SECTION A
Answer all questions in this section
-
- What is geography? (2marks)
- Name the two types of environment.(2marks)
- Give three proofs that the earth is almost spherical in shape. (3marks)
- Use the diagram below to answer questions (a) below.
-
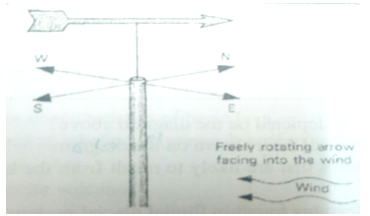
- Name the weather measuring instrument shown in the diagram. (2marks)
- State the element of weather measured by the instrument named in a. (i) above. (2marks)
- From the diagram, which direction is the wind blowing. (2marks)
- Differentiate between absolute humidity and relative humidity. (2marks)
-
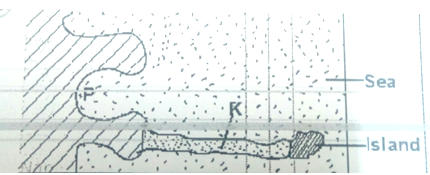
- The diagram below shows a coastal landform.
- Name the features marked P and K. (2marks)
- List down three types of ocean tides. (3marks)
-
- Name the types of earth movements that occur within the earth’s crust. (2marks)
- Describe the origin of continents according to the theory of continental drift. (3marks)
SECTION B
Answer question 6 and any other two from this section.
- Study the map of Taita Hills (1:50,000 (189/4) provided and answer the questions that follows
-
- Identify the Province and the District shown on the map. (2marks)
- Which two methods of showing relief have been used in the map? (3 marks)
-
- Calculate the area covered by Ronge forest. (2marks)
- Give two natural features found in the grid square 3419. (2marks)
- Calculate the bearing of the church in grid square 3218 from the school in grid square 3522. (2marks)
-
- Using a vertical scale of 1cm to represent 100Metres, draw a cross section between Grid reference 300190 and grid reference 360190. (4marks)
- On the cross section, mark and label the following features; (4 marks)
- A hill
- A river
- Thicket
- Main track (motorable)
- Calculate the vertical exaggeration of the cross section. (2marks)
- Citing evidence from the map, explain two factors influencing the distribution of settlement in the area covered by the map (4 marks)
-
-
-
- Name three types of faults. (3marks)
- Apart from compressional forces, describe two other processes that may cause faulting.(4 marks)
- With the aid of diagrams, describe how compressional forces may have led to the formation of the Great Rift Valley. (8marks)
- Explain five effects of faulting on human activities. (10 marks)
-
-
-
- Define the term Aridity. (2marks)
- State three factors that makes wind an effective agent of erosion and deposition in the hot deserts. (3 marks)
- Describe how a rock pedestal is formed. (5 marks)
- Explain four significance of desert features to human activities. (8 marks)
- A group of form four students went out for a field study on action of water in an arid area.
- Give three methods of data collection they may have used. (3 marks)
- State four problems they have encountered during the field study. (4marks)
-
-
- Describe plucking as a process in glacial erosion. (4 marks)
- Explain three conditions that lead to glacial deposition. (6 marks)
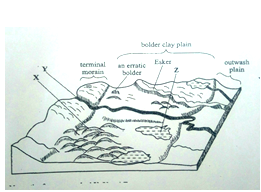
- The diagram below shows features resulting from glacial deposition in a lowland area.
- Name the features marked X, Y, and Z. (3 marks)
- Describe how terminal moraine is formed. (4 Marks)
- Explain four positive effects of glaciation in low land area. (8 marks)
-
-
- What is soil catena? (2 marks)
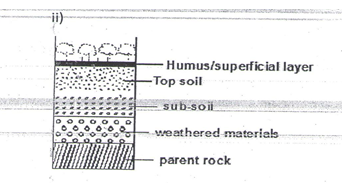
- Draw a well labeled diagram showing the structure of a well-developed soil profile.(5 marks)
- Differentiate between mineralization and humification in soil formation. (2 marks)
- State three factors that determine the color of soil. (3 marks)
-
- State four factors that influence soil formation. (4 marks)
- Explain how the following farming practices can cause soil degradation:
- Continuous application of fertilizer on farm land. (2 marks)
- Burning
- Monoculture
- State three uses of soil. (3 marks)
-

MARKING SCHEME
-
- What is Geography? (2 Mks)
Geography is the study of the distribution and interrelationships of natural and human phenomena in relation to the earth’s surface/It is the study of the earth as a home of human kind. - Name the two types of environment. (2 Mks)
Physical environment
Human environment
- What is Geography? (2 Mks)
-
- Give three proofs that the earth is almost spherical in shape. (3 Mks)
- Circumnavigation of the earth. When one sails or flies along a straight path without changing direction, he or she comes back to the starting point.
