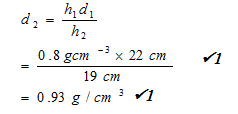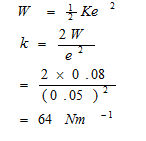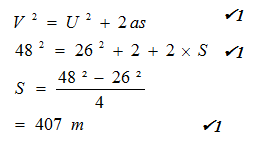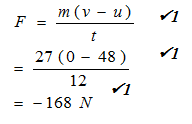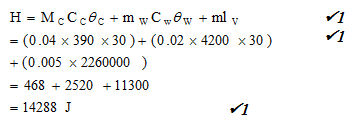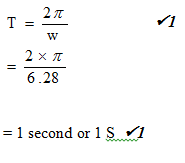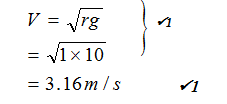SECTION A (25 marks)
Answer ALL the questions in the spaces provided.
- Some water was put in a burette so that the level read 35.6cm³. 50 drops were then allowed to fall from the burette. The average volume of one drop was 0.14cm³. What is the new reading of the burette? (2 marks)
- Explain why water curves in a test as shown in figure 1 below. (1 mark)
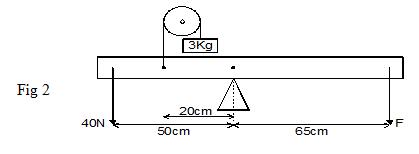
- Figure 2 below represents a system in equilibrium
Determine the force F needed to maintain the equilibrium. (3 marks)
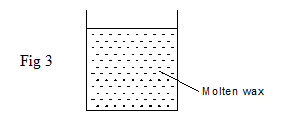
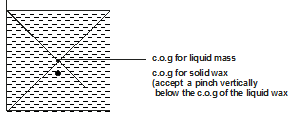
- The figure 3 below shows a beaker containing molten candle wax. Indicate on the same diagram the position of the centre of gravity when the candle wax solidifies. (1mark)
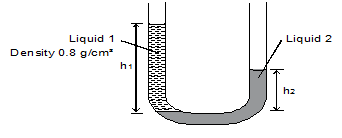
- Figure 4 below shows a U tube manometer containing two liquids. Given that h1 and h2 are 22cm and 19cm respectively, find the density of the liquid 2. Give your answer to 2 significant figures. (3 marks)
- Explain why the rate of diffusion of a gas decreases with decrease in temperature. (1 mark)
- State the reason why steel is normally used to reinforce concrete in construction other than aluminium (1 mark)
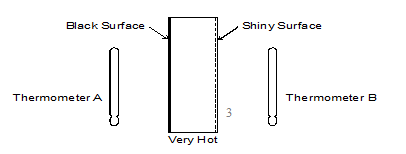
- Figure 5 below shows a thick copper plate that is very hot, one side is black and the other is shiny. Two thermometers are placed at the same distance from each side as shown.
Neglecting heat loss to the surrounding, state with a reason which thermometer records a higher temperature after 10 minutes.(2 marks)
- The work done in stretching a spring by 50mm is given as 0.08J. Calculate the spring constant. (3 marks)
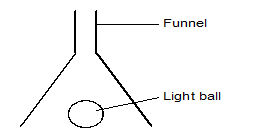
- Figure 6 below shows an inverted funnel placed above a light ball.
Fast moving air is then blown through the neck of the funnel. State and explain the observation made.(2 marks)
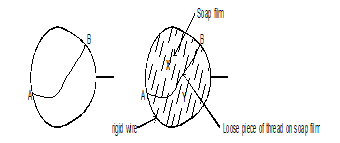
- Figure 7(a) below shows a loop of a wire with a string tied loosely at point A and B. When the loop was dipped into a soap solution and then moved out a soap film is formed as shown. In fig 7(b) below. State and hence explain the observation made when side X of the film is broken. (2 marks)
- Differentiate between speed and velocity. (1 mark)
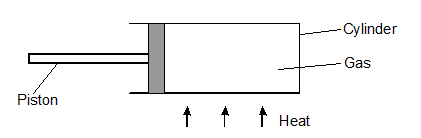
- Figure 8 below shows a gas enclosed in a container.
State and explain using the kinetic theory of matter. What will happen to the piston when the cylinder is heated. (2 marks)
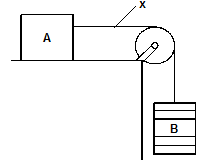
- Figure 9 below shows block A placed on a bench connected with a piece of thread through a pulley to a pan B where masses are being added.
