced with copper electrodes in the cell above, write the equation for the reaction that would occur at the anode. [1mk]
- During electrolysis of copper [II] sulphate using copper electrodes, a current of 0.2 ampheres was passed through the cell for 5 hours. Determine the change in mass of the cathode that occurred as a result of the electrolysis process. (Cu=64, IF=96500C). [3mks]
- Use the standard electrode potentials for A, B, C, D andF given below to answer the questions that follow.
-
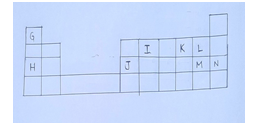
- The grid below is part of the periodic table. Letters are not actual symbols. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
- Give the letters representing atoms that can form a singly charged ion. [1mk]
- Identify the most electronegative element in the grid. Explain. [2mks]
- Identify the strongest reducing agent. [1mk]
- Write the formula of the most stable compound formed when J and K react. [1mk]
- Give the name of the type of bond in the compound formed in (IV) above. [1mk]
- Give the chemical family name of L and M. [1mk]
- Write the ionic equation for the reaction in which gas L is bubbled through a solution with ions of M. [1mk]
- Element P is an alkaline earth metal and belongs to periodic 2.Indicate its position on the grid.[1mk]
- Use the information in the table below to answer the questions that follow.
ELEMENT
ATOMIC NUMBER
MELTING POINT(
Q
11
98
R
12
650
S
14
1410
T
17
-102
U
18
-189
V
19
64
Give a reason why the melting point of- Q is higher than of V. [1mk]
- R is higher than Q. [1mk]
- S is the highest [1mk]
- The grid below is part of the periodic table. Letters are not actual symbols. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
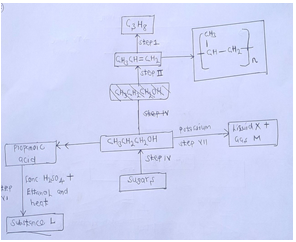
- Study the flow chart below and answer the questions that follow.
-
- Name the type of reaction in the following steps.
- Step III [1mk]
- step IV. [1mk]
- Name the important reagents and conditions in
Step1: Reagent [1mk]
Condition [1mk]
Step II: Reagent [1mk]
Condition [1mk]
Step V: Reagent [1mk]
Condition [1mk]
- Name the type of reaction in the following steps.
-
- Write a balanced equation for the reaction taking place in
Step VI. [1mk]
Step VII [1mk] - Give the systematic name of liquid X and substance L
Liquid X [1mk]
Substance L [1mk]
- Write a balanced equation for the reaction taking place in
-
- If the relative molecular mass of compound formed in step III is 42 000, determine the value of n in the compound. (C=12.0, H=1.0). [2mks]
- State one disadvantage of continued use of items made from the compound formed in d (i) above.[1mk]
-
- Use the flow chart below to answer the questions that follow.
- Name:
- Substance C
- Compound K
- Write the formula of compound K. [1mk]
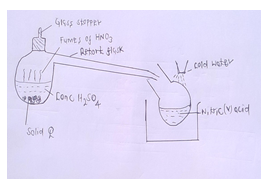
- The following set-up is used to prepare nitric [v] acid in the laboratory.
- All the apparatus used during preparation of nitric [v]acid are made by glass. Give a reason.[1mk]
- Name solid Q. [1mk]
- Give a reason why it is possible to separate nitric (v) acid from the sulphuric (VI) acid used as one of the reagents. [1mk]
- Give 2 uses of Nitric (v) acid [2mks]
- In an experiment 1200cm3 of ammonia gas measured at r.t.p reacted completely with copper (ii) oxide. Calculate
- The mass of copper formed given the formula of reaction. [3mks]
3CUO[s]+2NH3 [g] → 3CU [s]+3H2O[l]+N2[g] - The volume of Nitrogen gas formed N=14, H=1.0, O=16.0) [2mks]
CU=64MGV at r.t.p=24 dm3.
- The mass of copper formed given the formula of reaction. [3mks]
- Name:

MARKING SCHEME
-
-
- I & II
- A and C
- I & II
- Submission would separated the two since ammonium (NH4cl) sublimes but calcium chloride (Cacl2) does not. Heat the mixture. Ammonium chloride sublimes into vapour and deposited on the cooler part of the boiling tube.
