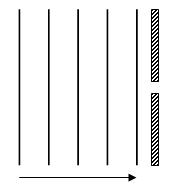
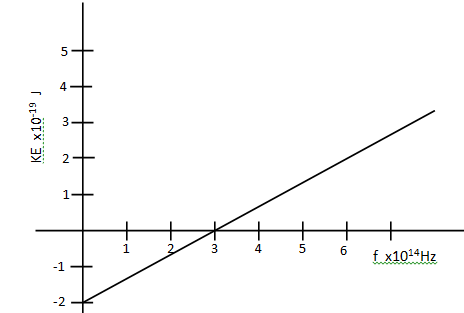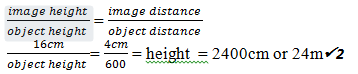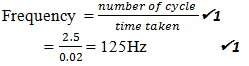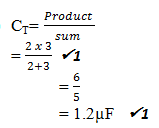- In a certain pinhole camera, the screen is 4cm from the pinhole. When the camera is placed 6m away from a tree, a sharp image of the tree 16cm high is formed on the screen. Determine the height of the tree (2 mks)
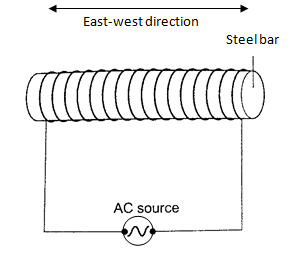
- A student set up the apparatus shown below to magnetise a steel bar
State two mistakes in the set- up (2 mks)
- When a bulb is connected between two plates of a simple cell the bulb lights up. However, the brightness of the bulb fades after a while
- Explain why the bulb lights up (1 mk)
- Why does the brightness fall (1 mk)
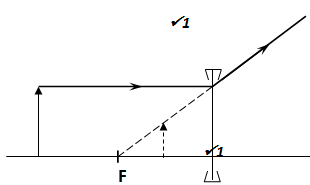
- An object is placed infront of a diverging lens and forms an image at the position shown in the diagram below.
Use a ray diagram to locate the principal focus of the diverging lens above (2 mks)
- An electric heater rated 240v, 3kw is to be connected toa 240v mains supply through a 10A fuse. Determine whether the fuse is suitable or not (2 mks)
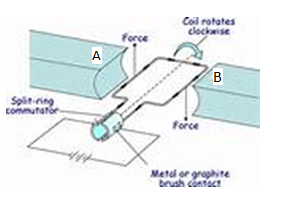
- The figure below shows a current carrying coil in a magnetic field. The direction of current and the resultant force are shown. Study the figure and answer the questions below
- Label the poles marked A and B
- Explain the purpose of the split ring in the diagram (2 mks)
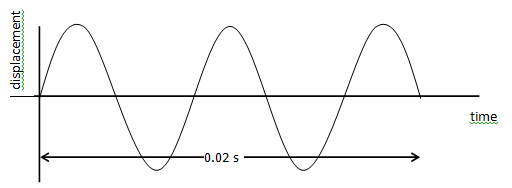
- The figure below shows a displacement time graph for a wave motion
What is the frequency of the wave (2 mks)
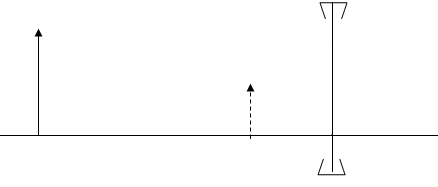
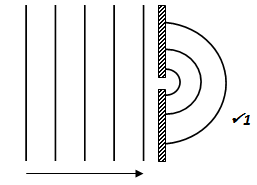
- The figure below shows a series of wave fronts one wavelength apart approaching a gap between barriers in a ripple tank
On the same diagram, show what happens when the waves pass through the gap (1 mk)
- A thunderclap is heard 3.2 seconds after the lighting is seen. If the speed of sound is 340m\s, determine the distance of the lighting flash (2 mks)
- State one cause of power loss in a long distance transmission wires and how this loss can be minimized (2 mks)
- For a given source of x-rays, how would the following be controlled
- Penetrating power (1 mk)
- Intensity (1 mk)
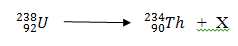
- In a certain radioactivity uranium- 238 undergoes decay to become Thorium – 234 as shown below
Identify the radiation X emitted (1 mk)
- What is doping as applied in electronics (1 mk)
SECTION B: (55MKS)
-
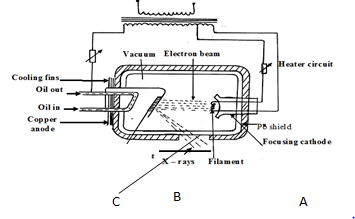
- The figure below shows a modern X-ray tube
- Name the part labeled C (1 mk)
- Name a metal that can be used as B in the diagram and state the reason why it is appropriate (2 mks)
- Why is the tube evaluated (1 mk)