- The earth’s horizon appears spherical when observed from a high point.
- Rising and setting of the sun, since people living in the east see the sun earlier than those in the west.
- When a ship is approaching the land from the sea, an observer standing on a high cliff first sees the smoke, then the mast and finally the rest of the ship’s body.
- During the eclipse of the moon, (lunar eclipse), a spherical shadow of the earth is cast on the moon.
- All other planets are spherical, hence the Earth being a planet, is not an exception.
- Photographs of the earth taken from the space by satellites show that the earth has a spherical shape.
- Give three proofs that the earth is almost spherical in shape. (3 Mks)
- Use the diagram below to answer questions (a)below
-
- Name the weather measuring instrument shown in the diagram. (2 Mks)
Wind vane. - State the element of weather measured by the instrument named in a (i) above (2 Mks)
Wind direction/Wind. - From the diagram, from which direction is the wind blowing? (2 Mks)
North-East direction.
- Name the weather measuring instrument shown in the diagram. (2 Mks)
- Differentiate between absolute humidity and relative humidity. (2 Mks)
Absolute humidity is the actual amount of water vapour in a given volume of air, whereas Relative humidity is the ratio of the actual amount of water vapour present in a given volume of air to the amount that would be present if the air were saturated with moisture at the same temperature.
-
- The diagram below shows a coastal landform.
- Name the features marked P and K. (2 Mks)
- P – Bay
- K – Tombolo
- List down three types of ocean tides. (3 Mks)
- Perigian tides.
- Apogean tides.
- Spring tides.
- Neap tides.
- Name the features marked P and K. (2 Mks)
-
- Name the types of earth movements that occur within the earth’s crust. (2 Mks)
- Horizontal earth movement
- Vertical earth movement
- Describe the origin of continents according to the theory of continental drift. (3 Mks)
- There was initially one super continent/Landmass known as Pangaea.
- It was surrounded by large water mass known as panthalassa.
- Later Pangaea broke into two continents namely Laurasia (Northern continent) and Gondwanaland (Southern continent).
- The two were separated by a narrow ocean called Tethys.
- Laurasia split into the current Northern continents: North America, Europe and Asia, while Gondwanaland split to the current Southern continents: Africa, South America, India, Australia, New Zealand and Antarctica.
- Name the types of earth movements that occur within the earth’s crust. (2 Mks)
SECTION B
Answer question 6 and any other two from this section.
- Study the map of Taita Hills (1:50,000 (189/4) provided and answer the questions that follow
-
- Identify the Province and the District shown on the map. (2 Mks)
- Coast province
- Taita district
- Which two methods of showing relief have been used in the map? (3 Mks)
- Trigonometrical station
- Spot height
- Contours
- Identify the Province and the District shown on the map. (2 Mks)
-
- Calculate the area covered by Ronge forest. (2 Mks)
- complete square 0
- incomplete square 10 = 5km2
- Give two natural features/gentle slopes found in the grid square 3419.
-Steep slope
-Scrub
-River
- Scattered trees - Calculate the bearing of the church in grid square 3218 from the school in the grid square 3522.
2110 +10 (2100, 2110,2120) (2Mks)
- Calculate the area covered by Ronge forest. (2 Mks)
-
- Using a vertical scale of 1cm to represent 100m, draw cross section between grid reference 300190 and grid reference 360190. (4 Mks)
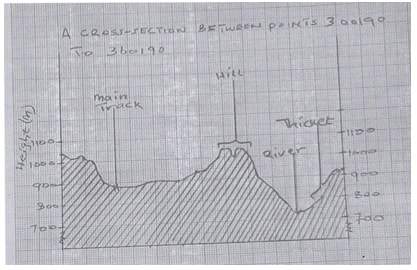
Marks distribution
Title 1 mk
Hill 1mk
Starting point (1040) ½ mk
motorable track 1mk
End point (920m) ½ mk
River 1 mk
Labelled Y axis 1 mk
Thicket 1mk
Trend 1 mk - Calculate the vertical exaggeration of the cross section, (2 Mks)
V.E = Vertical scale (V.S)
Horizontal scale (H.S)
= 1 = 1 × 50000
10000 10,000 1
1
50000
V.E = 5 times
- Using a vertical scale of 1cm to represent 100m, draw cross section between grid reference 300190 and grid reference 360190. (4 Mks)
- Citing evidence from the map, explain two factors influencing the distribution of settlement in the area covered by the map.(4 Mks)
- Steep slopes as shown by closely packed contours are sparsely settled, since it is difficult to construct houses.
- There are few settlements along river valleys, since they are prone to flooding and waterborne diseases.
- Few settlements in the forests because they are government reserved areas.
- Dense settlements along main roads for movement of goods and people.