State a condition that must be met for block A to slide towards the right. (1 mark)
SECTION B (55 marks)
-
- Differentiate between speed and velocity. (1 mark)
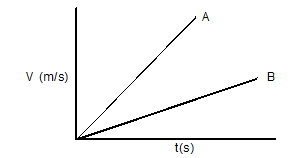
- Figure 10 below shows velocity-time graphs for two objects A and B drawn on the same axes.
State with a reason which of the two objects stops in a shorter distance when the same size of force in applied against each given that they are of equal masses. (2 marks) - An object moving at 26m/s starts to accelerate at 2m/s² so that its velocity becomes 48m/s. Find
- The distance moved during this acceleration. (3 marks)
- The object is now braked so that it comes to rest in a time of 12 seconds. Find the braking force if its mass was 27000g. (3 marks)
-
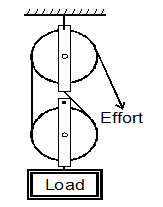
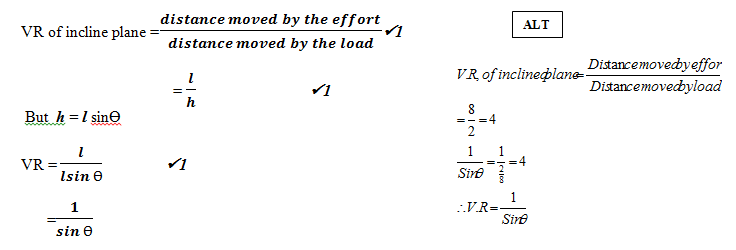
- Figure (11) below shows a pulley system used to lift a load.
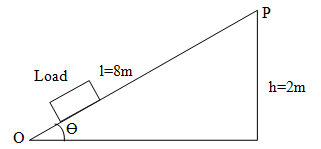
Determine the velocity ratio. (1 mark) - The figure (12) below shows a loading ramp of length l, 8m and height h, 2m. Bags weighing 1000N each are conveyed from point O to P along the plane. Each bag experiences a friction force of 50N.
Show that the velocity ratio is given by 1/Sin q(3 marks) - State how you can increase for the arrangement
- Velocity ratio (1 mark)
- Mechanical advantage (1 mark)
-
- The total work done by the effort on each bag. (3 marks)
- The efficiency of this system. (2 marks)
- Figure (11) below shows a pulley system used to lift a load.
-
- Define specific heat capacity. (1 mark)
- To determine the specific heat capacity of a solid by the method of mixtures, a solid of known mass was heated to very high temperature then quickly transferred to a liquid in a well lagged calorimeter.
- Give a reason why the solid was quickly transferred.(1 mark)
- List two possible sources of error in this experiment. (2 marks)
- 50g of a metal was heated to a temperature of 600°C. The metal was then quickly transferred to a copper calorimeter of mass 40g containing 20g of water at 70°C. It was observed that 5g of water vapourised. Given that the specific heats capacity of water and copper are 4200J/kgK, 390J/kgK respectively and specific latent heat of vaporization in 2260000 J/kg
- An expression for the heat lost by the metal given that its specific heat capacity in Cm (2 marks)
- The heat gained by water and calorimeter. (3 marks)
- The specific heat capacity of the metal. (3 marks)
-
- State Archimedes principle (1 mark)
- Figure 13 below shows a test tube floating in water in a tall beaker.
- State what can be done to make the text tube float vertically upright. (1 mark)
- Explain how the test tube may be calibrated to measure relative densities of liquids.(2 marks)
- State what can be done to increase the sensitivity of such an instrument.(1 mark)
- Figure 14 below shows a block of dimensions 2cm × 4cm × 12cm floating in a liquid of density 1250kg/m³
Find- The upthrust on the block. (3 marks)
- The weight of the block. (1 mark)
- The force needed to just submerge the block completely. (3 marks)
-
- Define angular velocity. (1 mark)
- Figure 15 below shows a small mass being rotated in a horizontal circle through a plastic tube. It is observed that as the small mass is rotated at constant speed, the heavy mass remains at the same horizontal level.
- State one adjustment that can be done to make the heavy mass move upwards. (1 mark)
- State the effect on the small mass if a heavier mass was used in place of the one above and the radius of rotation remains constants. (1 mark)
- A stone of mass 200g tied to a long string 1m long and whirled round in a vertical circle at an angular speed of 6.28 rad/s.