- Given that 99% of the energy of the electrons to converted into heat while the rest is converted into x-rays, determine the frequency of the x-rays produced given that the accelerating potential is 100KV (plank constant = 6.63 x 10 -34 Js, e = 1.6x 10-19c ) (3 mks)
- State one application of x-rays in medical field (1 mk)
-
- state two characteristics of electromagnetic radiation (2 mks)
- Arrange the following electromagnetic radiations in order of their increasing wavelength infrared, ultra violet, gamma rays, X- rays (1 mk)
- The figure below shows a modern X-ray tube
-
- State the Ohm’s law (1 mk)
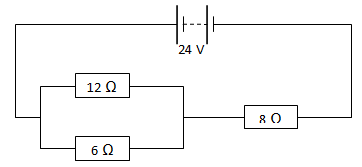
- the figure below shows an electric circuit
- calculate the effective resistance of the circuit (2 mks)
- The current flowing through the 8Ω resistor (2 mks)
- The current through the 6Ω resistor (2 mks)
- In large current circuits, large resistors in parallel are preferred to low resistors in series Explain (2 mks)
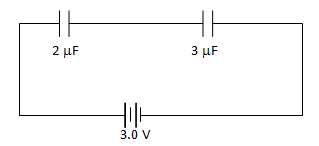
- A 2 µF capacitor is connected in series with a 3µF capacitor as shown below.
Determine- The effective capacitance of the circuit (2 mks)
- The charge stored in the 2µF capacitor (2 mks)
-
- state two factors that affect photoelectric effect (2 mks)
- The diagram below shows a graph of kinetic energy KE against frequencyfof incident radiation for a given metal surface
Given the equation of the graph is KE = hf –W0
Use the graph to determine- Plank’s constant h (3 mks)
- threshold frequency f0 (1 mk)
- Work function W0 (1 mk)
- A surface whose work function w0 = 6.4 x 10-19 J is illuminated with light of frequency 3.0 x 10-15 Hz. Find the minimum KE of the emitted electrons ( h= 6.4 x 10-34 Js) (4 mks)
-
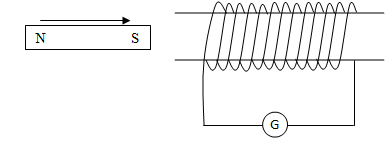
- State the lenz’s law of electromagnetic induction ( 1 mk)
- A bar magnet is moved into a coil of an insulated copper wire connected to a zero centre galvanometer as shown below
- show on the figure above the direction of the induced current in the coil (1 mk)
- State and explain what is observed on the galvanometer when the south pole of the magnet is moved into and then withdrawn from the coil (2 mks)
- A transformer has 800 turns in the primary and 40 turns in the secondary winding. The alternating voltage connected to the primary is 240V and current of 0.5.A. Determine
- the power in the secondary if transformer is 95% efficient (2 mks)
- explain how power losses in a transformer are reduced by having
- soft iron core (1 mk)
- lamination (1 mk)
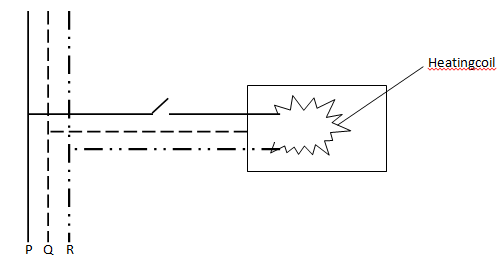
- The figure below shows the electric wiring of an electric iron box
- identify wires P and R (2 mks)
- The heating element of the iron box in (i) above is made of a wire of resistance 28.8 Ω and is connected to a 240V mains supply.