- Dense settlements in the urban centres due to availability of goods/services/social amenities.
-
-
-
- Name three types of faults. (3Mks)
- Normal fault
- Reverse fault
- Tear/shear fault/slip/transform/wrench/strike slip
- Thrust fault
- Anticlinal fault
- Apart from compression forces, describe two other processes that may cause faulting. (4 Mks)
- Faulting may be caused by force acting horizontally away from each other which cause tension in the crystal rocks. Due to tensional forces the rocks stretch and fracture causing faults.
- Faulting may occur where horizontal forces act parallel to each other in the opposite/same direction resulting in
- Faulting may occur due to vertical movements which may exert a strain in the rocks making them to fracture.
- With the aid of diagrams, describe how compression forces may have led to the formation of the Great Rift Valley. (8 Mks)
- Layers of rocks are subjected to compression forces
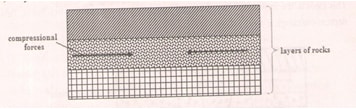
- Two parallel lines of weaknesses develop/reverse faults
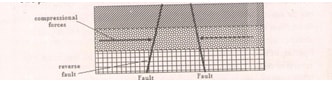
- Compression forces may take the outer blocks towards each other. The outer blocks ride over the middle block and the middle block sinks or subsides or may remain stable. The sunken middle part forms a depression called a rift valley.
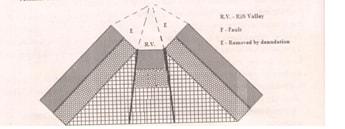
- Compression forces may push the outer blocks towards each other (the outer blocks ride over the middle block) the middle block sinks/subside/may remain stable.
- The overhanging edges undergo denudation/are eroded.
- This widens the depression.
- The sunken middle part forms a depression called a rift valley.
- Diagrams (3 mks) (forces, reverse faults, Rift valley)Description (5 mks)
- Layers of rocks are subjected to compression forces
- Name three types of faults. (3Mks)
- Explain five effects of faulting on human activities. (10 Mks)
- Fault blocks form beautiful scenery which attracts tourists, hence foreign exchange.
- Fault block causes displacement of rocks which exposes valuable minerals.
- Block mountains formed through faulting experience rainfall on the windward side give rise to rivers which provide water for industrial/domestic/agricultural use/Industrial use for production of H.E.P.
- Block mountains formed through faulting lead to formation of relief rainfall on the windward side which favours agriculture/and settlement/forestry.
- Rivers flowing over faults blocks from waterfalls which are sites for H.E.P production.
- Faulting creates deep faults which are passages of steam jets which may be utilized for geothermal power production.
- Rivers flowing over fault scarps may form waterfalls which can be harnessed to produce H.E.P for industries.
- Springs occurring at the foot of fault scarps attract settlements.
-
-
-
- Define the term aridity. (2Mks)
It is the state of land being deficient in moisture, leading to scanty vegetation/lack of it. - State three factors that make wind an effective agent of erosion and deposition in the hot deserts. (3 Mks)
- Materials are unconsolidated/loose sand.
- Absence of vegetation/scanty vegetation.
- Winds are strong/storms.
- Low moisture content in the soil.
- Define the term aridity. (2Mks)
- Describe how a rock pedestal is formed. (5 Mks)
- A rock outcrop exists in the desert.
- It’s made of alternating hard and soft rock layers.
- Abrasion attacks soft rock wearing away it. The hard layers protrudes out horizontally.
- Wind is more active at the base hence undercutting the rock outcrop.
- This, queer shaped feature is known as a rock pedestal.
- Explain four significance of desert feature to human activities. (8 Mks)
- Water from oasis is used for irrigation and domestic purposes.
- Desert land forms are ideal for military training/testing weapons.
- Loess forms fertile soils for agricultural purposes.
- Some desert features like rock pedestal, zeugens and yadangs are fascinating and attract tourists, earning foreign exchange.
- Desert features like badlands hinder transport lines construction.
- Hot sun in the deserts provides potential for solar energy.
- Sand dunes migration may destroy rich agricultural farms/and interfere with transport lines.
- A group of form four students went out for a field study on action of water in an arid area.
- Give three methods of data collection they may have used. (3 Mks)
- Observation
- Photographing/taking photographs
- Taking samples
- Content analysis/Reading from secondary sources.
- State four problems they may have encountered during the field study. (4 Mks)
- Attack by snakes/insect bites
- High temperatures/Hot weather
- Poor visibility due to dust.
- Difficulty in movement due to gulleys
- Shortage of water/thirst.
- Give three methods of data collection they may have used. (3 Mks)
-
-
- Describe plucking as a process of glacial erosion. (4 Mks)
- Pressure from the overlying mass of ice causes freeze thaw action.
- Melting water fills the cracks/joints in the bed rock.