-
- Fractional distillation
- Separating funnel/density separation method since the two liquids are immiscible, pour both the liquids in a separating funnel and allow to settle, the denser liquid will settle down and less dense will form a second layer on top. Open the tap and run out the liquid in the second layer in the funnel.
-
-
- To a sample of the ore add dilute sulphuric acid or hydrochloric acid and warm. Filter the mixture.
To a portion of the filtrate, add sodium hydroxide or ammonium hydroxide drop wise until in excess. Formation of the green precipitate or brown precipitate shows presence of iron. -
- Mass of oxygen =13.30-12.66=0.64g
Mass of iron=12.66-10.98=1.68g
FE
O
0.03
0.04
3
4
Molecular formula=Fe3O4 - Fe3O4[s]+4CO[g] →3Fe[s]+4CO2[g]
- Mass of oxygen =13.30-12.66=0.64g
-
- Oxygen, water
- Galvanizing, painting, electroplating
- Sea water is salty. Salty water accelerates the rate of corrosion.
- To a sample of the ore add dilute sulphuric acid or hydrochloric acid and warm. Filter the mixture.
-
- The heat change of a reaction is the same regardless of the route (path)followed.
-
- Ca[s]+C[s]+ O2[g]→CaCO3[s]
- CaO[s] +CO2[g]
DH1=DH2+DH3+DH4
=-635+(-394)-(+178)
=-1207KJmol-1
- C-C C-H Cl-Cl C-C C-Cl C-H H-Cl
348+(414) 6+243→348+432+5(414)+340
3075KJ 3190KJ
DH=EP-ER
=3190-3075
=+115KJmol-1
-
-
- C It has an Eθof zero or REFFERENCE ELECtrodeor used as the standard electrode.
- -2.90V reject A or A-
- E cell=E(reduced)-E(oxidised)
+0.34- - 2.38
=+2.72V
-
- B
- 4OH-[aq] → 2H2O[l] +O2[g]+4e-
- Becomes acidic //ph-lower/reduces-H+ions remains in solution as OH- ions are discharged.
- Cu[s] → Cu2+[aq]+2e-
- Q=It→Q=0.2 c
Cu2+ +2e→Cu[s]
64g→2 C
? 3600C
=1.194g
This cathode increased in mass by 1.194g
-
-
-
- Land M
- L Non-metal with the smallest atomic size hence the highest electron affinity.
- H
- J2K3
- Ionic/electrovalent
- Halogens (reject group seven)
- L2[g]+2M-[aq] → 2 L-[aq] +M2[g]
- Position
G
P
H
-
- V has a larger atomic size hence metallic bond weaker.
- R has more protons, hence greater nuclear charge making the metallic bond stronger.
- Giant atomic structure.
-
-
-
- Polymerization
Fermentation - Step I
Reagent: hydrogen gas
Condition: Nickel or platinum catalyst
STEP II
Reagent: concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid
Condition-temp (160 C -180 C)
Reagent: acidified potassium manganete (vii)
Condition-heat
- Polymerization
- STEP VI
CH3CH3CH2OH+CH3CH2OH→CH3CH2COOCH2CH3+H2O
STEP VII
2CH3CH2CH2OH+2K→2CH3CH2CH2OK - Potassium proxide
Ethylpropanoate
- STEP VI
- C3H6 decolourises acidified purple KMNO4 while C3H8 do not
C3H6 decolourises brown/yellow bromine water while C3H8 do not.
C3H6 burns with sooty flame while C3H8 burns with a blue flame. -
- (C3H6) n=42000
42n=42000 - Non-biodegradable
- (C3H6) n=42000
-
-
-
- Ammonium chloride/Ammonium sulphite
- Ammonium nitrate
-
- Nitric (v) acid attacks rubber and cork connections.
- Potassium nitrate
- Nitric [v] acid is more volatile and is readily displaced from nitrates by the less volatile sulphuric (VI) acid.
- Manufacture of fertilizers, explosives, dyes and drugs, purification of metals.
2NH3[g]+3CUO[S] →3CU[s]+3H20[l]+N2[g]
2 24dm3 of NH3=3 64gof CU
1.2dm3of NH3=?
=4.8 gof CU - 2 24dm3 of NH3=24dm3 of N2
1.2dm3ofNH3=?
=0.6 dm3/600cm3of N2
-
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download CHEMISTRY PAPER 2 - KCSE 2019 MARANDA MOCK EXAMINATION.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students