Determine- The power rating of the iron box (3 mks)
- The current flowing in the circuit (2 mks)
- The cost of using the iron box for half an hour per day for 30days if the cost per unit is sh 12.50 (3 mks)

MARKING SCHEME
- Used an a.c instead of d.c √1
Placed the steel bar in East- West direction√1
-
- Due to flow of charge/ current through it√1
- Polarization occurs/ bubbles covers the positive plate
-
- P = IV
3000 = I x 240
I = 12.5A √1
hence not suitable v1
-
- A= North
B= South √1
Deny if north–north or south – south - Helps reversing the direction of the current in the coil √1
This ensures that the force on the coil remain the same direction.√1
- A= North
-
-
- Speed =distance/time
340m/s =distance/3.2
Distance = 340x 3.2 = 1088m √1
- Heating
High resistance √1
Transmitting at high voltage /low current √1
Use of thicker cables
-
- Accelerating voltage √1
- Heating current √1
- Alpha radiation√1
- Doping is introduction of a foreign atom into crystal of pure – semi conductor .√1
-
-
- copper anode
- molybdenum / tungsten
– has high melting point - To maintain high speed of the electrons/ to maintain high energy of the electrons.
- copper anode
- E = hf
1/100 x ev = hf
= 0.241 x 1018Hz
= 2.41 x 1017Hz - -Treatment of cancer
-x- ray photograph any one
-sterilizing medical equipment - Travels with velocity of light
-Carry no charge any two
-Possess energy @√1
-Do not get deflected by magnetic or electric field - Gamma ray, x-rays ultraviolet, infrared .
-
-
- Current flowing through a metallic conductor is directly proportional to the p.d across its ends provided temperature and other physical factors are kept constant. √1
- RE = + 8
= 12 Ω - I = V/R
= 2A - P.d across 8 Ω resistor = 2 x 8 = 16V √1
P.d across 6Ω resistor = 24-16= 8V √1
OR
V = IR
2 x = 2 x 4 = 8V - I = V/R√1
= 1.333A √1
OR
12/18 X 2A = 1.333A - The effective resistance reduces when large resistors are arranged in parallel. √1
Since current is divided this also reduced the overheating effect due to high resistance √1 -
-
- Q = CV
= 1.2 x 10-6 x 3
= 3.6 x 10-6C
-
- Current flowing through a metallic conductor is directly proportional to the p.d across its ends provided temperature and other physical factors are kept constant. √1
-
- - Energy of incident radiation
Type of metal any two @ √1
Intensity of incident radiation -
- h = gradient of graph√1
= 6.667 x JS √1 - fo= x- intercept √1
= 3 x Hz - Y – intercept = wo
= 2 x J
- h = gradient of graph√1
- wo = hfo
f0 = W0/h√1
= 1.0 x Hz √1
k.e = hf – hfo
=h (f- fo)
= 6.4 x 10-34 ( 3.0 x 1015 – 1.0 x 1015)√1
= 6.4 x 2 x 10-19J
= 12.8 x 10-18J √1
- - Energy of incident radiation
-
- The direction of the induced e.m.f is such that the current which it causes to flow causes magnetism which oppose the change producing it.√1
-
- induced current flows in the clockwise direction.√1
- pointer of the galvanometer moves anticlockwise when south poles moves inward; end becomes south to oppose the motion of the magnet; √1 the pointer moves clockwise when south pole moves outward, end becomes north to oppose the outward motion of the magnet. √1
- power Ps =95/100 x IPx VP √1
= 95/100x 240 X 0.5
=114W √1 -
- for quick magnetization and demagnetization√1
- to reduce eddy currents
- for quick magnetization and demagnetization√1
-
- P – line/ live cable
R - Neutral - 1. P= v2/r
P= 2000w- P= IV
2000 = 240 x In
I = 8.333A√1 - Cost = number of units x cost per unit√1
= 2 x0.5 x 30 x 12.50√1
= sh 375.√1
- P= IV
- P – line/ live cable
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download PHYSICS PAPER 2 - KCSE 2019 MARANDA MOCK EXAMINATION.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students