- As water freezes it exerts pressure on the cracks enlarging them.
- The enlarged cracks lead to disintegration of the rock.
- The rock debris are scoured or pulled off the mother rock by the moving ice.
- The disintegrated rocks eventually get embedded within the mass of ice.
- As the ice moves, it pulls out or gorges out the embedded rock from the mother rock.
- This process is called plucking.
- Explain three conditions that lead to glacial deposition. (6 Mks)
- Rising temperature lead to melting of ice thereby causing the ice to deposit its load.
- Change of gradient to relatively flat surface will reduce the velocity of the glacial movement which will subsequently lead to deposition of glacial materials.
- Alternating warm and cold periods lead to seasonal melting of ice which allows materials embedded in the ice to be released and deposited.
- Stagnation/accumulation of glaciers leads to pressure at the base of the glacier which in turn leads to melting of ice at the base. The melt water then carries and deposits materials underneath which loosens the heavy materials beneath the mass ice and is subsequently deposited.
- Friction at the base and sides of a glacier and a rough surface leads to melting of ice, causing the ice to deposit its load.
- The diagram below shows features resulting from glacial deposition on a lowland area.
- Name the features marked X, Y and Z. (3 Mks)
- X - Drumlins
- Y – A river/melt water
- Z – kettle lake/lake
- Describe how terminal moraine is formed. (4 Mks)
- Moving ice carries solid materials
- Moving ice stagnates and ice at the snout melts.
- Melting ice releases its load
- Gradually the load piles into a ridge
- Over time the ridge forms a horse shoe shape/block of solid materials called terminal moraine
- Name the features marked X, Y and Z. (3 Mks)
- Explain four positive effects of glaciations in lowland areas. (8 Mks)
- Glacial till provides fertile soils which are suitable for arable farming.
- Ice sheets in their scouring effect may expose the minerals making them easy to extract.
- Out wash plains comprise of sand and gravel which are used as building/construction materials.
- Glacial lakes found in lowland areas can be exploited for various economic uses such as fishing and transportation.
- Glaciation forms features such as drumlins, eskers which are tourists attraction hence foreign exchange earnings.
- Glaciated lowlands are generally flat and ideal for establishment of settlements/development of transportation network.
- Describe plucking as a process of glacial erosion. (4 Mks)
-
-
- What is soil catena? (2 Mks)
It is the arrangement of soil along a slope from top to bottom. - Draw a well labelled diagram to show the structure of a well-developed soil profile.(5 Mks)
- What is soil catena? (2 Mks)
- Differentiate between mineralization and humification in soil formation. (2 Mks)
Mineralization is the biological and chemical breakdown of dead plant tissues by soil micro organisms to produce simple organic substances while Humification is the process through which organic matter is changed into humus. - State three factors that determine the colour of soil. (3 Mks)
- Humus content/ content of organic matter present in the soil: black/dark brown colour indicates a soil rich in humus
- Drainage of the area in which the soil is found: grey colour denotes a poorly drained and water logged soil
- Acidity/salinity/soil PH/ chemical composition of the soil: White colour denotes a soil with high salts concentration
- Type of parent material from which a soil has developed.
-
- Outline four factors that influence soil formation. (4 Mks)
- Nature of the parent rock material
- Climate
- Influence of living organisms
- Topography/Relief
- Time factor
- Explain how the following farming practices that cause soil degradation:
- Burning
- Kills soil micro-organisms and robs the soil of organic matter/humus
- Kills nitrogen fixing bacteria resulting to lack of nitrogen in the soil
- Continuous application of fertilizer on farm land. (2 Mks)
- Leads to increase acidity in the soil which interferes with soil formation micro-organisms like bacteria and fungi thus lowering the level of humus content.
- monoculture
- Results in the crops using all the minerals that it requires, which increases a deficiency of the mineral in the soil
- State three uses of soil. (3 Mks)
- Give physical support for the rooting system of plants and protects root system from damage.
- Habitat for borrowing animals and bacteria necessary for breakdown of organic matter into humus.
- Medium through which nutrients and air are made available to plants.
- Provides mineral elements to plants e.g. nitrogen, calcium, phosphates, etc.
- Is used in building and construction e.g. clay for making bricks and tiles.
- Clay soils are used for decorative purpose e.g. ache used among Maasai.
- Sources of minerals especially to expectant mothers.
- Soil contains valuable minerals such as alluvial gold.
- Soils supports plant life which is source of food for people and animals especially herbivores.
- Soils are used for medicinal purposes e.g. clay is mixed with some herbs for medical purpose in some communities.
(Any 3×1=3 marks)
- Outline four factors that influence soil formation. (4 Mks)
-
Download GEOGRAPHY PAPER 1 - KCSE 2019 BAHATI MOCK EXAMINATION (WITH MARKING SCHEME).
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students