- Why is the stone said to be accelerating. (1 mark)
- Determine the linear velocity. (2 marks)
- Its periodic time. (2 marks)
- The critical speed of the stone if it is to describe a vertical circle. (2 marks)
- State a factor that determines the angle at which a road should be banked at a bend. (1 mark)

MARKING SCHEME
- Volume of 50 drops
= 0.14cm³ × 50
= 7 cm³ √1
Burette reading
= 35.6cm³ + 7cm
= 42.6cm³ √1
- Adhesive forces are greater than the cohesive forces. √1
- Clockwise moments = anticlockwise moments √1
Accept F1d1 = f2d2 for formula mark
(20cm × 30N)+(65cm × F) = 50cm×40 N
600 + 65F = 2000
65F = 1400
F = 1400
65
= 21.54N √1 -
- h1d1g = h2d2g √1
h1d1 = h2d2
(Answer should be given to 2.sf)
- As the temperature decreases, the kinetic energy of the gas molecules / particles decreases and thus rate of movement decreases √1
OR
As the temperature decreases, the velocity of the gas molecules decreases and thus they move at a lower rate.
- Steel and concrete expand / contract at the same rate unlike steel and aluminium which expand/ contract at different rates. √1
Accept: Steel and concrete have the same linear expansivity unlike aluminium and concrete.
- -A √1
-Black surface is a better emitter of radiation as compared to the shiny surface and thus more heat is absorbed by thermometer A compared to thermometer B. √1
-
- The light ball moves upwards. √1
The pressure above the ball is lowered / becomes lower / reduces and thus atmospheric pressure / pressure below the ball pushes it upwards.√1 - The piece of thread becomes tight and stretches towards region Y.√1
Surface tension force pulls the thread towards region Y.√1
- Displacement is distance in a specified direction while distance is length of space between the two points.√1
- The piston moves outwards / the piston moves towards the left. √1
As the temperature increases, kinetic energy of the gas molecules increases and this increases the rate of collision between the gas molecules and walls of the container. This causes pressure of the gas to increase thus pushing the piston outwards.√1
- Weight of B should be greater than the frictional force between block A and the surface.√1
SECTION B -
- Speed is rate of change distance moved with time taken while velocity is rate of change of displacement covered with the time taken.√1
- B √1
Acceleration of A is greater than that of B and thus A needs greater force than B.√1 -
-
-
- 2√1
-
-
- -increase the length of the incline √1
- reduce the angle of inclination - - reduce the angle of inclination √1
- reduce friction between load and inclined surface.
- -increase the length of the incline √1
-
- W = work done against gravity + work done against friction
= mgh + Fd √1
= 1000 × 2 + 50 × 8 √1
= 2000 + 400
= 2400J √1 -
- W = work done against gravity + work done against friction
-
- Amount of heat required to raise temperature of a unit mass of a substance by 1k.√1
-
- To ensure that the temperature of the furnace is maintained by the solid material / to ensure minimum heat loss to the surroundings during transfer.√1
- Error while reading the thermometer √1
Error while taking reading of the mass.
There is heat lost to the surrounding during transfer.
-
- H=mCmΔƟ √1
= 0.05 × Cm × (600 - 100)
= 25 Cm √1 -
- H = MCq √1
14288 = 25Cm √1
Cm = 14288
25
= 571.52 Jkg-1k-1√1
- H=mCmΔƟ √1
-
- When a body is wholly or partially immersed in a fluid, it experiences an upthrust equal to the weight of the fluid displaced √1
-
- Adding some heavy mass / sand into the test-tube
- Dip the test-tube in liquids of different densities and mark the level to which the tube floats in each.√1
- Using a test-tube of lower radius / using a thinner test tube.√1
- Adding some heavy mass / sand into the test-tube
-
- Upthrust = weight of liquid displaced
= 2 × 4 × 8 × 1250 × 10
100 100 100
= 0.8 N - Weight of block = Upthrust = 0.8 N √1
- Force = weight of fluid to be displaced √1
= 0.04 × 0.04 × 0.02 × 1250 × 10 √1
= 0.4N √1
- Upthrust = weight of liquid displaced
-
- Angular velocity is the rate of change of angular displacement with time.√1
-
- Increasing the speed of rotation of the small mass √1
- Velocity of the small mass increases.√1
-
- Direction of motion of the stone changes continuously. √1
- V = wr √1
= 6.28 × 1
= 6.28 ms-1 √1 -
-
- Frictional force between the road and the tyre.
radius of the bend
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download PHYSICS PAPER 1 - KCSE 2019 MARANDA MOCK EXAMINATION.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students